9.3: Hybrid Atomic Orbitals
- Page ID
- 370740
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Explain the concept of atomic orbital hybridization
- Determine the hybrid orbitals associated with various molecular geometries
The localized valence bonding theory uses a process called hybridization, in which atomic orbitals that are similar in energy, but not equivalent are combined mathematically to produce sets of equivalent orbitals that are properly oriented to form bonds. These new combinations are called hybrid atomic orbitals because they are produced by combining (hybridizing) two or more atomic orbitals from the same atom.
Underpinning hybrid orbitals (or really all orbitals in general) is the mathematical expression known as the wave function, ψ, which contains information about each orbital and the wavelike properties of electrons in an isolated atom. When atoms are bound together in a molecule, the wave functions combine to produce new mathematical descriptions that have different shapes. This process of combining the wave functions for atomic orbitals is called hybridization and is mathematically accomplished by the linear combination of atomic orbitals, LCAO, (a technique that we will encounter again later). The new orbitals that result are called hybrid orbitals.
The following ideas are important in understanding hybridization:
- Hybrid orbitals do not exist in isolated atoms. They are formed only in covalently bonded atoms.
- Hybrid orbitals have shapes and orientations that are very different from those of the atomic orbitals in isolated atoms.
- A set of hybrid orbitals is generated by combining atomic orbitals. The number of hybrid orbitals in a set is equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined to produce the set.
- All orbitals in a set of hybrid orbitals are equivalent in shape and energy.
- The type of hybrid orbitals formed in a bonded atom depends on its electron-pair geometry as predicted by the VSEPR theory.
- Hybrid orbitals overlap to form σ bonds. Unhybridized orbitals overlap to form π bonds.
In the following sections, we shall discuss the common types of hybrid orbitals.
Hybridization of s and p Orbitals
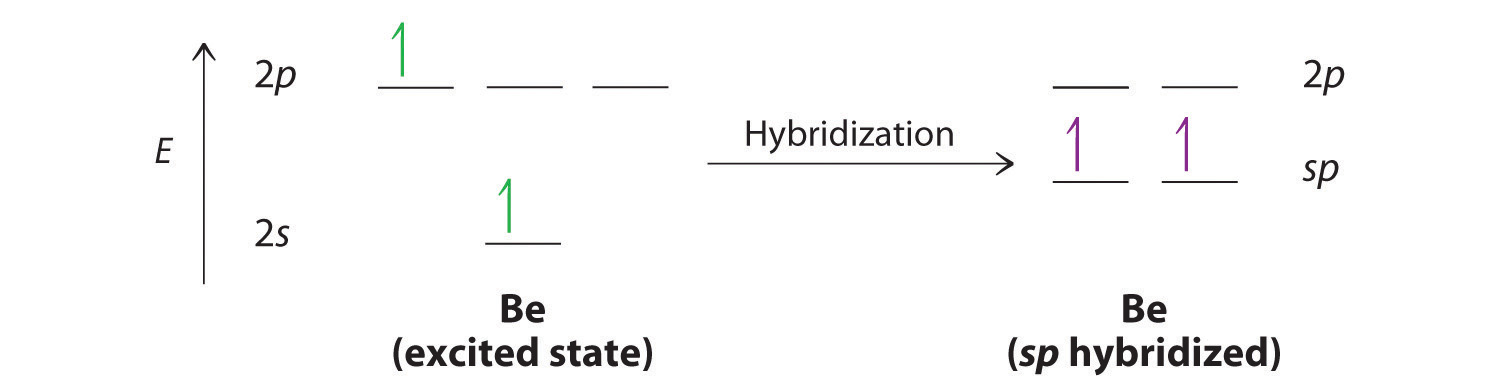
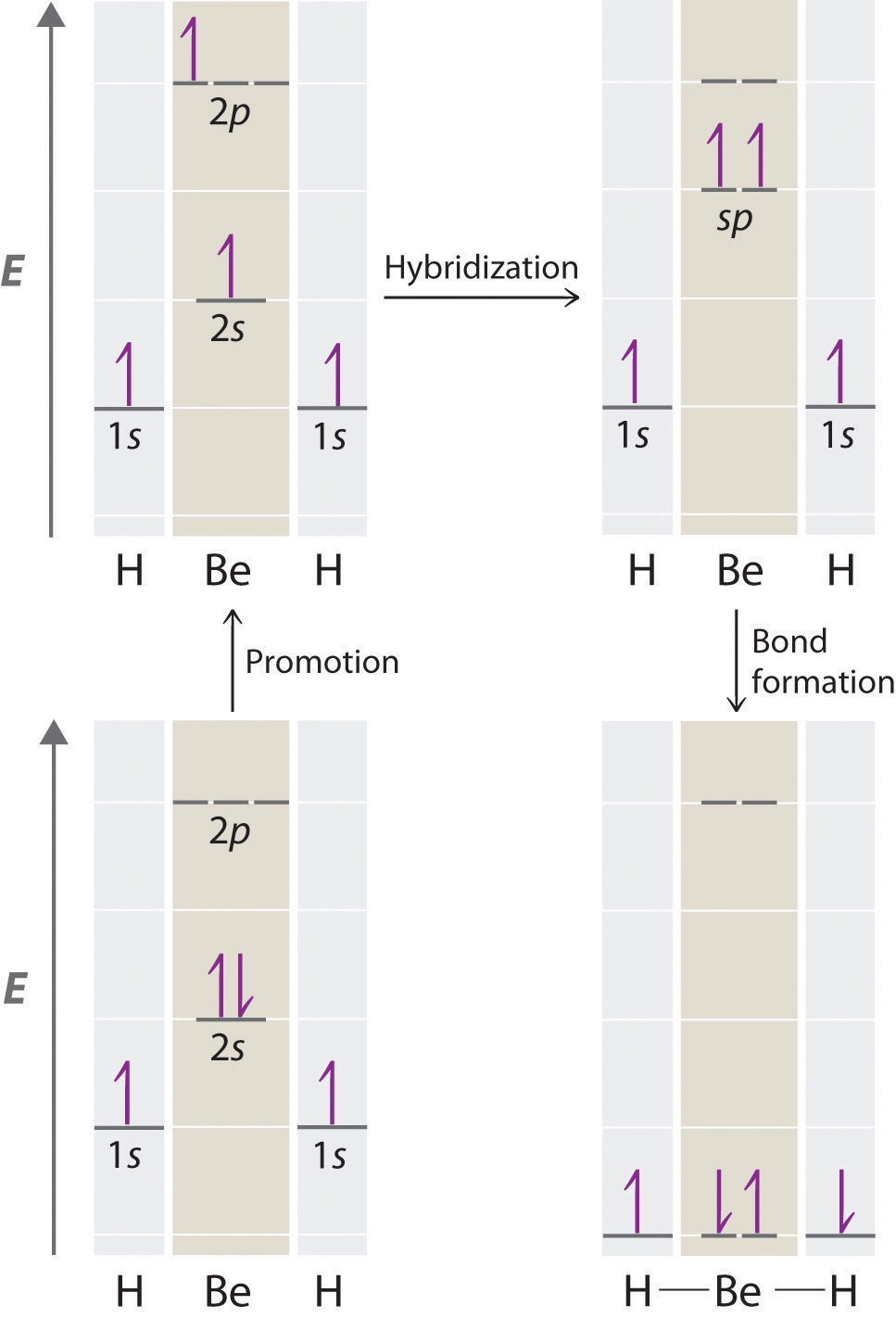
Let’s examine the bonds in BeH2, for example. According to the VSEPR model, BeH2 is a linear compound with four valence electrons and two Be–H bonds. Its bonding can also be described using an atomic orbital approach. Beryllium has a 1s22s2 electron configuration, and each H atom has a 1s1 electron configuration. Because the Be atom has a filled 2s subshell, however, it has no singly occupied orbitals available to overlap with the singly occupied 1s orbitals on the H atoms. If a singly occupied 1s orbital on hydrogen were to overlap with a filled 2s orbital on beryllium, the resulting bonding orbital would contain three electrons, but the maximum allowed by quantum mechanics is two. How then is beryllium able to bond to two hydrogen atoms? One way would be to add enough energy to excite one of its 2s electrons into an empty 2p orbital and reverse its spin, in a process called promotion:

In this excited state, the Be atom would have two singly occupied atomic orbitals (the 2s and one of the 2p orbitals), each of which could overlap with a singly occupied 1s orbital of an H atom to form an electron-pair bond. Although this would produce BeH2, the two Be–H bonds would not be equivalent: the 1s orbital of one hydrogen atom would overlap with a Be 2s orbital, and the 1s orbital of the other hydrogen atom would overlap with an orbital of a different energy, a Be 2p orbital. Experimental evidence indicates, however, that the two Be–H bonds have identical energies. To resolve this discrepancy and explain how molecules such as BeH2 form, scientists developed the concept of hybridization.
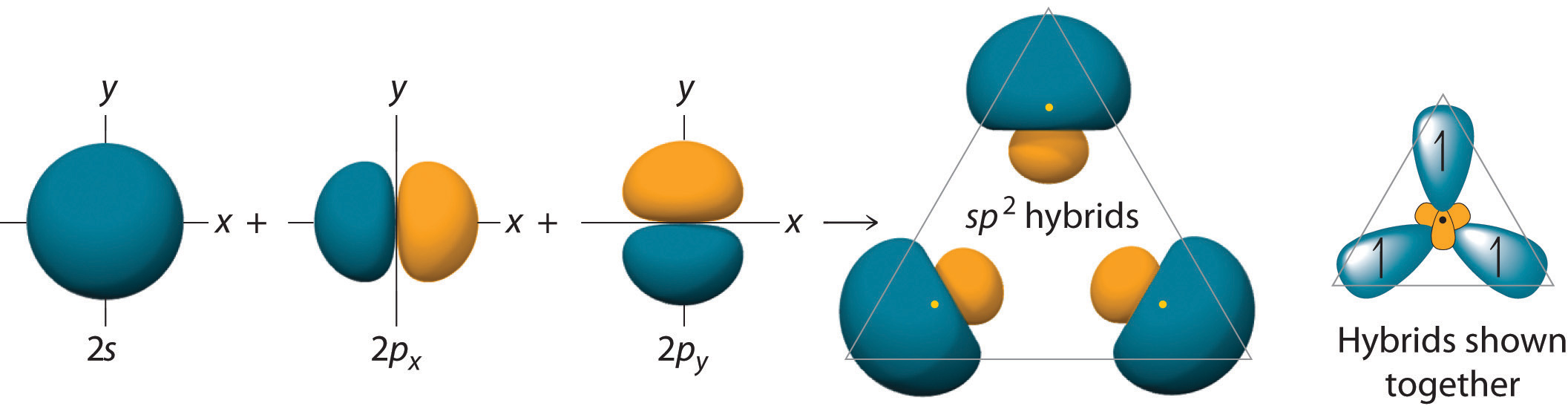
In BeH2, we can generate two equivalent orbitals by combining the 2s orbital of beryllium and any one of the three degenerate 2p orbitals. By taking the sum and the difference of Be 2s and 2pz atomic orbitals, for example, we produce two new orbitals with major and minor lobes oriented along the z-axes, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{0}\).

Because the difference A − B can also be written as A + (−B), in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) and subsequent figures we have reversed the phase(s) of the orbital being subtracted, which is the same as multiplying it by −1 and adding. This gives us Equation 11.3.1, where the value \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) is needed mathematically to indicate that the 2s and 2p orbitals contribute equally to each hybrid orbital.
\[sp = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} (2s + 2p_z) \label{11.3.1a}\]
and
\[sp = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} (2s - 2p_z) \label{11.3.1b}\]
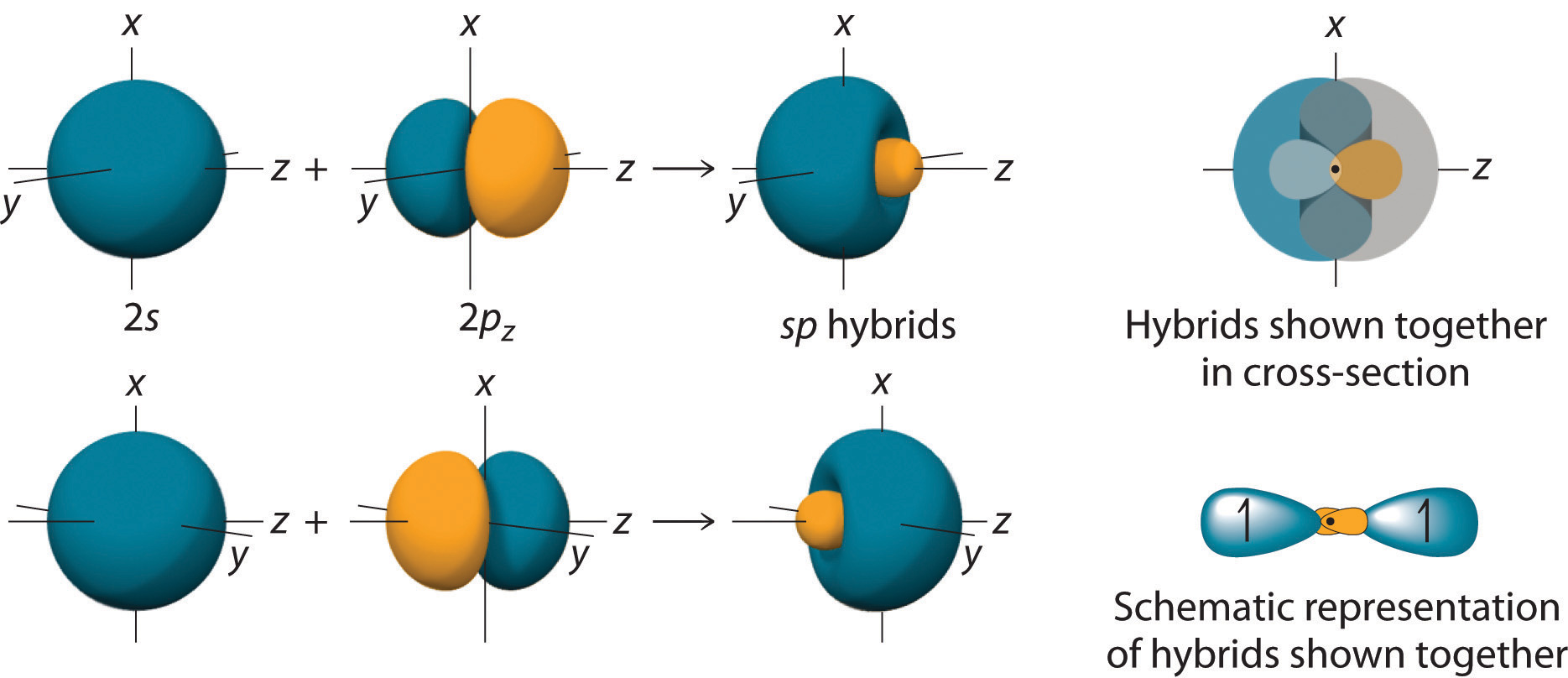
The nucleus resides just inside the minor lobe of each orbital. In this case, the new orbitals are called sp hybrids because they are formed from one s and one p orbital. The two new orbitals are equivalent in energy, and their energy is between the energy values associated with pure s and p orbitals, as illustrated in this diagram:
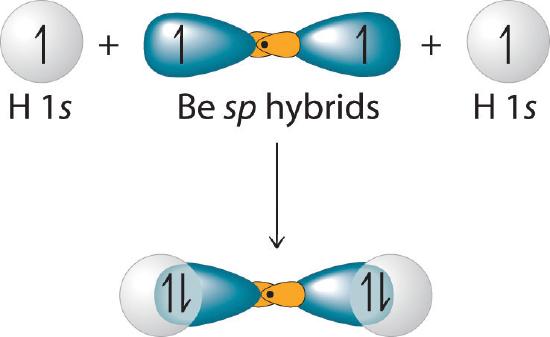
Because both promotion and hybridization require an input of energy, the formation of a set of singly occupied hybrid atomic orbitals is energetically uphill. The overall process of forming a compound with hybrid orbitals will be energetically favorable only if the amount of energy released by the formation of covalent bonds is greater than the amount of energy used to form the hybrid orbitals (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). As we will see, some compounds are highly unstable or do not exist because the amount of energy required to form hybrid orbitals is greater than the amount of energy that would be released by the formation of additional bonds.
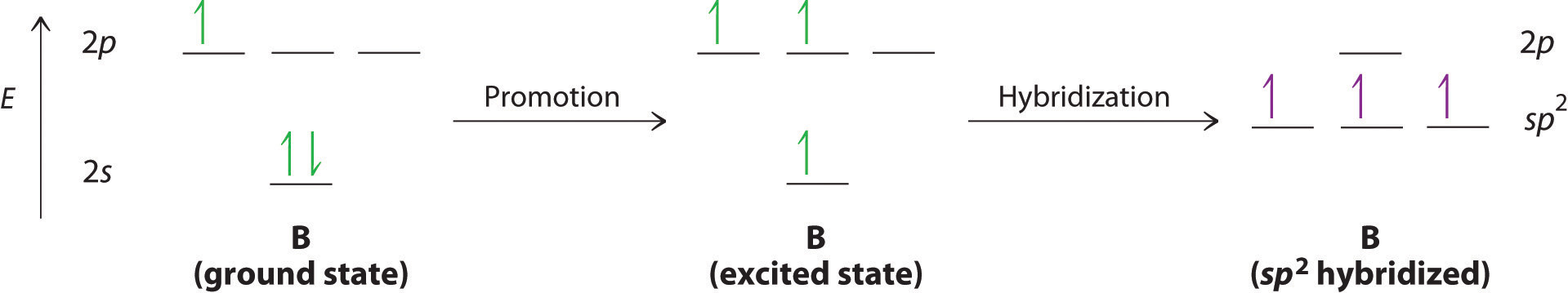
The concept of hybridization also explains why boron, with a 2s22p1 valence electron configuration, forms three bonds with fluorine to produce BF3, as predicted by the Lewis and VSEPR approaches. With only a single unpaired electron in its ground state, boron should form only a single covalent bond. By the promotion of one of its 2s electrons to an unoccupied 2p orbital, however, followed by the hybridization of the three singly occupied orbitals (the 2s and two 2p orbitals), boron acquires a set of three equivalent hybrid orbitals with one electron each, as shown here:
Looking at the 2s22p2 valence electron configuration of carbon, we might expect carbon to use its two unpaired 2p electrons to form compounds with only two covalent bonds. We know, however, that carbon typically forms compounds with four covalent bonds. We can explain this apparent discrepancy by the hybridization of the 2s orbital and the three 2p orbitals on carbon to give a set of four degenerate sp3 (“s-p-three” or “s-p-cubed”) hybrid orbitals, each with a single electron:
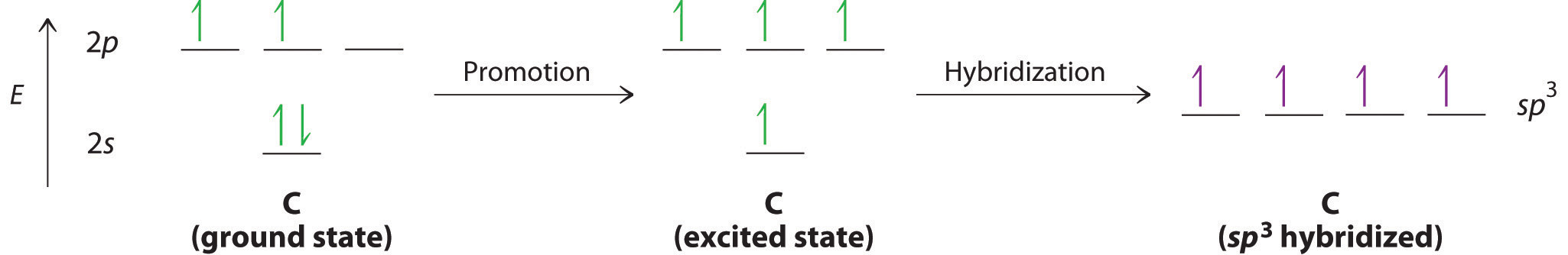
The large lobes of the hybridized orbitals are oriented toward the vertices of a tetrahedron, with 109.5° angles between them (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Like all the hybridized orbitals discussed earlier, the sp3 hybrid atomic orbitals are predicted to be equal in energy.

In addition to explaining why some elements form more bonds than would be expected based on their valence electron configurations, and why the bonds formed are equal in energy, valence bond theory explains why these compounds are so stable: the amount of energy released increases with the number of bonds formed. In the case of carbon, for example, much more energy is released in the formation of four bonds than two, so compounds of carbon with four bonds tend to be more stable than those with only two. Carbon does form compounds with only two covalent bonds (such as CH2 or CF2), but these species are highly reactive, unstable intermediates that form in only certain chemical reactions.
Valence bond theory explains the number of bonds formed in a compound and the relative bond strengths.
The bonding in molecules such as NH3 or H2O, which have lone pairs on the central atom, can also be described in terms of hybrid atomic orbitals. In NH3, for example, N, with a 2s22p3 valence electron configuration, can hybridize its 2s and 2p orbitals to produce four sp3 hybrid orbitals. Placing five valence electrons in the four hybrid orbitals, we obtain three that are singly occupied and one with a pair of electrons:
![]()
The three singly occupied sp3 lobes can form bonds with three H atoms, while the fourth orbital accommodates the lone pair of electrons. Similarly, H2O has an sp3 hybridized oxygen atom that uses two singly occupied sp3 lobes to bond to two H atoms, and two to accommodate the two lone pairs predicted by the VSEPR model. Such descriptions explain the approximately tetrahedral distribution of electron pairs on the central atom in NH3 and H2O. Unfortunately, however, recent experimental evidence indicates that in CH4 and NH3, the hybridized orbitals are not entirely equivalent in energy, making this bonding model an active area of research.
Valence Bond Method & sp3 Hybridization: https://youtu.be/2hxKLGWQ5EQ
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Use the VSEPR model to predict the number of electron pairs and molecular geometry in each compound and then describe the hybridization and bonding of all atoms except hydrogen.
- H2S
- CHCl3
Given: two chemical compounds
Asked for: number of electron pairs and molecular geometry, hybridization, and bonding
Strategy:
- Using the VPSER approach to determine the number of electron pairs and the molecular geometry of the molecule.
- From the valence electron configuration of the central atom, predict the number and type of hybrid orbitals that can be produced. Fill these hybrid orbitals with the total number of valence electrons around the central atom and describe the hybridization.
Solution:
- A H2S has four electron pairs around the sulfur atom with two bonded atoms, so the VSEPR model predicts a molecular geometry that is bent, or V shaped. B Sulfur has a 3s23p4 valence electron configuration with six electrons, but by hybridizing its 3s and 3p orbitals, it can produce four sp3 hybrids. If the six valence electrons are placed in these orbitals, two have electron pairs and two are singly occupied. The two sp3 hybrid orbitals that are singly occupied are used to form S–H bonds, whereas the other two have lone pairs of electrons. Together, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals produce an approximately tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs, which agrees with the molecular geometry predicted by the VSEPR model.
- A The CHCl3 molecule has four valence electrons around the central atom. In the VSEPR model, the carbon atom has four electron pairs, and the molecular geometry is tetrahedral. B Carbon has a 2s22p2 valence electron configuration. By hybridizing its 2s and 2p orbitals, it can form four sp3 hybridized orbitals that are equal in energy. Eight electrons around the central atom (four from C, one from H, and one from each of the three Cl atoms) fill three sp3 hybrid orbitals to form C–Cl bonds, and one forms a C–H bond. Similarly, the Cl atoms, with seven electrons each in their 3s and 3p valence subshells, can be viewed as sp3 hybridized. Each Cl atom uses a singly occupied sp3 hybrid orbital to form a C–Cl bond and three hybrid orbitals to accommodate lone pairs.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Use the VSEPR model to predict the number of electron pairs and molecular geometry in each compound and then describe the hybridization and bonding of all atoms except hydrogen.
- the BF4− ion
- hydrazine (H2N–NH2)
Answer
- B is sp3 hybridized; F is also sp3 hybridized so it can accommodate one B–F bond and three lone pairs. The molecular geometry is tetrahedral.
- Each N atom is sp3 hybridized and uses one sp3 hybrid orbital to form the N–N bond, two to form N–H bonds, and one to accommodate a lone pair. The molecular geometry about each N is trigonal pyramidal.
The number of hybrid orbitals used by the central atom is the same as the number of electron pairs around the central atom.
Hybridization Using d Orbitals
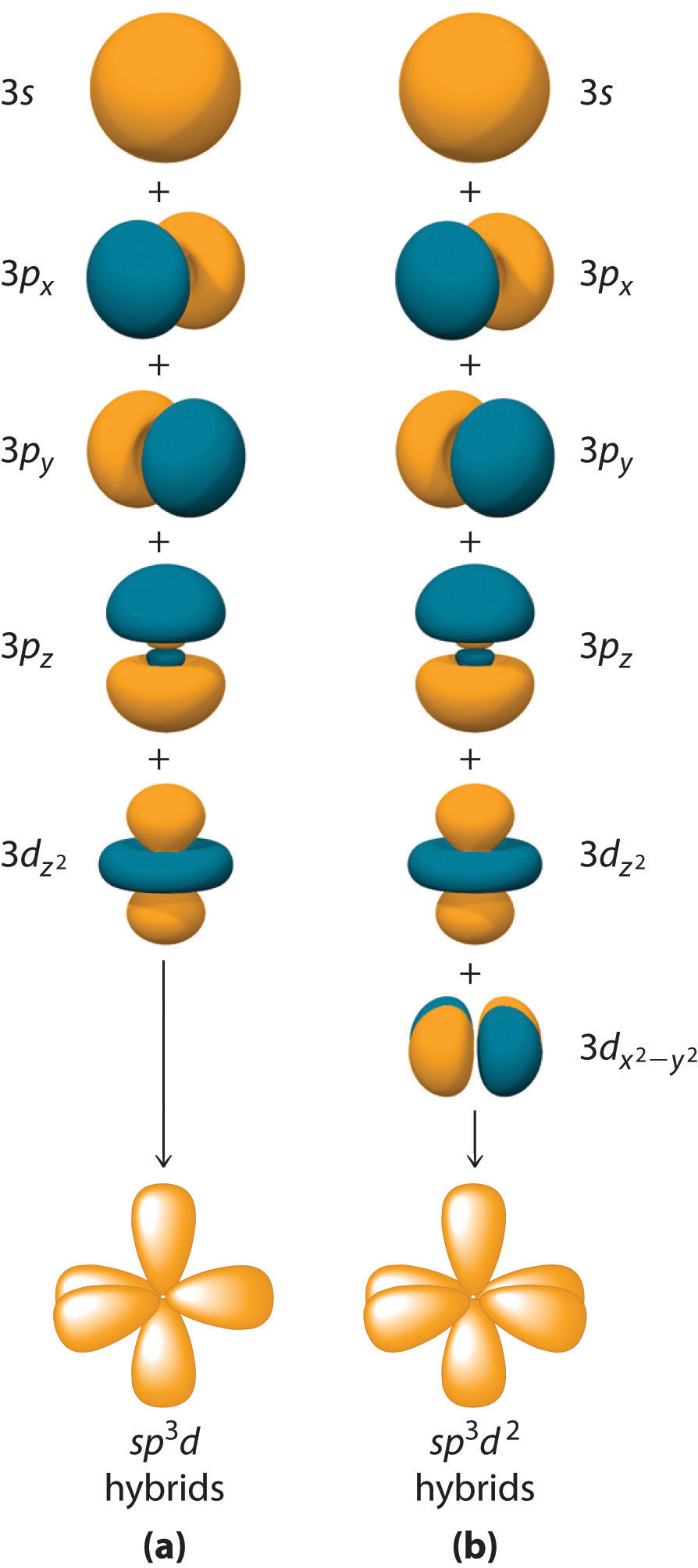
Hybridization is not restricted to the ns and np atomic orbitals. The bonding in compounds with central atoms in the period 3 and below can also be described using hybrid atomic orbitals. In these cases, the central atom can use its valence (n − 1)d orbitals as well as its ns and np orbitals to form hybrid atomic orbitals, which allows it to accommodate five or more bonded atoms (as in PF5 and SF6). Using the ns orbital, all three np orbitals, and one (n − 1)d orbital gives a set of five sp3d hybrid orbitals that point toward the vertices of a trigonal bipyramid (part (a) in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). In this case, the five hybrid orbitals are not all equivalent: three form a triangular array oriented at 120° angles, and the other two are oriented at 90° to the first three and at 180° to each other.
Similarly, the combination of the ns orbital, all three np orbitals, and two nd orbitals gives a set of six equivalent sp3d2 hybrid orbitals oriented toward the vertices of an octahedron (part (b) in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). In the VSEPR model, PF5 and SF6 are predicted to be trigonal bipyramidal and octahedral, respectively, which agrees with a valence bond description in which sp3d or sp3d2 hybrid orbitals are used for bonding.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
What is the hybridization of the central atom in each species? Describe the bonding in each species.
- XeF4
- SO42−
- SF4
Given: three chemical species
Asked for: hybridization of the central atom
Strategy:
- Determine the geometry of the molecule using the strategy in Example 1. From the valence electron configuration of the central atom and the number of electron pairs, determine the hybridization.
- Place the total number of electrons around the central atom in the hybrid orbitals and describe the bonding.
Solution:
- A Using the VSEPR model, we find that Xe in XeF4 forms four bonds and has two lone pairs, so its structure is square planar and it has six electron pairs. The six electron pairs form an octahedral arrangement, so the Xe must be sp3d2 hybridized. B With 12 electrons around Xe, four of the six sp3d2 hybrid orbitals form Xe–F bonds, and two are occupied by lone pairs of electrons.
- A The S in the SO42− ion has four electron pairs and has four bonded atoms, so the structure is tetrahedral. The sulfur must be sp3 hybridized to generate four S–O bonds. B Filling the sp3 hybrid orbitals with eight electrons from four bonds produces four filled sp3 hybrid orbitals.
- A The S atom in SF4 contains five electron pairs and four bonded atoms. The molecule has a seesaw structure with one lone pair:
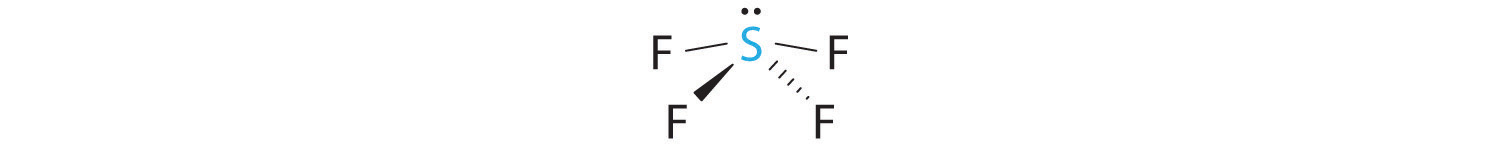
To accommodate five electron pairs, the sulfur atom must be sp3d hybridized. B Filling these orbitals with 10 electrons gives four sp3d hybrid orbitals forming S–F bonds and one with a lone pair of electrons.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
What is the hybridization of the central atom in each species? Describe the bonding.
- PCl4+
- BrF3
- SiF62−
Answer
- sp3 with four P–Cl bonds
- sp3d with three Br–F bonds and two lone pairs
- sp3d2 with six Si–F bonds
Hybridization using d orbitals allows chemists to explain the structures and properties of many molecules and ions. Like most such models, however, it is not universally accepted. Nonetheless, it does explain a fundamental difference between the chemistry of the elements in the period 2 (C, N, and O) and those in period 3 and below (such as Si, P, and S).
Period 2 elements do not form compounds in which the central atom is covalently bonded to five or more atoms, although such compounds are common for the heavier elements. Thus whereas carbon and silicon both form tetrafluorides (CF4 and SiF4), only SiF4 reacts with F− to give a stable hexafluoro dianion, SiF62−. Because there are no 2d atomic orbitals, the formation of octahedral CF62− would require hybrid orbitals created from 2s, 2p, and 3d atomic orbitals. The 3d orbitals of carbon are so high in energy that the amount of energy needed to form a set of sp3d2 hybrid orbitals cannot be equaled by the energy released in the formation of two additional C–F bonds. These additional bonds are expected to be weak because the carbon atom (and other atoms in period 2) is so small that it cannot accommodate five or six F atoms at normal C–F bond lengths due to repulsions between electrons on adjacent fluorine atoms. Perhaps not surprisingly, then, species such as CF62− have never been prepared.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): \(OF_4\)
What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in OF4? Is OF4 likely to exist?
Given: chemical compound
Asked for: hybridization and stability
Strategy:
- Predict the geometry of OF4 using the VSEPR model.
- From the number of electron pairs around O in OF4, predict the hybridization of O. Compare the number of hybrid orbitals with the number of electron pairs to decide whether the molecule is likely to exist.
Solution:
A The VSEPR model predicts that OF4 will have five electron pairs, resulting in a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with four bonding pairs and one lone pair. B To accommodate five electron pairs, the O atom would have to be sp3d hybridized. The only d orbital available for forming a set of sp3d hybrid orbitals is a 3d orbital, which is much higher in energy than the 2s and 2p valence orbitals of oxygen. As a result, the OF4 molecule is unlikely to exist. In fact, it has not been detected.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
What is the hybridization of the boron atom in \(BF_6^{3−}\)? Is this ion likely to exist?
Answer sp3d2 hybridization; no
Expanded Octet Hybridization: https://youtu.be/1WpxXcKl_Io
Assignment of Hybrid Orbitals to Central Atoms
The hybridization of an atom is determined based on the number of regions of electron density that surround it. The geometrical arrangements characteristic of the various sets of hybrid orbitals are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\). These arrangements are identical to those of the electron-pair geometries predicted by VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory predicts the shapes of molecules, and hybrid orbital theory provides an explanation for how those shapes are formed. To find the hybridization of a central atom, we can use the following guidelines:
- Determine the Lewis structure of the molecule.
- Determine the number of regions of electron density around an atom using VSEPR theory, in which single bonds, multiple bonds, radicals, and lone pairs each count as one region.
- Assign the set of hybridized orbitals from Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\) that corresponds to this geometry.
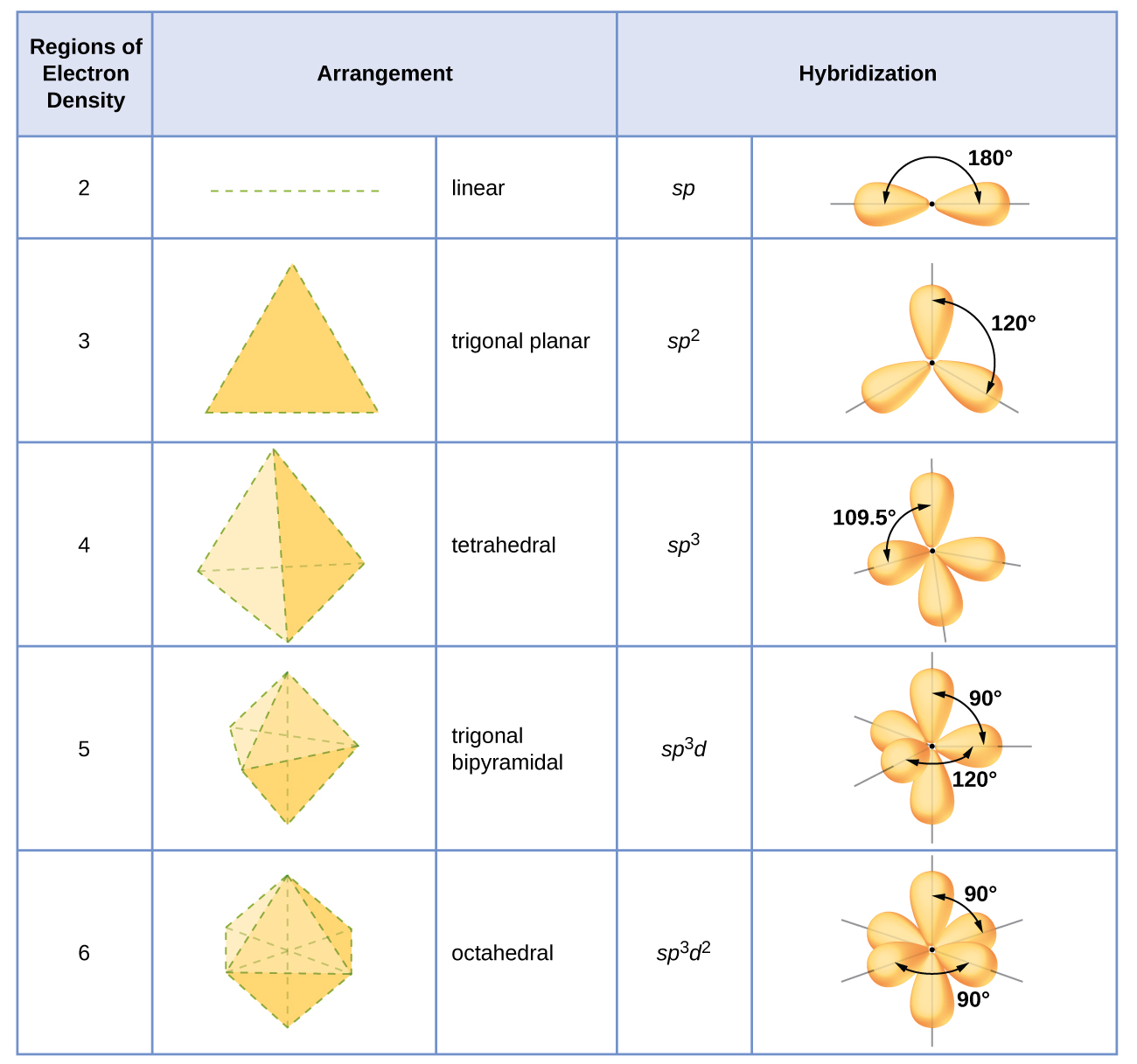
It is important to remember that hybridization was devised to rationalize experimentally observed molecular geometries, not the other way around.
The model works well for molecules containing small central atoms, in which the valence electron pairs are close together in space. However, for larger central atoms, the valence-shell electron pairs are farther from the nucleus, and there are fewer repulsions. Their compounds exhibit structures that are often not consistent with VSEPR theory, and hybridized orbitals are not necessary to explain the observed data.
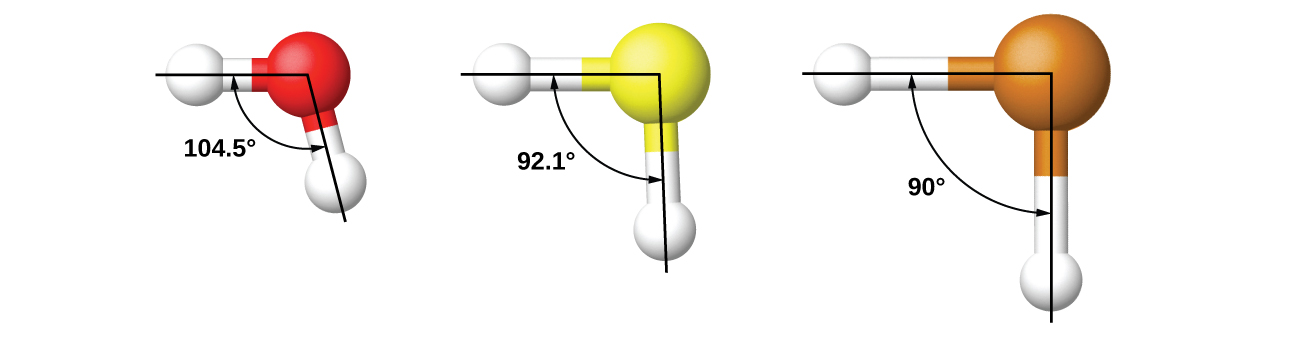
For example, we have discussed the H–O–H bond angle in H2O, 104.5°, which is more consistent with sp3 hybrid orbitals (109.5°) on the central atom than with 2p orbitals (90°). Sulfur is in the same group as oxygen, and H2S has a similar Lewis structure. However, it has a much smaller bond angle (92.1°), which indicates much less hybridization on sulfur than oxygen. Continuing down the group, tellurium is even larger than sulfur, and for H2Te, the observed bond angle (90°) is consistent with overlap of the 5p orbitals, without invoking hybridization. We invoke hybridization where it is necessary to explain the observed structures.
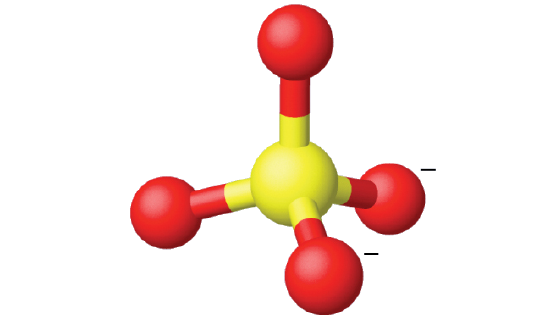
Ammonium sulfate is important as a fertilizer. What is the hybridization of the sulfur atom in the sulfate ion, \(\ce{SO4^2-}\)?
Solution
The Lewis structure of sulfate shows there are four regions of electron density.
What is the hybridization of the selenium atom in SeF4?
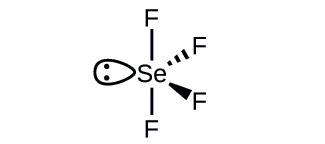
- Answer
-
The selenium atom is sp3d hybridized.
Urea, NH2C(O)NH2, is sometimes used as a source of nitrogen in fertilizers. What is the hybridization of each nitrogen and carbon atom in urea?
Solution
The Lewis structure of urea is
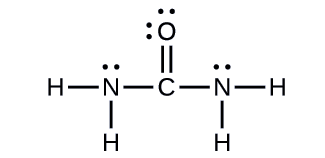
The carbon atom is surrounded by three regions of electron density, positioned in a trigonal planar arrangement. The hybridization in a trigonal planar electron pair geometry is sp2 (Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)), which is the hybridization of the carbon atom in urea.
Acetic acid, H3CC(O)OH, is the molecule that gives vinegar its odor and sour taste. What is the hybridization of the two carbon atoms in acetic acid?
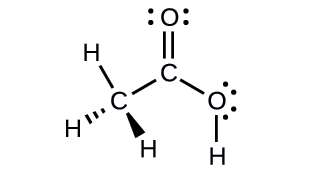
- Answer
-
H3C, sp3; C(O)OH, sp2
Determining the Hybridization of an Atom:
Summary
We can use hybrid orbitals, which are mathematical combinations of some or all of the valence atomic orbitals, to describe the electron density around covalently bonded atoms. These hybrid orbitals either form sigma (σ) bonds directed toward other atoms of the molecule or contain lone pairs of electrons. We can determine the type of hybridization around a central atom from the geometry of the regions of electron density about it. Two such regions imply sp hybridization; three, sp2 hybridization; four, sp3 hybridization; five, sp3d hybridization; and six, sp3d2 hybridization. Pi (π) bonds are formed from unhybridized atomic orbitals (p or d orbitals).
Footnotes
- Note that orbitals may sometimes be drawn in an elongated “balloon” shape rather than in a more realistic “plump” shape in order to make the geometry easier to visualize.
Glossary
- hybrid orbital
- orbital created by combining atomic orbitals on a central atom
- hybridization
- model that describes the changes in the atomic orbitals of an atom when it forms a covalent compound
- sp hybrid orbital
- one of a set of two orbitals with a linear arrangement that results from combining one s and one p orbital
- sp2 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of three orbitals with a trigonal planar arrangement that results from combining one s and two p orbitals
- sp3 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of four orbitals with a tetrahedral arrangement that results from combining one s and three p orbitals
- sp3d hybrid orbital
- one of a set of five orbitals with a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement that results from combining one s, three p, and one d orbital
- sp3d2 hybrid orbital
- one of a set of six orbitals with an octahedral arrangement that results from combining one s, three p, and two d orbitals


