8.E: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry- Homework
- Page ID
- 428743
Turn in your answers for the following questions - show your work
Draw Lewis dot structures, determine the molecular shape, electronic geometry, bond length, determine the bond energy, determine the bond polarity, and determine the formal charge for each atom.
- a. H2
- b. CH4
- c. NH3
- d. H2O
- e. HBr
- f. PCl5
- g. CO2
- h. BF3
- i. CF2Cl2
- j. C4H8 (3 different structures)
The Following Questions are for your practice - Do Not Turn In. They include answers so you can check your work
Ionic Bonding
- Predict the charge on the monatomic ions formed from the following atoms in binary ionic compounds:
- Mg
- Al
- O
- Cl
- answer
-
Mg2+; Al3+; O2–; Cl–
Covalent Bonding
- Predict which of the following compounds are ionic and which are covalent, based on the location of their constituent atoms in the periodic table:
- Cl2CO
- MnO
- NCl3
- CoBr2
- answer
-
ionic: (b), (d); covalent: (a), (c)
- From its position in the periodic table, determine which atom in each pair is more electronegative:
- Br or Cl
- N or O
- answer
-
Cl; O
- Identify the more polar bond in each of the following pairs of bonds:
- HF or HCl
- NO or CO
- answer
-
HF; CO
Lewis Symbols and Structures
- Write the Lewis symbols for each of the following ions:
- As3–
- I–
- answer
-
eight electrons:
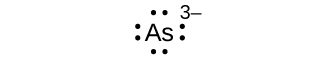
eight electrons:

- Write the Lewis symbols of the ions in each of the following ionic compounds and the Lewis symbols of the atom from which they are formed:
- MgS
- Al2O3
- answer
-
(a)
 ;
;(b)
 ;
;
- Write Lewis structures for the following:
- O2
- H2CO
- AsF3
- answer
-
(a)
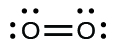
(b)
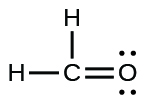 ;
;(c)
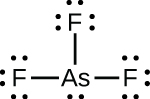 ;
;
- Write Lewis structures for the following:
- SeF6
- XeF4
- \(\ce{SeCl3+}\)
- answer
-
SeF6:
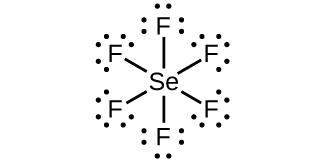 ;
;XeF4:
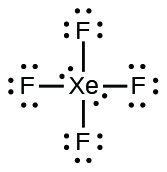 ;
;\(\ce{SeCl3+}\):
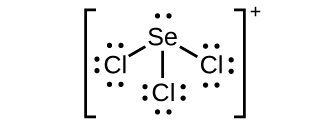
- Methanol, H3COH, is used as the fuel in some race cars. Ethanol, C2H5OH, is used extensively as motor fuel in Brazil. Both methanol and ethanol produce CO2 and H2O when they burn. Write the chemical equations for these combustion reactions using Lewis structures instead of chemical formulas.
- answer
-
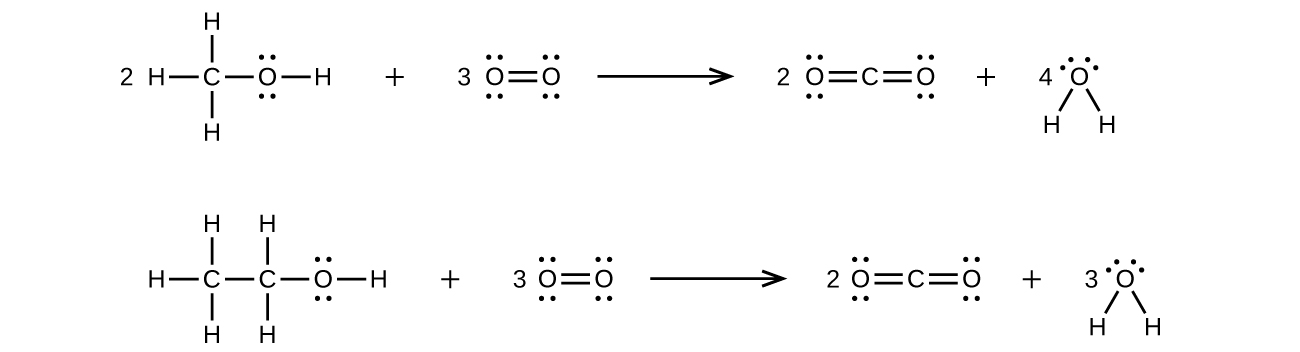
- The arrangement of atoms in several biologically important molecules is given here. Complete the Lewis structures of these molecules by adding multiple bonds and lone pairs. Do not add any more atoms.
the amino acid serine:
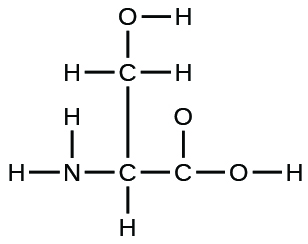
urea:
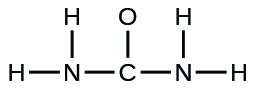
- answer
-
(a)
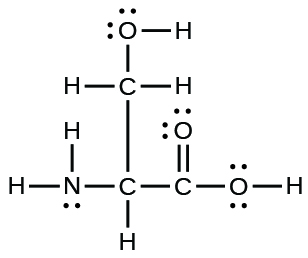 ;
;(b)
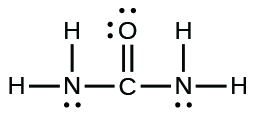 ;
;
Formal Charges and Resonance
- Draw all possible resonance structures for each of these compounds. Determine the formal charge on each atom in each of the resonance structures:
- SO2
- \(\ce{NO2-}\)
- answer
-
(a)
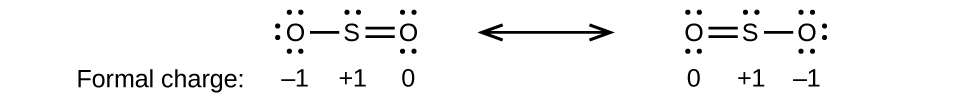 ;
;(b)
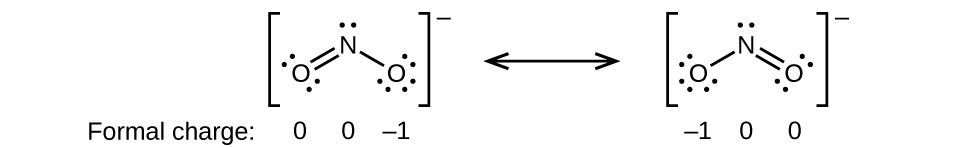
Strengths of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
- Using the table of bond energies determine the approximate enthalpy change for each of the following reactions:
- \(\ce{H2}(g)+\ce{Br2}(g)⟶\ce{2HBr}(g)\)
- answer
-
- −114 kJ;
- Complete the following Lewis structure by adding bonds (not atoms), and then indicate the longest bond:

- answer
-
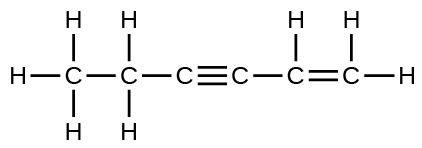
The C–C single bonds are longest.
Molecular Structure and Polarity
- A molecule with the formula AB2, in which A and B represent different atoms, could have one of three different shapes. Sketch and name the three different shapes that this molecule might have. Give an example of a molecule or ion for each shape.
- answer
-

- Predict the electron pair geometry and the molecular structure of each of the following molecules or ions:
- SF6
- PCl5
- (c) BeH2
- \(\ce{CH3+}\)
- answer
-
- Both the electron geometry and the molecular structure are octahedral.
- Both the electron geometry and the molecular structure are trigonal bipyramid.
- (c) Both the electron geometry and the molecular structure are linear.
- Both the electron geometry and the molecular structure are trigonal planar.
- Identify the electron pair geometry and the molecular structure of each of the following molecules:
- ClNO (N is the central atom)
- CS2
- (c) Cl2CO (C is the central atom)
- Cl2SO (S is the central atom)
- answer
-
(a) electron-pair geometry: trigonal planar, molecular structure: bent (120°); (b) electron-pair geometry: linear, molecular structure: linear; (c) electron-pair geometry: trigonal planar, molecular structure: (d) trigonal planar; electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral, molecular structure: trigonal pyramidal
- Which of the following molecules have dipole moments?
- CS2
- SeS2
- (c) CCl2F2
- PCl3 (P is the central atom)
- ClNO (N is the central atom)
- answer
-
SeS2, CCl2F2, PCl3, and ClNO all have dipole moments.
- Describe the molecular structure around the indicated atom or atoms:
- the sulfur atom in sulfuric acid, H2SO4 [(HO)2SO2]
- the chlorine atom in chloric acid, HClO3 [HOClO2]
- (c) the oxygen atom in hydrogen peroxide, HOOH
- the nitrogen atom in nitric acid, HNO3 [HONO2]
- answer
-
(a) tetrahedral; (b) trigonal pyramidal; (c) bent (109°); (d) trigonal planar; bent (109°);
- Use the Molecule Shape simulator to explore real molecules. On the Real Molecules tab, select H2O. Switch between the “real” and “model” modes. Explain the difference observed.
- answer
-
The structures are very similar. In the model mode, each electron group occupies the same amount of space, so the bond angle is shown as 109.5°. In the “real” mode, the lone pairs are larger, causing the hydrogens to be compressed. This leads to the smaller angle of 104.5°.


