2.1.6: Naming Transition Metal Complexes
- Page ID
- 200860
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Introduction
It's useful to be able to read the name of a complex or compound and understand what that means. First, let's get straight on some vocabulary:
COMPLEXES (metal directly bonded to ligands)
- Complex Cation: This is a metal complex with an overall positive charge. e.g. \([CO(NH_3)_6]^{3+}\)
- Complex Anion: This is a metal complex with an overall negative charge. e.g. \([CoCl_4(NH_3)_2]^-\)
- Neutral Complex: This is a metal complex with zero overall charge. e.g. \([CoCl_3(NH_3)_3]\)
COMPOUNDS (salt of one or more complexes)
- Coordination Compounds: This is a salt where either the cation and/or the anion are metal complexes. e.g. \(K_4[Fe(CN)_6]\)
The Rules: Naming Complexes and Coordination Compounds
|
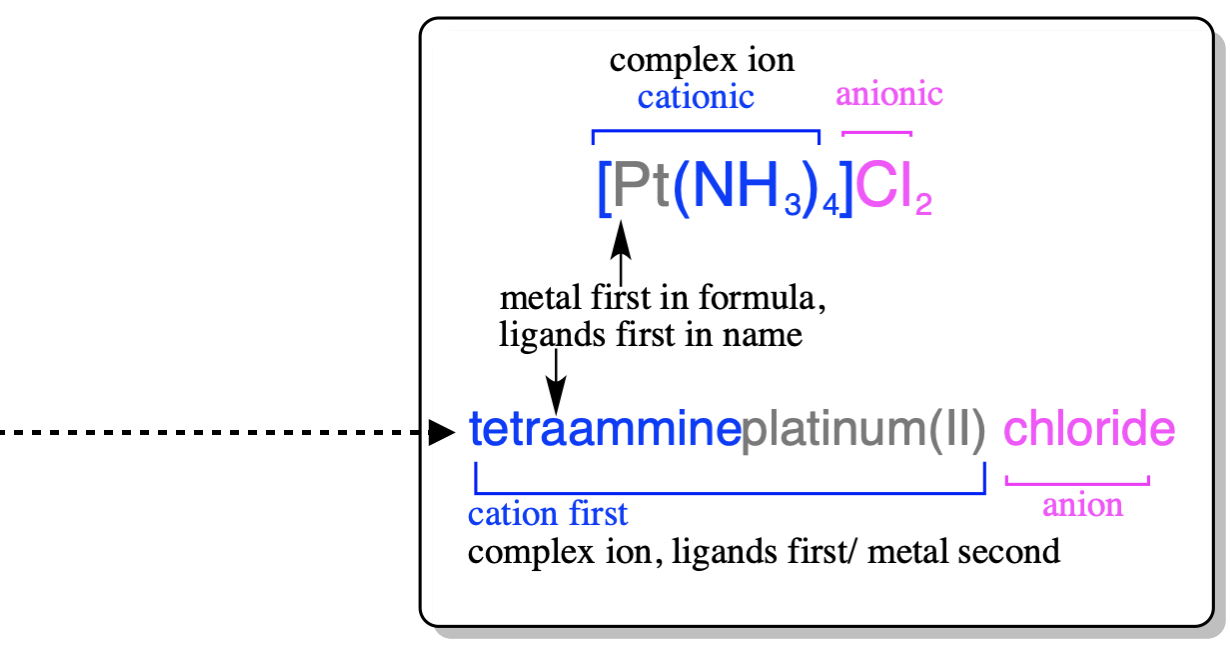
1. Naming a coordination compound (salt): (just like gen chem: NaCl = sodium chloride) |
 |
|
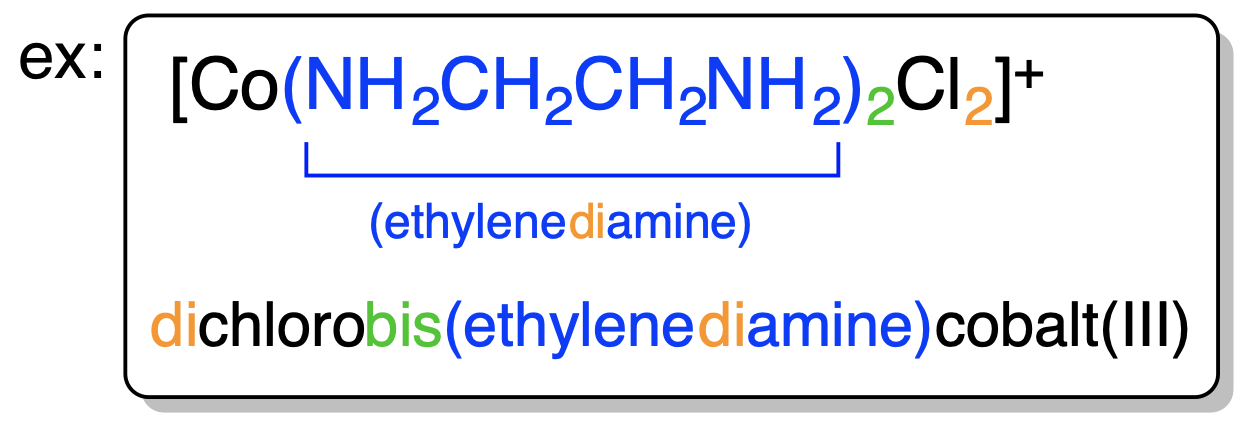
2. Naming a complex/complex ion: *in the formula, the complex ion is written in |
|
|
|
|
|
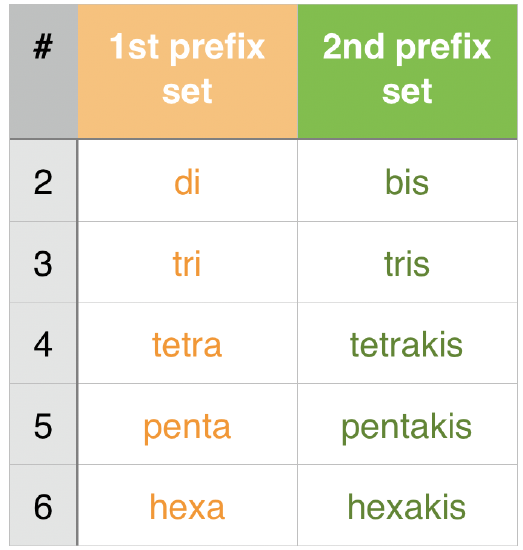
4. Ligands are named in alphabetical order. (see example above) |
|
| 5. Anionic ligands are given “o” suffix. Neutral Ligands retain usual name. (see example above) |  |
|
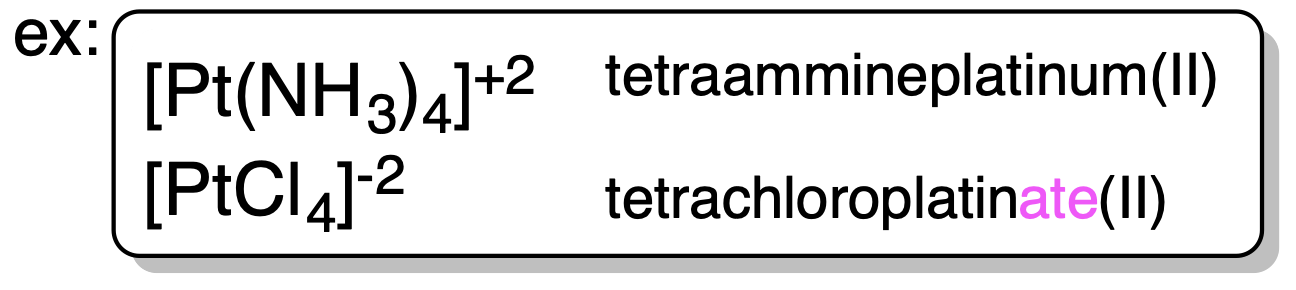
6. Oxidation number of transition metals is given by (Roman Numeral). |
|
| 7. Negatively charged complex ion is given suffix “-ate”. |
|
|
8. Arrangement of ligands must be specified for stereoisomers: Cis / Trans, Δ / Λ , mer / fac. 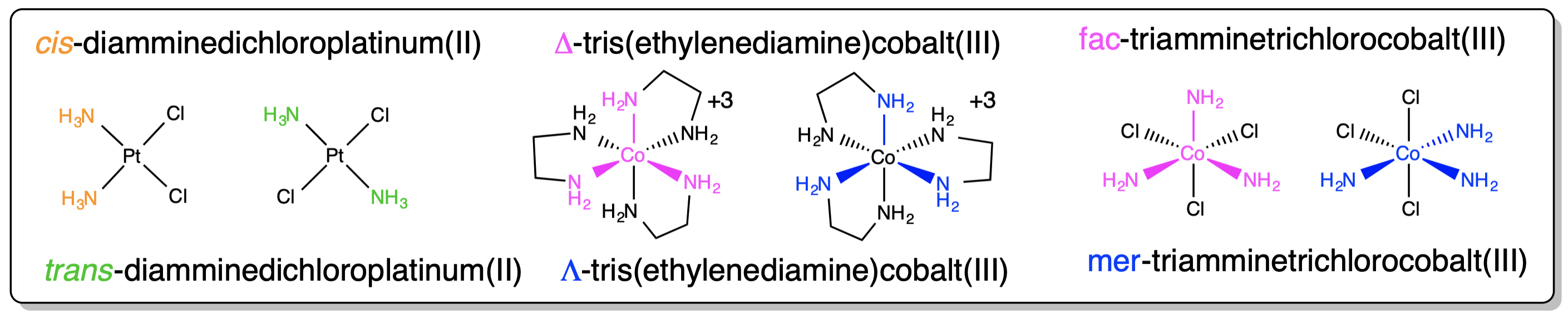 |
|
|
9. Bridging Ligands between metal ions have prefix μn (n=# of atoms bridged, usually dropped if n=2). |
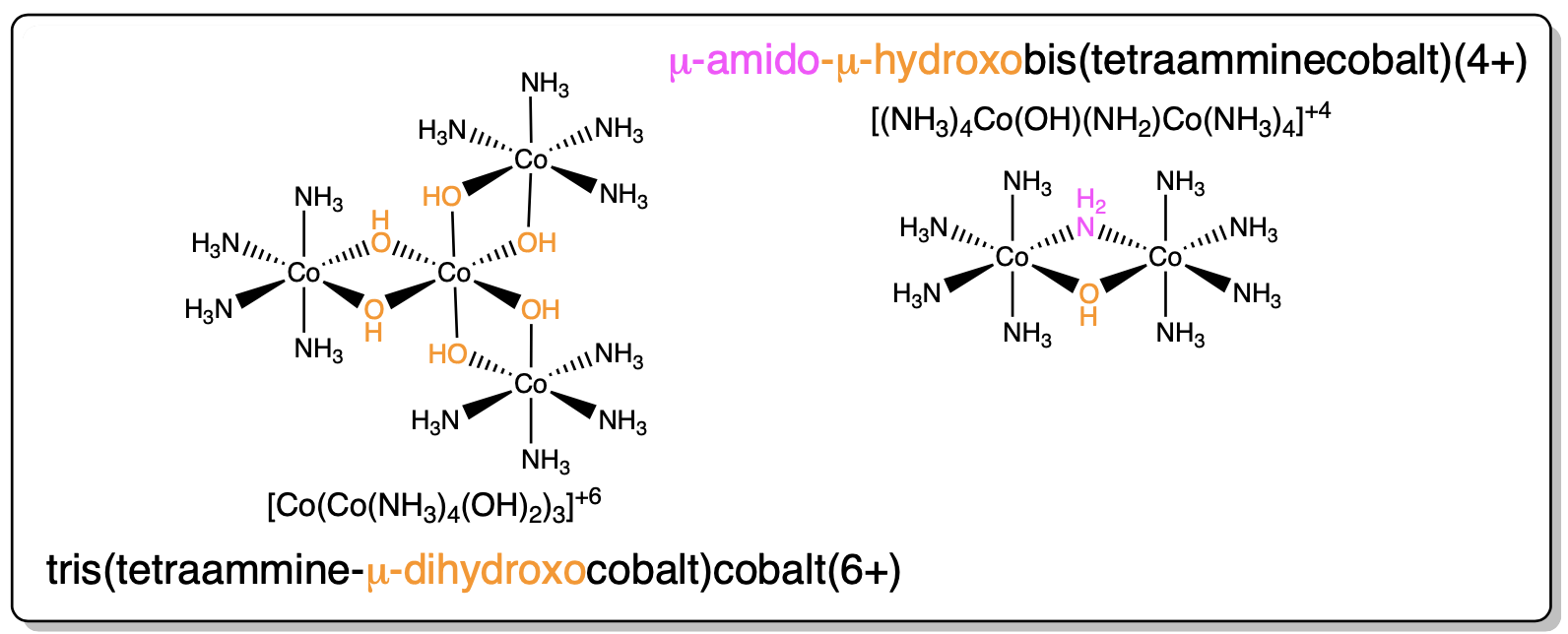 |
|
10. Ambidentate ligands use κ-X |
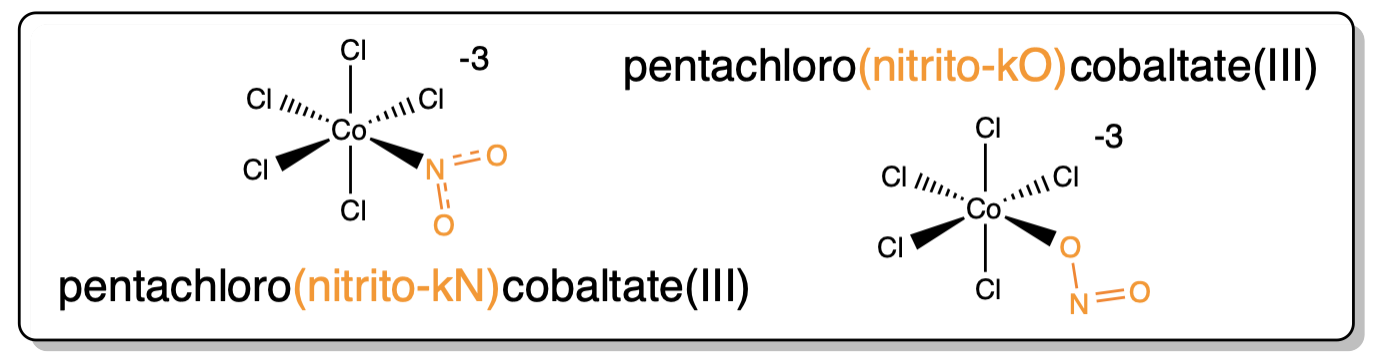 |
The Rules: Writing Formulas of Coordination Complexes
The formula of a coordination complex is written in a different order than its name. The chemical symbol of the metal center is written first. The ligands are written next, with anion ligands coming before neutral ligands. If there is more than one anion or neutral ligand, they are written in alphabetical order according to the first letter in their chemical formula.
In a coordination compound's name, when one of the ions is just an element, the number of atoms is not indicated with a prefix. Since it still has to be written in the formula, it is determined by balancing the overall charge of the compound. (For example, tetrafluorochromium(VI) chloride becomes [CrF4]Cl2.
Provide names for the following complexes:
a) K[Cr(ox)2(OH2)2] b) [Co(NH3)5Br](NO3)2 c) [Cr(en)2Cl2]PF6 d) [Co(bpy)2(OH)Cl]ClO4
e) [TiCl3(OH2)3] f) K3[Fe(CN)6] g) Na[Au(bpy)(CN)2]
- Answer a):
-
potassium diaquabis(oxalato)chromate(III)
- Answer b):
-
pentaamminebromocobalt(III) nitrate
- Answer c):
-
dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)chromium(III) hexafluorophosphate
- Answer d):
-
bis(bipyridine)chlorohydroxocobalt(III) perchlorate
- Answer e):
-
triaquatrichlorotitanium(III)
- Answer f):
-
potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
- Answer g):
-
sodium bipyridinedicyanoaurate(I)
Bipyridine is sometimes called "bipyridyl".
Draw the following structures:
a) dicarbonylbis(1,2-dimethylphosphino)ethaneruthenium (0)
b) potassium bipyridyltetracyanoferrate(II)
c) pentaamminechlorochromium(III) perchlorate
d) tetraacetonitrilecopper(I) tetrafluoroborate
e) sodium ethylenediaminebis(oxalato)cobalt(III)
f) chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I)
- Answer a):
-
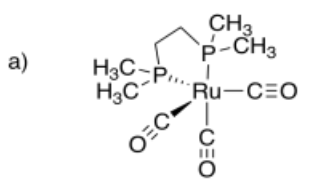
- Answer b):
-
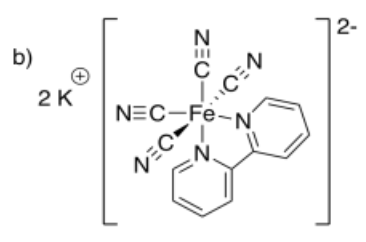
- Answer c):
-
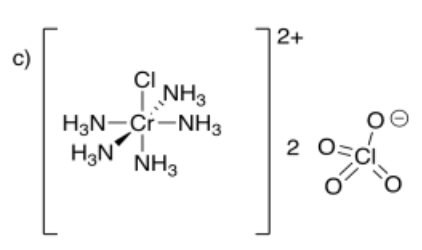
- Answer d):
-
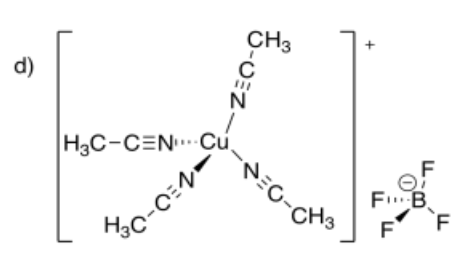
- Answer e):
-
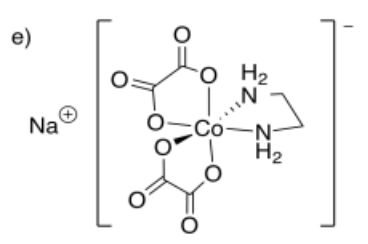
- Answer f):
-

Attribution
Curated or created by Kathryn Haas
This material is adapted from:
- Coordination Chemistry (Justin Hosung Lee (UCD), Sophia Muller (UCD))
- Naming Transition Metal Complexes (Chris Schaller)