1.3: Thermochemistry
- Page ID
- 398264
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)In this chapter we apply the first law of thermodynamics and the concept of enthalpy introduced in Chapter I.2 to chemical reactions. At standard state conditions we can use tabulated heats of formation to calculate the change in enthalpy for any reaction. At temperatures other than standard conditions we use the temperature dependence of the enthalpy to derive an expression for the change in enthalpy of a reaction at any temperature in relation to a reference temperature.
- Understand how the first law of thermodynamics describes energy changes in chemical reactions.
- Be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a reaction using the standard enthalpy of formation.
- Be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a reaction at non-standard temperature from a reference value and reference temperature.
Thermochemistry: Heat of reaction
Chemical reactions almost always involve heat transfer. In an exothermic reaction, heat is given off during the reaction, meaning that heat is transferred from the system to the surroundings. In an endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed during the reaction, meaning that heat is transferred from the surroundings into the system. Recall from Chapter I.2 that under the conditions of constant pressure, the amount of heat, \(\bf{q_p}\), is equal to the change in enthalpy. Most biochemical reactions occur under condition of constant pressure and so we can equate the change in enthalpy of a reaction \(\bf{\Delta_r H}\) with the heat of the reaction. The subscript in \(\bf{\Delta_r H}\) indicates that we are here concerned with a chemical reaction and the change of enthalpy associated with that reaction.
Since enthalpy is a state function (does not depend on the path) we can write:
\[\Delta_r H = H_{\text{products}} – H_{\text{reactants}}\label{EQ:thermochem1}\]
Equation \ref{EQ:thermochem1} says that the change in enthalpy of a reaction is the difference in enthalpies of the products and reactants. Consider the following reaction of the dimerization of nitrogen dioxide to form dinitrogen tetroxide:
\[\ce{2 NO2(g) → N2O4(g)} \tag{Reaction I}\]
For this reaction, 2 moles of NO2(g) react to form 1 mole of N2O4(g). The molar change in enthalpy will be: \[\Delta_r H = H (\text{N}_2\text{O}_4) – 2 H (\text{NO}_2)\]
Notice that because we have two moles of reactant NO2(g) for every one mole of product N2O4(g) we multiply the molar enthalpy of NO2(g) by the stoichiometric coefficient 2. The absolute molar enthalpies of the individual reactants and products are not easily measured. Fortunately, because enthalpy is a state function, the change in enthalpy for the reaction will be the same no matter what path is taken from reactant to product. To calculate \(\bf{\Delta_r H}\) for the reaction, we break the reaction into two intermediate steps, shown schematically in Figure I.3.A. We first break the reactants into their constituent elements at standard state and then form the products from their constituent elements in the standard state. The reason for breaking the reaction into these intermediate steps is that we can look-up tabulated values for the standard heats of formation for these reactions. We can then sum together the change in enthalpy for the individual steps to obtain the overall change in enthalpy.
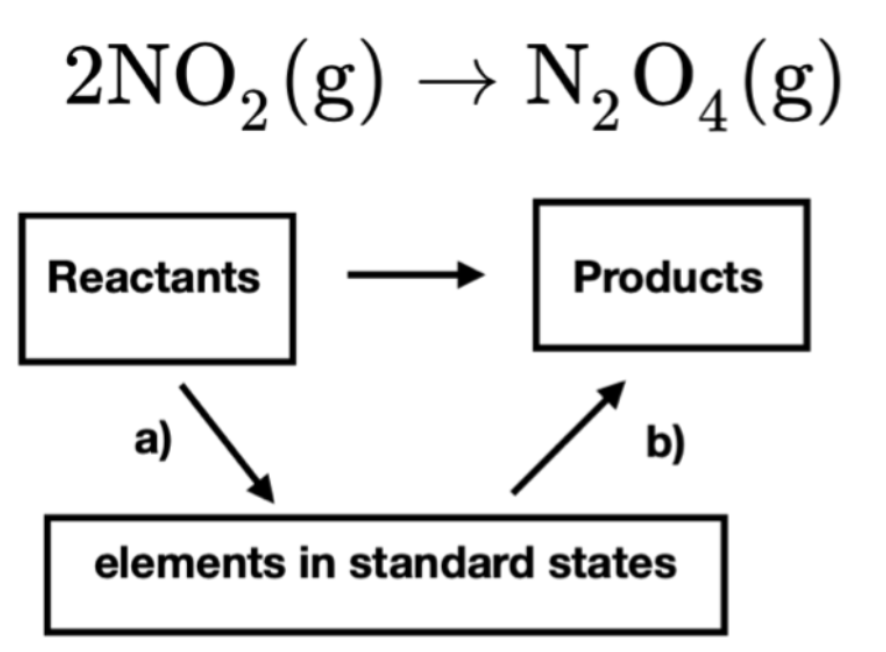
In our example, we first write the reaction for breaking reactant NO2(g) into its elements at standard state:
2 NO2 (g) → N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g) Reaction I.a
We can look up the change in molar enthalpy of formation, \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\), for NO2 (g). Notice that the superscript \(^{\circ}\) indicates standard state conditions. The change in enthalpy of formation, \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for NO2(g) is the formation of one mole of NO2 (g) from its constituent elements:
0.5 N2 (g) + O2 (g) → NO2 (g) \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) (NO2)
Notice that the \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) for Reaction I.a above is -2 \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for NO2 (g).
Similarly, for the products we write the reaction for the formation of products from their constituent elements:
N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → N2O4(g) Reaction I.b
We can look up in a table the value of \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for N2O4 (g). Notice that the \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) for Reaction I.b is equal to \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for N2O4 (g).
N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → N2O4(g) \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) (N2O4)
Summing Reaction I.a and Reaction I.b gives the overall reaction:

and we can write the \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) for the overall reaction as the sum of the two intermediate steps:
\[\Delta_r H^{\circ} = \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ} (\text{N}_2\text{O}_4) – 2 \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ} (\text{NO}_2)\label{EQ:DeltaHNO2}\]
In general, we can write the change of enthalpy of a reaction at standard conditions as
\[\Delta_r H^{\circ} = \sum \nu \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ} (\text{products}) – \sum \nu \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}(\text{reactants})\label{EQ:Hess}\]
where \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) are the standard molar heats of formation, \(\nu\) are the stoichiometric coefficients, and the sum is over the products minus the sum over the reactants. Equation \ref{EQ:Hess} is known as Hess's law which states that in a chemical reaction \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) does not depend on the intermediate steps.
See Practice Problems 1 and 2.
Temperature dependence of heat of reaction
Hess’s Law and Equation \ref{EQ:Hess} allows us to calculate \(\bf{\Delta_r H^{\circ}}\) at standard conditions using tabulated data for standard heats of formation. In order to calculate \(\Delta_r H\) at non-standard state conditions, we need to know how \(\Delta_r H\) varies with temperature. Recall that the slope of the enthalpy vs. temperature at constant pressure gives the heat capacity:
\[C_p = \left(\frac{\partial H}{\partial T} \right)_P\label{EQ:Cp1}\]
or, rearranging we get:
\[dH = C_p \cdot dT\label{EQ:Cp2}\]
For considering changes in \(\Delta_r H\) with temperature, we replace \(\bf{H}\) in Equation \ref{EQ:Cp2} with \(\bf{\Delta_r H}\) to get:
\[d\Delta_r H = \Delta_r C_p \cdot dT\label{EQ:Cp3}\]
where \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) is the difference in heat capacities of products and reactants and is given by a Hess’s Law-type analog:
\[\Delta_r C_p =\sum \nu C_p^{(\text{products})} – \sum \nu C_p^{(\text{reactants})}\label{EQ:Cp4}\]
where the sum is over the individual heat capacities of the products minus the reactants weighted by their stoichiometric coefficients. We integrate both sides of Equation \ref{EQ:Cp3} from an initial reference state to a final state:
\[\begin{eqnarray}\int_{T^{\circ}}^{T_2} d\Delta_r H &=& \int_{T^{\circ}}^{T_2} \Delta_r C_p \cdot dT \nonumber \\[4pt] \Delta_r H_{T_2} – \Delta_r H_{T^{\circ}} &=& \int_{T^{\circ}}^{T_2} \Delta_r C_p \cdot dT \nonumber \\[4pt] \Delta_r H_{T_2} &=& \Delta_r H_{T^{\circ}} + \int_{T^{\circ}}^{T_2} \Delta_r C_p \cdot dT\label{EQ:Kirschoff1}\end{eqnarray}\]
Equation \ref{EQ:Kirschoff1} allows us to compute the \(\bf{\Delta H}\) of a reaction at any non-standard temperature if we know how \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) depends on temperature. Usually this is determined experimentally and \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) is fit to a polynomial function that interpolates the data. However, if the heat capacity is independent of temperature (as it is for an ideal gas), we can take \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) out of the integral to obtain:
\[\begin{eqnarray}\Delta_r H_{T_2} &=& \Delta_r H_{T^{\circ}} + \Delta_r C_p \int_{T^{\circ}}^{T_2} dT \nonumber \\[4pt] \Delta_r H_{T_2} &=& \Delta_r H_{T^{\circ}} + \Delta_r C_p (T_2 – T^{\circ})\label{EQ:Kirchhoff2}\end{eqnarray}\]
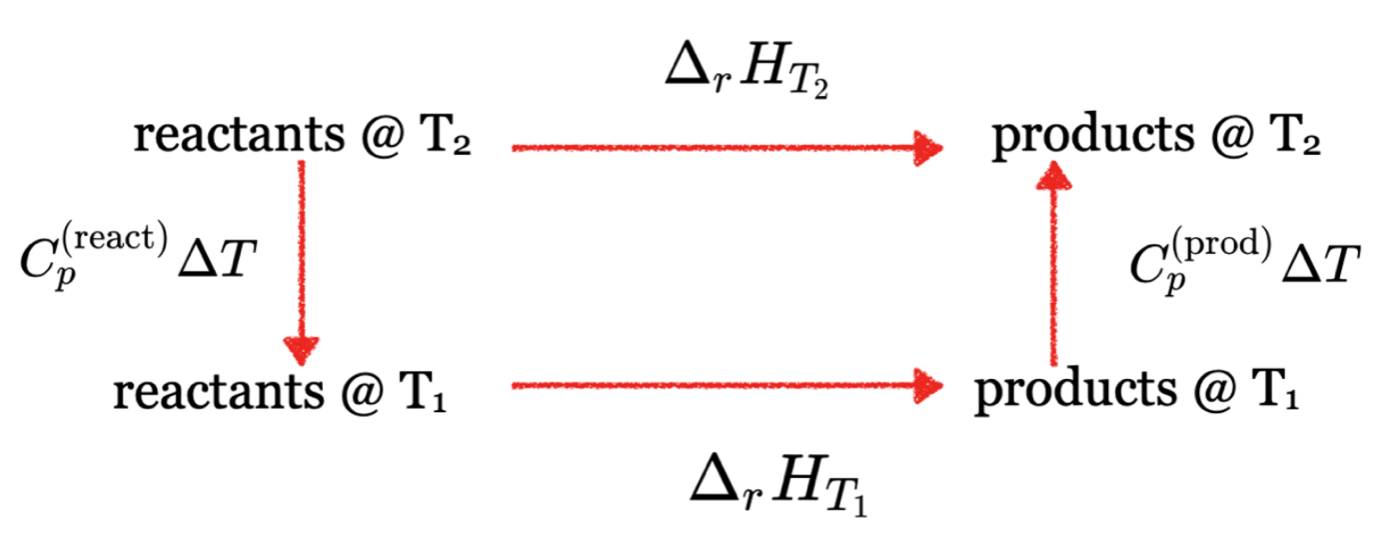
Equation \ref{EQ:Kirchhoff2} is known as Kirchhoff's law and is valid if \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) is independent of temperature. We can see schematically that Kirchhoff’s law results from taking the reaction at \(T_2\) and breaking it into three steps:
- Heat/cool the reactant from \(T_2\) to \(T^{\circ}\) using \(\Delta H = C^{reactants}_p \Delta T\).
- Find \(\Delta_r H\) of the reaction at \(T^{\circ}\) using the tabulated heats of formation and Hess’s law.
- Cool/heat the products from \(T^{\circ}\) back to \(T_2\) using \(\Delta H = C^{products}_p \Delta T\)
Summing these three steps results in Kirchhoff’s law Equation \ref{EQ:Kirchhoff2} where \(\bf{\Delta_r C_p}\) is the difference in heat capacities between the products and reactants. Figure I.3.B shows a schematic of this process.
See Practice Problem 3
Examples
Methane gas is burned in a Bunsen burner. Use Hess's law to calculate \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) of the combustion of methane at 298 K and 1 bar. The standard molar enthalpies of formation at 298 K and 1 bar are:
| CH4 (g) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = -74.85 kJ/mol |
| CO2 (g) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = -393.5 kJ/mol |
| H2O (g) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = -241.8 kJ/mol |
Solution
For the combustion of methane, the balanced chemical reaction is:
CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O (g)
From Equation \ref{EQ:Hess}:
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) = [ \(\Delta_f H^{\circ}\) (CO2)+ 2 \(\Delta_f H^{\circ}\) (H2O) ] - [\(\Delta_f H^{\circ}\) (CH4) + 2 \(\Delta_f H^{\circ}\) (O2)]
By convention, we assigne a value of zero to \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for elements in their most stable allotropic state, so \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) (O2) = 0 at 298 K. Using the tabulated values of \(\Delta_f H^{\circ}\):
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ} = [ -393.5 \ \text{kJ/mol} + 2 (-241.8 \ \text{kJ/mol}) ] - (-74.85 \ \text{kJ/mol}) \)
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ} = -802.3 \ \text{kJ/mol} \)
Calculate the value of \(\Delta_r \bar{H}\) for the dimerization of nitrogen dioxide to form dinitrogen tetroxide at 600 K.
\[\ce{2 NO2(g) → N2O4(g)} \]
The standard molar enthalpies of formation and molar heat capacities are:
| \(\ce{NO2(g)}\) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = 33.9 kJ/mol | \(\bar{C_p}\) = 37.9 J K-1 mol-1 |
| \(\ce{N2O4(g)}\) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = 9.7 kJ/mol | \(\bar{C_p}\) = 79.1 J K-1 mol-1 |
Solution
First, we use Hess's law to find \(\Delta_r \bar{H}^{\circ}\) of the reaction at standard conditions. From Equation \ref{EQ:DeltaHNO2} we have:
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ} = \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ} (\text{N}_2\text{O}_4) – 2 \Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ} (\text{NO}_2)\)
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ} = 9.7 \ \text{kJ/mol} – 2 (33.9 \ \text{kJ/mol}\)
\(\Delta_r H^{\circ} = -58.1 \ \text{kJ/mol}\)
To find \(\Delta_r \bar{H}\) at 600 K we use Equation \ref{EQ:Kirchhoff2}. Assuming the molar heat capacity is independent of temperature we use:
\( \Delta_r \bar{H} =\Delta_r H_{T^{\circ}} + \Delta_r C_p (T_2 – T^{\circ})\)
We find \(\Delta_r C_p\) from Equation \ref{EQ:Cp4}:
\(\Delta_r \bar{C_p} = \bar{C_p} (\text{N}_2\text{O}_4) – 2 \bar{C_p} (\text{NO}_2)\)
\(\Delta_r \bar{C_p} = 79.1 \ \text{J K}^{-1} \ \text{mol}^{-1}– 2 ( 37.9 \ \text{J K}^{-1} \ \text{mol}^{-1}) \)
\(\Delta_r \bar{C_p} = 3.3 \text{J K}^{-1} \ \text{mol}^{-1} \)
\(\Delta_r \bar{C_p} = 0.0033 \text{kJ K}^{-1} \ \text{mol}^{-1} \)
Finally, we compute \(\Delta_r \bar{H}\) at 600 K:
\( \Delta_r \bar{H} =-58.1 \ \text{kJ/mol} + 0.0033 \text{kJ K}^{-1} \ \text{mol}^{-1} (600 – 298)\)
\( \Delta_r \bar{H} =-57.1 \ \text{kJ/mol} \)
Notice that \(\Delta_r \bar{H}\) at 600 K is not very different from \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) at 298 K. For gas-phase reactions, the change in enthalpy due to the molar heat capacities tends to cancel between the reactants and products.
Practice Problems
Problem 1. Formamide (HCONH2) is used in the industrial production of hydrogen cyanide. Calculate the change in enthalpy for the dehydration of formamide to form water and hydrogen cyanide.

using the tabulated heat of formation data:
| Water (g) | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = -241.8 kJ/mol |
| Formamide | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = -188.79 kJ/mol |
| Hydrogen cyanide | \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) = 129.286 kJ/mol |
Problem 2. Alcohol fermentation is the process in which carbohydrates are broken down into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The overall reaction is
C6H12O6 (s) → 2 C2H5OH (l) + 2 CO2 (g)
Given that \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for C2H5OH (l) is -277.0 kJ/mol, \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for CO2 (g) is -393.5 kJ/mol, and \(\Delta_f \bar{H}^{\circ}\) for C6H12O6 (s) is -1274 kJ/mol, calculate \(\Delta_r H^{\circ}\) for the fermentation reaction shown.
Problem 3. The thermal denaturation of a globular protein with \(T_m=40\) °C has \(\Delta \bar{H} = 300\) kJ/mol for unfolding at the melting temperature (\(T_m\)). The difference in the constant-pressure molar heat capacity between the denatured state (unfolded) and the folded state (N) is 9.0 kJ mol\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\). Find the molar enthalpy of denaturation at \(T=25\) °C. (Assume the heat capacity does not depend on temperature).


