9.1: Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals
- Page ID
- 428745
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Describe the formation of covalent bonds in terms of atomic orbital overlap
- Define and give examples of σ and π bonds
- Explain the concept of atomic orbital hybridization
- Determine the hybrid orbitals associated with various molecular geometries
Valence Bond Theory
We have examined the basic ideas of bonding, showing that atoms share electrons to form molecules with stable Lewis structures and that we can predict the shapes of those molecules by valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. These ideas provide an important starting point for understanding chemical bonding. But these models sometimes fall short in their abilities to predict the behavior of real substances. How can we reconcile the geometries of s, p, and d atomic orbitals with molecular shapes that show angles like 120° and 109.5°?
As we know, a scientific theory is a strongly supported explanation for observed natural laws or large bodies of experimental data. For a theory to be accepted, it must explain experimental data and be able to predict behavior. For example, VSEPR theory has gained widespread acceptance because it predicts three-dimensional molecular shapes that are consistent with experimental data collected for thousands of different molecules. However, VSEPR theory does not provide an explanation of chemical bonding.
There are successful theories that describe the electronic structure of atoms. We can use quantum mechanics to predict the specific regions around an atom where electrons are likely to be located: A spherical shape for an s orbital, a dumbbell shape for a p orbital, and so forth. However, these predictions only describe the orbitals around free atoms. When atoms bond to form molecules, atomic orbitals are not sufficient to describe the regions where electrons will be located in the molecule. A more complete understanding of electron distributions requires a model that can account for the electronic structure of molecules. One popular theory holds that a covalent bond forms when a pair of electrons is shared by two atoms and is simultaneously attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. In the following sections, we will discuss how such bonds are described by valence bond theory and hybridization.
Valence bond theory describes a covalent bond as the overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals (each containing a single electron) that yield a pair of electrons shared between the two bonded atoms. We say that orbitals on two different atoms overlap when a portion of one orbital and a portion of a second orbital occupy the same region of space. According to valence bond theory, a covalent bond results when two conditions are met:
- an orbital on one atom overlaps an orbital on a second atom and
- the single electrons in each orbital combine to form an electron pair.
The mutual attraction between this negatively charged electron pair and the two atoms’ positively charged nuclei serves to physically link the two atoms through a force we define as a covalent bond. The strength of a covalent bond depends on the extent of overlap of the orbitals involved. Orbitals that overlap extensively form bonds that are stronger than those that have less overlap.
The energy of the system depends on how much the orbitals overlap. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) illustrates how the sum of the energies of two hydrogen atoms (the colored curve) changes as they approach each other. When the atoms are far apart there is no overlap, and by convention we set the sum of the energies at zero. As the atoms move together, their orbitals begin to overlap. Each electron is attracted to the nucleus in the other atom. In addition, the electrons begin to repel each other, as do the nuclei. As the atoms move closer together, the overlap increases, so the attraction of the nuclei for the electrons increases and the energy of the system decreases. This is the formation of a bond. As the atoms move close together the nuclei, which both have a positive charge, repel each other. When the atoms are widely separated the attraction is stronger than the repulsion and the atoms are pulled together. At some point the repulsions get stronger than the attraction and the atoms start to push apart. There is an optimum distance where the attraction and repulsion are balanced, this is the bond distance for an H2 molecule. The bond is stable because at this point because pulling the atoms apart requires adding enough energy to overcome the attraction. This corresponds to the depth of the energy well in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\).
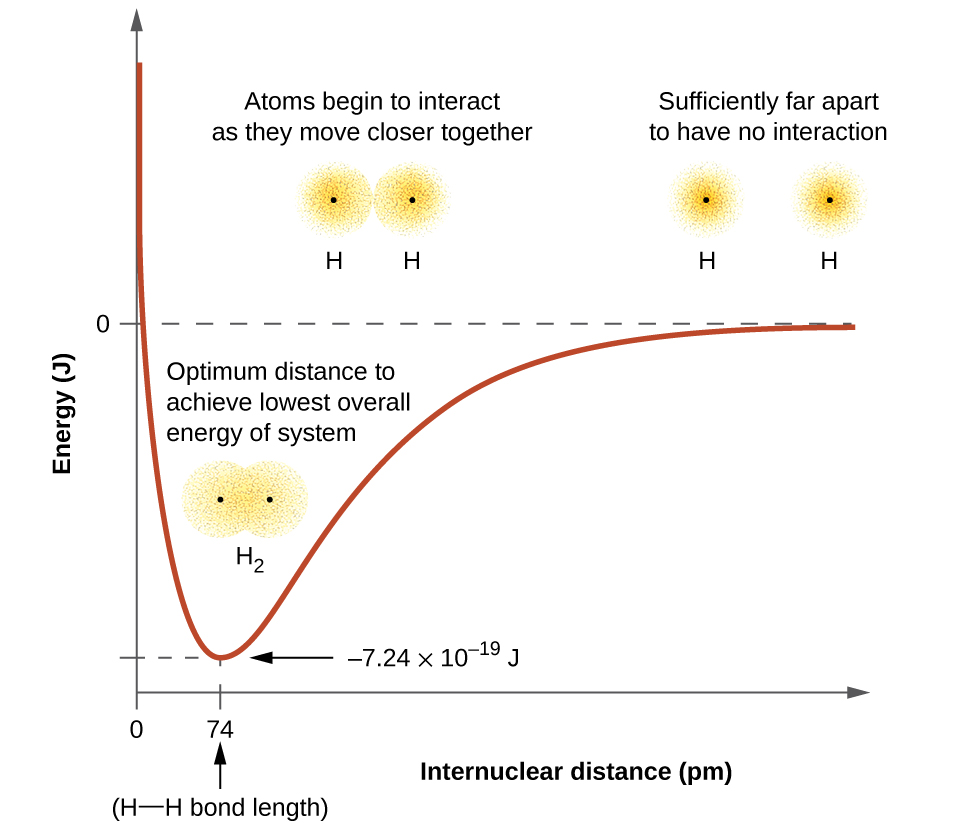
The bond energy is the difference between the energy minimum (which occurs at the bond distance) and the energy of the two separated atoms. This is the quantity of energy released when the bond is formed. Conversely, the same amount of energy is required to break the bond. For the \(H_2\) molecule shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), at the bond distance of 74 pm the system is \(7.24 \times 10^{−19}\, J\) lower in energy than the two separated hydrogen atoms. Multiplying this by avagadro's number gives a bond energy for \(H_2\) of \(4.36 \times 10^5\; J/mol\). Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows average bond lengths and energies for several different common bond types. It is important to note that these values are averages. For example Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) lists the average CH bond energy is 413 kJ/mole, but breaking the first C–H bond in CH4 requires 439.3 kJ/mol while breaking the first C–H bond in \(\ce{H–CH2C6H5}\) (a common paint thinner) requires 375.5 kJ/mol.
| Bond | Length (pm) | Energy (kJ/mol) | Bond | Length (pm) | Energy (kJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H–H | 74 | 436 | C–O | 140.1 | 358 | |
| H–C | 106.8 | 413 | \(\mathrm{C=O}\) | 119.7 | 745 | |
| H–N | 101.5 | 391 | \(\mathrm{C≡O}\) | 113.7 | 1072 | |
| H–O | 97.5 | 467 | H–Cl | 127.5 | 431 | |
| C–C | 150.6 | 347 | H–Br | 141.4 | 366 | |
| \(\mathrm{C=C}\) | 133.5 | 614 | H–I | 160.9 | 298 | |
| \(\mathrm{C≡C}\) | 120.8 | 839 | O–O | 148 | 146 | |
| C–N | 142.1 | 305 | \(\mathrm{O=O}\) | 120.8 | 498 | |
| \(\mathrm{C=N}\) | 130.0 | 615 | F–F | 141.2 | 159 | |
| \(\mathrm{C≡N}\) | 116.1 | 891 | Cl–Cl | 198.8 | 243 |
For H2 the overlap between the s orbitals does not depend on the orientation of the molecule. However, for most molecules both the distance between the atoms and the orientation of the orbitals affects the formation of the bond. Greater overlap is possible when orbitals are oriented in a direct line between the two nuclei. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) illustrates this for two p orbitals when they overlap end to end or at an angle. The overlap is greater when the orbitals overlap end to end rather than at an angle.
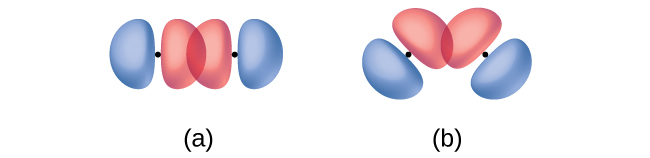
The overlap of two s orbitals (as in H2), the overlap of an s orbital and a p orbital (as in HCl), and the end-to-end overlap of two p orbitals (as in Cl2) all produce sigma bonds (σ bonds), as illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). A σ bond is a covalent bond in which the electron density is concentrated in the region along the internuclear axis; that is, a line between the nuclei would pass through the center of the overlap region. Single bonds in Lewis structures are described as σ bonds in valence bond theory.
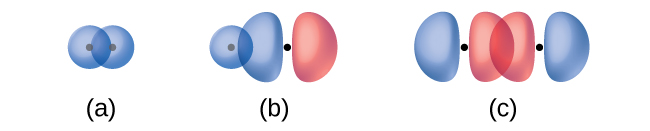
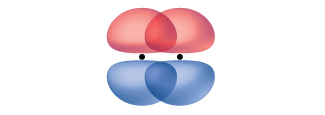
A pi bond (π bond) is a type of covalent bond that results from the side-by-side overlap of two p orbitals, as illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). In a π bond, the regions of orbital overlap lie on opposite sides of the internuclear axis. Along the axis itself, there is a node, that is, a plane with no probability of finding an electron. Although this figure shows the orbitals overlapping in two places for a π bond, this is still one bond.
While all single bonds are σ bonds, multiple bonds consist of both σ and π bonds. As the Lewis structures suggest, O2 contains a double bond, and N2 contains a triple bond. The double bond consists of one σ bond and one π bond, and the triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds. Between any two atoms, the first bond formed will always be a σ bond, but there can only be one σ bond in any one location. In any multiple bond, there will be one σ bond, and the remaining one or two bonds will be π bonds. These bonds are described in more detail later in this chapter.
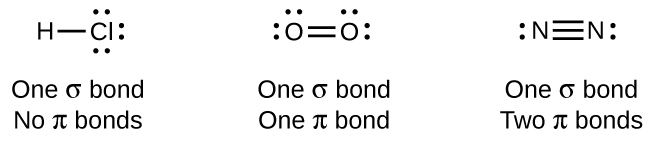
As seen in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\), an average carbon-carbon single bond energy is 347 kJ/mol. In a carbon-carbon double bond, the π bond increases the bond strength by 267 kJ/mol. Adding an second π bond to form a carbon-carbon tripple bond causes a additional increase of 225 kJ/mol. The σ and π bonds between other atoms follow the same trend and each individual π bond is weaker than the σ bond between the same two atoms. This happens because a σ bond has more overlap to generate attraction between the two atoms than in a π bond.
Butadiene, C4H6, is used to make synthetic rubber. Identify the number of σ and π bonds contained in this molecule.
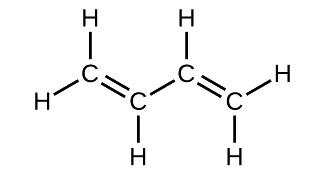
Solution
There are six σ C–H bonds and one σ C–C bond, for a total of seven from the single bonds. There are two double bonds that each have a π bond in addition to the σ bond. This gives a total nine σ and two π bonds overall.
Identify each illustration as depicting a σ or π bond:
- side-by-side overlap of a 4p and a 2p orbital
- end-to-end overlap of a 4p and 4p orbital
- end-to-end overlap of a 4p and a 2p orbital
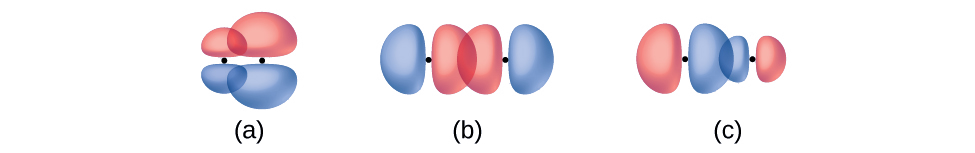
- Answer
-
(a) is a π bond with a node along the axis connecting the nuclei while (b) and (c) are σ bonds that overlap along the axis.
Hybrid Orbitals
Thinking in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals is one way for us to explain how chemical bonds form in diatomic molecules. However, to understand how molecules with more than two atoms form stable bonds, we require a more detailed model. As an example, let us consider the water molecule, in which we have one oxygen atom bonding to two hydrogen atoms. Oxygen has the electron configuration 1s22s22p4, with two unpaired electrons (one in each of the two 2p orbitals). Valence bond theory would predict that the two O–H bonds form from the overlap of these two 2p orbitals with the 1s orbitals of the hydrogen atoms. Since the p orbitals are aligned along the x, y, and z axis, this should result in a 90° bond angle, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\). This is different from the bond angle predicted by VSEPR - since the oxygen atom has four electron pairs around it VSEPR predicts a 109.5° bond angle, maybe a bit smaller to accommodate the two sets of lone pair electrons taking more space. VSEPR is consistent with experimental evidence which shows the bond angle is 104.5°. The oxygen atomic orbitals are not oriented to allow the correct molecular geometry using valence bond theory. A different model is needed.
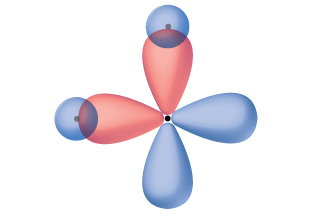
Quantum-mechanical calculations suggest why the observed bond angles in H2O differ from those predicted by the overlap of the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atoms with the 2p orbitals of the oxygen atom. The mathematical expression known as the wave function, ψ, describes the shape of each orbital using the wavelike properties of electrons. When atoms are bound together in a molecule, the wave functions combine and create new wave functions that have different shapes. This process of combining the wave functions for atomic orbitals is called hybridization and is mathematically accomplished by the linear combination of atomic orbitals. The new orbitals that result are called hybrid orbitals and they can explain the molecular geometry of the water molecule. The valence orbitals in an isolated oxygen atom are a 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. The valence orbitals in an oxygen atom in a water molecule differ; they consist of four equivalent hybrid orbitals that point approximately toward the corners of a tetrahedron (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Consequently, the overlap of the O and H orbitals should result in a tetrahedral bond angle (109.5°) as predicted by VSEPR. The observed angle of 104.5° is experimental evidence for which quantum-mechanical calculations give a useful explanation: Valence bond theory must include a hybridization component to explain molecular geometry.
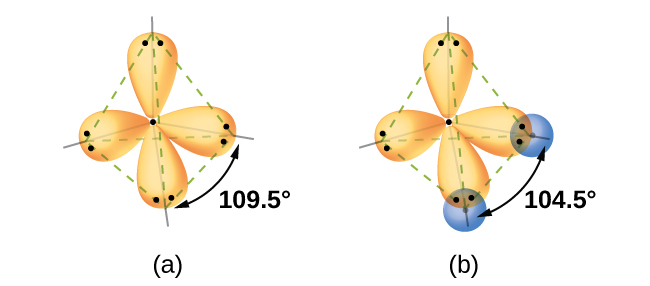
The following ideas are important in understanding hybridization:
- Hybrid orbitals do not exist in isolated atoms. They are formed only in covalently bonded atoms.
- Hybrid orbitals have shapes and orientations that are different from those of the atomic orbitals in isolated atoms.
- A set of hybrid orbitals is generated by combining atomic orbitals. The number of hybrid orbitals in a set is equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined to produce the set.
- All orbitals in a set of hybrid orbitals are equivalent in shape and energy.
- The type of hybrid orbitals formed in a bonded atom depends on its electron-pair geometry as predicted by the VSEPR theory.
- Hybrid orbitals overlap to form σ bonds. Unhybridized p orbitals overlap to form π bonds.
In the following sections, we shall discuss the common types of hybrid orbitals.
sp Hybridization
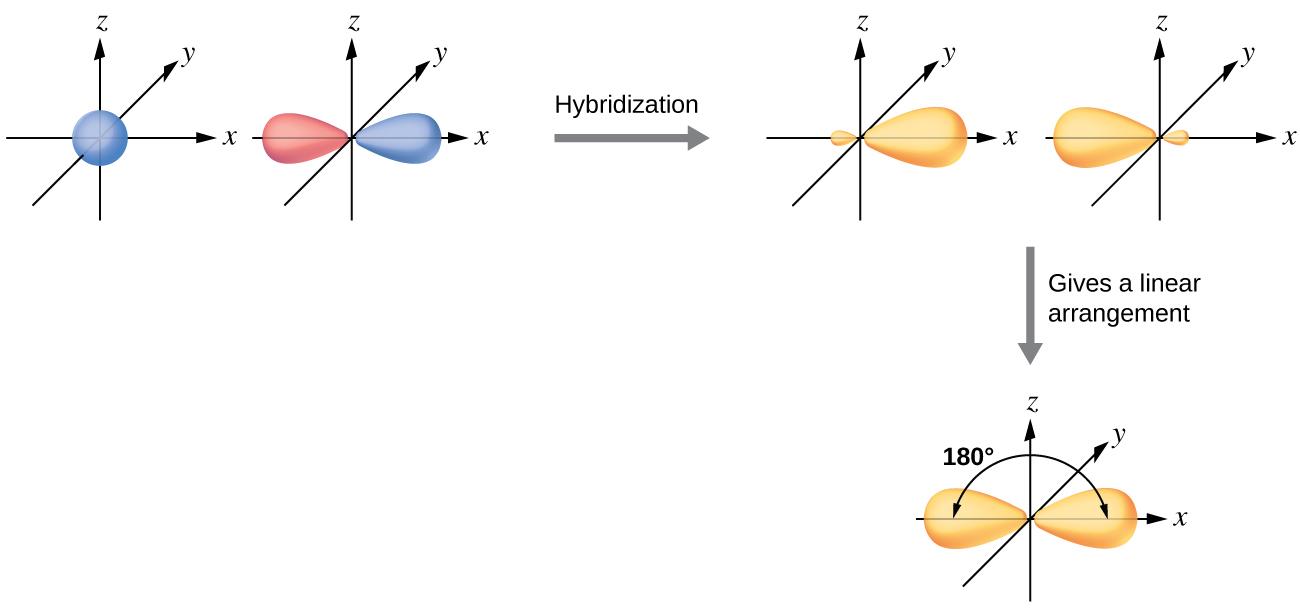
The beryllium atom in a gaseous BeCl2 molecule is an example of a central atom with no lone pairs of electrons in a linear arrangement of three atoms. There are two regions of valence electron density in the BeCl2 molecule that correspond to the two covalent Be–Cl bonds. According to VSEPR these two electron domains will result in a linear molecular geometry. To generate this geometry two of the Be atom’s four valence orbitals mix to yield two hybrid orbitals. This hybridization process involves mixing of the valence s orbital with one of the valence p orbitals to yield two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals that are oriented in the linear geometry shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). In this figure, the set of sp orbitals appears similar in shape to the original p orbital, but there is an important difference. The number of atomic orbitals combined always equals the number of hybrid orbitals formed. The p orbital is one orbital that can hold up to two electrons. The sp set is two equivalent orbitals that point 180° from each other. The two electrons that were originally in the s orbital are now distributed to the two new sp orbitals, which are half filled. The half-filled hybrid orbitals in BeCl2, overlap with orbitals from the chlorine atoms to form two identical σ bonds.
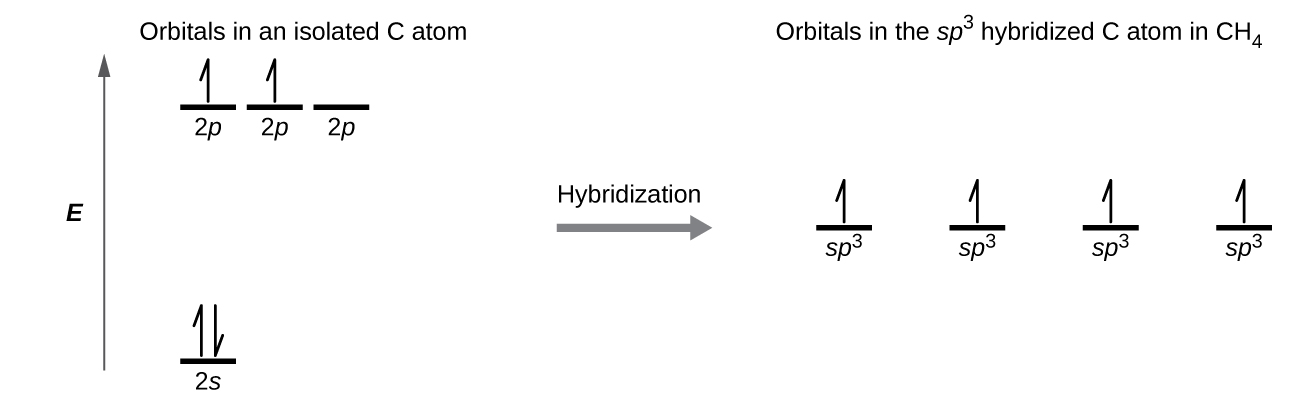
We illustrate the electronic differences in an isolated Be atom and in the bonded Be atom in the orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). These diagrams represent each orbital by a horizontal line (indicating its energy) and each electron by an arrow. Energy increases toward the top of the diagram. We use one upward arrow to indicate one electron in an orbital and two arrows (up and down) to indicate two electrons of opposite spin.
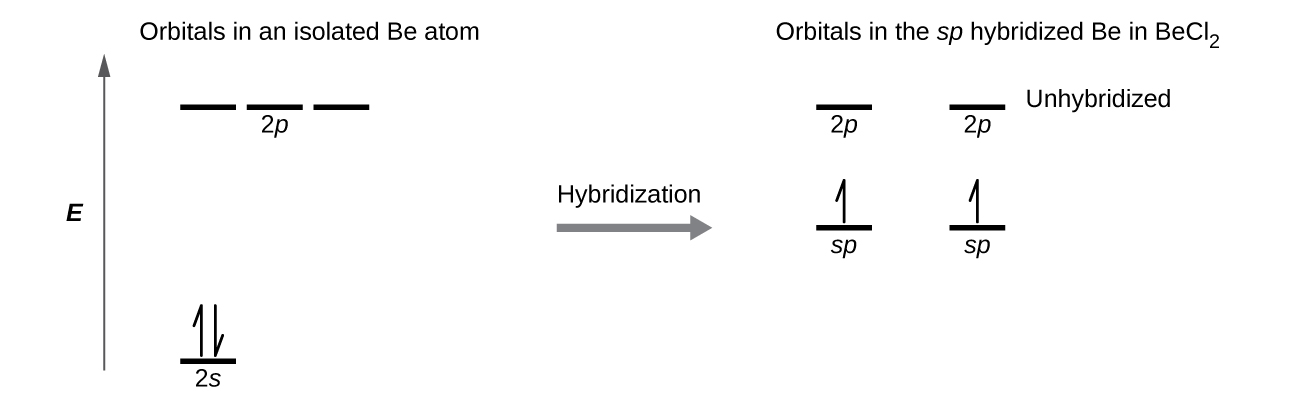
When atomic orbitals hybridize, the valence electrons occupy the newly created orbitals. The Be atom had two valence electrons, so each of the sp orbitals gets one of these electrons. Each of these electrons pairs up with the unpaired electron on a chlorine atom when a hybrid orbital and a chlorine orbital overlap during the formation of the Be–Cl bonds. Any central atom surrounded by just two regions of valence electron density in a molecule will exhibit sp hybridization. Other examples include the mercury atom in the linear HgCl2 molecule, the zinc atom in Zn(CH3)2, which contains a linear C–Zn–C arrangement, and the carbon atoms in HCCH and CO2.
sp2 Hybridization
The valence orbitals of a central atom surrounded by three regions of electron density create a trigonal planer geometry in VSEPR. This arrangement results from sp2 hybridization, the mixing of one s orbital and two p orbitals to produce three identical hybrid orbitals oriented in a trigonal planar geometry (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). This geometry is creates a central atom with a set of three sp2 hybrid orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital.
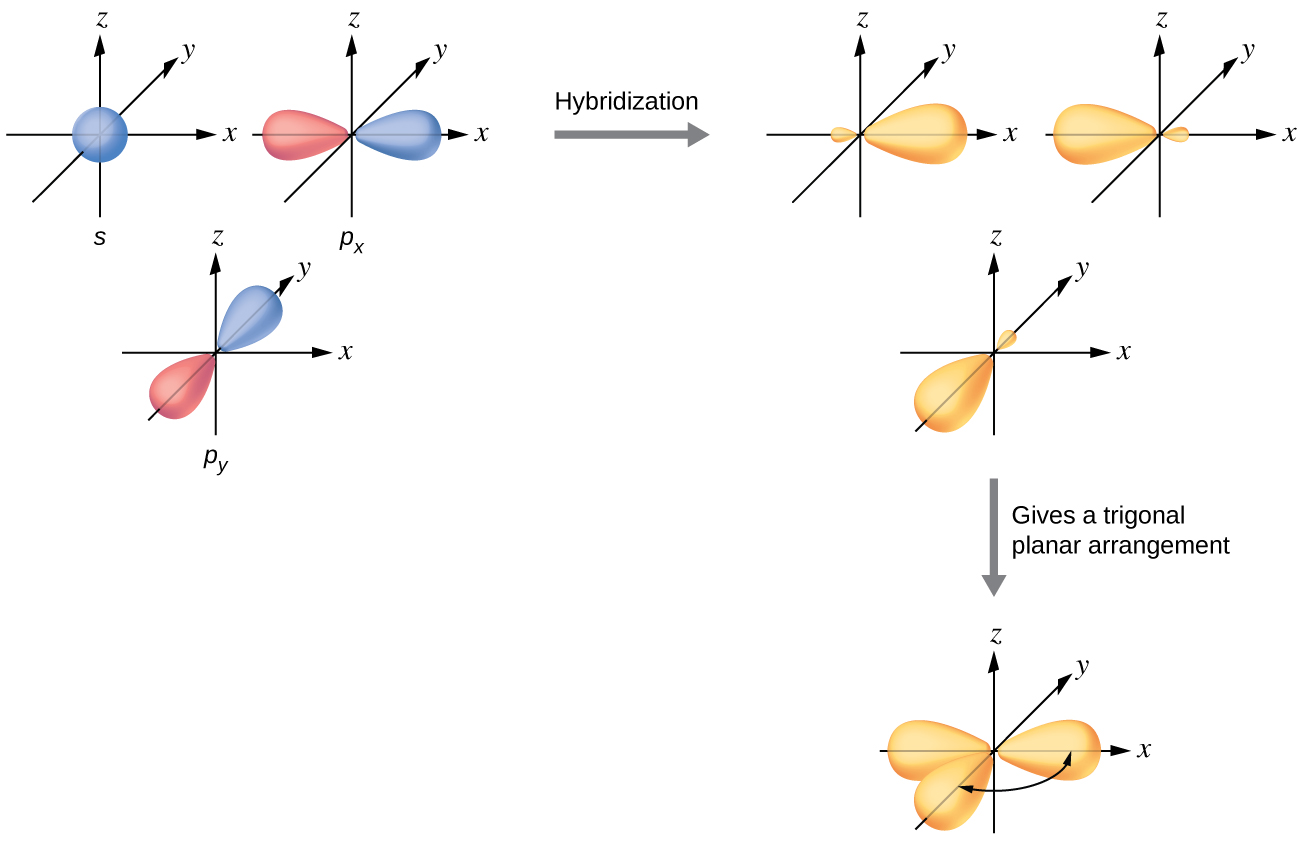
Although quantum mechanics yields the “plump” orbital lobes as depicted in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\), sometimes for clarity these orbitals are drawn thinner and without the minor lobes, as in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\), to avoid obscuring other features of a given illustration. We will use these “thinner” representations whenever the true view is too crowded to easily visualize.
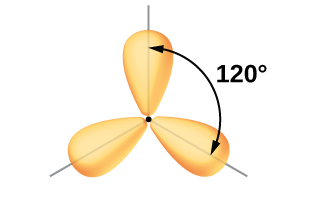
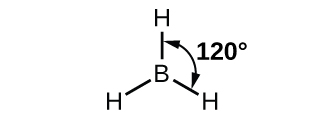
The observed structure of the borane molecule, BH3, suggests sp2 hybridization for boron in this compound. The molecule is trigonal planar, and the boron atom is involved in three bonds to hydrogen atoms ( Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)).
We can illustrate the comparison of orbitals and electron distribution in an isolated boron atom and in the bonded atom in BH3 as shown in the orbital energy level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\). We redistribute the three valence electrons of the boron atom in the three sp2 hybrid orbitals, and each boron electron pairs with a hydrogen electron when B–H bonds form.

Any central atom surrounded by three regions of electron density will exhibit sp2 hybridization. This includes molecules with a lone pair on the central atom, such as ClNO (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)), or molecules with two single bonds and a double bond connected to the central atom, as in formaldehyde, CH2O, and ethene, H2CCH2.
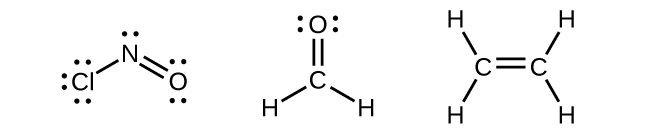
sp3 Hybridization
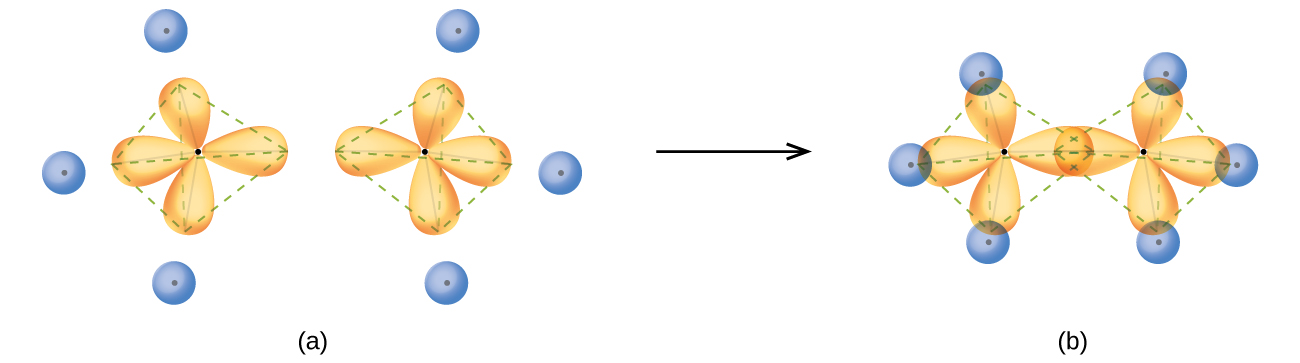
The valence orbitals of an atom surrounded by a tetrahedral arrangement of bonding pairs and lone pairs consist of a set of four sp3 hybrid orbitals. The hybrids result from the mixing of one s orbital and all three p orbitals that produces four identical sp3 hybrid orbitals (Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)). Each of these hybrid orbitals points toward a different corner of a tetrahedron.
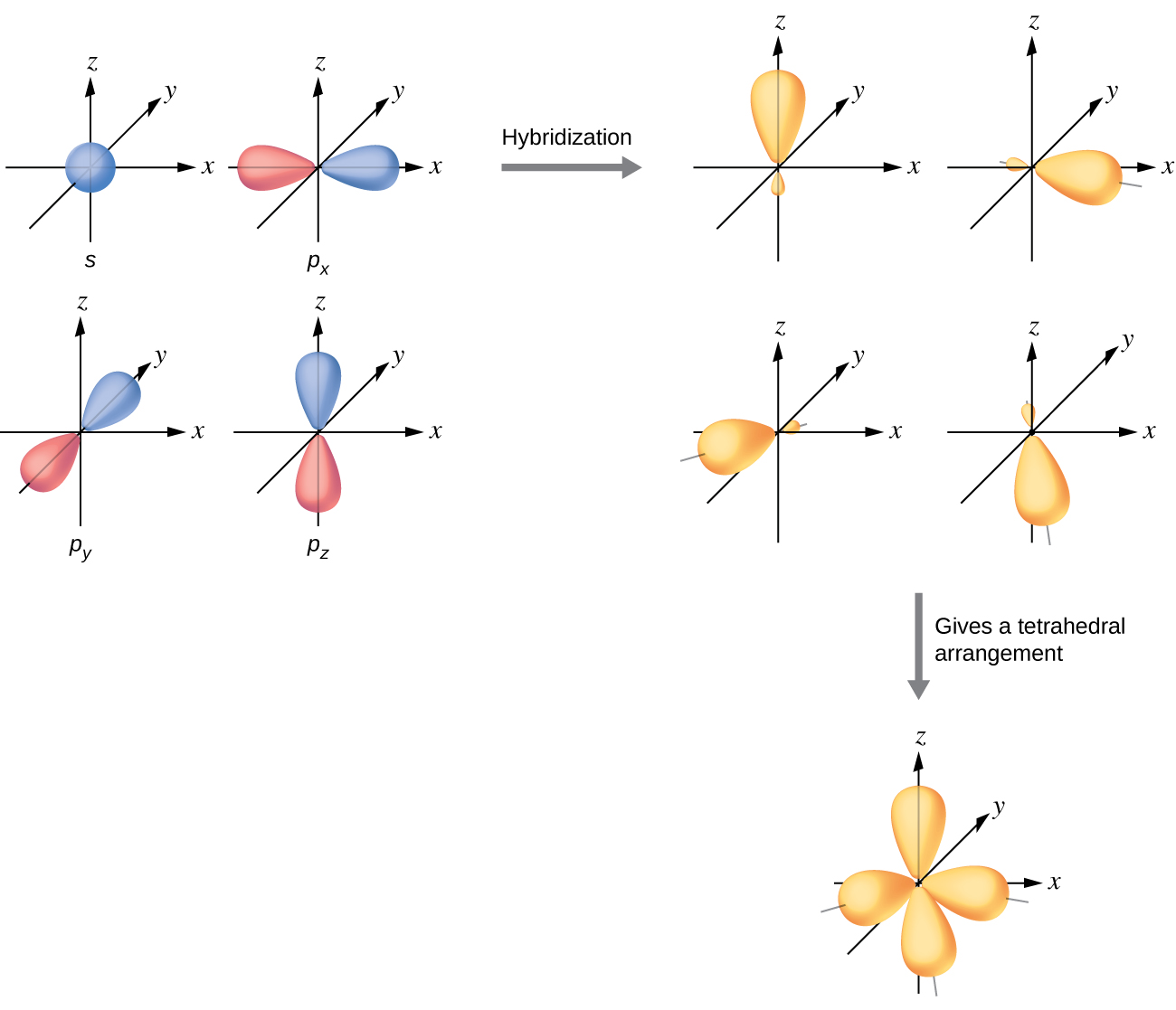
A molecule of methane, CH4, consists of a carbon atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms at the corners of a tetrahedron. The carbon atom in methane exhibits sp3 hybridization. We illustrate the orbitals and electron distribution in an isolated carbon atom and in the bonded atom in CH4 in Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\). The four valence electrons of the carbon atom are distributed equally in the hybrid orbitals, and each carbon electron pairs with a hydrogen electron when the C–H bonds form.
In a methane molecule, the 1s orbital of each of the four hydrogen atoms overlaps with one of the four sp3 orbitals of the carbon atom to form a sigma (σ) bond. This results in the formation of four strong, equivalent covalent bonds between the carbon atom and each of the hydrogen atoms to produce the methane molecule, CH4.
The structure of ethane, C2H6, is similar to that of methane in that each carbon in ethane has four neighboring atoms arranged at the corners of a tetrahedron—three hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom (Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)). However, in ethane an sp3 orbital of one carbon atom overlaps end to end with an sp3 orbital of a second carbon atom to form a σ bond between the two carbon atoms. Each of the remaining sp3 hybrid orbitals overlaps with an s orbital of a hydrogen atom to form carbon–hydrogen σ bonds. The structure and overall outline of the bonding orbitals of ethane are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\). The orientation of the two CH3 groups is not fixed relative to each other. Experimental evidence shows that rotation around σ bonds occurs easily.
An sp3 hybrid orbital can also hold a lone pair of electrons. For example, the nitrogen atom in ammonia is surrounded by three bonding pairs and a lone pair of electrons directed to the four corners of a tetrahedron. The nitrogen atom is sp3 hybridized with one hybrid orbital occupied by the lone pair.
The molecular structure of water is consistent with a tetrahedral arrangement of two lone pairs and two bonding pairs of electrons. Thus we say that the oxygen atom is sp3 hybridized, with two of the hybrid orbitals occupied by lone pairs and two by bonding pairs. Since lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs, structures that contain lone pairs have bond angles slightly distorted from the ideal. Perfect tetrahedra have angles of 109.5°, but the observed angles in ammonia (107.3°) and water (104.5°) are slightly smaller because the lone pair electrons occupy more space than the bonding electrons. Other examples of sp3 hybridization include CCl4, PCl3, and NCl3.
sp3d Hybridization
To describe the five bonding orbitals in a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, we must use five of the valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and one of the d orbitals), which gives five sp3d hybrid orbitals. These hybridizations are only possible for atoms that have d orbitals in their valence subshells. Elements in the first and second period of the periodic table can not form sp3d hybrid orbitals.
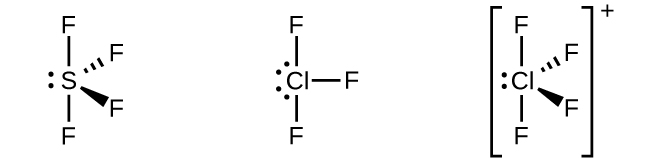
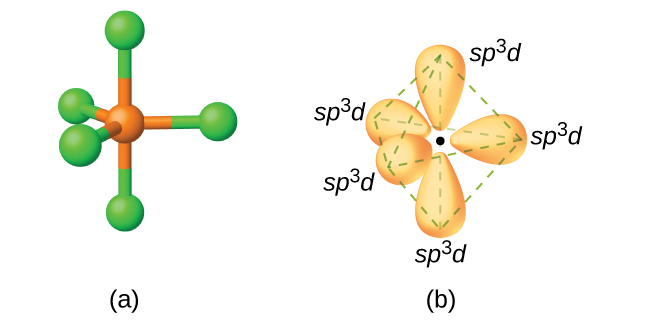
In a molecule of phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5, there are five P–Cl bonds (thus five pairs of valence electrons around the phosphorus atom) directed toward the corners of a trigonal bipyramid. We use the 3s orbital, the three 3p orbitals, and one of the 3d orbitals to form the set of five sp3d hybrid orbitals (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)) that are involved in the P–Cl bonds. Other atoms that exhibit sp3d hybridization include the sulfur atom in SF4 and the chlorine atoms in ClF3 and in \(\ce{ClF4+}\). (The electrons on fluorine atoms are omitted for clarity.)
sp3d2 Hybridization
With an octahedral arrangement of six hybrid orbitals, we must use six valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and two of the d orbitals in its valence shell), which gives six sp3d2 hybrid orbitals. These hybridizations are only possible for atoms that have d orbitals in their valence subshells. Elements in the first and second period of the periodic table can not form sp3d2 hybrid orbitals.
The sulfur atom in sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, exhibits sp3d2 hybridization. A molecule of sulfur hexafluoride has six bonding pairs of electrons connecting six fluorine atoms to a single sulfur atom. There are no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. To bond six fluorine atoms, the 3s orbital, the three 3p orbitals, and two of the 3d orbitals form six equivalent sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, each directed toward a different corner of an octahedron. Other atoms that exhibit sp3d2 hybridization include the phosphorus atom in \(\ce{PCl6-}\), the iodine atom in the interhalogens \(\ce{IF6+}\), IF5, \(\ce{ICl4-}\), \(\ce{IF4-}\) and the xenon atom in XeF4.
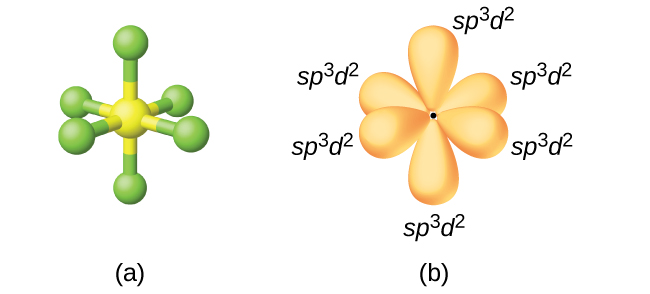
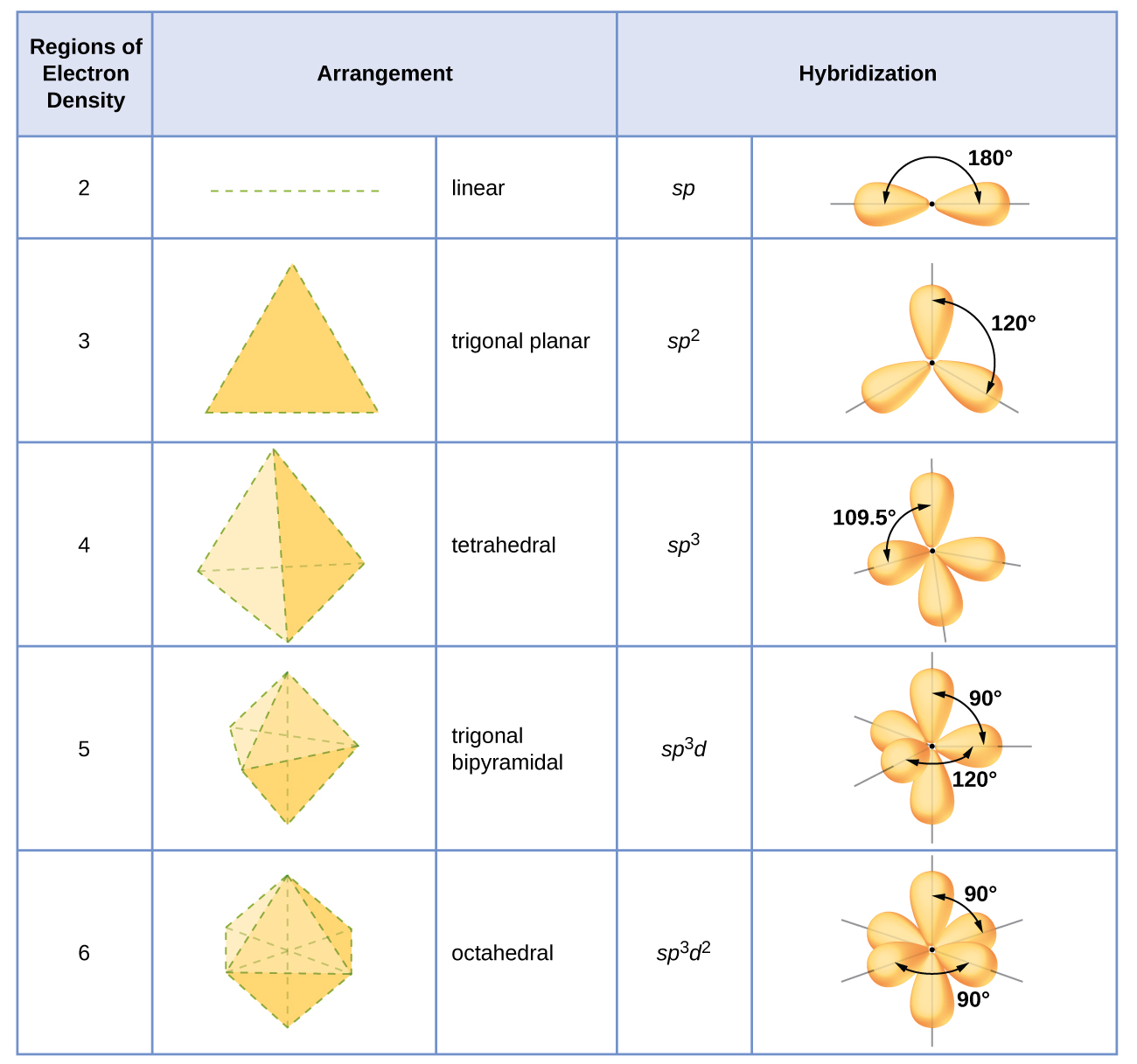
Assignment of Hybrid Orbitals to Central Atoms
The hybridization of an atom is determined based on the number of regions of electron density that surround it. The geometrical arrangements characteristic of the various sets of hybrid orbitals are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\). These arrangements are identical to those of the electron-pair geometries predicted by VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory predicts the shapes of molecules, and hybrid orbital theory provides an explanation for how those shapes are formed. To find the hybridization of a central atom, we can use the following guidelines:
- Determine the Lewis structure of the molecule.
- Determine the electron-pair geometry using VSEPR. Single bonds, multiple bonds, radicals, and lone pairs each count as one region.
- Assign the set of hybridized orbitals from Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\) that corresponds to this geometry.
It is important to remember that hybridization was devised to rationalize experimentally observed molecular geometries, not the other way around.
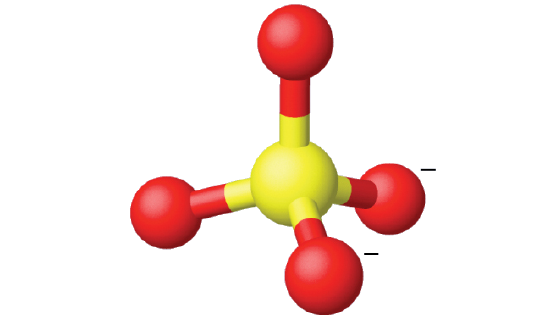
Ammonium sulfate is important as a fertilizer. What is the hybridization of the sulfur atom in the sulfate ion, \(\ce{SO4^2-}\)?
Solution
The Lewis structure of sulfate shows there are four regions of electron density.
What is the hybridization of the selenium atom in SeF4?
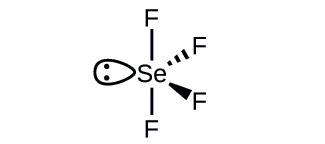
- Answer
-
The selenium atom is sp3d hybridized.
Urea, NH2C(O)NH2, is sometimes used as a source of nitrogen in fertilizers. What is the hybridization of each nitrogen and carbon atom in urea?
Solution
The Lewis structure of urea is
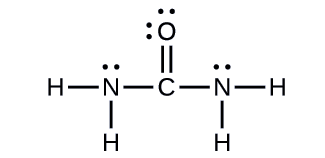
The carbon atom is surrounded by three regions of electron density, positioned in a trigonal planar arrangement. The hybridization in a trigonal planar electron pair geometry is sp2 (Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)), which is the hybridization of the carbon atom in urea.
The nitrogen atoms are both surrounded by four regions of electron density, three bonds and a lone pair of electrons. This results in a tetrahedral geometry and requires sp3 hybridization.
Acetic acid, H3CC(O)OH, is the molecule that gives vinegar its odor and sour taste. What is the hybridization of the two carbon atoms in acetic acid?
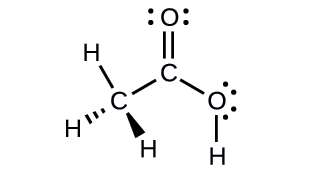
- Answer
-
H3C, sp3; C(O)OH, sp2
Summary
Valence bond theory describes bonding as a consequence of the overlap of two separate atomic orbitals on different atoms that creates a region with one pair of electrons shared between the two atoms. When the orbitals overlap along an axis containing the nuclei, they form a σ bond. When they overlap in a fashion that creates a node along this axis, they form a π bond.
We can use hybrid orbitals, which are mathematical combinations of some or all of the valence atomic orbitals, to describe the electron density around covalently bonded atoms. These hybrid orbitals either form sigma (σ) bonds directed toward other atoms of the molecule or contain lone pairs of electrons. We can determine the type of hybridization around a central atom from the geometry of the regions of electron density about it. Two such regions imply sp hybridization; three, sp2 hybridization; four, sp3 hybridization; five, sp3d hybridization; and six, sp3d2 hybridization. Pi (π) bonds are formed from unhybridized atomic orbitals (p or d orbitals).
Glossary
- hybrid orbital
- orbital created by combining atomic orbitals on a central atom
- hybridization
- model that describes the changes in the atomic orbitals of an atom when it forms a covalent compound
- overlap
- coexistence of orbitals from two different atoms sharing the same region of space, leading to the formation of a covalent bond
- node
- plane separating different lobes of orbitals, where the probability of finding an electron is zero
- pi bond (π bond)
- covalent bond formed by side-by-side overlap of atomic orbitals; the electron density is found on opposite sides of the internuclear axis
- sp hybrid orbital
- one of a set of two orbitals with a linear arrangement that results from combining one s and one p orbital
- sp2 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of three orbitals with a trigonal planar arrangement that results from combining one s and two p orbitals
- sp3 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of four orbitals with a tetrahedral arrangement that results from combining one s and three p orbitals
- sp3d hybrid orbital
- one of a set of five orbitals with a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement that results from combining one s, three p, and one d orbital
- sp3d2 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of six orbitals with an octahedral arrangement that results from combining one s, three p, and two d orbitals
- sigma bond (σ bond)
- covalent bond formed by overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis
- valence bond theory
- description of bonding that involves atomic orbitals overlapping to form σ or π bonds, within which pairs of electrons are shared
Contributors and Attributions
Paul Flowers (University of North Carolina - Pembroke), Klaus Theopold (University of Delaware) and Richard Langley (Stephen F. Austin State University) with contributing authors. Textbook content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/85abf193-2bd...a7ac8df6@9.110).


