13.4: Solutions of Gases in Water
- Page ID
- 47551
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Explain how temperature and pressure affect the solubility of gases.
In an earlier module of this chapter, the effect of intermolecular attractive forces on solution formation was discussed. The chemical structures of the solute and solvent dictate the types of forces possible and, consequently, are important factors in determining solubility. For example, under similar conditions, the water solubility of oxygen is approximately three times greater than that of helium, but 100 times less than the solubility of chloromethane, CHCl3. Considering the role of the solvent’s chemical structure, note that the solubility of oxygen in the liquid hydrocarbon hexane, C6H14, is approximately 20 times greater than it is in water.
Other factors also affect the solubility of a given substance in a given solvent. Temperature is one such factor, with gas solubility typically decreasing as temperature increases (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). This is one of the major impacts resulting from the thermal pollution of natural bodies of water.
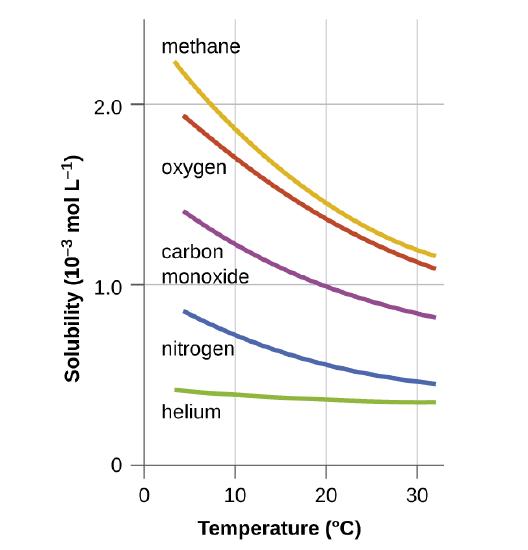
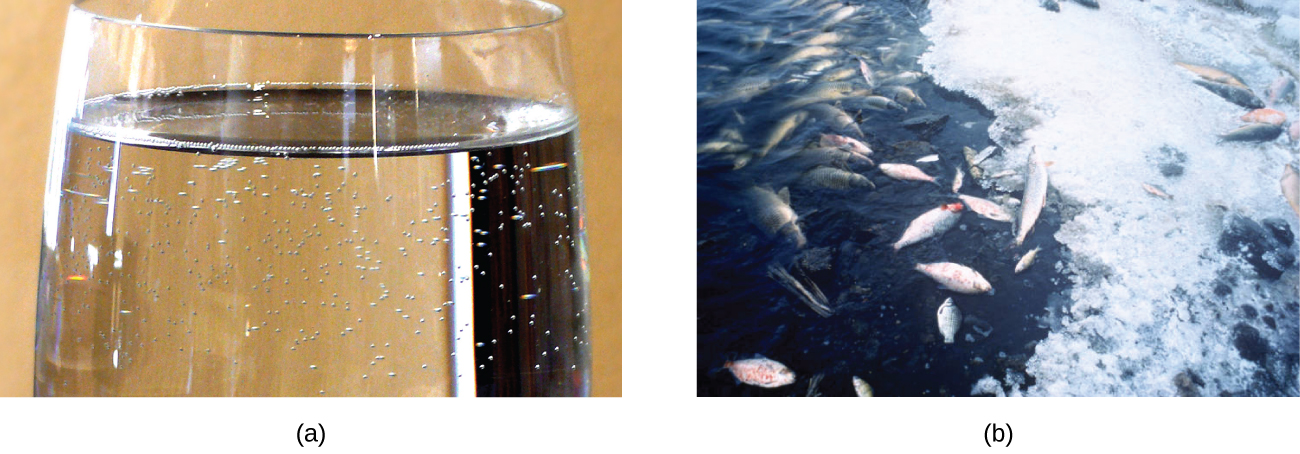
When the temperature of a river, lake, or stream is raised abnormally high, usually due to the discharge of hot water from some industrial process, the solubility of oxygen in the water is decreased. Decreased levels of dissolved oxygen may have serious consequences for the health of the water’s ecosystems and, in severe cases, can result in large-scale fish kills (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).

The solubility of a gaseous solute is also affected by the partial pressure of solute in the gas to which the solution is exposed. Gas solubility increases as the pressure of the gas increases. Carbonated beverages provide a nice illustration of this relationship. The carbonation process involves exposing the beverage to a relatively high pressure of carbon dioxide gas and then sealing the beverage container, thus saturating the beverage with CO2 at this pressure. When the beverage container is opened, a familiar hiss is heard as the carbon dioxide gas pressure is released, and some of the dissolved carbon dioxide is typically seen leaving solution in the form of small bubbles (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). At this point, the beverage is supersaturated with carbon dioxide and, with time, the dissolved carbon dioxide concentration will decrease to its equilibrium value and the beverage will become “flat.”
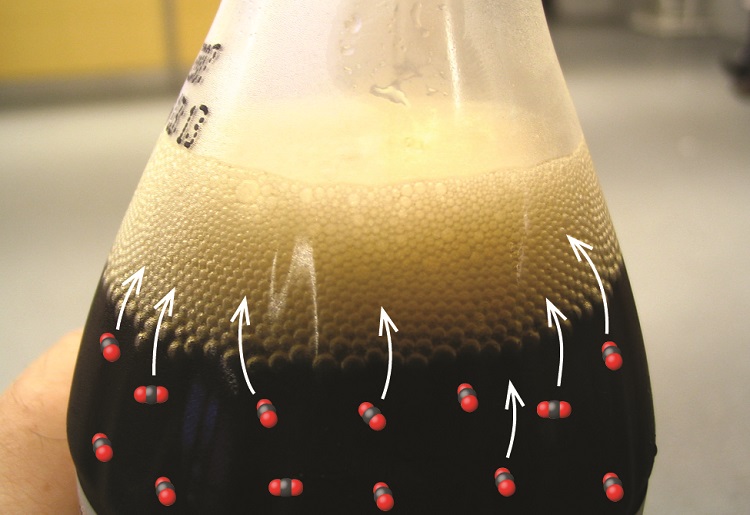

The dissolution in a liquid, also known as fizz, usually involves carbon dioxide under high pressure. When the pressure is reduced, the carbon dioxide is released from the solution as small bubbles, which causes the solution to become effervescent, or fizzy. A common example is the dissolving of carbon dioxide in water, resulting in carbonated water.
Carbon dioxide is weakly soluble in water, therefore it separates into a gas when the pressure is released. This process is generally represented by the following reaction, where a pressurized dilute solution of carbonic acid in water releases gaseous carbon dioxide at decompression:
\[\ce{H2CO3(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)} \nonumber \]
In simple terms, it is the result of the chemical reaction occurring in the liquid which produces a gaseous product.
For many gaseous solutes, the relation between solubility, \(C_g\), and partial pressure, \(P_g\), is a proportional one:
\[C_\ce{g}=kP_\ce{g} \nonumber \]
where k is a proportionality constant that depends on the identities of the gaseous solute and solvent, and on the solution temperature. This is a mathematical statement of Henry’s law: The quantity of an ideal gas that dissolves in a definite volume of liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas.
At 20 °C, the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water exposed to gaseous oxygen at a partial pressure of 101.3 kPa (760 torr) is 1.38 × 10−3 mol L−1. Use Henry’s law to determine the solubility of oxygen when its partial pressure is 20.7 kPa (155 torr), the approximate pressure of oxygen in earth’s atmosphere.
Solution
According to Henry’s law, for an ideal solution the solubility, \(C_g\), of a gas (1.38 × 10−3 mol L−1, in this case) is directly proportional to the pressure, \(P_g\), of the undissolved gas above the solution (101.3 kPa, or 760 torr, in this case). Because we know both \(C_g\) and \(P_g\), we can rearrange this expression to solve for k.
\[\begin{align*}
C_\ce{g}&=kP_\ce{g}\\
k&=\dfrac{C_\ce{g}}{P_\ce{g}}\\
&=\mathrm{\dfrac{1.38×10^{−3}\:mol\:L^{−1}}{101.3\:kPa}}\\
&=\mathrm{1.36×10^{−5}\:mol\:L^{−1}\:kPa^{−1}}\\
&\hspace{15px}\mathrm{(1.82×10^{−6}\:mol\:L^{−1}\:torr^{−1})}
\end{align*} \nonumber \]
Now we can use k to find the solubility at the lower pressure.
\[C_\ce{g}=kP_\ce{g} \nonumber \]
\[\mathrm{1.36×10^{−5}\:mol\:L^{−1}\:kPa^{−1}×20.7\:kPa\\
(or\:1.82×10^{−6}\:mol\:L^{−1}\:torr^{−1}×155\:torr)\\
=2.82×10^{−4}\:mol\:L^{−1}} \nonumber \]
Note that various units may be used to express the quantities involved in these sorts of computations. Any combination of units that yield to the constraints of dimensional analysis are acceptable.
A 100.0 mL sample of water at 0 °C to an atmosphere containing a gaseous solute at 20.26 kPa (152 torr) resulted in the dissolution of 1.45 × 10−3 g of the solute. Use Henry’s law to determine the solubility of this gaseous solute when its pressure is 101.3 kPa (760 torr).
- Answer
-
7.25 × 10−3 g
Decompression sickness (DCS), or “the bends,” is an effect of the increased pressure of the air inhaled by scuba divers when swimming underwater at considerable depths. In addition to the pressure exerted by the atmosphere, divers are subjected to additional pressure due to the water above them, experiencing an increase of approximately 1 atm for each 10 m of depth. Therefore, the air inhaled by a diver while submerged contains gases at the corresponding higher ambient pressure, and the concentrations of the gases dissolved in the diver’s blood are proportionally higher per Henry’s law.
As the diver ascends to the surface of the water, the ambient pressure decreases and the dissolved gases becomes less soluble. If the ascent is too rapid, the gases escaping from the diver’s blood may form bubbles that can cause a variety of symptoms ranging from rashes and joint pain to paralysis and death. To avoid DCS, divers must ascend from depths at relatively slow speeds (10 or 20 m/min) or otherwise make several decompression stops, pausing for several minutes at given depths during the ascent. When these preventative measures are unsuccessful, divers with DCS are often provided hyperbaric oxygen therapy in pressurized vessels called decompression (or recompression) chambers (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)).
Deviations from Henry’s law are observed when a chemical reaction takes place between the gaseous solute and the solvent. Thus, for example, the solubility of ammonia in water does not increase as rapidly with increasing pressure as predicted by the law because ammonia, being a base, reacts to some extent with water to form ammonium ions and hydroxide ions.
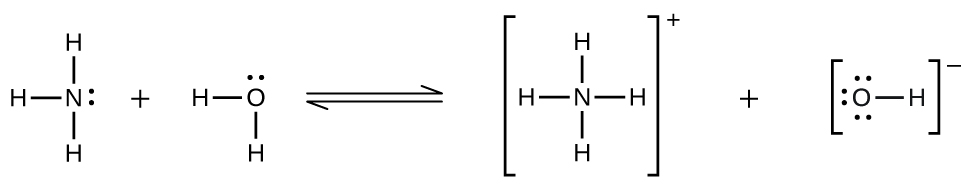
This reaction diagram shows three H atoms bonded to an N atom above, below, and two the left of the N. A single pair of dots is present on the right side of the N. This is followed by a plus, then two H atoms bonded to an O atom to the left and below the O. Two pairs of dots are present on the O, one above and the other to the right of the O. A double arrow, with a top arrow pointing right and a bottom arrow pointing left follows. To the right of the double arrow, four H atoms are shown bonded to a central N atom. These 5 atoms are enclosed in brackets with a superscript plus outside. A plus follows, then an O atom linked by a bond to an H atom on its right. The O atom has pairs of dots above, to the left, and below the atom. The linked O and H are enclosed in brackets with superscript minus outside.
Gases can form supersaturated solutions. If a solution of a gas in a liquid is prepared either at low temperature or under pressure (or both), then as the solution warms or as the gas pressure is reduced, the solution may become supersaturated.
Contributions & Attributions
- Wikipedia
Paul Flowers (University of North Carolina - Pembroke), Klaus Theopold (University of Delaware) and Richard Langley (Stephen F. Austin State University) with contributing authors. Textbook content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/85abf193-2bd...a7ac8df6@9.110).

