6.1: Energy Basics
- Page ID
- 428721
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Define energy, distinguish types of energy, and describe the nature of energy changes that accompany chemical and physical changes
- Distinguish the related properties of heat, thermal energy, and temperature
- Define and distinguish specific heat and heat capacity, and describe the physical implications of both
- Perform calculations involving heat, specific heat, and temperature change
Introduction
Chemical reactions, such as those that occur when you light a match, involve changes in energy as well as matter. Societies at all levels of development could not function without the energy released by chemical reactions. In 2012, about 85% of US energy consumption came from the combustion of petroleum products, coal, wood, and garbage. We use this energy to produce electricity (38%); to transport food, raw materials, manufactured goods, and people (27%); for industrial production (21%); and to heat and power our homes and businesses (10%).1 While these combustion reactions help us meet our essential energy needs, they are also a major contributor to global climate change.

Useful forms of energy are also available from a variety of chemical reactions other than combustion. For example, the energy produced by the batteries in a cell phone, car, or flashlight results from chemical reactions. This chapter introduces many of the basic ideas necessary to explore the relationships between chemical changes and energy, with a focus on thermal energy.
Chemical changes and their accompanying changes in energy are important parts of our everyday world (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). The macronutrients in food (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) undergo metabolic reactions that provide the energy to keep our bodies functioning. We burn a variety of fuels (gasoline, natural gas, coal) to produce energy for transportation, heating, and the generation of electricity. Industrial chemical reactions use enormous amounts of energy to produce raw materials (such as iron and aluminum). Energy is then used to manufacture those raw materials into useful products, such as cars, skyscrapers, and bridges.

Over 90% of the energy we use comes originally from the sun. Every day, the sun provides the earth with almost 10,000 times the amount of energy necessary to meet all of the world’s energy needs for that day. Our challenge is to find ways to convert and store incoming solar energy so that it can be used in reactions or chemical processes that are both convenient and nonpolluting. Plants and many bacteria capture solar energy through photosynthesis. We release the energy stored in plants when we burn wood or plant products such as ethanol. We also use this energy to fuel our bodies by eating food that comes directly from plants or from animals that got their energy by eating plants. Burning coal and petroleum also releases stored solar energy: These fuels are fossilized plant and animal matter.
This chapter will introduce the basic ideas of an important area of science concerned with the amount of heat absorbed or released during chemical and physical changes—an area called thermochemistry. The concepts introduced in this chapter are widely used in almost all scientific and technical fields. Food scientists use them to determine the energy content of foods. Biologists study the energetics of living organisms, such as the metabolic combustion of sugar into carbon dioxide and water. The oil, gas, and transportation industries, renewable energy providers, and many others endeavor to find better methods to produce energy for our commercial and personal needs. Engineers strive to improve energy efficiency, find better ways to heat and cool our homes, refrigerate our food and drinks, and meet the energy and cooling needs of computers and electronics, among other applications. Understanding thermochemical principles is essential for chemists, physicists, biologists, geologists, every type of engineer, and just about anyone who studies or does any kind of science.
Footnotes
- US Energy Information Administration, Primary Energy Consumption by Source and Sector, 2012, Total Energy [www.eia.gov]. Data derived from US Energy Information Administration, Monthly Energy Review (January 2014).
Energy
Energy can be defined as the capacity to supply heat or do work. One type of work (w) is the process of causing matter to move against an opposing force. For example, we do work when we inflate a bicycle tire—we move matter (the air in the pump) against the opposing force of the air surrounding the tire.
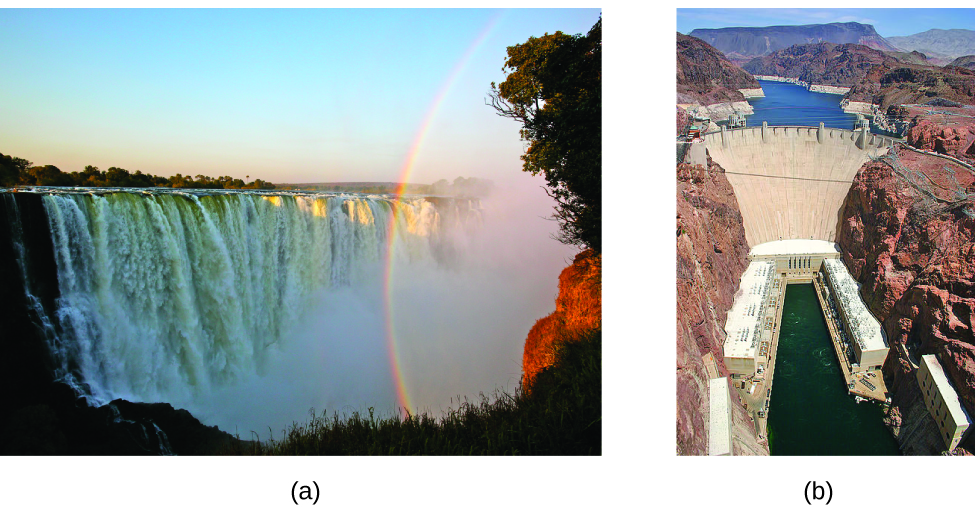
Like matter, energy comes in different types. One scheme classifies energy into two types: potential energy, the energy an object has because of its relative position, composition, or condition, and kinetic energy, the energy that an object possesses because of its motion. Water at the top of a waterfall or dam has potential energy because of its position; when it flows downward through generators, it has kinetic energy that can be used to do work and produce electricity in a hydroelectric plant (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). A battery has potential energy because the chemicals within it can produce electricity that can do work.

Energy can be converted from one form into another, but all of the energy present before a change occurs always exists in some form after the change is completed. This observation is expressed in the law of conservation of energy: during a chemical or physical change, energy can be neither created nor destroyed, although it can be changed in form. (This is also one version of the first law of thermodynamics, as you will learn later.)
When one substance is converted into another, there is always an associated conversion of one form of energy into another. Heat is usually released or absorbed, but sometimes the conversion involves light, electrical energy, or some other form of energy. For example, chemical energy (a type of potential energy) is stored in the molecules that compose gasoline. When gasoline is combusted within the cylinders of a car’s engine, the rapidly expanding gaseous products of this chemical reaction generate mechanical energy (a type of kinetic energy) when they move the cylinders’ pistons.
According to the law of conservation of matter (seen in an earlier chapter), there is no detectable change in the total amount of matter during a chemical change. When chemical reactions occur, the energy changes are relatively modest and the mass changes are too small to measure, so the laws of conservation of matter and energy hold well. However, in nuclear reactions, the energy changes are much larger (by factors of a million or so), the mass changes are measurable, and matter-energy conversions are significant. This will be examined in more detail in a later chapter on nuclear chemistry. To encompass both chemical and nuclear changes, we combine these laws into one statement: The total quantity of matter and energy in the universe is fixed.
Thermal Energy, Temperature, and Heat
Thermal energy is kinetic energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. Temperature is a quantitative measure of “hot” or “cold.” When the atoms and molecules in an object are moving or vibrating quickly, they have a higher average kinetic energy (KE), and we say that the object is “hot.” When the atoms and molecules are moving slowly, they have lower KE, and we say that the object is “cold” (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). Assuming that no chemical reaction or phase change (such as melting or vaporizing) occurs, increasing the amount of thermal energy in a sample of matter will cause its temperature to increase. And, assuming that no chemical reaction or phase change (such as condensation or freezing) occurs, decreasing the amount of thermal energy in a sample of matter will cause its temperature to decrease.

Most substances expand as their temperature increases and contract as their temperature decreases. This property can be used to measure temperature changes, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). The operation of many thermometers depends on the expansion and contraction of substances in response to temperature changes.
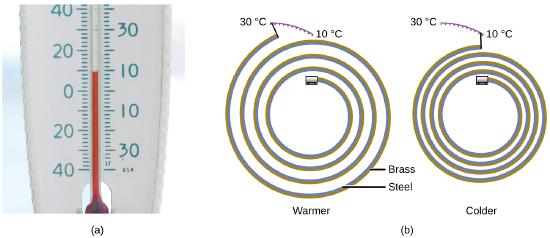

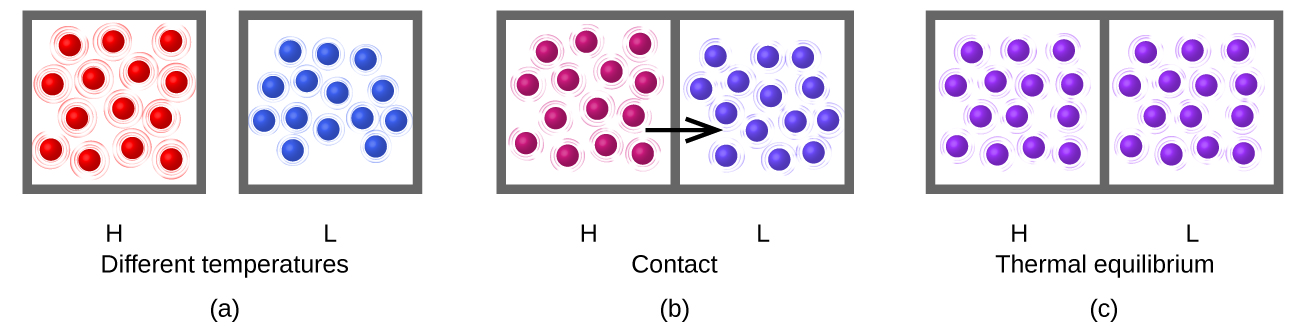
Heat (q) is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies at different temperatures. Heat flow increases the thermal energy of one body and decreases the thermal energy of the other. Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) shows what happens when two materials at different temperatures are in contact. Initially H, the material at high temperature and high thermal energy, and L, the material at low temperature and low thermal energy, are not in contact. If H is placed in contact with L, the thermal energy flows spontaneously from substance H to substance L. The temperature of substance H will decrease, as the kinetic energy transfers to L; the temperature of substance L will increase, as it gaines kinetic energy from H. Heat flow continues until the two substances are at the same temperature (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)).
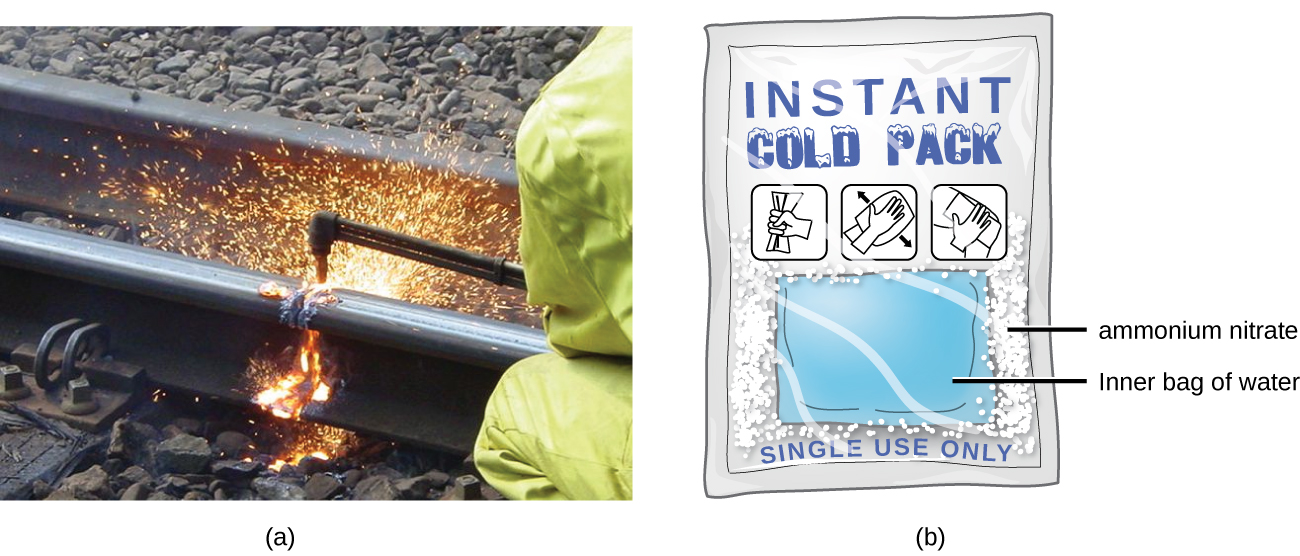
Matter undergoing chemical reactions and physical changes can release or absorb heat. A change that releases heat is called an exothermic process. For example, the combustion reaction that occurs when using an oxyacetylene torch is an exothermic process—this process also releases energy in the form of light as evidenced by the torch’s flame (Figure \(\PageIndex{7a}\)). A reaction or change that absorbs heat is an endothermic process. A cold pack used to treat muscle strains provides an example of an endothermic process. When the substances in the cold pack (water and a salt like ammonium nitrate) are brought together, the resulting process absorbs heat, leading to the sensation of cold.

Measuring Energy and Heat Capacity
Historically, energy was measured in units of calories (cal). A calorie is the amount of energy required to raise one gram of water by 1 degree C (1 kelvin). However, this quantity depends on the atmospheric pressure and the starting temperature of the water. The ease of measurement of energy changes in calories has meant that the calorie is still frequently used. The Calorie (with a capital C), or large calorie, commonly used in quantifying food energy content, is a kilocalorie. The SI unit of heat, work, and energy is the joule. A joule (J) is defined as the amount of energy used when a force of 1 newton moves an object 1 meter. It is named in honor of the English physicist James Prescott Joule. One joule is equivalent to 1 kg m2/s2, which is also called 1 newton–meter. A kilojoule (kJ) is 1000 joules. To standardize its definition, 1 calorie has been set to equal 4.184 joules.
We now introduce two concepts useful in describing heat flow and temperature change. The heat capacity (C) of a body of matter is the quantity of heat (q) it absorbs or releases when it experiences a temperature change (ΔT) of 1 degree Celsius (or equivalently, 1 kelvin)
\[C=\dfrac{q}{ΔT} \label{5.2.1} \]
Heat capacity is determined by both the type and amount of substance that absorbs or releases heat. It is therefore an extensive property—its value is proportional to the amount of the substance.
For example, consider the heat capacities of two cast iron frying pans. The heat capacity of the large pan is five times greater than that of the small pan because, although both are made of the same material, the mass of the large pan is five times greater than the mass of the small pan. More mass means more atoms are present in the larger pan, so it takes more energy to make all of those atoms vibrate faster. The heat capacity of the small cast iron frying pan is found by observing that it takes 18,150 J of energy to raise the temperature of the pan by 50.0 °C
\[C_{\text{small pan}}=\mathrm{\dfrac{18,140\; J}{50.0\; °C} =363\; J/°C} \label{5.2.2} \]
The larger cast iron frying pan, while made of the same substance, requires 90,700 J of energy to raise its temperature by 50.0 °C. The larger pan has a (proportionally) larger heat capacity because the larger amount of material requires a (proportionally) larger amount of energy to yield the same temperature change:
\[C_{\text{large pan}}=\mathrm{\dfrac{90,700\; J}{50.0\;°C}=1814\; J/°C} \label{5.2.3} \]
The specific heat capacity (c) of a substance, commonly called its “specific heat,” is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius (or 1 kelvin):
\[c = \dfrac{q}{\mathrm{m\Delta T}} \label{5.2.4} \]
Specific heat capacity depends only on the kind of substance absorbing or releasing heat. It is an intensive property—the type, but not the amount, of the substance is all that matters. For example, the small cast iron frying pan has a mass of 808 g. The specific heat of iron (the material used to make the pan) is therefore:
\[c_\ce{iron}=\mathrm{\dfrac{18,140\; J}{(808\; g)(50.0\;°C)} = 0.449\; J/g\; °C} \label{5.2.5} \]
The large frying pan has a mass of 4040 g. Using the data for this pan, we can also calculate the specific heat of iron:
\[c_\ce{iron}=\mathrm{\dfrac{90,700\; J}{(4,040\; g)(50.0\;°C)}=0.449\; J/g\; °C} \label{5.2.6} \]
Although the large pan is more massive than the small pan, since both are made of the same material, they both yield the same value for specific heat (for the material of construction, iron). Note that specific heat is measured in units of energy per temperature per mass and is an intensive property, being derived from a ratio of two extensive properties (heat and mass). The molar heat capacity, also an intensive property, is the heat capacity per mole of a particular substance and has units of J/mol °C (Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)).

Liquid water has a relatively high specific heat (about 4.2 J/g °C); most metals have much lower specific heats (usually less than 1 J/g °C). The specific heat of a substance varies somewhat with temperature. However, this variation is usually small enough that we will treat specific heat as constant over the range of temperatures that will be considered in this chapter. Specific heats of some common substances are listed in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
| Substance | Symbol (state) | Specific Heat (J/g °C) |
|---|---|---|
| helium | He(g) | 5.193 |
| water | H2O(l) | 4.184 |
| ethanol | C2H6O(l) | 2.376 |
| ice | H2O(s) | 2.093 (at −10 °C) |
| water vapor | H2O(g) | 1.864 |
| nitrogen | N2(g) | 1.040 |
| aluminum | Al(s) | 0.897 |
| carbon dioxide | CO2(g) | 0.853 |
| argon | Ar(g) | 0.522 |
| iron | Fe(s) | 0.449 |
| copper | Cu(s) | 0.385 |
| lead | Pb(s) | 0.130 |
| gold | Au(s) | 0.129 |
If we know the mass of a substance and its specific heat, we can determine the amount of heat, q, entering or leaving the substance by measuring the temperature change before and after the heat is gained or lost:
\[\begin{align*} q &= \ce{(specific\: heat)×(mass\: of\: substance)×(temperature\: change)}\label{5.2.7}\\q&=c×m×ΔT \\[4pt] &=c×m×(T_\ce{final}−T_\ce{initial})\end{align*} \]
In this equation, \(c\) is the specific heat of the substance, m is its mass, and ΔT (which is read “delta T”) is the temperature change, Tfinal − Tinitial. If a substance gains thermal energy, its temperature increases, its final temperature is higher than its initial temperature, Tfinal − Tinitial has a positive value, and the value of q is positive. If a substance loses thermal energy, its temperature decreases, the final temperature is lower than the initial temperature, Tfinal − Tinitial has a negative value, and the value of q is negative.
A flask containing \(\mathrm{8.0 \times 10^2\; g}\) of water is heated, and the temperature of the water increases from 21 °C to 85 °C. How much heat did the water absorb?
Solution
To answer this question, consider these factors:
- the specific heat of the substance being heated (in this case, water)
- the amount of substance being heated (in this case, 800 g)
- the magnitude of the temperature change (in this case, from 21 °C to 85 °C).
The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g °C, so to heat 1 g of water by 1 °C requires 4.184 J. We note that since 4.184 J is required to heat 1 g of water by 1 °C, we will need 800 times as much to heat 800 g of water by 1 °C. Finally, we observe that since 4.184 J are required to heat 1 g of water by 1 °C, we will need 64 times as much to heat it by 64 °C (that is, from 21 °C to 85 °C).
This can be summarized using the equation:
\[\begin{align*} q&=c×m×ΔT \\[4pt] &=c×m×(T_\ce{final}−T_\ce{initial}) \\[4pt] &=\mathrm{(4.184\:J/\cancel{g}°C)×(800\:\cancel{g})×(85−21)°C}\\[4pt] &=\mathrm{(4.184\:J/\cancel{g}°\cancel{C})×(800\:\cancel{g})×(64)°\cancel{C}}\\[4pt] &=\mathrm{210,000\: J(=210\: kJ)} \end{align*} \nonumber \]
Because the temperature increased, the water absorbed heat and \(q\) is positive.
How much heat, in joules, must be added to a \(\mathrm{5.00 \times 10^2 \;g}\) iron skillet to increase its temperature from 25 °C to 250 °C? The specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g °C.
Answer-
\(\mathrm{5.05 \times 10^4\; J}\)
Note that the relationship between heat, specific heat, mass, and temperature change can be used to determine any of these quantities (not just heat) if the other three are known or can be deduced.
A piece of unknown metal weighs 348 g. When the metal piece absorbs 6.64 kJ of heat, its temperature increases from 22.4 °C to 43.6 °C. Determine the specific heat of this metal (which might provide a clue to its identity).
Solution
Since mass, heat, and temperature change are known for this metal, we can determine its specific heat using the relationship:
\[\begin{align*} q&=c \times m \times \Delta T \\[4pt] &=c \times m \times (T_\ce{final}−T_\ce{initial}) \end{align*} \nonumber \]
Substituting the known values:
\[6,640\; \ce J=c \times \mathrm{(348\; g) \times (43.6 − 22.4)\; °C} \nonumber \]
Solving:
\[c=\mathrm{\dfrac{6,640\; J}{(348\; g) \times (21.2°C)} =0.900\; J/g\; °C} \nonumber \]
Comparing this value with the values in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\), this value matches the specific heat of aluminum, which suggests that the unknown metal may be aluminum.
A piece of unknown metal weighs 217 g. When the metal piece absorbs 1.43 kJ of heat, its temperature increases from 24.5 °C to 39.1 °C. Determine the specific heat of this metal, and predict its identity.
- Answer
-
\(c = \mathrm{0.45 \;J/g \;°C}\); the metal is likely to be iron from checking Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
Melting and Freezing
When we heat a crystalline solid, the average kinetic energy of its atoms, molecules, or ions increase and the solid gets hotter. At some point, the added energy becomes large enough to overcome the forces holding the molecules or ions of the solid in their fixed positions. At this temperature the solid begins to melt and turn into a liquid. When this happens the temperature of the solid stops rising. The additional heat continues to melt the solid. Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) shows that the temperature does not change until all the solid melts and then continued heating increases the temperature of the liquid.

If we stop heating during melting and place the mixture of solid and liquid in an insulated container the solid and liquid phases remain in equilibrium. This hapens with a mixture of ice and water in a good thermos; almost no heat gets in or out, and the mixture of solid ice and liquid water remains for hours. In a mixture of solid and liquid at equilibrium, the solid melts and the liquid freezes at the same rate, the amount of solid and liquid remains constant. The temperature with both the solid and liquid present is the melting point of the solid or the freezing point of the liquid. The terms melting or freezing depend on the direction. Solid to liquid is melting and liquid to solid is freezing).
The amount of heat required to change one mole of a substance from the solid state to the liquid state is the enthalpy of fusion, ΔHfus of the substance. The enthalpy of fusion of ice is 334 J/g at 0 °C. Fusion (melting) is an endothermic process so heat must be added to cause melting:
\[\ce{H2O}_{(s)} \rightarrow \ce{H2O}_{(l)} \;\; ΔH_\ce{fus}=\mathrm{334\; J/g} \]
The reciprocal process, freezing, is an exothermic process, so heat must be removed. The amount of heat removed to freeze a gram of water is the same as the amount of heat added to melt a gram of ice. All that changes is the sign, so the enthalpy change for freezing is −334 J/g at 0 °C:
\[\ce{H_2O}_{(l)} \rightarrow \ce{H_2O}_{(s)}\;\; ΔH_\ce{frz}=−ΔH_\ce{fus}=−334\;\mathrm{J/g} \]
The enthalpy of fusion and the melting point of a crystalline solid depend on the strength of the attractive forces between the units present in the crystal. Molecules with weak attractive forces form crystals with low melting points. Crystals consisting of particles with stronger attractive forces melt at higher temperatures.
Enthalpy of Vaporization
Vaporization, when a liquid changes into a gas, is an endothermic process that requires heat. This causes the cooling effect when you leave a swimming pool or a shower and the water on your skin evaporates. When the water evaporates, it removes heat from your skin and causes you to feel cold. The energy change associated with the vaporization process is the enthalpy of vaporization, \(ΔH_{vap}\). The vaporization of water at standard temperature is represented by:
\[\ce{H2O}(l)⟶\ce{H2O}(g)\hspace{20px}ΔH_\ce{vap}=\mathrm{2260\: J/g} \nonumber \]
As described in the chapter on thermochemistry, the reverse of an endothermic process is exothermic. And so, the condensation of a gas releases heat:
\[\ce{H2O}(g)⟶\ce{H2O}(l)\hspace{20px}ΔH_\ce{con}=−ΔH_\ce{vap}=\mathrm{−2260\:J/g} \nonumber \]
The enthalpy of vaporization is also the energy required when a liquid at the boiling point changes into a gas. As with melting, when you add heat to a liquid the temperature will rise until the liquid reaches a specific temperature - the boiling point. At this temperature any additional heat does not change the temperature of the liquid, instead it causes the liquid to change into a gas. If a system goes in the other direction and a gas condenses to a liquid, energy must be released for the phase change to occur.
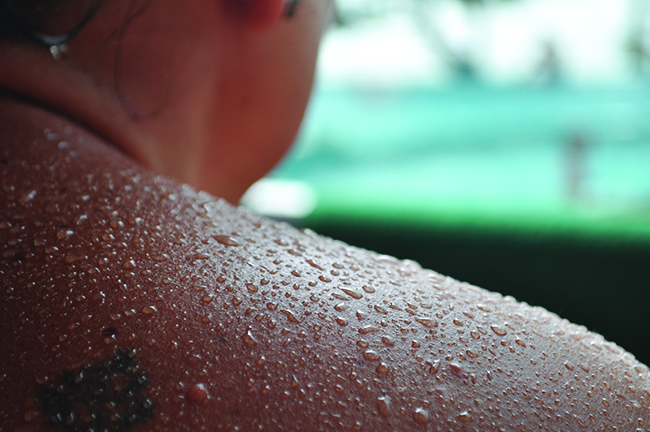
One way our body is cooled is by evaporation of the water in sweat (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)). In very hot climates, we can lose as much as 1.5 L of sweat per day. Although sweat is not pure water, we can get an approximate value of the amount of heat removed by evaporation by assuming that it is. How much heat is required to evaporate 1.5 L of water (1.5 kg) at T = 37 °C (normal body temperature); \(ΔH_{vap} = 2260\, J/g\) at 37 °C.

Solution We start with the known volume of sweat (approximated as just water) and use the given information to convert to the amount of heat needed:
\[\mathrm{1.5\cancel{L}×\dfrac{1000\cancel{g}}{1\cancel{L}}×\dfrac{2260\:J}{1\cancel{g}}=3.6×10^6\:J} \nonumber \]
Thus, 3600 kJ of heat are removed by the evaporation of 1.5 L of water.
How much heat is required to evaporate 100.0 g of liquid ammonia, \(\ce{NH3}\), at its boiling point if its enthalpy of vaporization is 4.8 kJ/mol?
- Answer
-
28 kJ
Heating and Cooling Curves
The heat required to change temperature, melt, and evaporate a sample can be combined into a heating curve like the one shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\). The relation between the amount of heat absorbed or related by a substance, q, and its accompanying temperature change, ΔT, is:
\[q=mcΔT \nonumber \]
Where m is the mass of the substance and c is its specific heat. The relation applies to matter being heated or cooled but not undergoing a change in state. These temperature changes are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) for water as a solid, liquid, and gas.
When a substance being heated or cooled reaches a temperature corresponding to one of its phase transitions, the melting or boiling points, additional heat is used to overcome intermolecular attractions, not to changing the kinetic energies or temperature. While a substance is undergoing a change in state the temperature remains constant, as shown in the horizontal regions of Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) where the solid melts and the liquid evaporates.
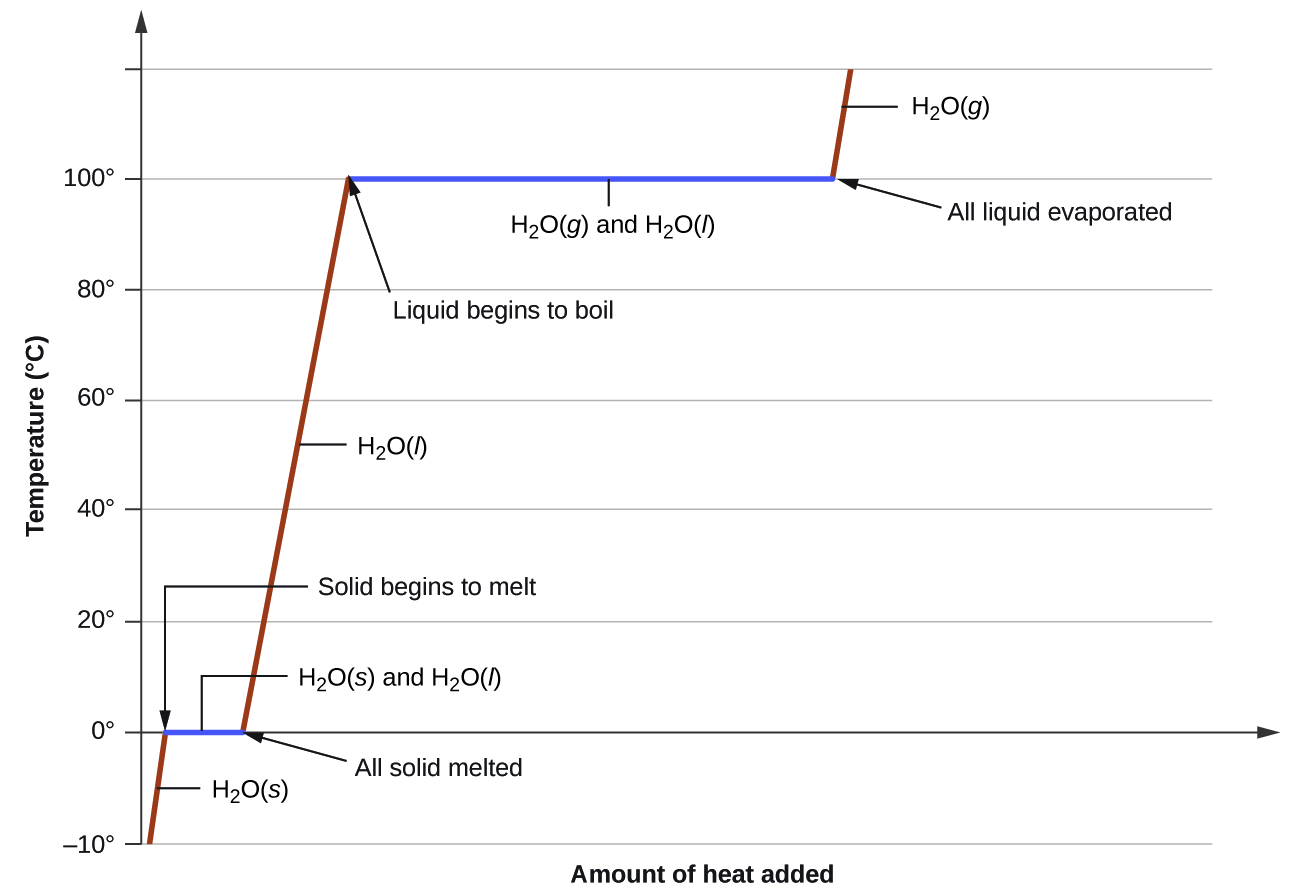
Consider the example of heating a pot of water to boiling. A stove burner will supply heat at a roughly constant rate; initially, this heat serves to increase the water’s temperature. When the water reaches its boiling point, the temperature remains constant despite the continued input of heat from the stove burner. This same temperature is maintained by the water as long as it is boiling. If the burner setting is increased to provide heat at a greater rate, the water temperature does not rise, but instead the boiling becomes more vigorous (rapid). This behavior is observed for other phase transitions as well: Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) shows the temperature remains constant while the ice melts.
How much heat is required to convert 135 g of ice at −15 °C into water vapor at 120 °C?
Solution
The transition described involves the following steps:
- Heat ice from −15 °C to 0 °C
- Melt ice
- Heat water from 0 °C to 100 °C
- Boil water
- Heat steam from 100 °C to 120 °C
The heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: q = m × c × ΔT (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). The heat needed to induce a given change in phase is given by q = n × ΔH.
Using these equations with the appropriate values for specific heat of ice, water, and steam, and enthalpies of fusion and vaporization, we have:
\[\begin{align*}
q_\ce{total}&=(m⋅c⋅ΔT)_\ce{ice}+n⋅ΔH_\ce{fus}+(m⋅c⋅ΔT)_\ce{water}+n⋅ΔH_\ce{vap}+(m⋅c⋅ΔT)_\ce{steam}\\[7pt]
&=\mathrm{(135\: g⋅2.09\: J/g⋅°C⋅15°C)+\left(135\: g⋅ 334\: J/g \right)}\\[7pt]
&\mathrm{+(135\: g⋅4.18\: J/g⋅°C⋅100°C)+\left(135\: g⋅2260\: J/g \right)}\\[7pt]
&\mathrm{+(135\: g⋅1.84\: J/g⋅°C⋅20°C)}\\[7pt]
&=\mathrm{4230\: J+45.0\: kJ+56,500\: J+305\: kJ+4970\: J}
\end{align*} \nonumber \]
Converting the quantities in J to kJ for convenience and adding the steps gives the total heat required:
\[\mathrm{=4.23\:kJ+45.0\: kJ+56.5\: kJ+305\: kJ+4.97\: kJ=416\: kJ} \nonumber \]
What is the total amount of heat released when 94.0 g water at 80.0 °C cools to form ice at −30.0 °C?
- Answer
-
40.5 kJ
Conservation of Energy Calcualtions - Video
Video Topics
The Law of conservation of energy says that the total energy between a system and its surroundings must remain constant. This means heat lost by a system is gained by its surroundings and vice versa. This idea is expressed by the equation q of the system = - q of the surroundings. Using this equation the moment of heat between two different bodies can be calculated. Also the final temperature of the combination can be found. This video contains a sample problem, which involves these concepts.
Link to Video
Conservation of Energy: The Movement of Heat between Substances: https://youtu.be/pGEYy-pNHBg
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)
Solar Thermal Energy Power Plants
The sunlight that reaches the earth contains thousands of times more energy than we presently capture. Solar thermal systems provide one possible solution to the problem of converting energy from the sun into energy we can use. Large-scale solar thermal plants have different design specifics, but all concentrate sunlight to heat some substance; the heat “stored” in that substance is then converted into electricity.
The Solana Generating Station in Arizona’s Sonora Desert produces 280 megawatts of electrical power. It uses parabolic mirrors that focus sunlight on pipes filled with a heat transfer fluid (HTF) (Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)). The HTF then does two things: It turns water into steam, which spins turbines, which in turn produces electricity, and it melts and heats a mixture of salts, which functions as a thermal energy storage system. After the sun goes down, the molten salt mixture can then release enough of its stored heat to produce steam to run the turbines for 6 hours. Molten salts are used because they possess a number of beneficial properties, including high heat capacities and thermal conductivities.
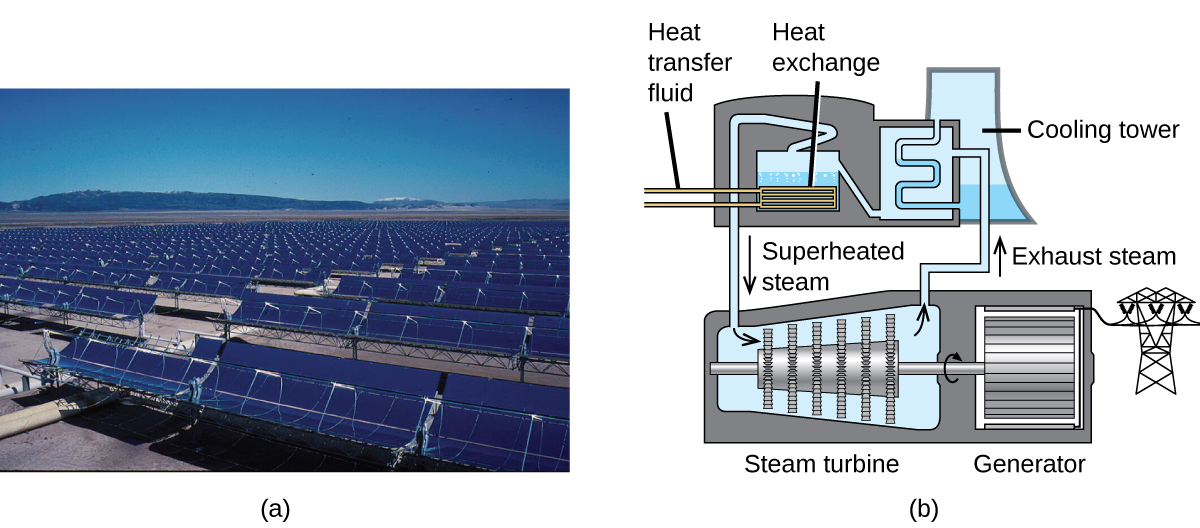
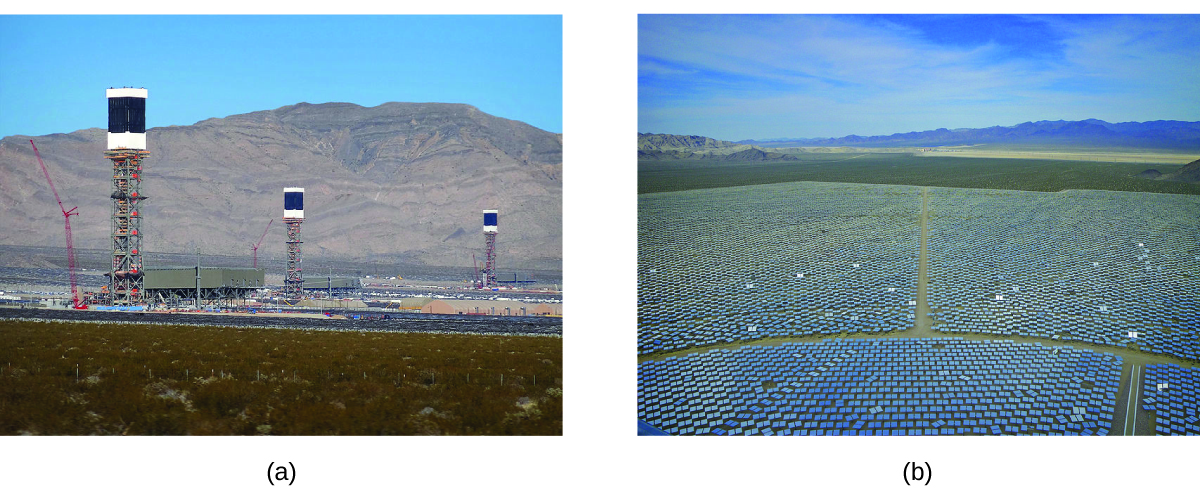
The 377-megawatt Ivanpah Solar Generating System, located in the Mojave Desert in California, is the largest solar thermal power plant in the world (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)). Its 170,000 mirrors focus huge amounts of sunlight on three water-filled towers, producing steam at over 538 °C that drives electricity-producing turbines. It produces enough energy to power 140,000 homes. Water is used as the working fluid because of its large heat capacity and heat of vaporization.

Summary
Energy is the capacity to do work (applying a force to move matter). Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy of motion; potential energy is energy due to relative position, composition, or condition. When energy is converted from one form into another, energy is neither created nor destroyed (law of conservation of energy or first law of thermodynamics). Matter has thermal energy due to the KE of its molecules and temperature that corresponds to the average KE of its molecules. Heat is energy that is transferred between objects at different temperatures; it flows from a high to a low temperature. Chemical and physical processes can absorb heat (endothermic) or release heat (exothermic). The SI unit of energy, heat, and work is the joule (J). Specific heat and heat capacity are measures of the energy needed to change the temperature of a substance or object. The amount of heat absorbed or released by a substance depends directly on the type of substance, its mass, and the temperature change it undergoes.
Key Equations
- \(q=c×m×ΔT=c×m×(T_\ce{final}−T_\ce{initial})\)
Glossary
- calorie (cal)
- unit of heat or other energy; the amount of energy required to raise 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius; 1 cal is defined as 4.184 J
- endothermic process
- chemical reaction or physical change that absorbs heat
- energy
- capacity to supply heat or do work
- exothermic process
- chemical reaction or physical change that releases heat
- heat (q)
- transfer of thermal energy between two bodies
- heat capacity (C)
- extensive property of a body of matter that represents the quantity of heat required to increase its temperature by 1 degree Celsius (or 1 kelvin)
- joule (J)
- SI unit of energy; 1 joule is the kinetic energy of an object with a mass of 2 kilograms moving with a velocity of 1 meter per second, 1 J = 1 kg m2/s and 4.184 J = 1 cal
- kinetic energy
- energy of a moving body, in joules, equal to \(\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2\) (where m = mass and v = velocity)
- potential energy
- energy of a particle or system of particles derived from relative position, composition, or condition
- specific heat capacity (c)
- intensive property of a substance that represents the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius (or 1 kelvin)
- temperature
- intensive property of matter that is a quantitative measure of “hotness” and “coldness”
- thermal energy
- kinetic energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules
- thermochemistry
- study of measuring the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction or a physical change
- work (w)
- energy transfer due to changes in external, macroscopic variables such as pressure and volume; or causing matter to move against an opposing force


