Lab Equipment
- Page ID
- 159616
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Table of Contents:
Glassware- not used for measurement
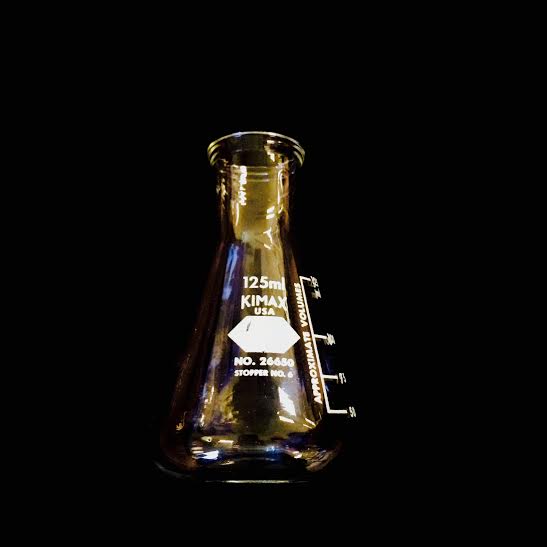
ERLENMEYER FLASK· Designed for easy stirring, can be swirled by hand without spilling · Not used for measuring as they are only accurate to 5% · Often used for titrations · A rubber stopper fits nicely in the opening the stopper size needed is shown with a number underneath the serial number. |
 |
BEAKER· Used to hold varying volumes of liquid · Not used for measuring volumes as it is only accurate to 5% · The spout lines up nicely with the rim of other glassware for easy pouring |
 |
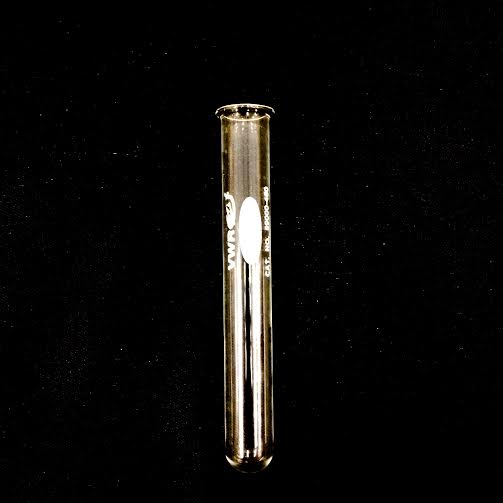
TEST TUBE· Used to hold and mix small samples · Stirred by tapping the bottom with two fingers · Fit into both a centrifuge and test tube rack · Often used in qualitative analysis |
 |
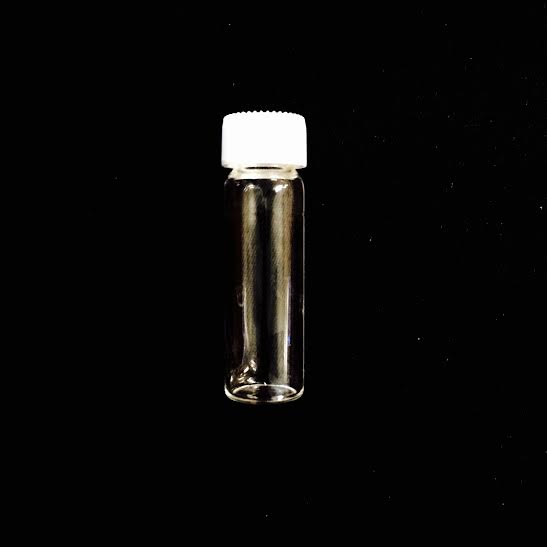
VIAL WITH CAP· Used to hold small portions of samples both solid and liquid · When labeling, if you label the cap it is easier to read if you write on the cap, but be sure not to separate the cap from the vial |
 |
Glassware- used for measurement
VOLUMETRIC FLASK· Measures one specific volume, marked by the etched line on the neck. · Easy to mix solutions, as they have glass stoppers and are designed to be inverted multiple times to mix. Size of glass stopper needed is listed on the bottle. Be sure to hold glass stopper while inverting. · Careful not to fill above the etched mark, see reading the meniscus |
 |
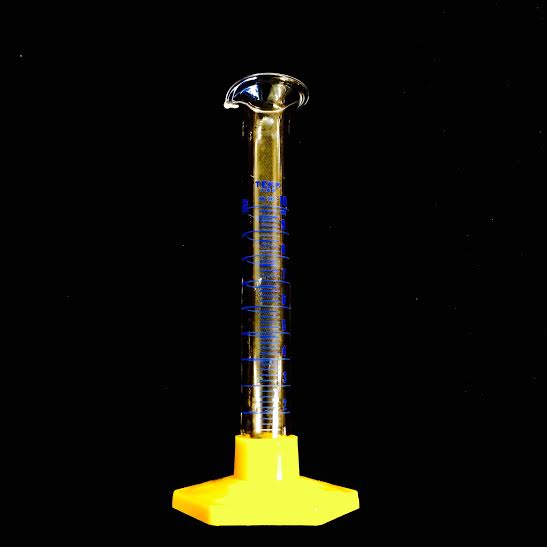
GRADUATED CYLINDER· Used for measuring many different volumes · The spout lines up nicely with the rim of other glassware for easy pouring · Carefully measure the amount you use, see reading the meniscus |
 |
PIPET· Used for measuring specific volumes · Used in conjunction with the pipet bulb, see pipetting Graduated Pipet · Can be used to any of the given markings along it's side. Note that there is a TD and a TC pipet shown in the figure at right. Volumetric Pipet · Extremely accurate, but only used for one volume Pasteur Pipet · Are used for very small but non specific volumes TD versus TC · To Deliver (TD) glassware measures the exact amount measured from line after allowing the contents to pour naturally using gravity out of the tip. To Contain (TC) glassware requires measuring both a beginning volume and a final volume in order to measure how much was removed from the original contained volume. |
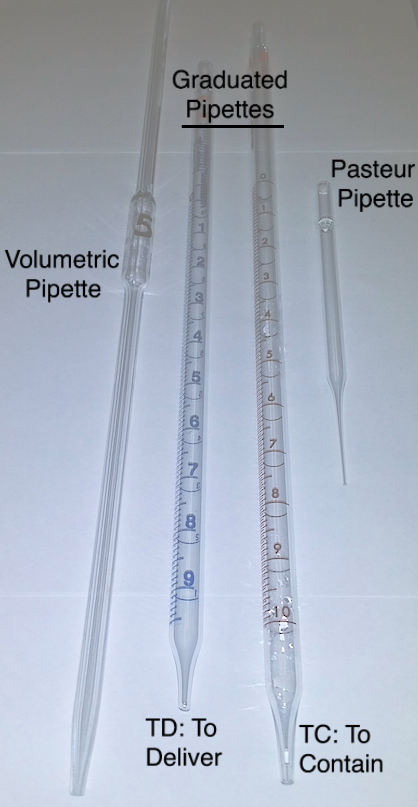 |
BURET· Often used for titrations or dispensing specific volumes of liquids · White plastic stop cock is open when parallel with the instrument and closed when perpendicular · When not in use should be stored upside down and open |
Equipment often used in Titrations
RING STAND· Used in conjunction with clamps to hold equipment that cannot stand up on its own |
 |
BURET CLAMP· Used to hold two burets once it is attached to a ring stand. · Burets in the clamp are free to move up and down or to spin so that they fit your height and handedness needs |
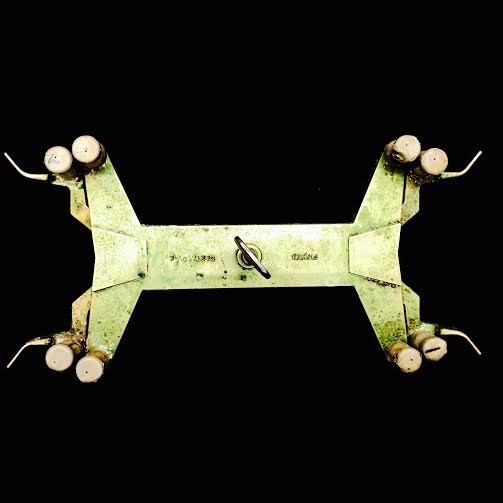 |
UTILITY CLAMP· Used to hold other glassware onto a ring stand |
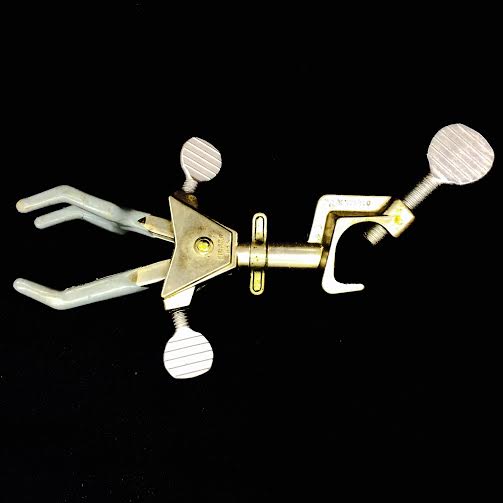 |
Miscellaneous
FUNNEL· Used to aide in the transfer of liquids · Be careful when using a funnel as they can cause you to add more liquid than you intend |
 |
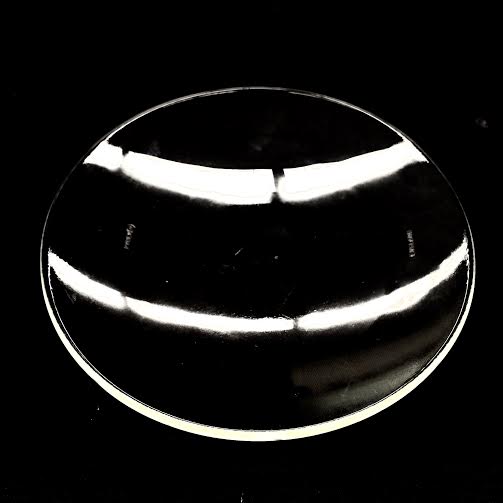
WATCH GLASS· Used to evaporate a liquid, to heat small portions of a substance · Often used to cover beakers with NaOH to avoid excess reaction with the CO2 in the atmosphere |
 |
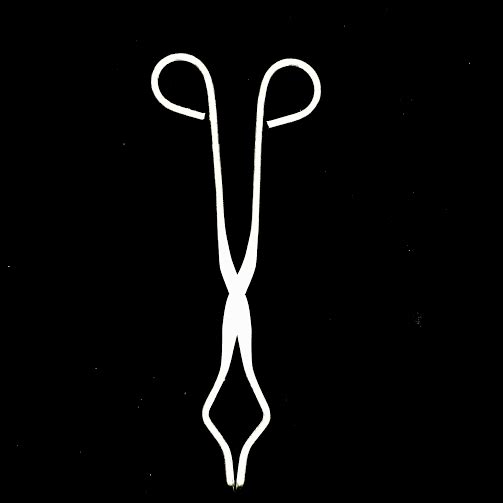
CRUCIBLE TONGS· Used to transfer a hot crucible inside/atop the curve at the end of the tongs · Can also be used to transfer other hot things by pinching them with the tongs |
 |
GLASS STIR BAR· Used to stir things that are often contained in beakers · Be careful not to scrape the glass stir bar against the glass of the beaker, or to apply a lot of pressure to the bar as they break relatively easily · May come with a rubber policeman on the end to avoid scratching |
 |
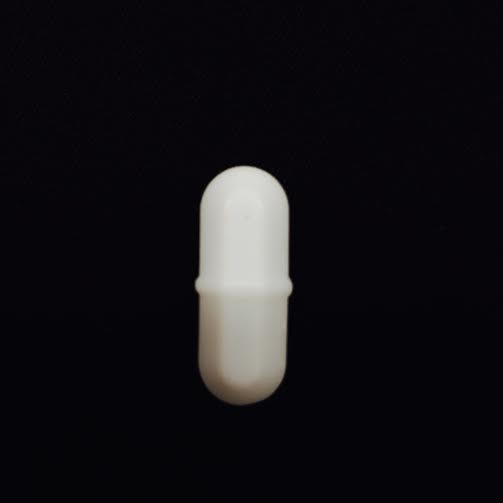
MAGNETIC STIR BAR· Used in conjunction with a stirring plate · When it is stirring it should not continually be hitting the side · Come in a variety of sizes, be sure that you have one that will fit well in your glassware · If your stir bar gets stuck in your glassware there is a magnetic rod to remove it |
 |
DISPOSABLE PIPET· Used to transfer small amounts of liquids · Often used to in qualitative analysis · Drops can be counted to make small measurements but this is not a very accurate method |
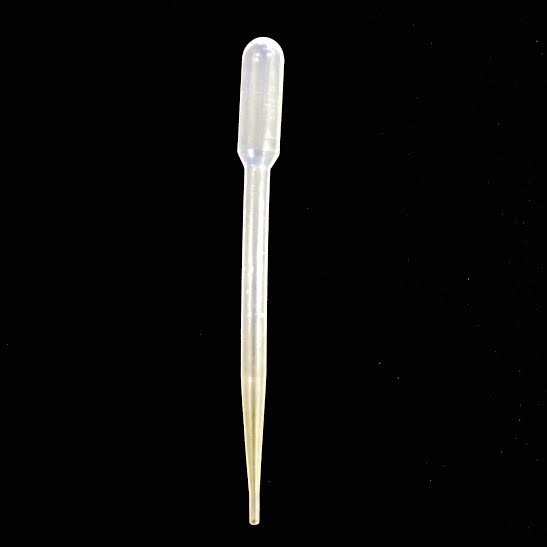 |
WASH BOTTLE· Used to dispense RO water · RO water can be found in the pointed sink faucets to refill the bottle |
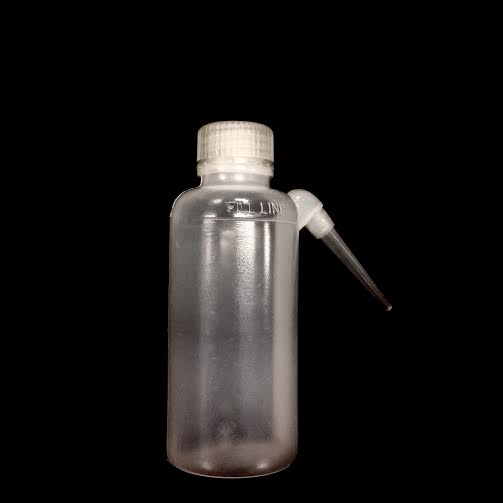 |
PIPET BULB· Used on the end of a pipet to aspirate liquid up into the pipet · Be careful not to aspirate too much so that the liquid goes into the bulb, this would contaminate it |
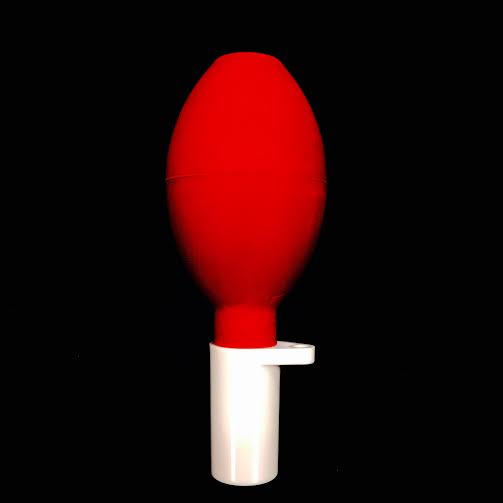 |
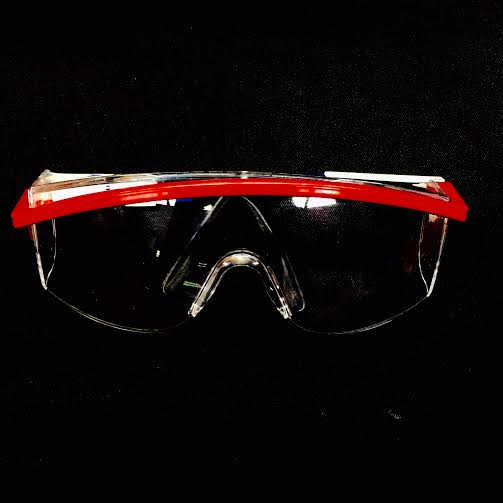
SAFETY GOGGLES· MUST BE WORN IN THE LAB AT ALL TIMES · Used to protect your eyes from fumes and spills |
 |
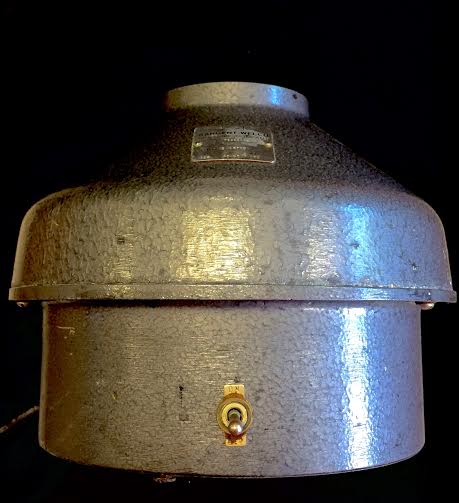
CENTRIFUGE· Used to separate solids out of liquids that are held in test tubes · Must have an even, balanced number of test tubes in the centrifuge to properly work · Listen to the centrifuge as it runs; a thumping sound means it is imbalanced and should be stopped and re-loaded. |
 |
BUNSEN BURNER· Used to heat things · The hottest part of the flame is at the top of the inner blue cone |
 |
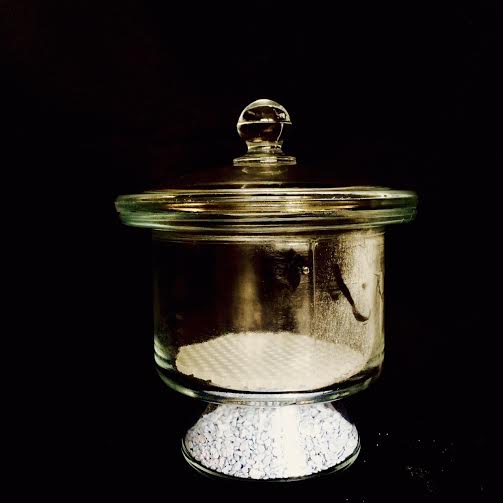
DESSICATOR· Used to remove moisture from substances or glassware |
 |

