12.7: Exercises
- Page ID
- 165341
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Multiple Choice
-
Which of the following is the name of the three-base sequence in the mRNA that binds to a tRNA molecule?
A. P site
B. codon
C. anticodon
D. CCA binding site2. Which component is the last to join the initiation complex during the initiation of translation?
A. the mRNA molecule
B. the small ribosomal subunit
C. the large ribosomal subunit
D. the initiator tRNA3. During elongation in translation, to which ribosomal site does an incoming charged tRNA molecule bind?
A. A site
B. P site
C. E site
D. B site4. Which of the following is the amino acid that appears at the N-terminus of all newly translated prokaryotic and eukaryotic polypeptides?
A. tryptophan
B. methionine
C. selenocysteine
D. glycine5. When the ribosome reaches a nonsense codon, which of the following occurs?
A. a methionine is incorporated
B. the polypeptide is released
C. a peptide bond forms
D. the A site binds to a charged tRNA6. Write the anticodon on tRNA that would pair with each mRNA codon.
- 5′‑UUU‑3′
- 5′‑CAU‑3′
- 5′‑AGC‑3′
- 5′‑CCG‑3
7. Write the codon on mRNA that would pair with each tRNA anticodon.
- 5′‑UUG‑3′
- 5′‑GAA‑3′
- 5′‑UCC‑3′
- 5′‑CAC‑3′
8. Which of the following types of RNA codes for a protein?
A. dsRNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. tRNA
9. A nucleic acid is purified from a mixture. The molecules are relatively small, contain uracil, and most are covalently bound to an amino acid. Which of the following was purified?
A. DNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. tRNA
10. Which of the following types of RNA is known for its catalytic abilities?
A. dsRNA
B. mRNA
C. rRNA
D. tRNA
11. Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and what other component?
- protein
- polypeptides
- DNA
- mRNA
12. Which of the following may use RNA as its genome?
- a bacterium
- an archaeon
- a virus
- a eukaryote
13. A nucleotide of DNA may contain ________.
- ribose, uracil, and a phosphate group
- deoxyribose, uracil, and a phosphate group
- deoxyribose, thymine, and a phosphate group
- ribose, thymine, and a phosphate group
14. The building blocks of nucleic acids are ________.
- sugars
- nitrogenous bases
- peptides
- nucleotides
15. The given nucleotide could be translated into a peptide of 7 amino acids, please provide the sequence of the peptide using one letter abbreviation. (7 points)
AUCGAGCUAUGCUGAUGACUGUGACAUACUAAAUCUCA
16. Which of the following polymerases do not have proof reading ability?
a. DNA polymerase I
b. DNA polymerase II
c. DNA polymerase III
d. DNA polymerase a (alpha)
e. DNA polymerase d (delta)
17. Which of teh following may detect G:T mismatch in bacterial genome?
a. exonuclease I
b. MutS
c. DNA polymerase III
d. Uracil DNA glycosidase
e. uvrABC excinuclease
18. Which of the following is the primary target of ciprofloxacin?
a. DNA topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase)
b. DNA topoisomerase I
c. Helicase
d. DnaA
e. DnaB
19. Which of the following is not a function of reverse transcriptase?
a. Synthesis of DNA complementary to RNA
b. Digestion of RNA
c. Synthesis of second strand of DNA
d. Incorporation of DNA fragment into host genome.
Free Response
What are the four types of RNA and how do they function?
Short Answer
1. Why does translation terminate when the ribosome reaches a stop codon? What happens?
2. How does the process of translation differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
3. What is meant by the genetic code being nearly universal?
4. Below is an antisense DNA sequence. Translate the mRNA molecule synthesized using the genetic code, recording the resulting amino acid sequence, indicating the N and C termini.
Antisense DNA strand: 3’-T A C T G A C T G A C G A T C-5’
5.What are the roles of mRNA and tRNA in protein synthesis?
6. What is the initiation codon?
7. What are the termination codons and how are they recognized?
8.What are the differences between DNA nucleotides and RNA nucleotides?
9. How is the information stored within the base sequence of DNA used to determine a cell’s properties?
10. How do complementary base pairs contribute to intramolecular base pairing within an RNA molecule?
11. If an antisense RNA has the sequence 5ʹAUUCGAAUGC3ʹ, what is the sequence of the mRNA to which it will bind? Be sure to label the 5ʹ and 3ʹ ends of the molecule you draw.
12. Why does double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) stimulate RNA interference?
13. A portion of an mRNA molecule has the sequence 5′‑AUGCCACGAGUUGAC‑3′. What amino acid sequence does this code for? Help: genetic code table
14. What are the benefits and drawbacks to translating a single mRNA multiple times?
15. What are the processing steps for messenger RNAs?
16. How does the structure of RNA differ from the structure of DNA?
17. Describe how DNA is replicated in eukaryotes (sq)
18. In base excision repair, which enzymes are specific for a particular kind of damage and which are used for all repair by this pathway?
19. Discuss the different types of mutations in DNA.
20. Explain DNA repair mechanisms.
21. What are the three types of RNA and how do they function?
Critical Thinking
Identify the location of mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA in the figure.
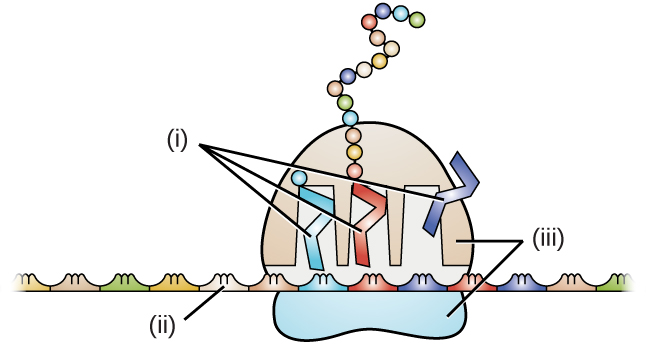
Why does it make sense that tRNA and rRNA molecules are more stable than mRNA molecules?
Critical Thinking
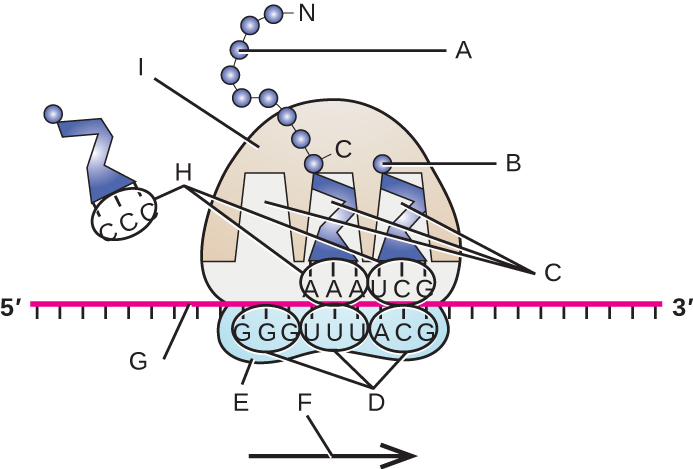
Label the following in the figure: ribosomal E, P, and A sites; mRNA; codons; anticodons; growing polypeptide; incoming amino acid; direction of translocation; small ribosomal unit; large ribosomal unit.
| Quiz: Read and translate the codons on mRNA into the appropriate amino acids. G U A C G A A A A |
| Quiz: Read and translate the codon on mRNA into the appropriate amino acid. AGA. What is the anticodon on the appropriate tRNA? |

