6: OuterSphereET
- Page ID
- 149275
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Name: ______________________________
Section: _____________________________
Student ID#:__________________________
Outer Sphere Electron Transfer
Electron transfer in biological pathways frequently involves metal ions. The electron may be transferred between a metal ion and an organic cofactor or from one metal ion to another.
For example, in the photosynthetic step involving conversion of oxygen to water via cytochrome c oxidase, there is a chain of electron transfers including the following, from a cytochrome c to a Cu center:
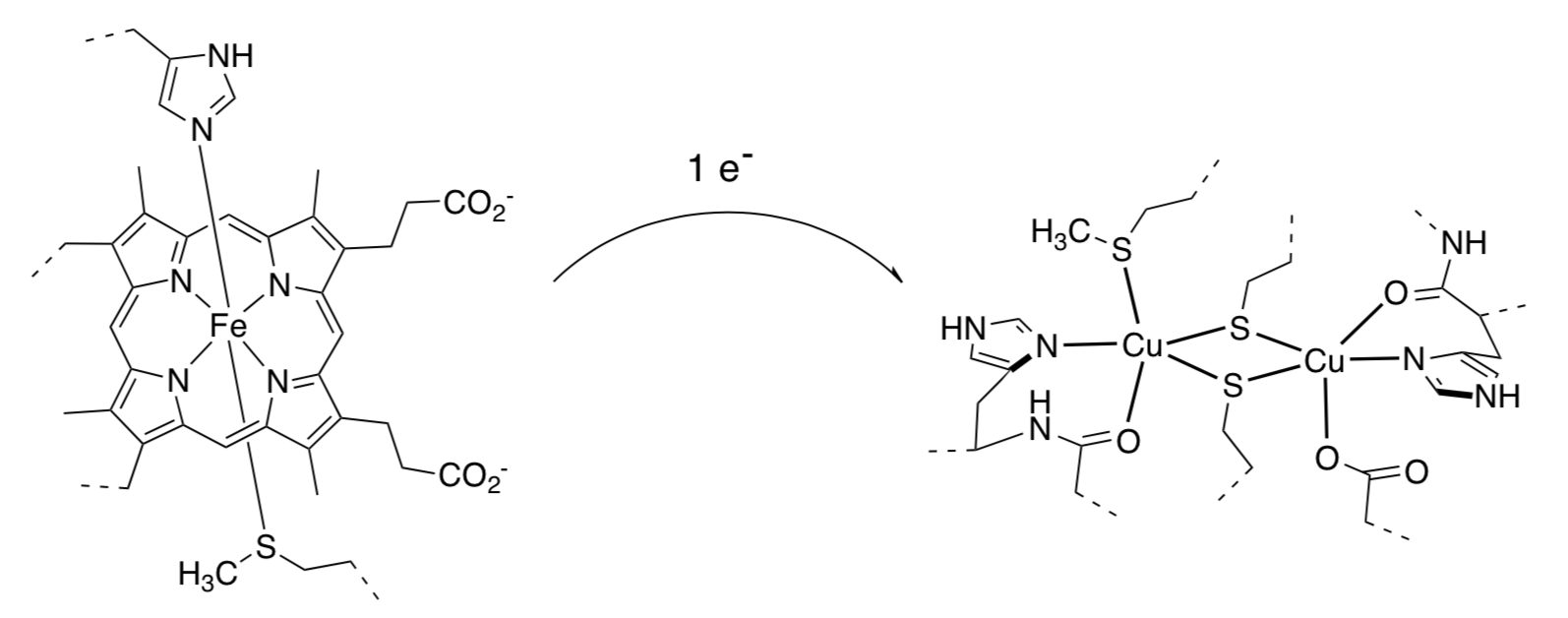
Note that the dashed lines are covalent connections to protein. The two metal complexes are held in position several angstroms apart from each other. Note:a typical C-C bond length is about 1.5 angstroms (150 pm).
- What is the oxidation state in each metal ion above (assuming the coordination complexes are overall neutral)?
- What is the oxidation state of each metal after the electron transfer?
- Predict what will happen to the Fe-ligand distances when an electron is transferred from the cytochrome to the Cu center in cytochrome c oxidase?
- Predict what will happen to the Cu-ligand distances when an electron is transferred from the cytochrome to the Cu center?
In an outer sphere electron transfer, an electron is simply sent across space from one metal atom to another.
- How do you think the distance between metal centers might influence the rate of the reaction?
Solvent reorganization is also important in electron transfer reactions.
- Draw a picture of an Fe(II) ion, a Cu(II) ion, and six water molecules in between them.
- Draw a picture of an Fe(III) ion, a Cu(I) ion, and six water molecules in between them.
- Why has the orientation of some of the solvent molecules changed after electron transfer?
- Given the nature of events that contribute to the activation barrier, explain why electron transfer may occur more quickly at higher temperature.
- Outer sphere electron transfer occurs more quickly in polar solvents. Propose a reason why.
Outer Sphere Electron Transfer: Relative Rates
Rudy Marcus, CalTech, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1992 for his work on electron transfer reactions.
Marcus begins by considering the energy of an electron on the metal, and how that energy varies with a change in the surroundings.
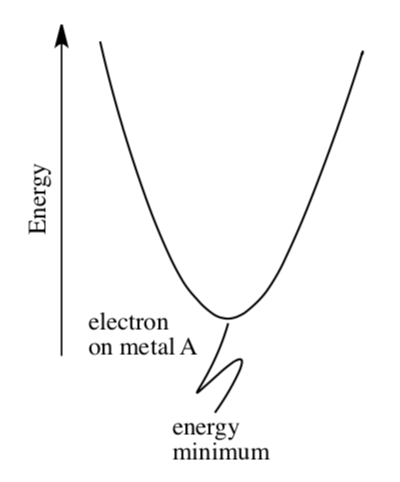
The x-axis is not labeled in this plot, but it could describe the change in energy with changing metal-ligand distance, for example.
- Explain why a change in M-L distance would influence the energy of the electron.
At some point, changes in surroundings allow the electron to cross over to another metal. For example, the electron may hop from a Cu(I) ion to a Cu(II) ion, below.
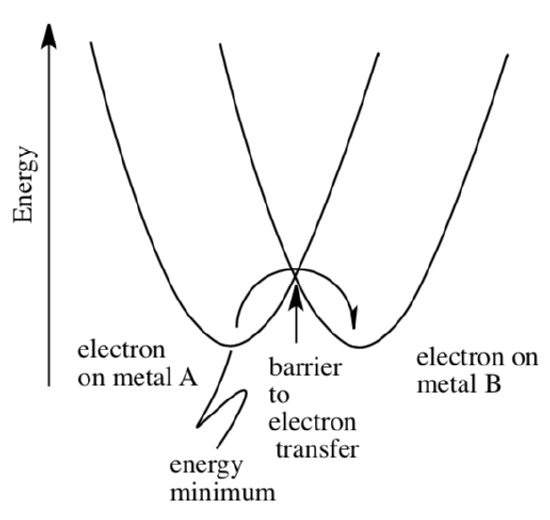
- Explain why the electron is at the same energy level in this case, whether it is on metal A or metal B.
- What might be happening to the M-L distance on metal A before the electron jumps?
- What might be happening to the M-L distance on metal B after the electron jumps?
When the electron is transferred to a different element, it will end up at a different energy level. The curve describing that electron shifts downward on the y-axis.
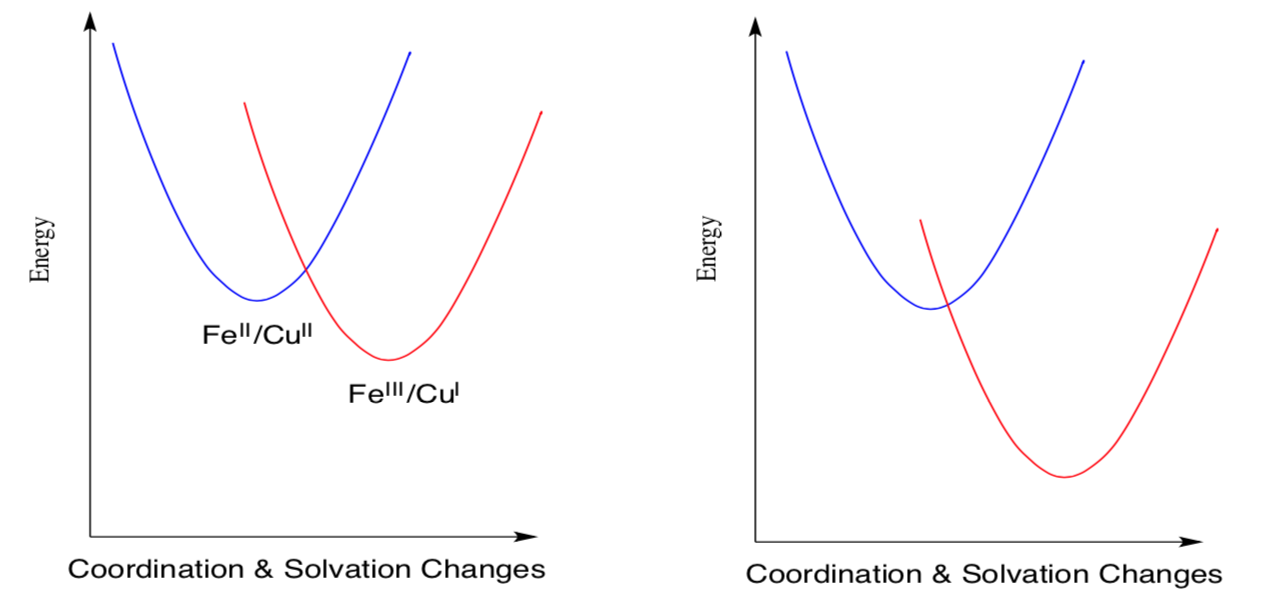
- Circle the transition state for the electron transfer on the left.
- Circle the transition state for the electron transfer on the right.
- Compare the donor-acceptor energy differences on the left and on the right.
- Compare the heights of the barriers for electron transfer on the left and on the right.
- Which electron transfer will occur more quickly?
- How is the rate of electron transfer related to the thermodynamic driving force for the reaction?
Marcus Inverted Region
Eventually, as the acceptor becomes even lower in energy, something unusual happens.

- Circle the transition state for the electron transfer on the left.
- Circle the transition state for the electron transfer on the right.
- Compare the donor-acceptor energy differences on the left and on the right.
- Compare the heights of the barriers for electron transfer on the left and on the right.
- Which electron transfer will occur more quickly?
The larger the potential, the faster the outer-sphere electron transfer occurs. When the barrier increases, the rate will then drop off.
Outer Sphere Electron Transfer: Relationship to Reduction Potential
One index of relative electron energy on one metal vs another is the reduction potential.
- Review: How does reduction potential (Eo) correlate to ΔG?
Directly | Inversely
For example, the following data was gathered for reductions by Ru(NH3)62+ ion.
| Oxidant | E0 (V) | k (M-1 s-1) (error in last digit) |
| Co(diene)(NH3)23+ | 0.12 | 3.0(4) |
| Co(diene)(H2O)NCS2+ | 0.38 | 11(1) |
| Co(diene)(H2O)23+ | 0.53 | 800(100) |
| Co(EDTA) | 0.60 | 6000(1000) |
- Which of the electron transfers is most favored thermodynamically?
- Which of the electron transfers is fastest?
- How does reduction potential (E0) correlate to the reaction rate (k)?
Directly | Inversely | Direct and Exponentially
- Which expression would best approximate the relationship? (A, B are constants)
k = AΔG | k = -A ΔG | k = A e(BΔG) | k = A e-(BΔG)


