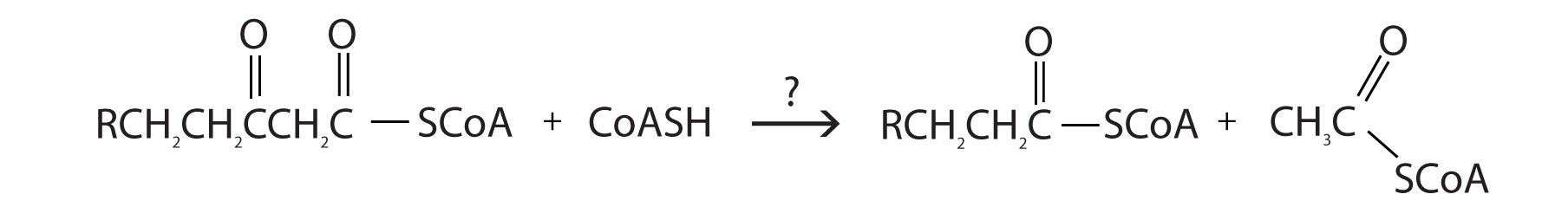10.9: Metabolism (Exercises)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 342880

- Anonymous
- LibreTexts
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
20.1: ATP- the Universal Energy Currency
Concept Review Exercise
- Why is ATP referred to as the energy currency of the cell?
Answer
- ATP is the principal molecule involved in energy exchange reactions in biological systems.
Exercises
- How do ATP and ADP differ in structure?
- Why does the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP involve the release of energy?
- Identify whether each compound would be classified as a high-energy phosphate compound.
- ATP
- glucose 6-phosphate
- creatine phosphate
- Identify whether each compound would be classified as a high-energy phosphate compound.
- ADP
- AMP
- glucose 1-phosphate
Answers
- ATP has a triphosphate group attached, while ADP has only a diphosphate group attached.
-
- yes
- no
- yes
20.2: Stage I of Catabolism
Concept Review Exercises
-
Distinguish between each pair of compounds.
- pepsin and pepsinogen
- chymotrypsin and trypsin
- aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase
-
What are the primary end products of each form of digestion?
- carbohydrate digestion
- lipid digestion
- protein digestion
-
In what section of the digestive tract does most of the carbohydrate, lipid, and protein digestion take place?
Answers
-
- Pepsinogen is an inactive form of pepsin; pepsin is the active form of the enzyme.
- Both enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Chymotrypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds following aromatic amino acids, while trypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds following lysine and arginine.
- Aminopeptidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of amino acids from the N-terminal end of a protein, while carboxypeptidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of amino acids from the C-terminal end of a protein.
-
- glucose, fructose, and galactose
- monoglycerides and fatty acids
- amino acids
-
the small intestine
Exercises
-
What are the products of digestion (or stage I of catabolism)?
-
What is the general type of reaction used in digestion?
-
Give the site of action and the function of each enzyme.
- chymotrypsin
- lactase
- pepsin
- maltase
-
Give the site of action and the function of each enzyme.
- α-amylase
- trypsin
- sucrase
- aminopeptidase
-
- What is the meaning of the following statement? “Bile salts act to emulsify lipids in the small intestine.”
- Why is emulsification important?
-
Using chemical equations, describe the chemical changes that triglycerides undergo during digestion.
-
What are the expected products from the enzymatic action of chymotrypsin on each amino acid segment?
- gly-ala-phe-thr-leu
- ala-ile-tyr-ser-arg
- val-trp-arg-leu-cys
-
What are the expected products from the enzymatic action of trypsin on each amino acid segment?
- leu-thr-glu-lys-ala
- phe-arg-ala-leu-val
- ala-arg-glu-trp-lys
Answers
-
proteins: amino acids; carbohydrates: monosaccharides; fats: fatty acids and glycerol
-
- Chymotrypsin is found in the small intestine and catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds following aromatic amino acids.
- Lactase is found in the small intestine and catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose.
- Pepsin is found in the stomach and catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, primarily those that occur after aromatic amino acids.
- Maltase is found in the small intestine and catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose.
-
- Bile salts aid in digestion by dispersing lipids throughout the aqueous solution in the small intestine.
- Emulsification is important because lipids are not soluble in water; it breaks lipids up into smaller particles that can be more readily hydrolyzed by lipases.
-
- gly-ala-phe and thr-leu
- ala-ile-tyr and ser-arg
- val-trp and arg-leu-cys
20.3: Overview of Stage II of Catabolism
Concept Review Exercises
- What is a metabolic pathway?
- What vitamin is required to make coenzyme A?
- What is the net yield of Glycolysis as far as ATP?
- Name the enzymes that are key regulatory sites in Glycolysis.
- Why are the enzymes in the previous question targets for regulation?
- Why is the priming phase necessary?
- Draw the entire pathway for glycolysis including enzymes, reactants and products for each step.
- Where does beta-oxidation occur?
- What is the average net yield of ATP per carbon?
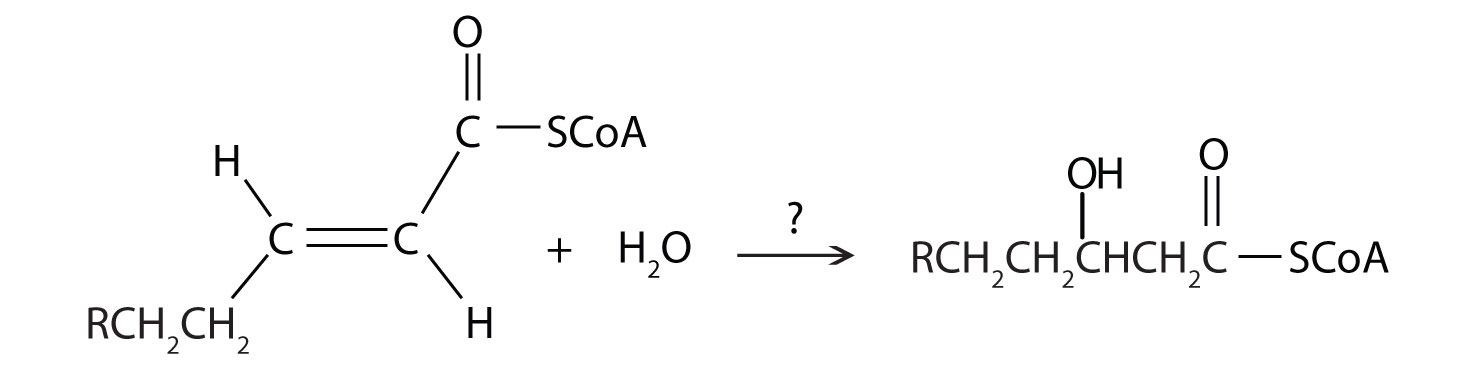
- Where exactly is water formed during the process of fatty acid degradation? (Hint: H2O is formed when when the one of the products of beta-oxidation is passed through another of the metabolic pathways)
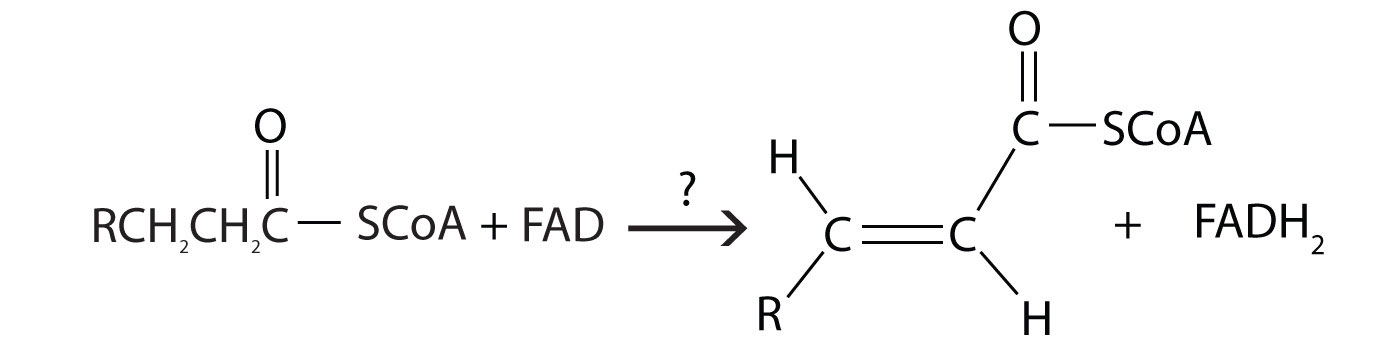
- During the process of beta-oxidation, why is it that [FAD] is used to oxidize an alkane to an alkene while NAD+ is used to oxidize an alchol to a carbonyl
- Draw out the entire process of the degradation of a triglyceride, include enzymes and products and reactants for each step.
Answers
- A metabolic pathway is a series of biochemical reactions by which an organism converts a given reactant to a specific end product.
- pantothenic acid
20.4: Stage III of Catabolism
Concept Review Exercises
- What is the main function of the citric acid cycle?
- Two carbon atoms are fed into the citric acid cycle as acetyl-CoA. In what form are two carbon atoms removed from the cycle?
- What are mitochondria and what is their function in the cell?
Answers
- the complete oxidation of carbon atoms to carbon dioxide and the formation of a high-energy phosphate compound, energy rich reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2), and metabolic intermediates for the synthesis of other compounds
- as carbon dioxide
- Mitochondria are small organelles with a double membrane that contain the enzymes and other molecules needed for the production of most of the ATP needed by the body.
Exercises
- Replace each question mark with the correct compound.
- \(\mathrm{?\xrightarrow{aconitase}isocitrate}\)
- \(\mathrm{?\, +\, ? \xrightarrow{citrate\: synthase} citrate + coenzyme\: A}\)
- \(\mathrm{fumarate \xrightarrow{fumarase}\, ?}\)
- \(\mathrm{isocitrate + NAD^+ \xrightarrow{?} \alpha\textrm{-ketoglurate} + NADH + CO_2}\)
- Replace each question mark with the correct compound.
- \(\mathrm{malate + NAD^+ \xrightarrow{?} oxaloacetate + NADH}\)
- \(\mathrm{?\, +\, ? \xrightarrow{nucleoside\: diphosphokinase} GDP + ATP}\)
- \(\mathrm{\textrm{succinyl-CoA} \xrightarrow{\textrm{succinyl-CoA synthetase}} \,?\, +\, ?}\)
- \(\mathrm{succinate + FAD \xrightarrow{succinate\: dehydrogenase}\, ? + FADH_2}\)
- From the reactions in Exercises 1 and 2, select the equation(s) by number and letter in which each type of reaction occurs.
- isomerization
- hydration
- synthesis
- From the reactions in Exercises 1 and 2, select the equation(s) by number and letter in which each type of reaction occurs.
- oxidation
- decarboxylation
- phosphorylation
- What similar role do coenzyme Q and cytochrome c serve in the electron transport chain?
- What is the electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain? To what product is this compound reduced?
- What is the function of the cytochromes in the electron transport chain?
-
- What is meant by this statement? “Electron transport is tightly coupled to oxidative phosphorylation.”
- How are electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation coupled or linked?
Answers
-
- citrate
- oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA
- malate
- α-ketoglutarate hydrogenase complex
-
- reaction in 1a
- reaction in 1c
- reaction in 1b
- Both molecules serve as electron shuttles between the complexes of the electron transport chain.
- Cytochromes are proteins in the electron transport chain and serve as one-electron carriers.
20.5: Stage II of Carbohydrate Catabolism
-
Concept Review Exercises
-
In glycolysis, how many molecules of pyruvate are produced from one molecule of glucose?
-
In vertebrates, what happens to pyruvate when
- plenty of oxygen is available?
- oxygen supplies are limited?
-
In anaerobic glycolysis, how many molecules of ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose?
Answers
-
two
-
- Pyruvate is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide.
- Pyruvate is reduced to lactate, allowing for the reoxidation of NADH to NAD+.
-
There is a net production of two molecules of ATP.
Exercises
-
Replace each question mark with the correct compound.
- \(\mathrm{fructose\: 1,6\textrm{-bisphosphate} \xrightarrow{aldolase}\, ?\, +\, ?}\)
- \(\mathrm{? + ADP \xrightarrow{pyruvate\: kinase} pyruvate + ATP}\)
- \(\mathrm{dihydroxyacetone\: phosphate \xrightarrow{?} glyceraldehyde\: 3\textrm{-phosphate}}\)
- \(\mathrm{glucose + ATP \xrightarrow{hexokinase} \, ? + ADP}\)
-
Replace each question mark with the correct compound.
- \(\mathrm{fructose\: 6\textrm{-phosphate} + ATP \xrightarrow{?} fructose\: 1,6\textrm{-bisphosphate} + ADP}\)
- \(\mathrm{? \xrightarrow{phosphoglucose\: isomerase} fructose\: 6\textrm{-phosphate}}\)
- \(\mathrm{glyceraldehyde\: 3\textrm{-phosphate} + NAD^+ + P_i \xrightarrow{?} 1,3\textrm{-bisphosphoglycerate} + NADH}\)
- \(\mathrm{3\textrm{-phosphoglycerate} \xrightarrow{phosphoglyceromutase} \, ?}\)
-
From the reactions in Exercises 1 and 2, select the equation(s) by number and letter in which each type of reaction occurs.
- hydrolysis of a high-energy phosphate compound
- synthesis of ATP
-
From the reactions in Exercises 1 and 2, select the equation(s) by number and letter in which each type of reaction occurs.
- isomerization
- oxidation
-
What coenzyme is needed as an oxidizing agent in glycolysis?
-
Calculate
- the total number of molecules of ATP produced for each molecule of glucose converted to pyruvate in glycolysis.
- the number of molecules of ATP hydrolyzed in phase I of glycolysis.
- the net ATP production from glycolysis alone.
-
How is the NADH produced in glycolysis reoxidized when oxygen supplies are limited in
- muscle cells?
- yeast?
-
- Calculate the number of moles of ATP produced by the aerobic oxidation of 1 mol of glucose in a liver cell.
- Of the total calculated in Exercise 9a, determine the number of moles of ATP produced in each process.
- glycolysis alone
- the citric acid cycle
- the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
Answers
-
- glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- phosphoenolpyruvate
- triose phosphate isomerase
- glucose 6-phosphate
-
- reactions 1b, 1d, and 2a
- reaction 1b
-
NAD+
-
- Pyruvate is reduced to lactate, and NADH is reoxidized to NAD+.
- Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide, and NADH is reoxidized to NAD+.
-
20.6: Stage II of Lipid Catabolism
-
Concept Review Exercises
- How are fatty acids activated prior to being transported into the mitochondria and oxidized?
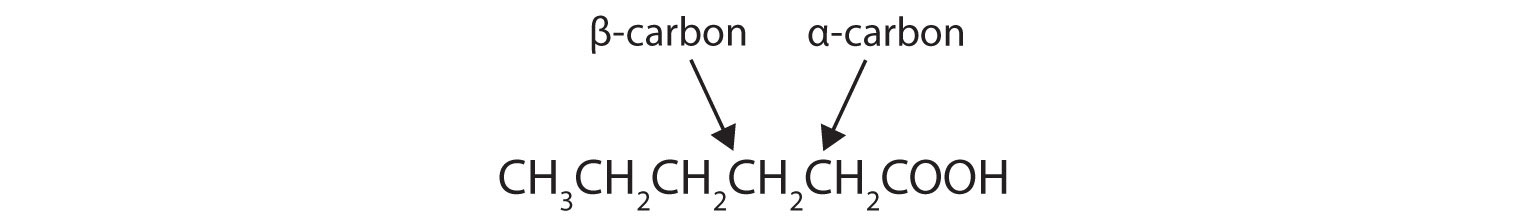
- Draw the structure of hexanoic (caproic) acid and identify the α-carbon and the β-carbon.
Answers
- They react with CoA to form fatty acyl-CoA molecules.
-
Key Takeaways
- Fatty acids, obtained from the breakdown of triglycerides and other lipids, are oxidized through a series of reactions known as β-oxidation.
- In each round of β-oxidation, 1 molecule of acetyl-CoA, 1 molecule of NADH, and 1 molecule of FADH2 are produced.
- The acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH2 are used in the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP.
Exercises
- For each reaction found in β-oxidation, identify the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction and classify the reaction as oxidation-reduction, hydration, or cleavage.
-
- What are the products of β-oxidation?
- How many rounds of β-oxidation are necessary to metabolize lauric acid (a saturated fatty acid with 12 carbon atoms)?
- How many rounds of β-oxidation are necessary to metabolize arachidic acid (a saturated fatty acid with 20 carbon atoms)?
- When myristic acid (a saturated fatty acid with 14 carbon atoms) is completely oxidized by β-oxidation, how many molecules of each are formed?
- acetyl-CoA
- FADH2
- NADH
- When stearic acid (a saturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms) is completely oxidized by β-oxidation, how many molecules of each are formed?
- acetyl-CoA
- FADH2
- NADH
- What is the net yield of ATP from the complete oxidation, in a liver cell, of one molecule of myristic acid?
- What is the net yield of ATP from the complete oxidation, in a liver cell, of one molecule of stearic acid?
Answers
-
- enoyl-CoA hydratase; hydration
- thiolase; cleavage
- acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; oxidation-reduction
- five rounds
-
- 7 molecules
- 6 molecules
- 6 molecules
- 112 molecules
20.7: Stage II of Protein Catabolism
Concept Review Exercises
-
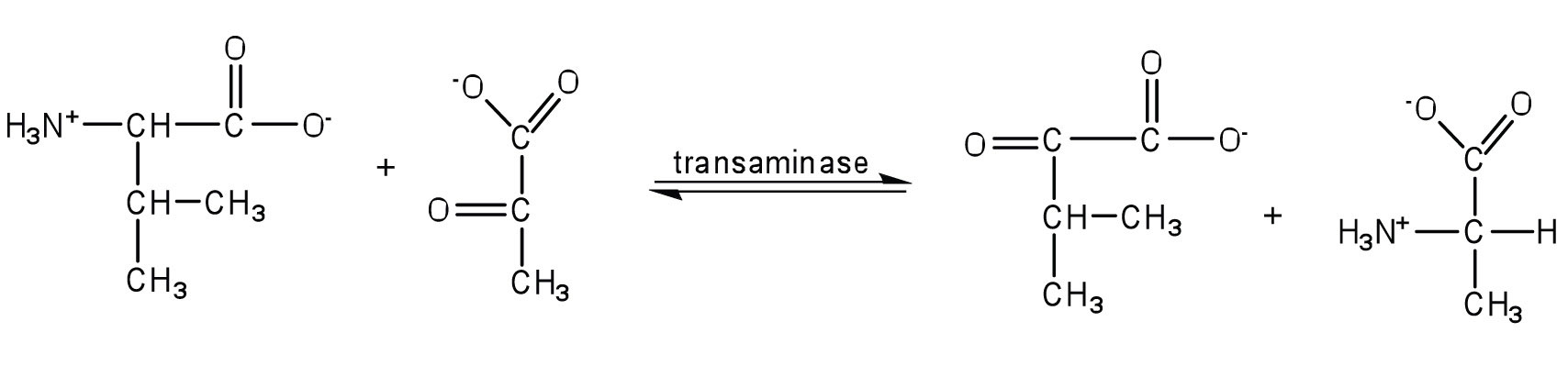
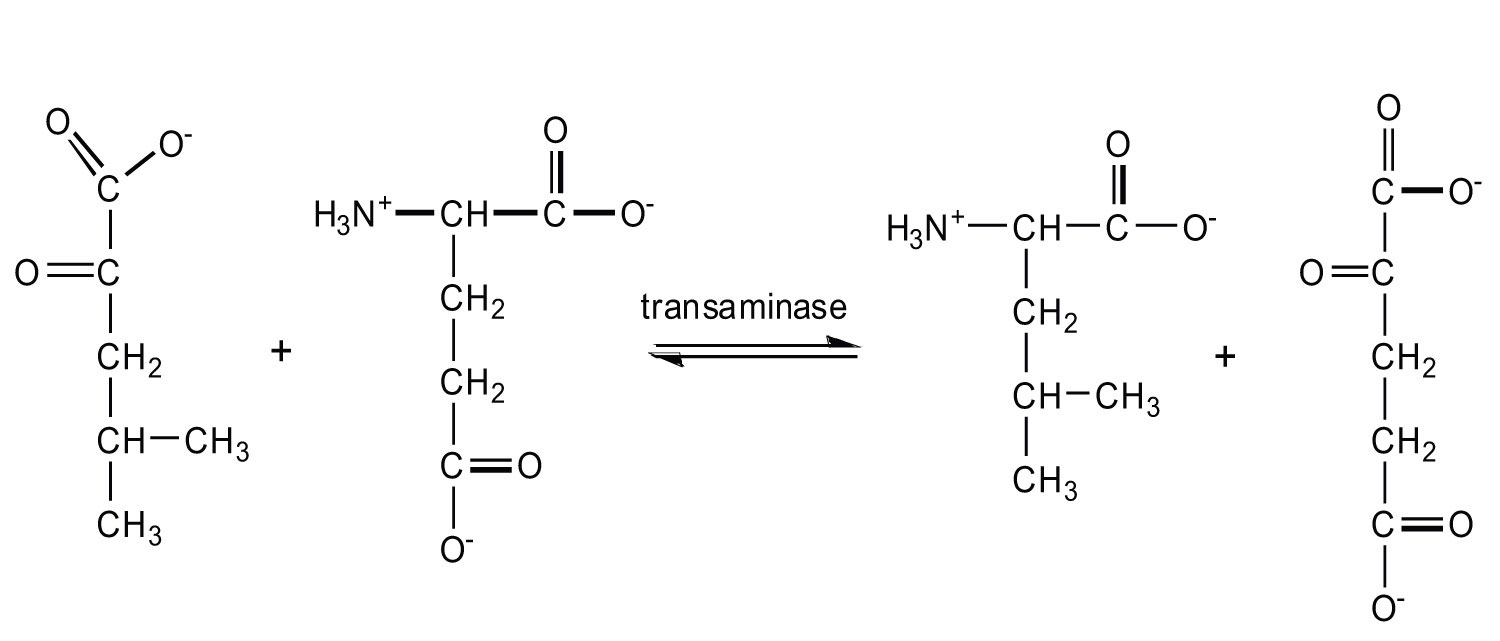
- Write the equation for the transamination reaction between alanine and oxaloacetate.
- Name the two products that are formed.
- What is the purpose of oxidative deamination?
Answers
-
-
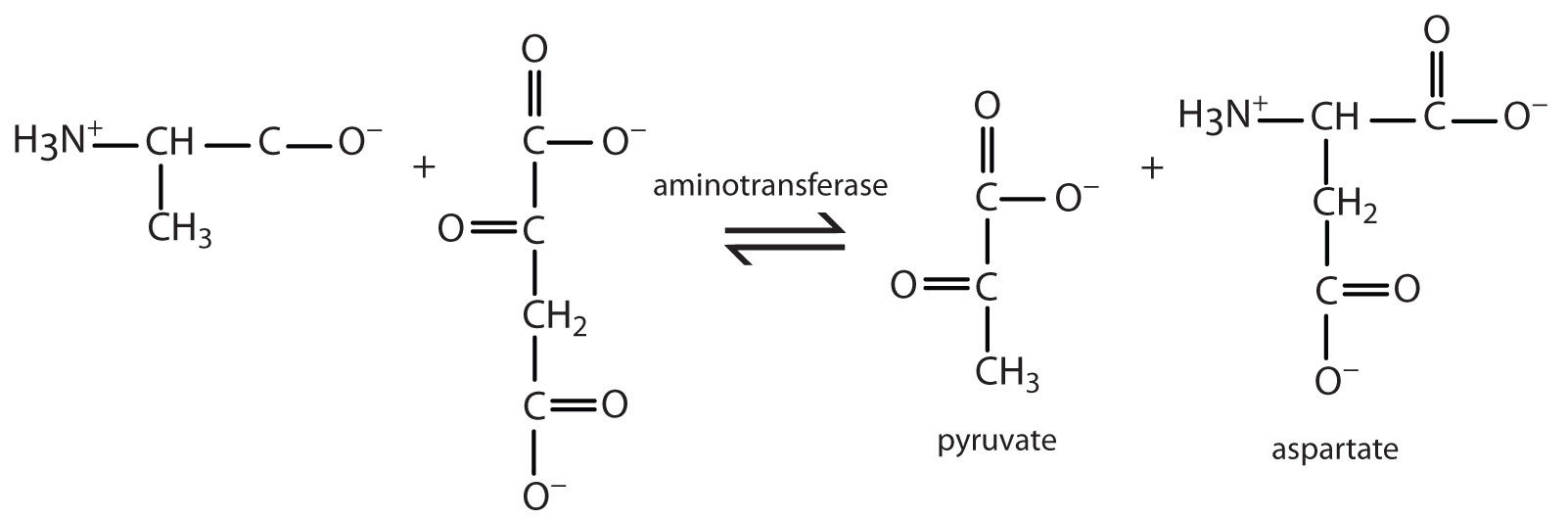
- pyruvate and aspartate
-
- Oxidative deamination provides a reaction in which the amino group [as the ammonium (NH4+) ion] is removed from a molecule, not simply transferred from one molecule to another. Most of the NH4+ ion is converted to urea and excreted from the body.
Exercises
- Write the equation for the transamination reaction between valine and pyruvate.
- Write the equation for the transamination reaction between phenylalanine and oxaloacetate.
- What products are formed in the oxidative deamination of glutamate?
- Determine if each amino acid is glucogenic, ketogenic, or both.
- phenylalanine
- leucine
- serine
- Determine if each amino acid is glucogenic, ketogenic, or both.
- asparagine
- tyrosine
- valine
Answers
- α-ketoglutarate, NADH, and NH4+
-
- glucogenic
- both
- glucogenic
Additional Exercises
-
Hydrolysis of which compound—arginine phosphate or glucose 6-phosphate—would provide enough energy for the phosphorylation of ATP? Why?
-
If a cracker, which is rich in starch, is chewed for a long time, it begins to develop a sweet, sugary taste. Why?
-
Indicate where each enzymes would cleave the short peptide ala-ser-met-val-phe-gly-cys-lys-asp-leu.
- aminopeptidase
- chymotrypsin
-
Indicate where each enzymes would cleave the short peptide ala-ser-met-val-phe-gly-cys-lys-asp-leu.
- trypsin
- carboxypeptidase
-
If the methyl carbon atom of acetyl-CoA is labeled, where does the label appear after the acetyl-CoA goes through one round of the citric acid cycle?
-
If the carbonyl carbon atom of acetyl-CoA is labeled, where does the label appear after the acetyl-CoA goes through one round of the citric acid cycle?
-
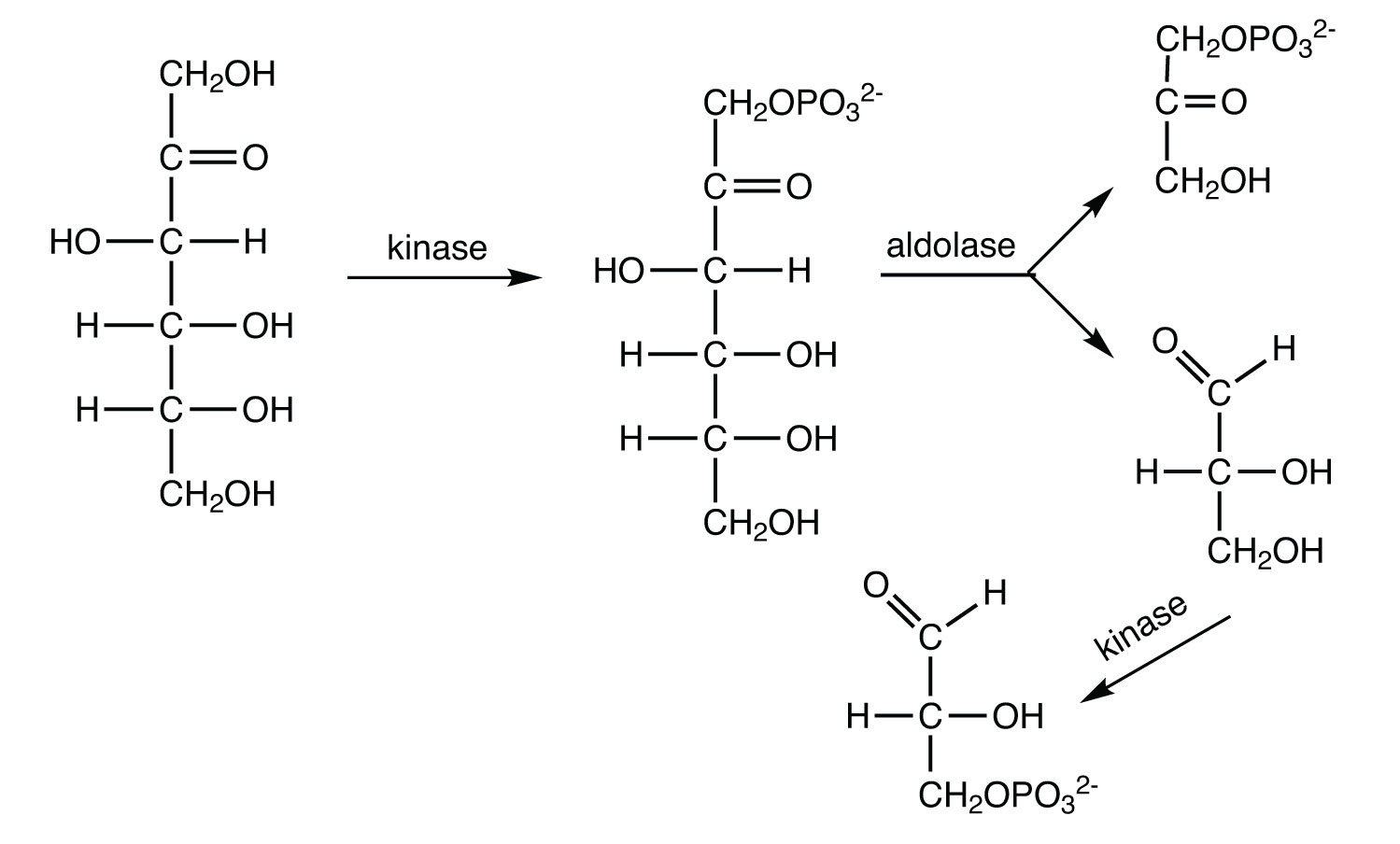
The average adult consumes about 65 g of fructose daily (either as the free sugar or from the breakdown of sucrose). In the liver, fructose is first phosphorylated to fructose 1-phosphate, which is then split into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde. Glyceraldehyde is then phosphorylated to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, with ATP as the phosphate group donor. Write the equations (using structural formulas) for these three steps. Indicate the type of enzyme that catalyzes each step.
-
What critical role is played by both BPG and PEP in glycolysis?
-
How is the NADH produced in glycolysis reoxidized when oxygen supplies are abundant?
-
When a triglyceride is hydrolyzed to form three fatty acids and glycerol, the glycerol can be converted to glycerol 3-phosphate and then oxidized to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate, an intermediate of glycolysis. (In this reaction, NAD+ is reduced to NADH.) If you assume that there is sufficient oxygen to completely oxidize the pyruvate formed from dihydroxyacetone phosphate, what is the maximum amount of ATP formed from the complete oxidation of 1 mol of glycerol?
-
How is the FADH2 from β-oxidation converted back to FAD?
-
If 1 mol of alanine is converted to pyruvate in a muscle cell (through transamination) and the pyruvate is then metabolized via the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation, how many moles of ATP are produced?
-
If the essential amino acid leucine (2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid) is lacking in the diet, an α-keto acid can substitute for it. Give the structure of the α-keto acid and the probable reaction used to form leucine from this α-keto acid.
Answers
-
The hydrolysis of arginine phosphate releases more energy than is needed for the synthesis of ATP, while hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate does not.
-
- The enzyme will cleave off amino acids one at a time beginning with alanine (the N-terminal end).
- following phenylalanine
-
Half of the label will be on the second carbon atom of oxaloacetate, while the other half will be on the third carbon atom.
-
When oxygen is abundant, NADH is reoxidized through the reactions of the electron transport chain.
-
FADH2 is reoxidized back to FAD via the electron transport chain.