12.10: Soap- an Application of Physical Properties
- Page ID
- 478367
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Describe the mechanism by which soaps exert their cleansing action.
Physical properties are all around us. Most of the matter that we encounter is a mixture of some sort. Because we know that the matter exists as mixtures, we are able to purify it if necessary using physical means. Evaporation of sweat from our bodies cools us off as our body heat provides the energy for the phase change. Henry's Law explains the carbonation of carbonated beverages, as well as why there are more fish to catch in shady water. We will focus on a few of the ways physical properties are important in our lives.
Personal Cleanliness
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, and precursors to catalysts.
When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and grime, which can then be separated from the article being cleaned. In hand washing, as a surfactant, when lathered with a little water, soap kills microorganisms by disorganizing their membrane lipid bilayer and denaturing their proteins. It also emulsifies oils, enabling them to be carried away by running water.[2]
Industrially manufactured bar soaps became available in the late 18th century, as advertising campaigns in Europe and America promoted popular awareness of the relationship between cleanliness and health.[35] In modern times, the use of soap has become commonplace in industrialized nations due to a better understanding of the role of hygiene in reducing the population size of pathogenic microorganisms (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). The details of how soap is created are beyond the scope of this text, but we can discuss how it works in a bit of detail.

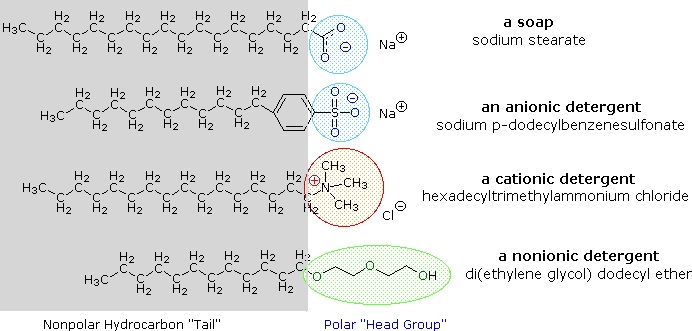
The cleansing action of soap is determined by its polar and non-polar structures in conjunction with an application of solubility principles. The long hydrocarbon chain is of course non-polar and hydrophobic (repelled by water). The "salt" end of the soap molecule is ionic and hydrophilic (water soluble). Examples of soap and detergent molecules, are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). The use of such compounds as cleaning agents is facilitated by their surfactant character, which lowers the surface tension of water, allowing it to penetrate and wet a variety of materials.
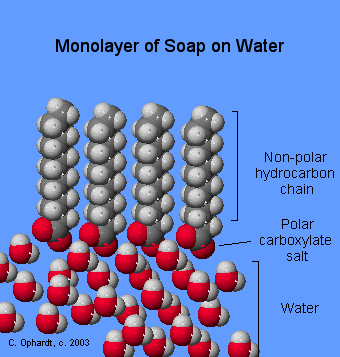
When soap is added to water, the ionic-salt end of the molecule is attracted to water and dissolved in it. The non-polar hydrocarbon end of the soap molecule is repelled by water. A drop or two of soap in water forms a monolayer (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)) on the water surface as shown in the graphics on the left. The soap molecules "stand up" on the surface as the polar carboxyl salt end is attracted to the polar water. The non-polar hydrocarbon tails are repelled by the water, which makes them appear to stand up.
Water alone is not able to penetrate grease or oil because they are of opposite polarity. When grease or oil (non-polar hydrocarbons) are mixed with a soap- water solution, the soap molecules work as a "bridge" between polar water molecules and non-polar oil molecules. Soap molecules have both properties of non-polar and polar at opposite ends of the molecule.
The oil is a pure hydrocarbon so it is non-polar. The non-polar hydrocarbon tail of the soap dissolves into the oil. That leaves the polar carboxylate ion of the soap molecules are sticking out of the oil droplets, the surface of each oil droplet is negatively charged. As a result, the oil droplets repel each other and remain suspended in solution (this is called an emulsion) to be washed away by a stream of water. The outside of the droplet is also coated with a layer of water molecules.
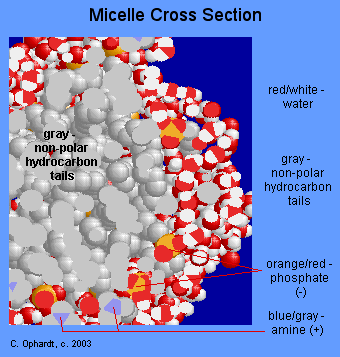
The graphic on Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) although not strictly a representation of the above description is a micelle that works in much the same fashion. The oil would be a the center of the micelle.
The followign video about the power of soap to kill the coronavirus was recorded in the spring of 2020. Soaps are quite effective at killing viruses.
Video \(\PageIndex{1}\) Soap and coronavirus.
Section Summary
- Soap, as a cleaning agent, solubilizes particles and grime, which can then be easily removed from the article being cleaned.
- Soap works by having some parts of the soap that dissolve in water and others that dissolve in oils.
Glossary
- soap
- A salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products.
- hydrophobic
- Repelled by water.
- hydrophilic
- Water soluble.
Contributors
- Remixed by Jamie MacArthur
- Wikipedia
- Libretext: Organic Chemistry (McMurry)
William Reusch, Professor Emeritus (Michigan State U.), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
- Charles Ophardt, Professor Emeritus, Elmhurst College; Virtual Chembook(opens in new window)
- Andrea Kubisch, Courtney Korff (UCD)


