4.3: Solution Concentrations
- Page ID
- 36990
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
- To describe the concentrations of solutions quantitatively
Many people have a qualitative idea of what is meant by concentration. Anyone who has made instant coffee or lemonade knows that too much powder gives a strongly flavored, highly concentrated drink, whereas too little results in a dilute solution that may be hard to distinguish from water. In chemistry, the concentration of a solution is the quantity of a solute that is contained in a particular quantity of solvent or solution. Knowing the concentration of solutes is important in controlling the stoichiometry of reactants for solution reactions. Chemists use many different methods to define concentrations, some of which are described in this section.
Molarity
The most common unit of concentration is molarity, which is also the most useful for calculations involving the stoichiometry of reactions in solution. The molarity (M) is a common unit of concentration and is defined as the number of moles of solute present in exactly 1 L of solution. It is, equivalently, the number of millimoles of solute present in exactly 1 mL of solution:
\( molarity = \dfrac{moles\: of\: solute}{liters\: of\: solution} = \dfrac{mmoles\: of\: solute} {milliliters\: of\: solution} \label{4.3.1}\)
The units of molarity are therefore moles per liter of solution (mol/L), abbreviated as \(M\). An aqueous solution that contains 1 mol (342 g) of sucrose in enough water to give a final volume of 1.00 L has a sucrose concentration of 1.00 mol/L or 1.00 M. In chemical notation, square brackets around the name or formula of the solute represent the molar concentration of a solute. Therefore,
\[[\rm{sucrose}] = 1.00\: M\]
is read as “the concentration of sucrose is 1.00 molar.” The relationships between volume, molarity, and moles may be expressed as either
\[ V_L M_{mol/L} = \cancel{L} \left( \dfrac{mol}{\cancel{L}} \right) = moles \label{4.3.2}\]
or
\[ V_{mL} M_{mmol/mL} = \cancel{mL} \left( \dfrac{mmol} {\cancel{mL}} \right) = mmoles \label{4.3.3}\]
Figure 4.3.1 illustrates the use of Equation 4.3.2 and Equation 4.3.3.

Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in 2.50 L of 0.100 M NaOH.
Given: identity of solute and volume and molarity of solution
Asked for: amount of solute in moles
Strategy:
Use either Equation 4.3.2 or Equation 4.3.3, depending on the units given in the problem.
Solution:
Because we are given the volume of the solution in liters and are asked for the number of moles of substance, Equation 4.3.2 is more useful:
\( moles\: NaOH = V_L M_{mol/L} = (2 .50\: \cancel{L} ) \left( \dfrac{0.100\: mol } {\cancel{L}} \right) = 0 .250\: mol\: NaOH \)
Calculate the number of millimoles of alanine, a biologically important molecule, in 27.2 mL of 1.53 M alanine.
Answer: 41.6 mmol
Concentrations are often reported on a mass-to-mass (m/m) basis or on a mass-to-volume (m/v) basis, particularly in clinical laboratories and engineering applications. A concentration expressed on an m/m basis is equal to the number of grams of solute per gram of solution; a concentration on an m/v basis is the number of grams of solute per milliliter of solution. Each measurement can be expressed as a percentage by multiplying the ratio by 100; the result is reported as percent m/m or percent m/v. The concentrations of very dilute solutions are often expressed in parts per million (ppm), which is grams of solute per 106 g of solution, or in parts per billion (ppb), which is grams of solute per 109 g of solution. For aqueous solutions at 20°C, 1 ppm corresponds to 1 μg per milliliter, and 1 ppb corresponds to 1 ng per milliliter (Table 4.3.1).
| Concentration | Units |
|---|---|
| m/m | g of solute/g of solution |
| m/v | g of solute/mL of solution |
| ppm | g of solute/106 g of solution |
| μg/mL | |
| ppb | g of solute/109 g of solution |
| ng/mL |
Calculations Involving Molarity (M): https://youtu.be/TVTCvKoSR-Q
The Preparation of Solutions
To prepare a solution that contains a specified concentration of a substance, it is necessary to dissolve the desired number of moles of solute in enough solvent to give the desired final volume of solution. Figure 4.3.1 illustrates this procedure for a solution of cobalt(II) chloride dihydrate in ethanol. Note that the volume of the solvent is not specified. Because the solute occupies space in the solution, the volume of the solvent needed is almost always less than the desired volume of solution. For example, if the desired volume were 1.00 L, it would be incorrect to add 1.00 L of water to 342 g of sucrose because that would produce more than 1.00 L of solution. As shown in Figure 4.3.2, for some substances this effect can be significant, especially for concentrated solutions.
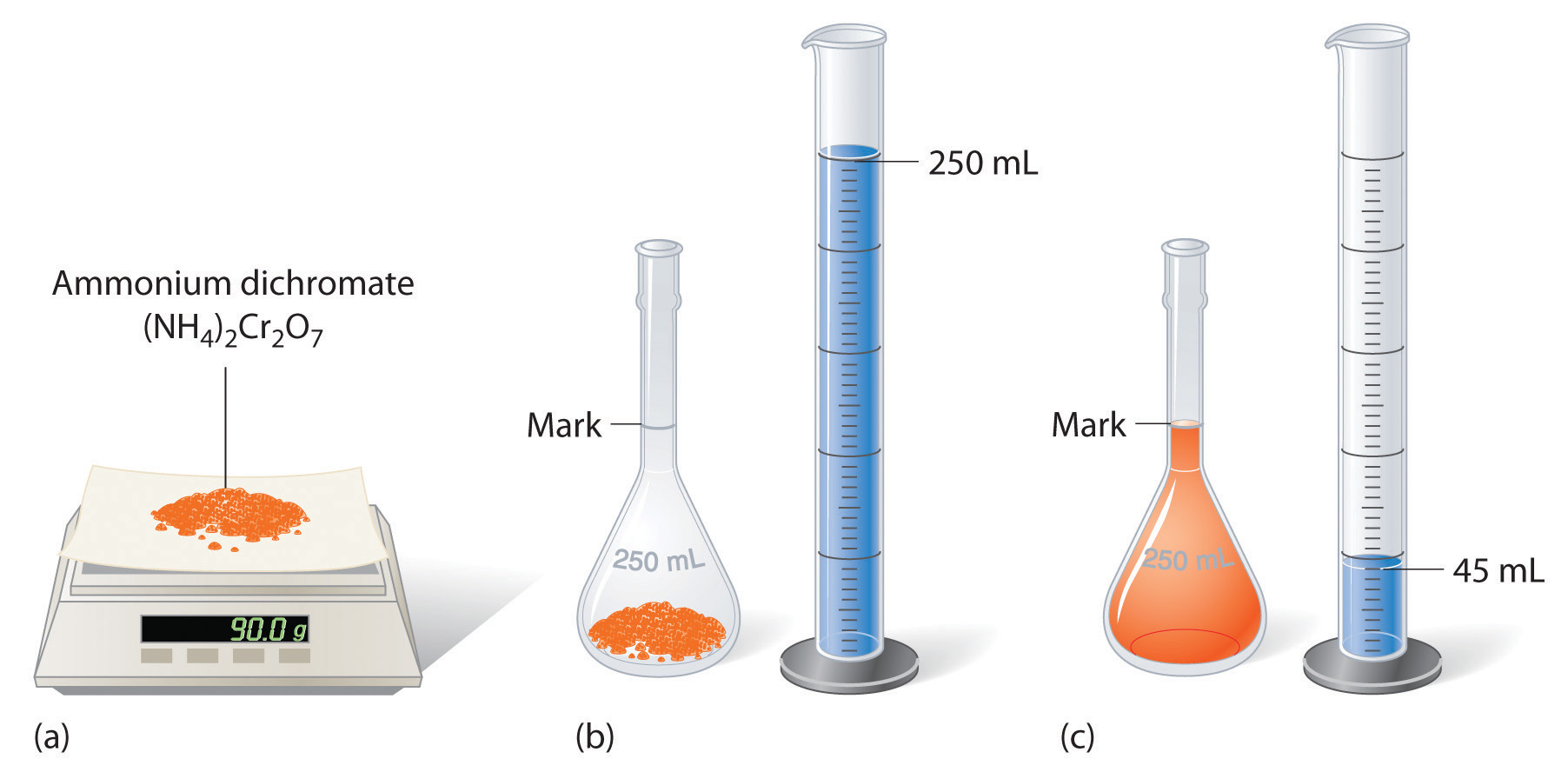
The solution in Figure 4.3.1 contains 10.0 g of cobalt(II) chloride dihydrate, CoCl2•2H2O, in enough ethanol to make exactly 500 mL of solution. What is the molar concentration of CoCl2•2H2O?
Given: mass of solute and volume of solution
Asked for: concentration (M)
Strategy:
To find the number of moles of CoCl2•2H2O, divide the mass of the compound by its molar mass. Calculate the molarity of the solution by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
Solution:
The molar mass of CoCl2•2H2O is 165.87 g/mol. Therefore,
\( moles\: CoCl_2 \cdot 2H_2O = \left( \dfrac{10.0 \: \cancel{g}} {165 .87\: \cancel{g} /mol} \right) = 0 .0603\: mol \)
The volume of the solution in liters is
\( volume = 500\: \cancel{mL} \left( \dfrac{1\: L} {1000\: \cancel{mL}} \right) = 0 .500\: L \)
Molarity is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, so the molarity of the solution is
\( molarity = \dfrac{0.0603\: mol} {0.500\: L} = 0.121\: M = CoCl_2 \cdot H_2O \)
The solution shown in Figure 4.3.2 contains 90.0 g of (NH4)2Cr2O7 in enough water to give a final volume of exactly 250 mL. What is the molar concentration of ammonium dichromate?
Answer: \((NH_4)_2Cr_2O_7 = 1.43\: M\)
To prepare a particular volume of a solution that contains a specified concentration of a solute, we first need to calculate the number of moles of solute in the desired volume of solution using the relationship shown in Equation 4.3.2. We then convert the number of moles of solute to the corresponding mass of solute needed. This procedure is illustrated in Example 4.3.3.
The so-called D5W solution used for the intravenous replacement of body fluids contains 0.310 M glucose. (D5W is an approximately 5% solution of dextrose [the medical name for glucose] in water.) Calculate the mass of glucose necessary to prepare a 500 mL pouch of D5W. Glucose has a molar mass of 180.16 g/mol.
Given: molarity, volume, and molar mass of solute
Asked for: mass of solute
Strategy:
- Calculate the number of moles of glucose contained in the specified volume of solution by multiplying the volume of the solution by its molarity.
- Obtain the mass of glucose needed by multiplying the number of moles of the compound by its molar mass.
Solution:
A We must first calculate the number of moles of glucose contained in 500 mL of a 0.310 M solution:
\( V_L M_{mol/L} = moles \)
\( 500\: \cancel{mL} \left( \dfrac{1\: \cancel{L}} {1000\: \cancel{mL}} \right) \left( \dfrac{0 .310\: mol\: glucose} {1\: \cancel{L}} \right) = 0 .155\: mol\: glucose \)
B We then convert the number of moles of glucose to the required mass of glucose:
\( mass \: of \: glucose = 0.155 \: \cancel{mol\: glucose} \left( \dfrac{180.16 \: g\: glucose} {1\: \cancel{mol\: glucose}} \right) = 27.9 \: g \: glucose \)
Another solution commonly used for intravenous injections is normal saline, a 0.16 M solution of sodium chloride in water. Calculate the mass of sodium chloride needed to prepare 250 mL of normal saline solution.
Answer: 2.3 g NaCl
A solution of a desired concentration can also be prepared by diluting a small volume of a more concentrated solution with additional solvent. A stock solution is a commercially prepared solution of known concentration and is a commercially prepared solution of known concentration, is often used for this purpose. Diluting a stock solution is preferred because the alternative method, weighing out tiny amounts of solute, is difficult to carry out with a high degree of accuracy. Dilution is also used to prepare solutions from substances that are sold as concentrated aqueous solutions, such as strong acids.
The procedure for preparing a solution of known concentration from a stock solution is shown in Figure 4.3.3. It requires calculating the number of moles of solute desired in the final volume of the more dilute solution and then calculating the volume of the stock solution that contains this amount of solute. Remember that diluting a given quantity of stock solution with solvent does not change the number of moles of solute present. The relationship between the volume and concentration of the stock solution and the volume and concentration of the desired diluted solution is therefore
\((V_s)(M_s) = moles\: of\: solute = (V_d)(M_d)\label{4.3.4}\)
where the subscripts s and d indicate the stock and dilute solutions, respectively. Example 5.5.4 demonstrates the calculations involved in diluting a concentrated stock solution.
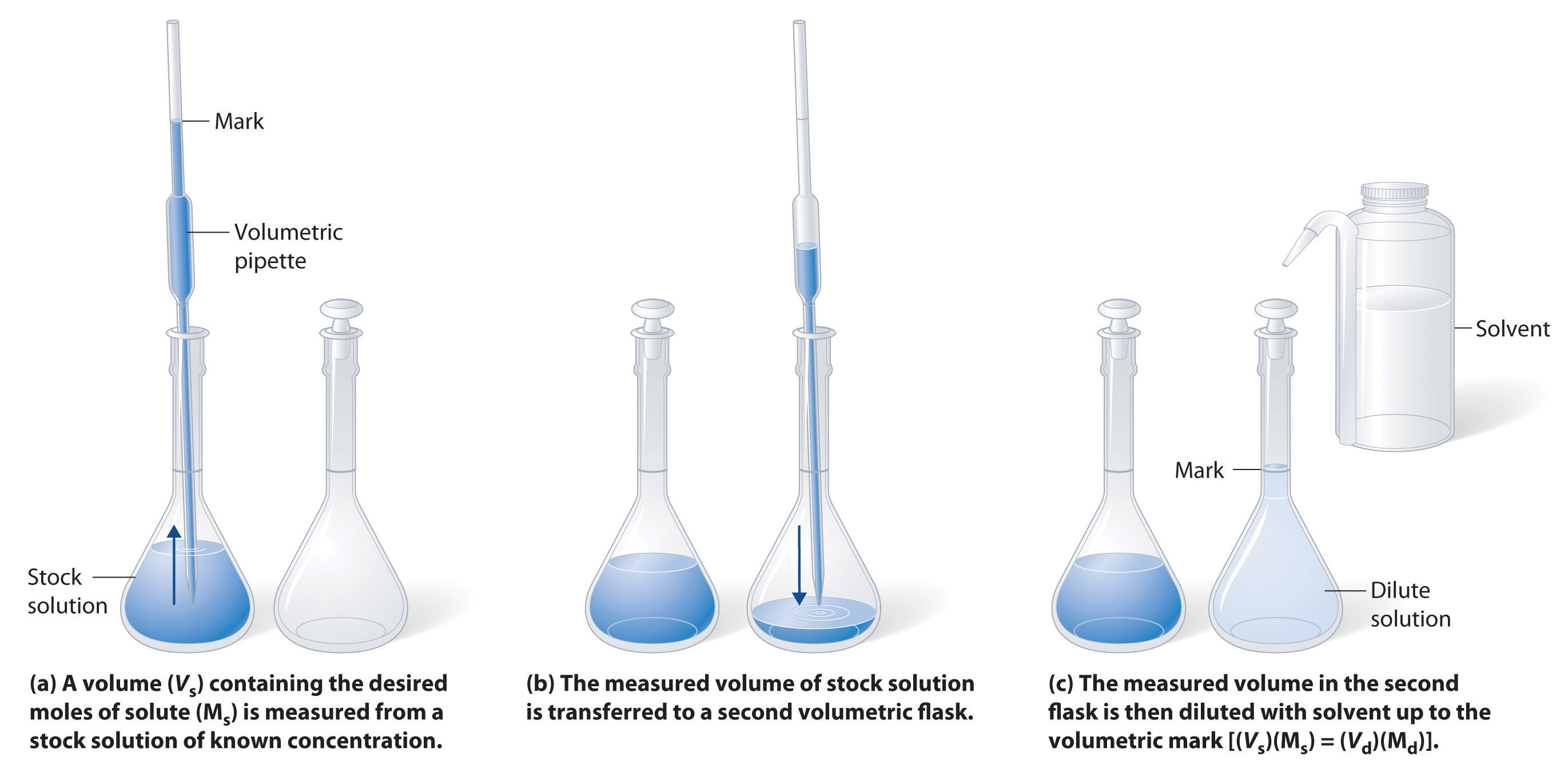
What volume of a 3.00 M glucose stock solution is necessary to prepare 2500 mL of the D5W solution in Example 4.3.3?
Given: volume and molarity of dilute solution
Asked for: volume of stock solution
Strategy:
- Calculate the number of moles of glucose contained in the indicated volume of dilute solution by multiplying the volume of the solution by its molarity.
- To determine the volume of stock solution needed, divide the number of moles of glucose by the molarity of the stock solution.
Solution:
A The D5W solution in Example 4.3.3 was 0.310 M glucose. We begin by using Equation 4.3.4 to calculate the number of moles of glucose contained in 2500 mL of the solution:
\( moles\: glucose = 2500\: \cancel{mL} \left( \dfrac{1\: \cancel{L}} {1000\: \cancel{mL}} \right) \left( \dfrac{0 .310\: mol\: glucose} {1\: \cancel{L}} \right) = 0 .775\: mol\: glucose \)
B We must now determine the volume of the 3.00 M stock solution that contains this amount of glucose:
\( volume\: of\: stock\: soln = 0 .775\: \cancel{mol\: glucose} \left( \dfrac{1\: L} {3 .00\: \cancel{mol\: glucose}} \right) = 0 .258\: L\: or\: 258\: mL \)
In determining the volume of stock solution that was needed, we had to divide the desired number of moles of glucose by the concentration of the stock solution to obtain the appropriate units. Also, the number of moles of solute in 258 mL of the stock solution is the same as the number of moles in 2500 mL of the more dilute solution; only the amount of solvent has changed. The answer we obtained makes sense: diluting the stock solution about tenfold increases its volume by about a factor of 10 (258 mL → 2500 mL). Consequently, the concentration of the solute must decrease by about a factor of 10, as it does (3.00 M → 0.310 M).
We could also have solved this problem in a single step by solving Equation 4.3.4 for Vs and substituting the appropriate values:
\( V_s = \dfrac{( V_d )(M_d )}{M_s} = \dfrac{(2 .500\: L)(0 .310\: \cancel{M} )} {3 .00\: \cancel{M}} = 0 .258\: L \)
As we have noted, there is often more than one correct way to solve a problem.
What volume of a 5.0 M NaCl stock solution is necessary to prepare 500 mL of normal saline solution (0.16 M NaCl)?
Answer: 16 mL
Calculating Moles from Volume
Quantitative calculations involving reactions in solution are carried out with masses, however, volumes of solutions of known concentration are used to determine the number of moles of reactants. Whether dealing with volumes of solutions of reactants or masses of reactants, the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation give the number of moles of each reactant needed and the number of moles of each product that can be produced.
The flowchart for stoichiometric calculations illustrated in Figure 4.3.4 shows that in the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and either the masses of solid reactants and products or the volumes of solutions of reactants and products can be used to determine the amounts of other species.
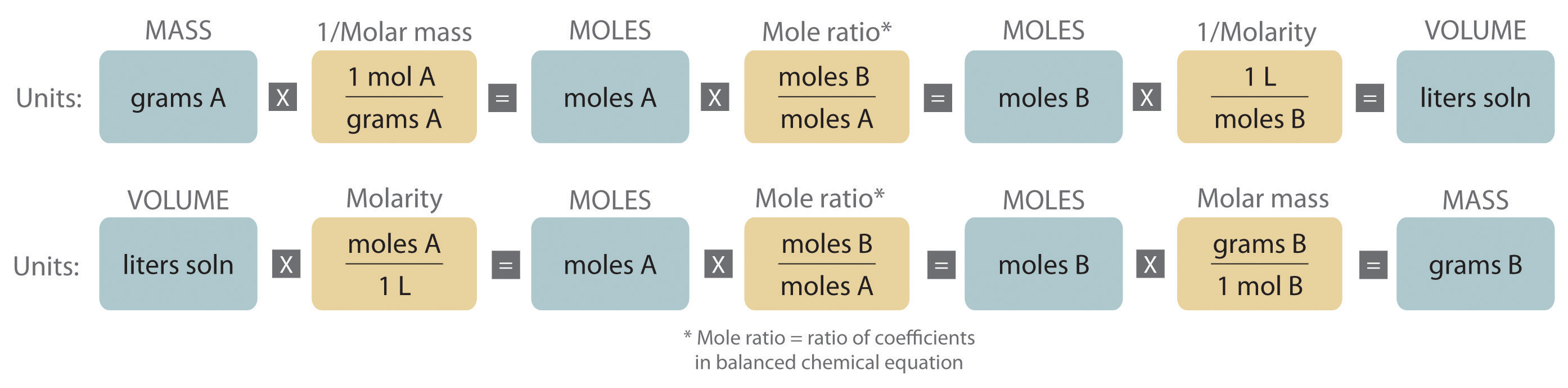
The balanced chemical equation for a reaction and either the masses of solid reactants and products or the volumes of solutions of reactants and products can be used in stoichiometric calculations.
Gold is extracted from its ores by treatment with an aqueous cyanide solution, which causes a reaction that forms the soluble [Au(CN)2]− ion. Gold is then recovered by reduction with metallic zinc according to the following equation:
\[ Zn(s) + 2[Au(CN)_2]^-(aq) \rightarrow [Zn(CN)_4]^{2-}(aq) + 2Au(s) \]
What mass of gold can be recovered from 400.0 L of a 3.30 × 10−4 M solution of [Au(CN)2]−?
Given: chemical equation and molarity and volume of reactant
Asked for: mass of product
Strategy:
- Check the chemical equation to make sure it is balanced as written; balance if necessary. Then calculate the number of moles of [Au(CN)2]− present by multiplying the volume of the solution by its concentration.
- From the balanced chemical equation, use a mole ratio to calculate the number of moles of gold that can be obtained from the reaction. To calculate the mass of gold recovered, multiply the number of moles of gold by its molar mass.
Solution:
A The equation is balanced as written; proceed to the stoichiometric calculation. Figure 4.3.2 is adapted for this particular problem as follows:
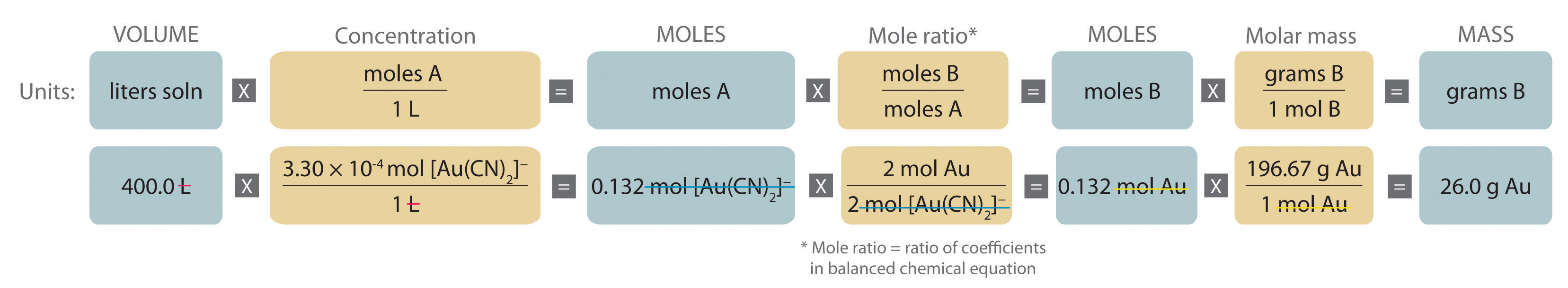
As indicated in the strategy, start by calculating the number of moles of [Au(CN)2]− present in the solution from the volume and concentration of the [Au(CN)2]− solution:
\( \begin{align} moles\: [Au(CN)_2 ]^-
& = V_L M_{mol/L} \\
& = 400 .0\: \cancel{L} \left( \dfrac{3 .30 \times 10^{4-}\: mol\: [Au(CN)_2 ]^-} {1\: \cancel{L}} \right) = 0 .132\: mol\: [Au(CN)_2 ]^- \end{align} \)
B Because the coefficients of gold and the [Au(CN)2]− ion are the same in the balanced chemical equation, assuming that Zn(s) is present in excess, the number of moles of gold produced is the same as the number of moles of [Au(CN)2]− (i.e., 0.132 mol of Au). The problem asks for the mass of gold that can be obtained, so the number of moles of gold must be converted to the corresponding mass using the molar mass of gold:
\( \begin{align} mass\: of\: Au &= (moles\: Au)(molar\: mass\: Au) \\
&= 0 .132\: \cancel{mol\: Au} \left( \dfrac{196 .97\: g\: Au} {1\: \cancel{mol\: Au}} \right) = 26 .0\: g\: Au \end{align}\)
At a 2011 market price of over $1400 per troy ounce (31.10 g), this amount of gold is worth $1170.
\( 26 .0\: \cancel{g\: Au} \times \dfrac{1\: \cancel{troy\: oz}} {31 .10\: \cancel{g}} \times \dfrac{\$1400} {1\: \cancel{troy\: oz\: Au}} = \$1170 \)
What mass of solid lanthanum(III) oxalate nonahydrate [La2(C2O4)3•9H2O] can be obtained from 650 mL of a 0.0170 M aqueous solution of LaCl3 by adding a stoichiometric amount of sodium oxalate?
Answer: 3.89 g
Ion Concentrations in Solution
In Example 4.3.2, the concentration of a solution containing 90.00 g of ammonium dichromate in a final volume of 250 mL were calculated to be 1.43 M. Let’s consider in more detail exactly what that means. Ammonium dichromate is an ionic compound that contains two NH4+ ions and one Cr2O72− ion per formula unit. Like other ionic compounds, it is a strong electrolyte that dissociates in aqueous solution to give hydrated NH4+ and Cr2O72− ions:
\[ (NH_4 )_2 Cr_2 O_7 (s) \xrightarrow {H_2 O(l)} 2NH_4^+ (aq) + Cr_2 O_7^{2-} (aq)\label{4.3.5} \]
Thus 1 mol of ammonium dichromate formula units dissolves in water to produce 1 mol of Cr2O72− anions and 2 mol of NH4+ cations (see Figure 4.3.4).
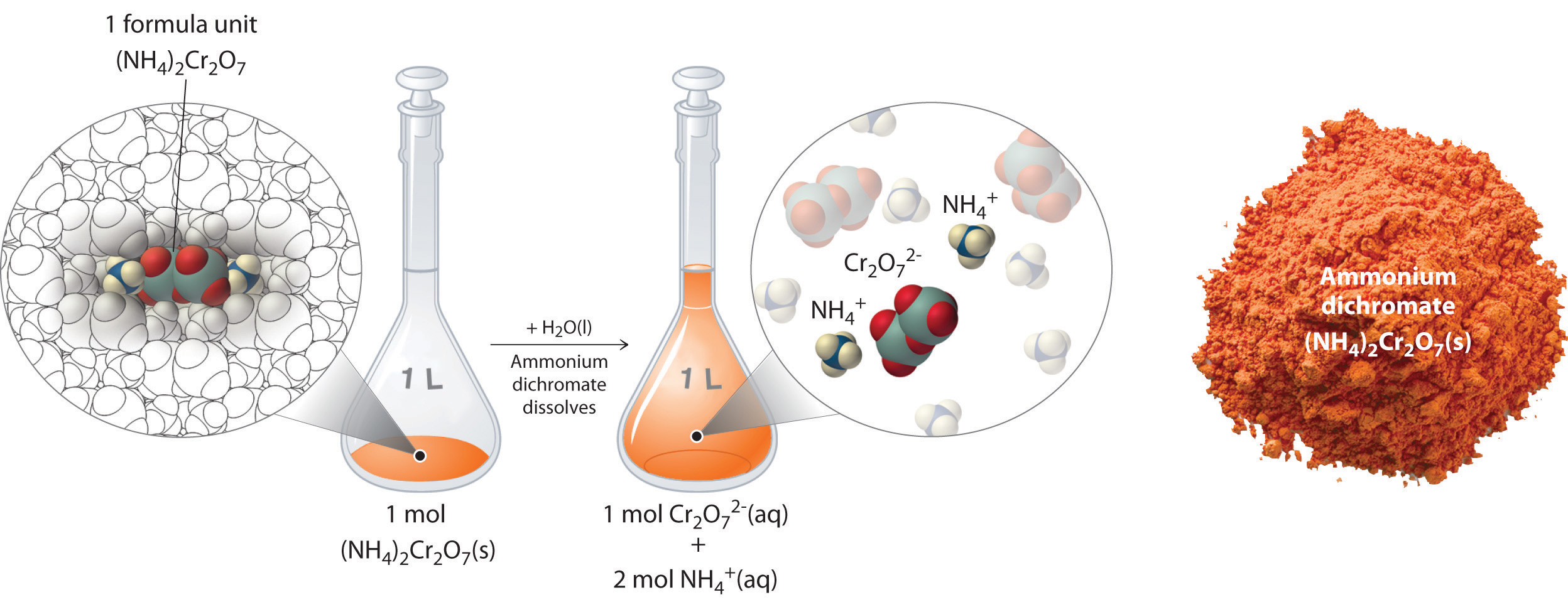
When carrying out a chemical reaction using a solution of a salt such as ammonium dichromate, it is important to know the concentration of each ion present in the solution. If a solution contains 1.43 M (NH4)2Cr2O7, then the concentration of Cr2O72− must also be 1.43 M because there is one Cr2O72− ion per formula unit. However, there are two NH4+ ions per formula unit, so the concentration of NH4+ ions is 2 × 1.43 M = 2.86 M. Because each formula unit of (NH4)2Cr2O7 produces three ions when dissolved in water (2NH4+ + 1Cr2O72−), the total concentration of ions in the solution is 3 × 1.43 M = 4.29 M.
What are the concentrations of all species derived from the solutes in these aqueous solutions?
- 0.21 M NaOH
- 3.7 M (CH3)CHOH
- 0.032 M In(NO3)3
Given: molarity
Asked for: concentrations
Strategy:
A Classify each compound as either a strong electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte.
B If the compound is a nonelectrolyte, its concentration is the same as the molarity of the solution. If the compound is a strong electrolyte, determine the number of each ion contained in one formula unit. Find the concentration of each species by multiplying the number of each ion by the molarity of the solution.
Solution:
- Sodium hydroxide is an ionic compound that is a strong electrolyte (and a strong base) in aqueous solution: \( NaOH(s) \xrightarrow {H_2 O(l)} Na^+ (aq) + OH^- (aq) \)
B Because each formula unit of NaOH produces one Na+ ion and one OH− ion, the concentration of each ion is the same as the concentration of NaOH: [Na+] = 0.21 M and [OH−] = 0.21 M.
- A The formula (CH3)2CHOH represents 2-propanol (isopropyl alcohol) and contains the –OH group, so it is an alcohol. Recall from Section 4.1 that alcohols are covalent compounds that dissolve in water to give solutions of neutral molecules. Thus alcohols are nonelectrolytes.
B The only solute species in solution is therefore (CH3)2CHOH molecules, so [(CH3)2CHOH] = 3.7 M.
- A Indium nitrate is an ionic compound that contains In3+ ions and NO3− ions, so we expect it to behave like a strong electrolyte in aqueous solution:
\( In(NO _3 ) _3 (s) \xrightarrow {H_ 2 O(l)} In ^{3+} (aq) + 3NO _3^- (aq) \)
B One formula unit of In(NO3)3 produces one In3+ ion and three NO3− ions, so a 0.032 M In(NO3)3 solution contains 0.032 M In3+ and 3 × 0.032 M = 0.096 M NO3–—that is, [In3+] = 0.032 M and [NO3−] = 0.096 M.
What are the concentrations of all species derived from the solutes in these aqueous solutions?
- 0.0012 M Ba(OH)2
- 0.17 M Na2SO4
- 0.50 M (CH3)2CO, commonly known as acetone
Answer
- \([Ba^{2+}] = 0.0012\: M; \: [OH^-] = 0.0024\: M\)
- \([Na^+] = 0.34\: M; \: [SO_4^{2-}] = 0.17\: M\)
- \([(CH_3)_2CO] = 0.50\: M\)
Concentration of Ions in Solution from a Soluble Salt: https://youtu.be/qsekSJBLemc
Summary
- Solution concentrations are typically expressed as molarities and can be prepared by dissolving a known mass of solute in a solvent or diluting a stock solution.
- definition of molarity: \[ molarity = \dfrac{moles\: of\: solute}{liters\: of\: solution} = \dfrac{mmoles\: of\: solute} {milliliters\: of\: solution} \]
- relationship among volume, molarity, and moles: \[ V_L M_{mol/L} = \cancel{L} \left( \dfrac{mol}{\cancel{L}} \right) = moles \]
- relationship between volume and concentration of stock and dilute solutions: \[(V_s)(M_s) = moles\: of\: solute = (V_d)(M_d)\]
The concentration of a substance is the quantity of solute present in a given quantity of solution. Concentrations are usually expressed in terms of molarity, defined as the number of moles of solute in 1 L of solution. Solutions of known concentration can be prepared either by dissolving a known mass of solute in a solvent and diluting to a desired final volume or by diluting the appropriate volume of a more concentrated solution (a stock solution) to the desired final volume.
Contributors and Attributions
Modified by Joshua Halpern (Howard University)

