5.2: Covalent Bonding
- Page ID
- 109935
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Describe the formation of covalent bonds
- Define electronegativity and assess the polarity of covalent bonds
In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). For example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an H2 molecule; each hydrogen atom in the H2 molecule has two electrons stabilizing it, giving each atom the same number of valence electrons as the noble gas He.
Compounds that contain covalent bonds exhibit different physical properties than ionic compounds. Because the attraction between molecules, which are electrically neutral, is weaker than that between electrically charged ions, covalent compounds generally have much lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. Furthermore, whereas ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water, most covalent compounds, being electrically neutral, are poor conductors of electricity in any state.
Formation of Covalent Bonds
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, H2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) illustrates why this bond is formed. Starting on the far right, we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, indicated by the red line. Along the x-axis is the distance between the two atoms. As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x-axis), their valence orbitals (1s) begin to overlap. The single electrons on each hydrogen atom then interact with both atomic nuclei, occupying the space around both atoms. The strong attraction of each shared electron to both nuclei stabilizes the system, and the potential energy decreases as the bond distance decreases. If the atoms continue to approach each other, the positive charges in the two nuclei begin to repel each other, and the potential energy increases. The bond length is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved.
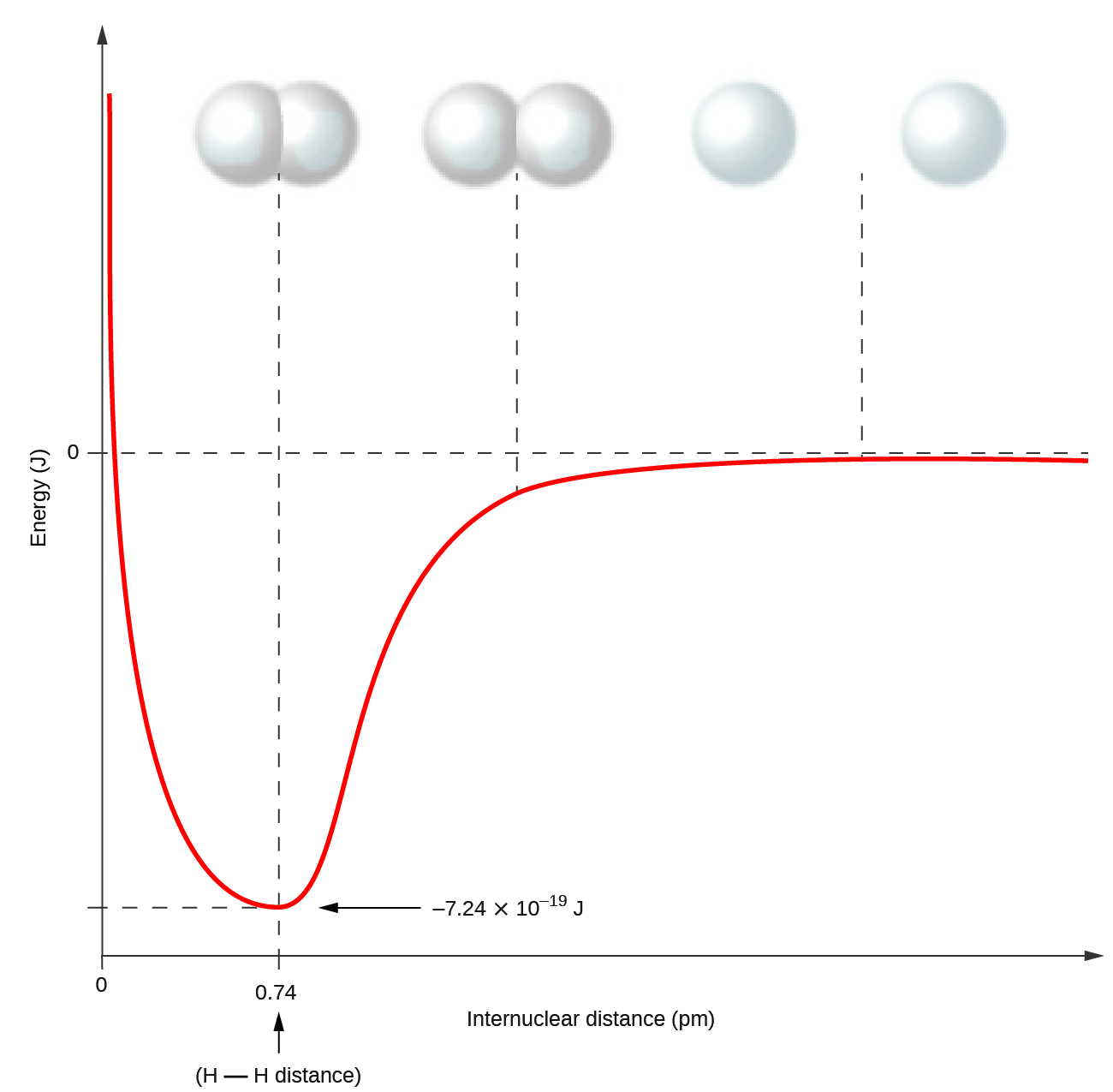
It is essential to remember that energy must be added to break chemical bonds (an endothermic process), whereas forming chemical bonds releases energy (an exothermic process). In the case of H2, the covalent bond is very strong; a large amount of energy, 436 kJ, must be added to break the bonds in one mole of hydrogen molecules and cause the atoms to separate:
\[\ce{H2}(g)⟶\ce{2H}(g)\hspace{20px}ΔH=\mathrm{436\:kJ} \nonumber \]
Conversely, the same amount of energy is released when one mole of H2 molecules forms from two moles of H atoms:
\[\ce{2H}(g)⟶\ce{H2}(g)\hspace{20px}ΔH=\mathrm{−436\:kJ} \nonumber \]
Pure vs. Polar Covalent Bonds
If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical, as in H2, Cl2, and other diatomic molecules, then the electrons in the bond must be shared equally. We refer to this as a pure covalent bond. Electrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus. In the case of Cl2, each atom starts off with seven valence electrons, and each Cl shares one electron with the other, forming one covalent bond:
\[\ce{Cl + Cl⟶Cl2} \nonumber \]
The total number of electrons around each individual atom consists of six nonbonding electrons and two shared (i.e., bonding) electrons for eight total electrons, matching the number of valence electrons in the noble gas argon. Since the bonding atoms are identical, Cl2 also features a pure covalent bond.
When the atoms linked by a covalent bond are different, the bonding electrons are shared, but no longer equally. Instead, the bonding electrons are more attracted to one atom than the other, giving rise to a shift of electron density toward that atom. This unequal distribution of electrons is known as a polar covalent bond, characterized by a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. The atom that attracts the electrons more strongly acquires the partial negative charge and vice versa. For example, the electrons in the H–Cl bond of a hydrogen chloride molecule spend more time near the chlorine atom than near the hydrogen atom. Thus, in an HCl molecule, the chlorine atom carries a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows the distribution of electrons in the H–Cl bond. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H2 nonpolar bond.

We sometimes designate the positive and negative atoms in a polar covalent bond using a lowercase Greek letter “delta,” δ, with a plus sign or minus sign to indicate whether the atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) or a partial negative charge (δ–). This symbolism is shown for the H–Cl molecule in Figure \(\PageIndex{2b}\).
Electronegativity
Whether a bond is nonpolar or polar covalent is determined by a property of the bonding atoms called electronegativity. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity. Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. The greater the difference in electronegativity, the more polarized the electron distribution and the larger the partial charges of the atoms.
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) shows the electronegativity values of the elements as proposed by one of the most famous chemists of the twentieth century: Linus Pauling. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down a group. Thus, the nonmetals, which lie in the upper right, tend to have the highest electronegativities, with fluorine the most electronegative element of all (EN = 4.0). Metals tend to be less electronegative elements, and the group 1 metals have the lowest electronegativities. Note that noble gases are excluded from this figure because these atoms usually do not share electrons with others atoms since they have a full valence shell. (While noble gas compounds such as XeO2 do exist, they can only be formed under extreme conditions, and thus they do not fit neatly into the general model of electronegativity.)
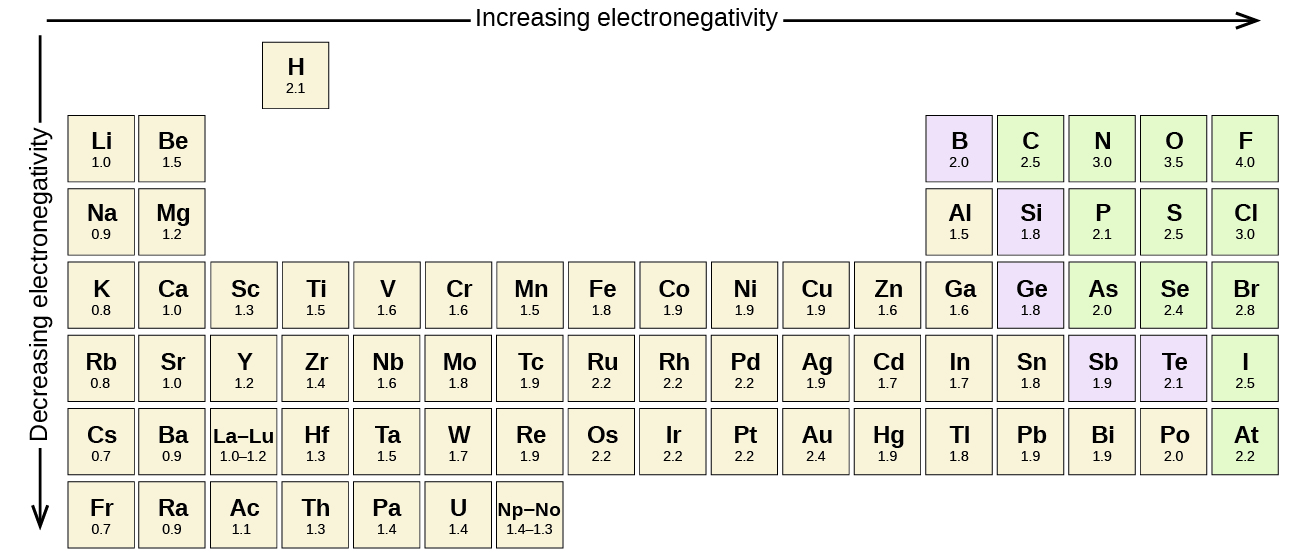
Linus Pauling is the only person to have received two unshared (individual) Nobel Prizes: one for chemistry in 1954 for his work on the nature of chemical bonds and one for peace in 1962 for his opposition to weapons of mass destruction. He developed many of the theories and concepts that are foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures.

Pauling also contributed to many other fields besides chemistry. His research on sickle cell anemia revealed the cause of the disease—the presence of a genetically inherited abnormal protein in the blood—and paved the way for the field of molecular genetics. His work was also pivotal in curbing the testing of nuclear weapons; he proved that radioactive fallout from nuclear testing posed a public health risk.
Electronegativity versus Electron Affinity
We must be careful not to confuse electronegativity and electron affinity. The electron affinity of an element is a measurable physical quantity, namely, the energy released or absorbed when an isolated gas-phase atom acquires an electron, measured in kJ/mol. Electronegativity, on the other hand, describes how tightly an atom attracts electrons in a bond. It is a dimensionless quantity that is calculated, not measured. Pauling derived the first electronegativity values by comparing the amounts of energy required to break different types of bonds. He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4.
Electronegativity and Bond Type
The absolute value of the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN) of two bonded atoms provides a rough measure of the polarity to be expected in the bond and, thus, the bond type. When the difference is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and nonpolar. When it is large, the bond is polar covalent or ionic. The absolute values of the electronegativity differences between the atoms in the bonds H–H, H–Cl, and Na–Cl are 0 (nonpolar), 0.9 (polar covalent), and 2.1 (ionic), respectively. The degree to which electrons are shared between atoms varies from completely equal (pure covalent bonding) to not at all (ionic bonding). Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) shows the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type.
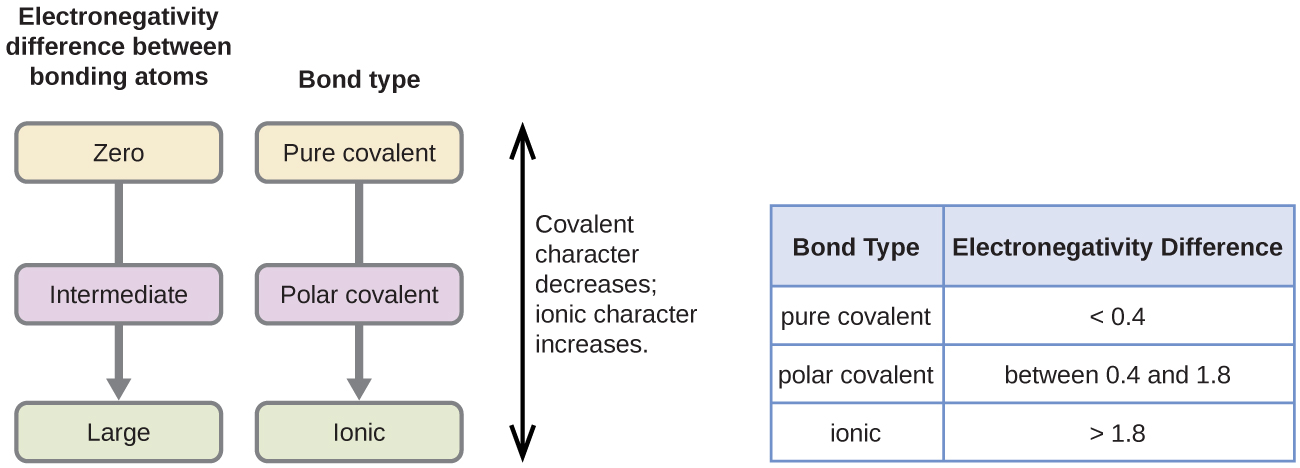
A rough approximation of the electronegativity differences associated with covalent, polar covalent, and ionic bonds is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). This table is just a general guide, however, with many exceptions. For example, the H and F atoms in HF have an electronegativity difference of 1.9, and the N and H atoms in NH3 a difference of 0.9, yet both of these compounds form bonds that are considered polar covalent. Likewise, the Na and Cl atoms in NaCl have an electronegativity difference of 2.1, and the Mn and I atoms in MnI2 have a difference of 1.0, yet both of these substances form ionic compounds.
The best guide to the covalent or ionic character of a bond is to consider the types of atoms involved and their relative positions in the periodic table. Bonds between two nonmetals are generally covalent; bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic.
Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. The atoms in polyatomic ions, such as OH–, \(\ce{NO3-}\), and \(\ce{NH4+}\), are held together by polar covalent bonds. However, these polyatomic ions form ionic compounds by combining with ions of opposite charge. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \(\ce{NO3-}\) anion. Thus, bonding in potassium nitrate is ionic, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the ions K+ and \(\ce{NO3-}\), as well as covalent between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in \(\ce{NO3-}\).
Bond polarities play an important role in determining the structure of proteins. Using the electronegativity values in Table A2, arrange the following covalent bonds—all commonly found in amino acids—in order of increasing polarity. Then designate the positive and negative atoms using the symbols δ+ and δ–:
C–H, C–N, C–O, N–H, O–H, S–H
Solution
The polarity of these bonds increases as the absolute value of the electronegativity difference increases. The atom with the δ– designation is the more electronegative of the two. Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows these bonds in order of increasing polarity.
| Bond | ΔEN | Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| C–H | 0.4 | \(\overset{δ−}{\ce C}−\overset{δ+}{\ce H}\) |
| S–H | 0.4 | \(\overset{δ−}{\ce S}−\overset{δ+}{\ce H}\) |
| C–N | 0.5 | \(\overset{δ+}{\ce C}−\overset{δ−}{\ce N}\) |
| N–H | 0.9 | \(\overset{δ−}{\ce N}−\overset{δ+}{\ce H}\) |
| C–O | 1.0 | \(\overset{δ+}{\ce C}−\overset{δ−}{\ce O}\) |
| O–H | 1.4 | \(\overset{δ−}{\ce O}−\overset{δ+}{\ce H}\) |
Silicones are polymeric compounds containing, among others, the following types of covalent bonds: Si–O, Si–C, C–H, and C–C. Using the electronegativity values in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\), arrange the bonds in order of increasing polarity and designate the positive and negative atoms using the symbols δ+ and δ–.
Answer
| Bond | Electronegativity Difference | Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| C–C | 0.0 | nonpolar |
| C–H | 0.4 | \(\overset{δ−}{\ce C}−\overset{δ+}{\ce H}\) |
| Si–C | 0.7 | \(\overset{δ+}{\ce{Si}}−\overset{δ−}{\ce C}\) |
| Si–O | 1.7 | \(\overset{δ+}{\ce{Si}}−\overset{δ−}{\ce O}\) |
Summary
Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. In pure covalent bonds, the electrons are shared equally. In polar covalent bonds, the electrons are shared unequally, as one atom exerts a stronger force of attraction on the electrons than the other. The ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity. The difference in electronegativity between two atoms determines how polar a bond will be. In a diatomic molecule with two identical atoms, there is no difference in electronegativity, so the bond is nonpolar or pure covalent. When the electronegativity difference is very large, as is the case between metals and nonmetals, the bonding is characterized as ionic.
Glossary
- bond length
- distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms at which the lowest potential energy is achieved
- covalent bond
- bond formed when electrons are shared between atoms
- electronegativity
- tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a bond to itself
- polar covalent bond
- covalent bond between atoms of different electronegativities; a covalent bond with a positive end and a negative end
- pure covalent bond
- (also, nonpolar covalent bond) covalent bond between atoms of identical electronegativities


