5.18: The Principle of Microscopic Reversibility
- Page ID
- 152019
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The equilibrium constant expression is an important and fundamental relationship that relates the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. We deduce it above from a simple model for the concentration dependence of elementary-reaction rates. In doing so, we use the criterion that the time rate of change of any concentration must be zero at equilibrium. Clearly, this is a necessary condition; if any concentration is changing with time, the reaction is not at equilibrium. However, our deduction uses another assumption that we have not yet emphasized. We assume that the forward and reverse rates of each elementary step are equal when the overall reaction is at equilibrium. This is a special case of the principle of microscopic reversibility
Any molecular process and its reverse occur with equal rates at equilibrium
The principle of microscopic reversibility applies to any molecular process; it is inferred from the fact that such processes can be described by their equations of motion if the initial state of the constituent particles can be specified. The equations of motion can be either classical mechanical or quantum mechanical. We consider the implications of the principle for molecular processes that constitute elementary reactions. However, the principle also applies to equilibria in other molecular processes, notably the absorption and emission of radiation.
When we apply it to elementary reactions, we see that the principle of microscopic reversibility provides a necessary and sufficient condition for equilibrium from a reaction-mechanism perspective. The principle also imposes several significant conditions on the sequences of elementary processes that constitute a mechanism and on their relative rates.
In the previous section, we see that microscopic reversibility provides a sufficient basis for deducing the relationship relating reactant and product concentrations at equilibrium—the equilibrium constant expression—from our rate equations for elementary reactions. We now want to see that the principle of microscopic reversibility is indeed necessary. That is, setting \({\boldsymbol{d}{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\boldsymbol{x}}}/{\boldsymbol{dt}\boldsymbol{=}\boldsymbol{0}}\) for all species, \(\boldsymbol{X}\), involved in the reaction is not in itself sufficient to assure that the system is at equilibrium.
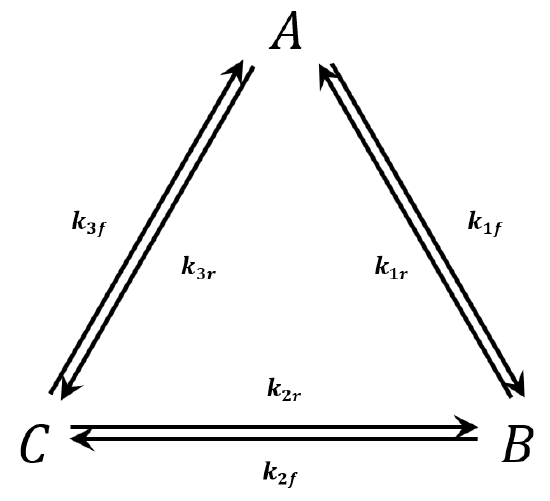
We consider the triangular network of elementary reactions\({}^{3,4}\) shown in Figure 3. This network gives rise to the following reaction-rate equations:
\[V^{-1}\dfrac{{dn}_A}{dt}=-k_{1f}\left[A\right]+k_{1r}\left[B\right]+k_{3f}\left[C\right]-k_{3r}\left[A\right] \nonumber \]
\[V^{-1}\dfrac{{dn}_B}{dt}=+k_{1f}\left[A\right]-k_{1r}\left[B\right]+k_{2r}\left[C\right]-k_{2f}\left[B\right] \nonumber \]
\[V^{-1}\dfrac{{dn}_C}{dt}=+k_{2f}\left[B\right]-k_{2r}\left[C\right]+k_{3r}\left[A\right]-k_{3f}\left[C\right] \nonumber \]
At equilibrium each of these equations must equal zero. Since we have three equations in three unknowns, it might at first appear that we can solve for the three unknowns \(\left[A\right]\), \(\left[B\right]\), and \(\left[C\right]\). We can see, however, either from the equations themselves or by considering the physical situation that they represent, that only two of these equations are independent. That is, we have
\[\frac{dn_A}{dt}+\frac{dn_B}{dt}+\frac{dn_C}{dt}=0 \nonumber \]
While we cannot solve for \(\left[A\right]\), \(\left[B\right]\), and \(\left[C\right]\) independently, we can solve for their ratios, which are
\[\frac{\left[B\right]}{\left[A\right]}=\frac{k_{1f}k_{2r}+k_{2r}k_{3r}+k_{1f}k_{3f}}{k_{2f}k_{3f}+k_{1f}k_{3f}+k_{1r}k_{2r}} \nonumber \]
\[\frac{\left[C\right]}{\left[B\right]}=\frac{k_{1f}k_{2f}+k_{1r}k_{3r}+k_{2f}k_{3r}}{k_{1f}k_{2r}+k_{2r}k_{3r}+k_{1f}k_{3f}} \nonumber \]
\[\frac{\left[A\right]}{\left[C\right]}=\frac{k_{2f}k_{3f}+k_{1r}k_{3f}+k_{1r}k_{2r}}{k_{1f}k_{2f}+k_{1r}k_{3r}+k_{2f}k_{3r}} \nonumber \]
Since we deduce these equations from the condition that all the time derivatives are zero, it might seem that they should represent the criteria for the system of reactions to be at equilibrium. Purely as a name for easy reference, let us call these equations the cyclic equilibrium set.
When we consider the reactions one at a time, we deduce the following equilibrium relationships:
\[\frac{\left[B\right]}{\left[A\right]}=\frac{k_{1f}}{k_{1r}}\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \frac{\left[C\right]}{\left[B\right]}=\frac{k_{2f}}{k_{2r}}\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \frac{\left[A\right]}{\left[C\right]}=\frac{k_{3f}}{k_{3r}} \nonumber \]
For easy reference, let us call these equations the one-at-a-time set.
Now, it cannot be true that both sets of relationships specify a sufficient condition for the system to be at equilibrium. To see this, let us first suppose that the principle of microscopic reversibility is a sufficient condition for equilibrium. Then the one-at-a-time set of equations must be sufficient to uniquely specify the position of equilibrium. It is easy to show that a set of rate constants that satisfies the one-at-a-time set also satisfies the cyclic set. Therefore, if microscopic reversibility is a sufficient condition for equilibrium, the cyclic network rate equations are necessarily equal to zero at equilibrium. In short, if we assume that microscopic reversibility is a sufficient condition for equilibrium, we encounter no inconsistencies, because the cyclic set of equations is satisfied by the same equilibrium-concentration ratios.
On the other hand, if we suppose that setting \({dn_x}/{dt=0}\) for all species, \(X\), is a sufficient condition for equilibrium, then the cyclic set of equations must be sufficient to uniquely specify the position of equilibrium. Let us consider a particular set of rate constants:
- \(k_{1f}=k_{2f}=k_{3f}=1\) and
- \(k_{1r}=k_{2r}=k_{3r}=2\).
This set of rate constants satisfies the cyclic set of equations and requires that each of the equilibrium-concentration ratios be equal to 1. In this case, the one-at-a-time set of equations implied by microscopic reversibility cannot be satisfied. (We have \({\left[B\right]}/{\left[A\right]}=1\) and \({k_{1f}}/{k_{1r}}={1}/{2}\). Therefore, \({\left[B\right]}/{\left[A\right]}\neq {k_{1f}}/{k_{1r}}\).) That is, if we assume that setting \({dn_x}/{dt=0}\), for all species, \(X\), is a sufficient condition for equilibrium, we must conclude that the principle of microscopic reversibility is false. Using the contrapositive: If the principle of microscopic reversibility is true, it is false that setting \({dn_x}/{dt=0}\) for all species, \(X\), is a sufficient condition for equilibrium.
Setting the derivatives for the reaction network equal to zero is not sufficient to assure that the system is at equilibrium. It is merely necessary. To assure that the network is at equilibrium, we must apply the principle of microscopic reversibility and require that each elementary process in the network be at equilibrium.
The principle of microscopic reversibility requires that any elementary process occur via the same sequence of transitory molecular structures in both the forward and reverse directions. Consequently, if a sequence of elementary steps is a mechanism for a forward reaction, the same sequence of steps—traversed backwards—must be a mechanism for the reverse reaction. The principle does not exclude the possibility that a given reaction can occur simultaneously by two different mechanisms. However, it does mean that a given reaction cannot have one mechanism in the forward direction and a second, different mechanism in the reverse direction.
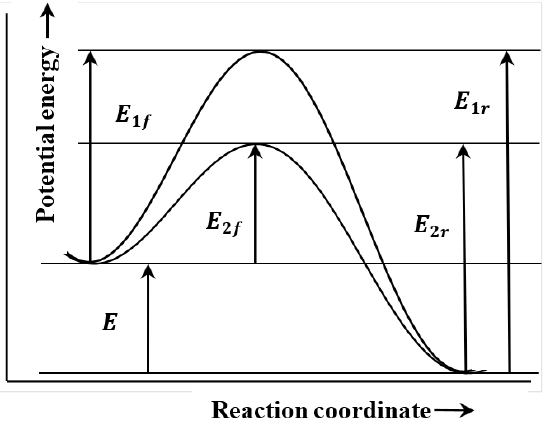
In describing reaction mechanisms, we assume that the energy of the reacting molecules depends on their progress along the path that they follow during the course of the reaction. We call this path the reaction coordinate. We suppose that we can plot the energy of the system as a function of the system’s position on the path, or displacement along the reaction coordinate. In the context of such a graph, the principle of microscopic reversibility is essentially the observation that the path is the same irrespective of the direction in which it is traversed. Two such paths are sketched in Figure 4. In this sketch, \(E_{1f}\) and \(E_{2f}\) are the activation energies for the two forward reactions; \(E_{1r}\) and \(E_{2r}\) are the activation energies for the reverse reactions.


