7.1: General Approaches to Naming Organic Compounds
- Page ID
- 22188
There are two aspects to consider: how to derive the name from the structure, and how to derive the structure from the name. We will discuss each by example.
Naming a Compound of Known Structure
You first should decide what type of compound it is. The decision usually is straightforward for hydrocarbons, which will fall in one or the other of the categories alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, arenes, cycloalkanes, and so on. But when the compound has more than one functional group it is not always obvious which is the parent function. For example, Compound \(1\) could be named as an alkene (because of the double-bond function) or as an alcohol (because of the \(OH\) function):
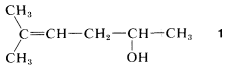
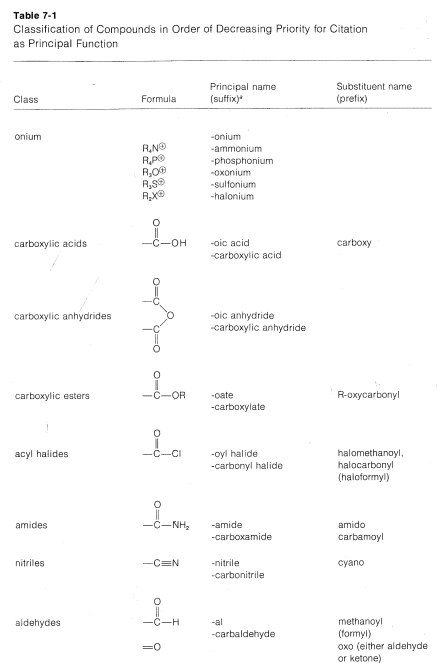
There are no simple rules to follow that dictate which is the parent function, and we suggest that the order of precedence of functional groups set by Chemical Abstracts be used whenever possible (see Table 7-1). By this system, the \(OH\) group takes precedence over hydrocarbons, and Compound \(1\) therefore is named as an alcohol, not as an alkene.
Having decided on the main classification, our next step is to identify the longest chain that includes the main functional group. Then this chain is numbered, starting at the end that gives the main function the lowest possible number. The remaining groups, functional or nonfunctional, are taken as substituents and are assigned numbers according to their position along the chain. Thus for Compound \(1\):
1. The longest continuous carbon chain carrying the \(OH\) group is a six-carbon unit. The prefix for a six-carbon hydrocarbon is hex-.
2. The chain is numbered so the \(OH\) group is at \(C2\), the lowest possible number. Therefore the IUPAC suffix is -2-ol, in which ol signifies alcohol (see Section 7-2).
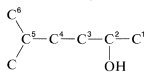
3. The remaining functions are methyl (at \(C5\)) and -en(e) (at \(C4\)). The complete name is
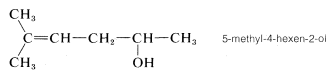
(Notice that the final e is dropped from the suffix -ene when followed by another suffix beginning with a vowel.)
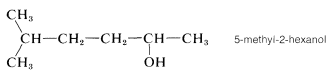
One further point of possible confusion is where to locate the numerical symbol for the main functional group in the name. For instance, if the double bond in \(1\) were absent, we could name the compound either 5-methylhexan-2-ol or 5-methyl-2-hexanol. The rule is to not divide the name unnecessarily. Thus 5-methyl-2-hexanol would be correct and 5-methylhexan-2-ol would be incorrect:
Translating a Name into its Chemical Structure
1. The first step is to identify the parent function, which usually is determined from the suffix or word at the end of the name. Suppose, for example, that a structure is to be written for a compound having the name 3-methoxybutanal. The suffix -al is the IUPAC suffix for aldehyde; therefore the compound is an aldehyde and the function is \(-CHO\).
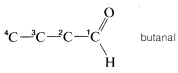
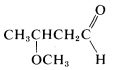
3. The rest of the name, which generally precedes the parent name, describes the substituent and its position on the parent chain. In our example, 3-methoxy means a \(CH_3O-\) group at \(C3\). Thus the complete structure of 3-methoxybutanal is
The foregoing examples illustrate that naming compounds from structures or deducing structures from names requires knowledge of both the parent names and the substituent names of the important types of functional and nonfunctional groups. This information is summarized in the following sections and in Table 7-1.

Contributors and Attributions
John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and performance of this work in any format."


