9.1: Gas Pressure
- Page ID
- 414655
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define the property of pressure
- Define and convert among the units of pressure measurements
- Describe the operation of common tools for measuring gas pressure
The earth’s atmosphere exerts a pressure, as does any other gas. Although we do not normally notice atmospheric pressure, we are sensitive to pressure changes—for example, when your ears “pop” during take-off and landing while flying, or when you dive underwater. Gas pressure is caused by the force exerted by gas molecules colliding with the surfaces of objects (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Although the force of each collision is very small, any surface of appreciable area experiences a large number of collisions in a short time, which can result in a high pressure. In fact, normal air pressure is strong enough to crush a metal container when not balanced by equal pressure from inside the container.
A dramatic illustration of atmospheric pressure is provided in this brief video, which shows a railway tanker car imploding when its internal pressure is decreased.
A smaller scale demonstration of this phenomenon is briefly explained.
Atmospheric pressure is caused by the weight of the column of air molecules in the atmosphere above an object, such as the tanker car. At sea level, this pressure is roughly the same as that exerted by a full-grown African elephant standing on a doormat, or a typical bowling ball resting on your thumbnail. These may seem like huge amounts, and they are, but life on earth has evolved under such atmospheric pressure. If you actually perch a bowling ball on your thumbnail, the pressure experienced is twice the usual pressure, and the sensation is unpleasant.
In general, pressure is defined as the force exerted on a given area: \(P=\frac{F}{A}). Note that pressure is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to area. Thus, pressure can be increased either by increasing the amount of force or by decreasing the area over which it is applied; pressure can be decreased by decreasing the force or increasing the area.
Let’s apply this concept to determine which exerts a greater pressure in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) —the elephant or the figure skater? A large African elephant can weigh 7 tons, supported on four feet, each with a diameter of about 1.5 ft (footprint area of 250 in2), so the pressure exerted by each foot is about 14 lb/in2:
\[\text { pressure per elephant foot }=14,000 \frac{ lb }{\text { elephant }} \times \frac{1 \text { elephant }}{4 \text { feet }} \times \frac{1 \text { foot }}{250 in^2}=14 lb / in^2 \nonumber \]
The figure skater weighs about 120 lbs, supported on two skate blades, each with an area of about 2 in2, so the pressure exerted by each blade is about 30 lb/in2:
\[\text { pressure per skate blade }=120 \frac{ lb }{\text { skater }} \times \frac{1 \text { skater }}{2 \text { blades }} \times \frac{1 \text { blade }}{2 \text { in }^2}=30 lb / in^2 \nonumber \]
Even though the elephant is more than one hundred-times heavier than the skater, it exerts less than one-half of the pressure. On the other hand, if the skater removes their skates and stands with bare feet (or regular footwear) on the ice, the larger area over which their weight is applied greatly reduces the pressure exerted:
\[\text { pressure per human foot }=120 \frac{ lb }{\text { skater }} \times \frac{1 \text { skater }}{2 \text { feet }} \times \frac{1 \text { foot }}{30 in^2}=2 lb / in^2 \nonumber \]
The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), with 1 Pa = 1 N/m2, where N is the newton, a unit of force defined as 1 kg m/s2. One pascal is a small pressure; in many cases, it is more convenient to use units of kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa) or bar (1 bar = 100,000 Pa). In the United States, pressure is often measured in pounds of force on an area of one square inch—pounds per square inch (psi)—for example, in car tires. Pressure can also be measured using the unit atmosphere (atm), which originally represented the average sea level air pressure at the approximate latitude of Paris (45°). Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) provides some information on these and a few other common units for pressure measurements
| Unit Name and Abbreviation | Definition or Relation to Other Unit |
|---|---|
| pascal (Pa) | 1 Pa = 1 N/m2 recommended IUPAC unit |
| kilopascal (kPa) | 1 kPa = 1000 Pa |
| pounds per square inch (psi) | air pressure at sea level is ~14.7 psi |
| atmosphere (atm) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa = 760 torr air pressure at sea level is ~1 atm |
| bar (bar, or b) | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa (exactly) commonly used in meteorology |
| millibar (mbar, or mb) | 1000 mbar = 1 bar |
| inches of mercury (in. Hg) | 1 in. Hg = 3386 Pa used by aviation industry, also some weather reports |
| torr | named after Evangelista Torricelli, inventor of the barometer |
| millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) | 1 mm Hg ~1 torr |
The United States National Weather Service reports pressure in both inches of Hg and millibars. Convert a pressure of 29.2 in. Hg into:
- torr
- atm
- kPa
- mbar
Solution
This is a unit conversion problem. The relationships between the various pressure units are given in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
- \[29.2 \text { in } Hg_{ g } \times \frac{25.4 mm }{1 im } \times \frac{1 \text { torr }}{1 mm Hg_{ g }}=742 \text { torr } \nonumber \]
- \[742 \text { torr } \times \frac{1 atm }{760 \text { torr }}=0.976 atm \nonumber \]
- \[742 \text { torr } \times \frac{101.325 kPa }{760 \text { torr }}=98.9 kPa \nonumber \]
- \[98.9 kPa \times \frac{1000 Pa }{1 kPa } \times \frac{1 bar }{100,000 Pa } \times \frac{1000 mbar }{1 bar }=989 mbar \nonumber \]
A typical barometric pressure in Kansas City is 740 torr. What is this pressure in atmospheres, in millimeters of mercury, in kilopascals, and in bar?
- Answer
-
0.974 atm; 740 mm Hg; 98.7 kPa; 0.987 bar
We can measure atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the atmosphere on the earth’s surface, with a barometer (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). A barometer is a glass tube that is closed at one end, filled with a nonvolatile liquid such as mercury, and then inverted and immersed in a container of that liquid. The atmosphere exerts pressure on the liquid outside the tube, the column of liquid exerts pressure inside the tube, and the pressure at the liquid surface is the same inside and outside the tube. The height of the liquid in the tube is therefore proportional to the pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
If the liquid is water, normal atmospheric pressure will support a column of water over 10 meters high, which is rather inconvenient for making (and reading) a barometer. Because mercury (Hg) is about 13.6-times denser than water, a mercury barometer only needs to be \(\frac{1}{13.6}}\) as tall as a water barometer—a more suitable size. Standard atmospheric pressure of 1 atm at sea level (101,325 Pa) corresponds to a column of mercury that is about 760 mm (29.92 in.) high. The torr was originally intended to be a unit equal to one millimeter of mercury, but it no longer corresponds exactly. The pressure exerted by a fluid due to gravity is known as hydrostatic pressure, \(p\):
\[p=h \rho g \nonumber \]
where h is the height of the fluid, ρ (lowercase Greek letter rho) is the density of the fluid, and g is acceleration due to gravity.
Show the calculation supporting the claim that atmospheric pressure near sea level corresponds to the pressure exerted by a column of mercury that is about 760 mm high. The density of mercury = 13.6 g/cm3.
Solution
The hydrostatic pressure is given by p = hρg, with h = 760 mm, ρ = 13.6 g/cm3, and g = 9.81 m/s2. Plugging these values into the equation and doing the necessary unit conversions will give us the value we seek. (Note: We are expecting to find a pressure of ~101,325 Pa.)
\[101,325 N / m^2=101,325 \frac{ kg \cdot m / s^2}{ m^2}=101,325 \frac{ kg }{ m \cdot s^2} \nonumber \]
\[\begin{gathered}
p=\left(760 mm \times \frac{1 m }{1000 mm }\right) \times\left(\frac{13.6 g }{1 cm^3} \times \frac{1 kg }{1000 g } \times \frac{(100 cm )^3}{(1 m )^3}\right) \times\left(\frac{9.81 m }{1 s^2}\right) \\[4pt]
=(0.760 m )\left(13,600 kg / m^3\right)\left(9.81 m / s^2\right)=1.01 \times 10^5 kg / ms^2=1.01 \times 10^5 N / m^2 \\[4pt]
=1.01 \times 10^5 Pa
\end{gathered} \nonumber \]
Calculate the height of a column of water at 25 °C that corresponds to normal atmospheric pressure. The density of water at this temperature is 1.0 g/cm3.
- Answer
-
10.3 m
A manometer is a device similar to a barometer that can be used to measure the pressure of a gas trapped in a container. A closed-end manometer is a U-shaped tube with one closed arm, one arm that connects to the gas to be measured, and a nonvolatile liquid (usually mercury) in between. As with a barometer, the distance between the liquid levels in the two arms of the tube (h in the diagram) is proportional to the pressure of the gas in the container. An open-end manometer (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)) is the same as a closed-end manometer, but one of its arms is open to the atmosphere. In this case, the distance between the liquid levels corresponds to the difference in pressure between the gas in the container and the atmosphere.
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured with a closed-end manometer, as shown to the right. The liquid in the manometer is mercury. Determine the pressure of the gas in:
- torr
- Pa
- bar
Solution
The pressure of the gas is equal to a column of mercury of height 26.4 cm. (The pressure at the bottom horizontal line is equal on both sides of the tube. The pressure on the left is due to the gas and the pressure on the right is due to 26.4 cm Hg, or mercury.) We could use the equation \(p = hρg\) as in Example \(\PageIndex{2}\), but it is simpler to just convert between units using Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
- \[26.4 em Hg_{ g } \times \frac{10 mm Hg_{ g }}{1 emHg } \times \frac{1 \text { torr }}{1 mm \Pi Hg }=264 \text { torr } \nonumber \]
- \[264 \text { torr } \times \frac{1 \text { atm }}{760 \text { torr }} \times \frac{101,325 Pa }{1 \text { atm }}=35,200 Pa \nonumber \]
- \[35,200 Pa \times \frac{1 bar }{100,000 Pa }=0.352 bar \nonumber \]
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured with a closed-end manometer. The liquid in the manometer is mercury. Determine the pressure of the gas in:
- torr
- Pa
- bar
- Answer
-
(a) ~150 torr; (b) ~20,000 Pa; (c) ~0.20 bar
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured at sea level with an open-end Hg (mercury) manometer, as shown to the right. Determine the pressure of the gas in:
- mm Hg
- atm
- kPa
Solution
The pressure of the gas equals the hydrostatic pressure due to a column of mercury of height 13.7 cm plus the pressure of the atmosphere at sea level. (The pressure at the bottom horizontal line is equal on both sides of the tube. The pressure on the left is due to the gas and the pressure on the right is due to 13.7 cm of Hg plus atmospheric pressure.)
- In mm Hg, this is: 137 mm Hg + 760 mm Hg = 897 mm Hg
- \[897 mm Hg_{ g } \times \frac{1 atm }{760 mm Hg_{ g }}=1.18 atm \nonumber \]
- \[1.18 \text { atm } \times \frac{101.325 kPa }{1-20 \times 10^2 kPa }=1.20 \nonumber \]
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured at sea level with an open-end Hg manometer, as shown to the right. Determine the pressure of the gas in:
- mm Hg
- atm
- kPa
- Answer
-
(a) 642 mm Hg; (b) 0.845 atm; (c) 85.6 kPa
Blood pressure is measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer (Greek sphygmos = “pulse”). It consists of an inflatable cuff to restrict blood flow, a manometer to measure the pressure, and a method of determining when blood flow begins and when it becomes impeded (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Since its invention in 1881, it has been an essential medical device. There are many types of sphygmomanometers: manual ones that require a stethoscope and are used by medical professionals; mercury ones, used when the most accuracy is required; less accurate mechanical ones; and digital ones that can be used with little training but that have limitations. When using a sphygmomanometer, the cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated until blood flow is completely blocked, then slowly released. As the heart beats, blood forced through the arteries causes a rise in pressure. This rise in pressure at which blood flow begins is the systolic pressure—the peak pressure in the cardiac cycle. When the cuff’s pressure equals the arterial systolic pressure, blood flows past the cuff, creating audible sounds that can be heard using a stethoscope. This is followed by a decrease in pressure as the heart’s ventricles prepare for another beat. As cuff pressure continues to decrease, eventually sound is no longer heard; this is the diastolic pressure—the lowest pressure (resting phase) in the cardiac cycle. Blood pressure units from a sphygmomanometer are in terms of millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Throughout the ages, people have observed clouds, winds, and precipitation, trying to discern patterns and make predictions: when it is best to plant and harvest; whether it is safe to set out on a sea voyage; and much more. We now face complex weather and atmosphere-related challenges that will have a major impact on our civilization and the ecosystem. Several different scientific disciplines use chemical principles to help us better understand weather, the atmosphere, and climate. These are meteorology, climatology, and atmospheric science. Meteorology is the study of the atmosphere, atmospheric phenomena, and atmospheric effects on earth’s weather. Meteorologists seek to understand and predict the weather in the short term, which can save lives and benefit the economy. Weather forecasts (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)) are the result of thousands of measurements of air pressure, temperature, and the like, which are compiled, modeled, and analyzed in weather centers worldwide.
In terms of weather, low-pressure systems occur when the earth’s surface atmospheric pressure is lower than the surrounding environment: Moist air rises and condenses, producing clouds. Movement of moisture and air within various weather fronts instigates most weather events.
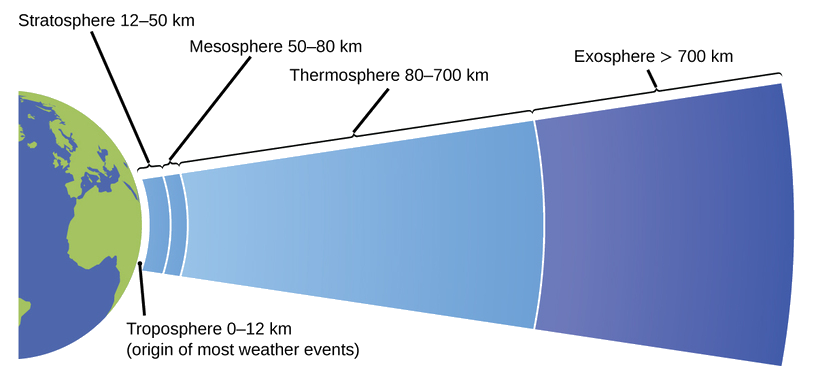
The atmosphere is the gaseous layer that surrounds a planet. Earth’s atmosphere, which is roughly 100–125 km thick, consists of roughly 78.1% nitrogen and 21.0% oxygen, and can be subdivided further into the regions shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) the exosphere (furthest from earth, > 700 km above sea level), the thermosphere (80–700 km), the mesosphere (50–80 km), the stratosphere (second lowest level of our atmosphere, 12–50 km above sea level), and the troposphere (up to 12 km above sea level, roughly 80% of the earth’s atmosphere by mass and the layer where most weather events originate). As you go higher in the troposphere, air density and temperature both decrease.
Climatology is the study of the climate, averaged weather conditions over long time periods, using atmospheric data. However, climatologists study patterns and effects that occur over decades, centuries, and millennia, rather than shorter time frames of hours, days, and weeks like meteorologists. Atmospheric science is an even broader field, combining meteorology, climatology, and other scientific disciplines that study the atmosphere.


