10.9: Hydrohalogenation—Electrophilic Addition of HX
- Page ID
- 30468
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)his page looks at the reaction of the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes such as ethene with hydrogen halides such as hydrogen chloride and hydrogen bromide.
Symmetrical alkenes (like ethene or but-2-ene) are dealt with first. These are alkenes where identical groups are attached to each end of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Addition to symmetrical alkenes
What happens?
All alkenes undergo addition reactions with the hydrogen halides. A hydrogen atom joins to one of the carbon atoms originally in the double bond, and a halogen atom to the other.
For example, with ethene and hydrogen chloride, you get chloroethane:
![]()
![]()
With but-2-ene you get 2-chlorobutane:
![]()
![]()
What happens if you add the hydrogen to the carbon atom at the right-hand end of the double bond, and the chlorine to the left-hand end? You would still have the same product.
The chlorine would be on a carbon atom next to the end of the chain - you would simply have drawn the molecule flipped over in space.
That would be different of the alkene was unsymmetrical - that's why we have to look at them separately.
Mechanism
The addition of hydrogen halides is one of the easiest electrophilic addition reactions because it uses the simplest electrophile: the proton. Hydrogen halides provide both a electrophile (proton) and a nucleophile (halide). First, the electrophile will attack the double bond and take up a set of
Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halide to Ethene
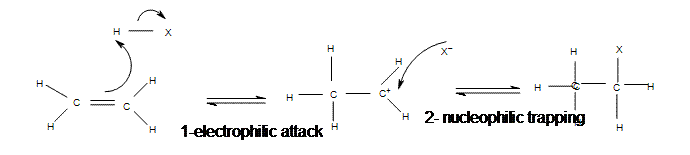
Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halide to Propene
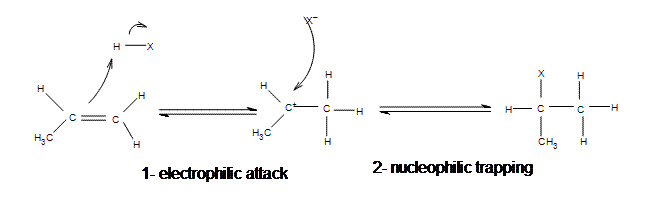
All of the halides (HBr, HCl, HI, HF) can participate in this reaction and add on in the same manner. Although different halides do have different rates of reaction, due to the H-X bond getting weaker as X gets larger (poor overlap of orbitals)s.
Reaction rates
Variation of rates when you change the halogen
Reaction rates increase in the order HF - HCl - HBr - HI. Hydrogen fluoride reacts much more slowly than the other three, and is normally ignored in talking about these reactions.
When the hydrogen halides react with alkenes, the hydrogen-halogen bond has to be broken. The bond strength falls as you go from HF to HI, and the hydrogen-fluorine bond is particularly strong. Because it is difficult to break the bond between the hydrogen and the fluorine, the addition of HF is bound to be slow.
Variation of rates when you change the alkene
This applies to unsymmetrical alkenes as well as to symmetrical ones. For simplicity the examples given below are all symmetrical ones- but they don't have to be.
Reaction rates increase as the alkene gets more complicated - in the sense of the number of alkyl groups (such as methyl groups) attached to the carbon atoms at either end of the double bond.
For example:
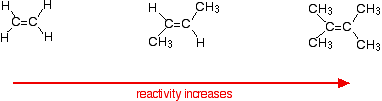
There are two ways of looking at the reasons for this - both of which need you to know about the mechanism for the reactions.
Alkenes react because the electrons in the pi bond attract things with any degree of positive charge. Anything which increases the electron density around the double bond will help this.
Alkyl groups have a tendency to "push" electrons away from themselves towards the double bond. The more alkyl groups you have, the more negative the area around the double bonds becomes.
The more negatively charged that region becomes, the more it will attract molecules like hydrogen chloride.
The more important reason, though, lies in the stability of the intermediate ion formed during the reaction. The three examples given above produce these carbocations (carbonium ions) at the half-way stage of the reaction:
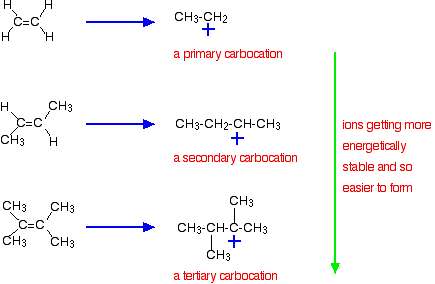
The stability of the intermediate ions governs the activation energy for the reaction. As you go towards the more complicated alkenes, the activation energy for the reaction falls. That means that the reactions become faster.
Addition to unsymmetrical alkenes
What happens?
In terms of reaction conditions and the factors affecting the rates of the reaction, there is no difference whatsoever between these alkenes and the symmetrical ones described above. The problem comes with the orientation of the addition - in other words, which way around the hydrogen and the halogen add across the double bond.
Orientation of addition
If HCl adds to an unsymmetrical alkene like propene, there are two possible ways it could add. However, in practice, there is only one major product.
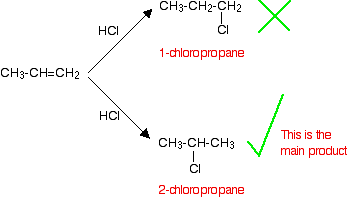
This is in line with Markovnikov's Rule which says:
-
When a compound HX is added to an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen becomes attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens attached to it already.
In this case, the hydrogen becomes attached to the CH2 group, because the CH2 group has more hydrogens than the CH group.
Notice that only the hydrogens directly attached to the carbon atoms at either end of the double bond count. The ones in the CH3 group are totally irrelevant.
Contributors
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)
William Reusch, Professor Emeritus (Michigan State U.), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry With a Biological Emphasis by Tim Soderberg (University of Minnesota, Morris)
Jim Clark (Chemguide.co.uk)

