9.1: Questions
- Page ID
- 134594
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)For each of the following test items, select the option that you think is the correct one.
- Each response below lists an ion by name and by chemical formula. Also,each ion is classified as monatomic or polyatomic and as a cation or anion.Which particular option is incorrect?
- carbonate, CO3 2-, polyatomic anion.
- ammonium, NH4 +, polyatomic cation.
- magnesium, Mg2+, monatomic cation.
- hydroxide, OH-, monatomic anion.
- sulfite, SO3 2-, polyatomic anion.
- Equal number of moles of different compounds
- May or may not have the same number of atoms
- Have the same number of molecules
- Have equal weights
- Have the same number of atom
- A & B
- What do you understand by the term “molecular mass of a molecule”?
- The summation of atomic masses, in grams, of all the atoms in the mo- lecule.
- The mass, in grams of the molecule.
- The gram molecular weight of a substance.
- The mass, in grams of a substance.
- The mass, in grams of the heaviest atom of the molecule
- Calculate the molecular mass of NaCl?
- 58
- 23
- 35
- 28
- 51
- All of the substances listed below are fertilizers that contribute nitrogen to the soil. Which of these is the richest source of nitrogen on a mass perentage basis?
- Urea, (NH2)2CO
- Ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
- Guanidine, HNC(NH2)2
- Ammonia, NH3
- Potassium nitrate, KNO3
- What do 2.4 moles of CO and CO2 have in common?
- same mass
- contain the same mass of carbon and oxygen
- contain the same mass of oxygen
- contain the same number of molecules
- contain the same number of total atoms
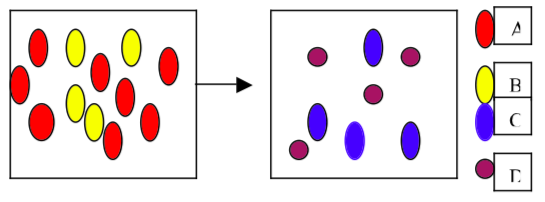
- Which of the following equations best represents the reaction shown in the diagram above? This can be answered by simple elimination.
- 8A + 4B → C + D
- 4A + 8B → 4C + 4D
- 2A + B →C + D
- 4A + 2B → 4C + 4D
- 2A + 4B → C + D
- Which of the following can be used to measure a more accurate volume of a liquid?
- Beaker
- Graduated cylinder
- Burrette
- Bottle
- All
- How can one prepare 750 mL solution of 0.5 M H2SO4, from 2.5 M H2SO4stock solution?
- by mixing 250 mL of the stock solution with 500 mL of water
- by mixing 150 mL of the stock solution with 600 mL of water
- by mixing 600 mL of the stock solution with 150 mL of water
- by mixing 375 mL of the stock solution with 375 mL of water
- none
- If the concentration of H+ ions in an aqueous solution is 2.5 x 10-4 then,
- its pH is less than 7
- the solution is acidic
- its pOH is greater than 7
- its OH- concentration is less than the concentration of OH- in neutral solution
- All
- What do you understand by the term “Quantitative analysis”?
- Involves determining the individual constituents of a given sample.
- Involves the determination of the relative or absolute amount of an analytein a given sample
- Involves the addition of measured volume of a known concentration of reagent into a solution of the substance to be determined (analyte).
- Involves determining the level of purity of an analyte.
- Involves determining the quality of a sample.
- Which of the following statements does not appropriately describe a stage in a titration process?
- Before equivalence point is reached, the volume of a reagent added to the analyte does not make the reaction complete (when there is excess of analyte).
- At equivalence point the reagent added is the amount that is chemically equivalent to the amount of substance being determined (analyte).
- After equivalence point, the amount of reagent added is higher than the amount of substance being determined.
- After equivalence point, the amount of reagent added cannot be higher than the amount of substance being determined.
- At the beginning of a titration, the number of moles of the reagent added is always less than that of the analyte present (when there is excess analyte).
- Which of the following is correct about titration of a polyprotic weak acid such as orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) with a strong base such as NaOH?
- H3PO4 titration curve has only one equivalence point.
- H3PO4 titration curve has only two equivalence points.
- H3PO4 titration curve has only three equivalence points.
- H3PO4 titration curve does not have any equivalence point.
- H3PO4 titration curve has only seven equivalence points.
- Which of the following reactions is not a redox reaction?
- H2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
- CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
- 2NaI + Cl2 → 2NaCl + I2
- C + O2 → CO2
- None
Answer questions 15 to 18 based on the following chemical equation:
CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
- Which of the following is a reducing agent if the reaction is a redox reac- tion?
- CuSO4
- Zn
- ZnSO4
- Cu
- the reaction is not a redox reaction
- Which of the following species gained electrons?
- CuSO4
- Zn
- ZnSO4
- Cu
- None
- What is the number of electrons gained per mole of the oxidizing agent?
- 1 mole
- 2 moles
- 3 moles
- 4 moles
- 0 moles
- What is the number of electrons lost per mole of the reducing agent?
- 1 mole
- 2 moles
- 3 moles
- 4 moles
- 0 moles
- Which one of the following is a redox reaction?
- H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)
- 2 KBr (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 KNO3 (aq) + PbBr2 (s)
- CaBr2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + 2 HBr (g)
- 2 Al (s) + 3 H2SO4 (aq) → Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
- CO3 2- (aq) + HSO4 - (aq)
→ HCO3 - (aq) + SO4 2- (aq)
- In the reaction, Zn(s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g), what is the oxidation number of H2?
- +1
- -1
- 0
- +2
- -2


