11: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids
- Page ID
- 204590
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Prelude
What are the four common types of bonds?
- Answer
-
Ionic, Polar covalent, covalent and metallic
Do metals have high or low electronegativities?
- Answer
-
low.
Do nonmetals have high or low electronegativities?
- Answer
-
high.
Which element has the highest electronegativy
- Answer
-
Fluorine.
States of Matter
What are the three common exothermic transitions
- Answer
-
Freezing, Condensation and deposition.
What are the three common endothermic transitions
- Answer
-
sublimation, boiling and melting
When a substance freezes does it gain or lose heat?
- Answer
-
It loses heat
Ion-Dipole Forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3a}\)
For each pair, predict which would have the greater ion-dipole interaction with water.
- Lithium or potassium cations
- Lithium or Boron cations
- fluoride or chloride
- sulfide or chloride
- Answer a
-
Lithium as they have the same charge and it is smallest
- Answer b
-
Boron as it is both smaller and has a higher charge
- Answer c
-
fluoride as they have the same charge and it is smaller
- Answer d
-
sulfide as although it is larger, it has a greater charge
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4a}\)
Choose the following molecule that exhibits dipole-dipole attractions? (AsH3, BCl3, Cl2, CO2, XeF4)
- Answer
-
AsH3
Dispersive Forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5a}\)
Which is more polarizable? (O, S, Se, Te)
- Answer
-
d. Te
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5b}\)
Which compound is the most polarizable? (I2, H2, F2, Br2)
- Answer
-
I2
Hydrogen Bonding
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6a}\)
Hydrogen bonding is a special case of:
- dipole-dipole forces
- ion-dipole forces
- covalent bonding
- London Dispersion Forces
- Answer
-
a. dipole-dipole force
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6b}\)
Which of the following molecules are not involved with hydrogen bonding?
- H2,NH3
- HI,HBr
- HF,NH3
- HCOOH,H2O
- Answer
-
b. HI, HBr
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6c}\)
Which species cannot be involved with hydrogen bonding? (HF, H2O, NH3, NH4+)
- Answer
-
NH4+
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6d}\)
What angle best approximates the geometric structure of ice? (90°, 109°, 120°, 180°)
- Answer
-
109°
Properties of Liquids
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7a}\)
Which has the highest boiling point? (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2)
- Answer
-
d. I2, these are all homonuclear diatomics, and Iodine is both the heaviest (largest mass) and most polarizable (largest volume).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7b}\)
Which has the highest boiling point? (HF, HCl, HI, HBr)
- Answer
-
a. HF, although it is the lightest (which would have you think it would have a low boiling point), it has strong hydrogen bonds, which take a lot of energy to overcome, and so has a high boiling point.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7c}\)
Which has the lowest boiling point? (He, Ne, Kr, Ar)
- Answer
-
a. He, it is the lightest and least polarizable (so it has weakest intermolecular forces) and thus the easiest to boil
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7d}\)
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling points. (H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te)
- Answer
-
H2S < H2Se < H2Te < H2O
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7e}\)
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point. (H2O, HF, NH3, CH4)
- Answer
-
CH4 < NH3 < HF < H2O
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7f}\)
Which has the highest boiling point? (CH4, SiH4, GeH4, SnH4)
- Answer
-
SnH4
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7g}\)
Which has the lowest boiling point? (CH4, SiH4, GeH4, SnH4)
- Answer
-
CH4
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7h}\)
Which has the highest boiling point? (NH3, PH3, CH4, SiH4)
- Answer
-
NH3
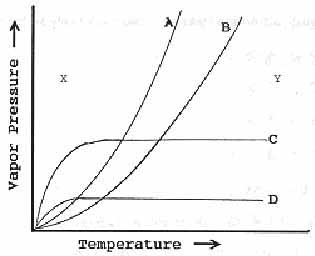
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7i}\)
Which set of curves would represent the effect of increasing temperature on the vapor pressure of a liquid?
- A & B
- C & D
- All of them
- None of them
- Answer
-
a. A & B
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7j}\)
If one of the compounds in the above question is diethyl ether and the other is water, curve___is diethyl ether and curve___is water.
- A,B
- B,A
- C,D
- D,C
- Answer
-
a. A,B
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7k}\)
The normal boiling point is defined as:
-
100°C
-
The boiling pt. at 1 atm
-
The boiling pt. on planet earth
-
None of the above
- Answer
-
b. The boiling pt. at 1 atm
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7L}\)
The normal boiling point of diethyl ether is 34.6°C and of water is 100°C. Which has the higher vapor pressure at 20°C?
- water
- diethyl ether
- they are the same
- it depends on your elevation
- Answer
-
b. diethyl ether
e
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7M}\)
If one of the compounds in question 1 is diethyl ether and the other is water, curve___is diethyl ether and curve___is water.
- A,B
- B,A
- C,D
- D,C
- Answer
-
a. A,B
e
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7n}\)
A liquid is _____ and assumes _____ of its container whereas a gas is _____ and assumes _____ of its container.
- Compressible, the volume and shape, condensed, the shape
- Compressible, the volume, compressible, the volume and shape
- Condensed, the volume and shape, condensed, the volume and shape
- Incompressible, the shape of a portion, compressible, the volume and shape
- Incompressible, the volume and shape, compressible, the shape
- Answer
-
d. Incompressible, the shape of a portion, compressible, the volume and shape
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7o}\)
Choose the molecule that has the highest boiling point.
- C2Br6
- C2Cl6
- C2F6
- C2H6
- C2I6
- Answer
-
e. C2I6
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7p}\)
Which of the following has the highest boiling point? (N2, Br2, H2, Cl2, O2)
- Answer
-
Br2
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7q}\)
The shape of a liquid’s meniscus is determined by _____.
- the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its container
- the type of material the container is made of
- the viscosity of the liquid
- the volume of the liquid
- Answer
-
a. the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its container
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7r}\)
Viscosity is _____.
- Inversely proportional to molar mass
- The “skin” on a liquid surface caused by intermolecular attraction
- The resistance to flow
- The same as density
- Unaffected by temperature
- Answer
-
c. The resistance to flow
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7s}\)
What property is responsible for the “beading up” of water?
- density
- hydrogen bonding
- surface tension
- vapor pressure
- viscosity
- Answer
-
c. surface tension
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7t}\)
Explain which substance in each of the following pairs is likely to have the higher normal melting point:
(a) HCl or NaCl;
(b) C2H5OC2H5 (diethyl ether) or C4H9OH (butanol);
(c) CHI3 or CHF3;
(d) C2H4 or CH3OH
- Answer a
-
NaCl, because it is an ionic compound not molecular
- Answer b
-
butanol due to hydrogen bonding in butanol not in diethyl ether
- Answer c
-
CHI3 because it is much heavier, even though CHF3 is polar. It also has strong London dispersion forces
- Answer d
-
CH3OH due to hydrogen bonding
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7u}\)
Explain which substance in each of the following pairs is likely to have the higher normal melting point:
(a) H2S or H2O;
(b) NH3 or PH3;
(c) KBr or CH3Br;
(d) CH4 or SiH4.
- Answer a
-
H2O because hydrogen bonding is stronger than dipole-dipole bonds
- Answer b
-
NH3 because hydrogen bonding can occur with 2 of the molecules
- Answer c
-
KBr due to being an ionic compound not molecular
- Answer d
-
SiH4 due to it being more polarizable and having a heavier mass
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7v}\)
Predict the shapes of each of the following molecules and identify the member of each pair with the higher boiling point using VESPR models: (a) PBr3 or PF3; (b) SO2 or CO2; (c) BF3 or BCl3.
- Answer a
-
PBr3 due to heavier mass
- Answer b
-
SO2 due to dipole-dipole bonds being stronger than London dispersion forces
- Answer c
-
BCl3 has stronger van der Waal's forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7w}\)
Determine which liquid in each of the following pairs has the greater surface tension:
(a) cis-dichloroethene or trans-dichloroethene;
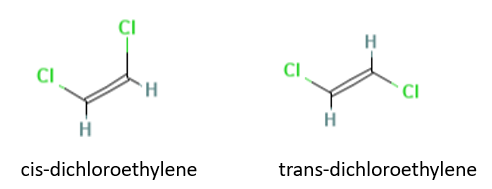
(b) benzene at 20°C or benzene at 60°C.
- Answer a
-
cis-dichloroethene due to the molecule being polar and having both dipole-dipole and van der Waals forces
- Answer b
-
benzene at 20°C due to there being less kinetic energy
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7x}\)
Rank the following molecules in order of increasing viscosity at 50°C: C6H5SH, C6H5OH, C6H6.
- Answer
-
C6H6 < C6H5SH < C6H5OH
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7y}\)
The boiling point of chloroform (CHCl3) is lower than that of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Since chloroform is polar and carbon tetrachloride is not, with consideration of the dipole-dipole forces would predict that chloroform would have the higher boiling point. How can we account for the observed order of the boiling points?
- Answer
-
Carbon tetrachloride is much heavier, and it has very high dispersion forces, even though chlorform has a permenant dipole
General Questions
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8a}\)
What is the dominant intermolecular force in H2?
- London Dispersion (instantaneous dipole-induced dipole)
- dipole-dipole
- ion-dipole
- hydrogen bonding
- Answer
-
a. London Dispersion (instantaneous dipole-induced dipole)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8b}\)
What is the major intermolecular force in H2O?
- London Dispersion (induced dipole-induced dipole)
- dipole-dipole
- ion-dipole
- hydrogen bonding
- Answer
-
d. hydrogen bonding
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8c}\)
What is the major intermolecular force responsible for the dissolution of NaCl in H2O?
- London Dispersion (induced dipole-induced dipole)
- dipole-dipole
- ion-dipole
- hydrogen bonding
- Answer
-
c. ion-dipole
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8d}\)
Which force is strongest?
- dipole/dipole
- ion/dipole
- London Dispersion
- covalent
- Answer
-
d. covalent
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8e}\)
Place the following compounds in the order of instantaneous dipole, dipole/dipole and hydrogen bonding as the primary intermolecular forces. (H2O, H2Se, CH4)
- Answer
-
CH4, H2Se, H2O
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8f}\)
What intermolecular force is responsible for the dissolution of oxygen into water?
- hydrogen bonding
- instantaneous-induced dipole
- dipole-induced dipole
- dipole-dipole
- Answer
-
C. dipole-induced dipole
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8g}\)
What is the predominant force in KBr?
- Dipole-dipole attraction
- Hydrogen-bonding
- Ion-dipole attraction
- Ionic bonding
- London-dispersion forces
- Answer
-
d. Ionic bonding
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8h}\)
Explain the reason why iodine is a solid, bromine is a liquid, and fluorine is a gas at room temperature.
- Answer
-
They are all symetric homonuclear diatomics with London dispersion forces. Iodine is the heaviest and most polarizable, and so has the highest boiling point. Flourine is the lightest and least polarizable, so it has the lowest boiling point (it is easier to boil), and Bromine is in the middle.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8i}\)
The _____ is the attractive force between an instantaneous dipole and an induced dipole.
- Dipole-dipole attraction
- Hydrogen-bonding
- Ion-dipole attraction
- Ionic bonding
- London dispersion forces
- Answer
-
e. London dispersion forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8j}\)
What is the major attractive force that exists among different I2 (elemental iodine, I2, is a solid at room temperature) molecules in the solid?
- Covalent-ionic interactions
- Dipole-dipole attractions
- Dipole-dipole rejections
- Ionic-dipole interactions
- London dispersion forces
- Answer
-
e. London dispersion forces
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8k}\)
The molecules in liquid C12H26 are held together by _____.
- Dipole-dipole interactions
- Dispersion forces
- Hydrogen bonding
- Ion-dipole interactions
- Ion-ion interactions
- Answer
-
b. Dispersion forces

