2.E: Exercises
- Page ID
- 438369
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Types of Units
Match the most appropriate units for each of the examples below:
| The amount of acetaminophen in a tablet of Tylenol: __________ | a. L |
| b. kg | |
| The volume of an oral suspension of dextromethorphan (cough suppressant) to administer to a patient: __________ | c. m |
| d. mL | |
| The length of a suture needle: ___________ | e. mg |
| f. cm |
Match the most appropriate metric units and its symbol:
| Prefix | Symbol |
|---|---|
| mega | M |
| kilo | k |
| micro | \(\mu\) |
| nano | n |
| femto | f |
| pico | p |
Match the most appropriate metric units and its value in scientific notation:
| Prefix | Scientific Notation |
|---|---|
| mega | \(10^6\) |
| kilo | \(10^3\) |
| micro | \(10^{-6}\) |
| nano | \(10^{-9}\) |
| femto | \(10^{-15}\) |
| pico | \(10^{-12}\) |
A measurement always has a number and a unit. Select all that apply for the units of pressure.
a. mL
b. lbs
c. s
d. psi
e. atm
f. mmHg
g. g
h. cm\(^3\)
i. L
A measurement always has a number and a unit. Select all that apply for the units of volume.
a. mL
b. lbs
c. s
d. psi
e. atm
f. mmHg
g. g
h. cm\(^3\)
i. L
A measurement always has a number and a unit. Select all that apply for the units of mass.
a. mL
b. lbs
c. s
d. psi
e. atm
f. mmHg
g. g
h. cm\(^3\)
i. L
A vehicle is moving at 65 mi/hr. Which of the following is the correct equality we could write from this speed to convert between miles and hours?
a. 65 miles = 65 hours
b. 65 miles = 1 hour
c. 1 hour = 60 miles
d. 1 hour = 1 mile
How long will it take a vehicle traveling at 65 mi/hr to travel 185 miles?
A medicine has a dosage of 7.2 mg/kg. Which of the following is the correct equality we could write from this dosage to convert between milligrams of medicine and kilograms of body mass?
a. 7.2 mg = 1 kg
b. 7.2 mg = 7.2 kg
c. 1 mg = 7.2 kg
d. 1 mg = 1 kg
A certain solution has a density of 1.05 mg/mL. Which of the following is the correct equality we could write from this density to convert between milligrams and milliliters?
a. 1.05 mg = 1.05 mL
b. 1 mg = 1.05 mL
c. 1.05 mg = 1 mL
d. 1 mg = 1 mL
A medicine has a dosage of 7.2 mg/kg. How many milligrams of this medicine should be given to a 12.2 kg toddler?
A certain solution has a density of 1.05 mg/mL. What is the volume of 122 mg of the solution?
Match the following measured quantities with the type of measurements to which it refers:
a. 37.0 \(^{\circ}\)C = temperature
b. 1 cm\(^3\) = volume
c. 60.0 kg = mass
d. 1.3 m = length
e. 44, 444 s = time
Measured numbers and significant figures
Indicate the correct number of significant figures in each of the following numbers:
a. 0.0062
b. 2.70
c. 43300
d. 154.6
e. -13796
Identify each of the following as a measured or exact number:
a. The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is stored at -80 \(^{\circ}\)C.
b. There are 7 nurses on the ICU floor at Eastside Medical.
c. The 2018 soccer world cup winner team France featured 18 players of African descent.
d. GGC now seats on what was once 261 acres of rolling terrain.
A balance measures mass to 0.001 g. If you determine the mass of an object that weighs about 41 g, what mass would you record in your lab notebook?
a. 41 g
b. 41.0 g
c. 41.08 g
d. 41.056 g
e. 41.0075 g
What is the volume of water measured from the cylinder below?

a. 5.45 mL
b. 5.457 mL
c. 5 mL
d. 5.4 mL
Read the following measurement to the correct number of significant figures:

a. 3 cm
b. 3.86 cm
c. 3.80 cm
d. 3.8 cm
e. 3.7 cm
How many significant figures are in the measurement of the mass of an object?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
For each of the following, indicate whether we have an exact number or a measured quantity. Answer by stating Exact or Measured.
a. 11 girls
b. 6.345 gm
c. 1 hour = 60 minutes
d. \(3.0 \times 10^8 \) m
What is the volume of liquid measured from the cylinder below?
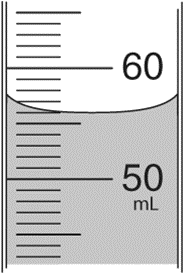
a. 50 mL
b. 50.5 mL
c. 55.5 mL
d. 56.0 mL
e. 60 mL
Round the following measurements to three (3) significant figures.
a. 1.2954 in _______________________________________
b. 16,275 cm _______________________________________
c. 0.003400 s _______________________________________
Determine how many significant figures for each of the following numbers.
a. 1,869.000 s ________s.f.
b. 003005750 J ________s.f.
c. 0.004070 lb ________s.f.
Represent the following measurements in scientific notation and ROUND to the correct number of significant figures
a. 2, 500, 760.0054 ft (to four significant figures)
b. 0.008976100 dm (to two significant figures)
Represent the following measurements in scientific notation and ROUND to the correct number of significant figures
a. 25.66 cm\(^3\) (to two significant figures)
b. 1.00056 (to five significant figures)
Significant Figures in Calculations
Perform the calculation: \(3.167 + 4\) to the correct number of significant figures:
a. 6.57
b. 6.6
c. 7
d. 7.57
e. 7.6
Perform the calculation to the correct number of significant figures.
\[(8.01-7.50) /(3.002) \nonumber\]
a. 0.17
b. 0.170
c. 0.1698867
d. 0.1700
Write the answer to the following problem with the correct number of significant figures:
\[32.0 \cdot 0.0344 \cdot 110.0 / (12.5 \cdot 0.900) = \nonumber\]
The correct answer for the addition of 6.5 g + 2.16 g + 1.411 g + 3 g is:
a. 14.071 g
b. 14 g
c. 14.0 g
d. 10 g
e. 14.1 g
Estimate the volume of the object to the correct number of significant figures:

a. 45 cm
b. 45 cm\(^3\)
c. 50 cm\(^3\)
d. 45.00 cm\(^3\)
e. 45.0 cm\(^3\)
Which of the following statements is correct? In a calculation that involves addition and subtraction:
a. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest significant figures
b. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the most significant figures
c. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest decimal places
d. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the most decimal places
e. the final answer should have the same decimal places as the measurement with the most decimal places
f. the final answer should have the same decimal places as the measurement with the fewest decimal places
Which of the following statements is correct? In a calculation that involves multiplication and division:
a. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest significant figures
b. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the most significant figures
c. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest decimal places
d. the final answer should have the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the most decimal places
e. the final answer should have the same decimal places as the measurement with the most decimal places
f. the final answer should have the same decimal places as the measurement with the fewest decimal places
Perform the following calculations to the correct number of significant figures.
a. \((9.43 \times 10^2) / (8.1 \times 10^{-4}) =\) __________
b. \((249.362 + 41) / 63.498 =\) __________
c. \((433.621 - 333.9) \times 11.900 =\) __________
Prefixes and equalities
Which of the following values is the same as 400.0 mm?
a. 4.000 m
b. 4.000 \(\times 10^{-4}\) km
c. 4.000 \(\times 10^6\) nm
d. 4.000 \(\times 10^6\) \(\mu\)m
e. 4.0 \(\times 10^3\) cm
During a work at the GGC gym you set the treadmill at a pace of 55.0 m/min. Generate a useful conversion factor or equality from this information. Select all that apply
a. 60 min = 55.0 m
b. 55.0 m = 1 min
c. 1 min = 60 m
d. 60 s = 1 min
e. 55 min = 1 m
Identify the name (prefix + unit) that can be used to represent each measurement
a. \(1 \times 10^{-6}\) g: __________
b. 1000 g: __________
c. 0.01 g: __________
Which of the following is a larger volume: 2.50 mL or 2.50 \(\mu\)L? __________
Which of the following is a larger volume: 4.21 L or 4.21 nL? __________
Fill in the blanks with the missing measurements:
a. 15.0 km = ___________ cm = ___________ miles
b. 8.5 lbs = ___________ kg = ___________ g
c. 6.5 lbs = ___________ kg = ___________ g
Writing Conversion factors
You are asked to administer a daily IV drip of 45.0 mL of ceftriaxone for meningitis for a 5-yr-old weighing 18.0 kg. The IV solution has a concentration of 40.0 mg/mL. What would be the calculated dose per day in mg/kg?
a. 16.0
b. 20.3
c. 100.
d. 60.0
e. 50.0
If your goal is to convert 121 lb to kilograms, what is the correct conversion factor to use? Note that 1 kg = 2.20 lb.
a. 1 kg/2.20 lb
b. 2.20 lb/1 kg
c. 121 lb/1 kg
d. 1 kg/121 lb
Problem solving
The number 420 001 000 expressed correctly using scientific notation is:
a. \(4.2 \times 10^8\)
b. \(4.2 \times 10^6\)
c. \(420001 \times 10^3\)
d. \(4.20001 \times 10^8\)
e. \(4.20 \times 10^7\)
Ganciclovir is used to treat cytomegalovirus, a deadly viral infection common in immunocompromised patients. The doctor places an order for a dose of 2.5 mg/kg of body weight. What dose will the nurse administer for a 141 lb patient?
a. 160 mg
b. 56.4 mg
c. 352 mg
d. 124 mg
A nurse practitioner places an order for a heparin infusion to start at 18 units/kg\(\cdot\)hour. The patient's weight is 85 kg, and the heparin infusion comes in bags described by label below. Use the information provided to calculate the rate of infusion (mL/hour).

a. 1.5 mL/hour
b. 2.3 mL/hour
c. 0.15 mL/hour
d. 0.18 mL/hour
A nurse notes a patient’s IV pump is set at 12 mL/hr. The IV bag holds 20 units of Pitocin mixed in 500. mL of Lactated Ringers. How many mu/min is the patient receiving. Note mu is milliunits.
a. 8 mu/min
b. 12 mu/min
c. 6 mu/min
d. 0.48 mu/min
e. 48 mu/min
Begin a Pitocin infusion at 5.0 mu/min via IV pump for labor induction. On hand is Pitocin 40. units in 1000 mL Lactated Ringers. How many mL/hr will the IV run?
a. 7.5 mL/hr
b. 15 mL/hr
c. 0.25 mL/hr
d. 5.0 mL/hr
A jar of peanut butter contains 130 mg of potassium per serving. If the jar contains 15 servings, how many grams of potassium are in the entire jar? __________
The maximum allowed daily dosage of Imitrex is 0.200 g. If tablets contain 25 mg, how many tablets are able to be ingested in a day? __________
A Chemistry student had a cold and took 2.5 teaspoons (tsp) of cough syrup. If the syrup had a density of 0.950 g/mL and there is 5.0 mL in 1 tsp, what was the mass, in grams, of the cough syrup? __________
The prescribed dose of ferrous sulfate solution for a toddler is 2.5 mL taken twice a day. If the ferrous sulfate concentration is 220 mg/5 mL, how many milligrams (mg) is the toddler taking per day? __________
A dose of aspirin of 5.0 mg per kilogram of body weight has been prescribed to reduce the fever of an infant weighing 8.5 pound. (1 kg = 2.20 lb). The number of milligrams of aspirin that should be administered is __________
A doctor's order is 0.134 g of ampicillin. The liquid suspension on hand contains 240 mg/5.0 mL. How many milliliters of the suspension are required?

How many milliliters (mL) are equivalent to 10.0 deciliters (dL)?
a. 0.1
b. 1
c. 10
d. 100
e. 1000
Density
Mercury has a density of 13.5 g/mL. What would be the volume of 50.0 g of mercury in mL?
a. 3.70 mL
b. 0.270 mL
c. 2.70 mL
d. 675 mL
e. None of the above
Platinum alloys are used for several medical applications associated with coronary artery disease due to chemical inertness, durability and electrical conductivity. The range of platinum alloy devices extends from 0.0254 mm to 3.175 mm. Convert the high end of this range, 3.175 mm, to inches. (1 inch = 2.54 cm) __________
Use the information below to identify the metal that is weighed and submerged in water:

a. Rhenium
b. Copper
c. Gold
d. Lead
Use the PhET density simulation link and determine the mass, volume and density of the Gold:
a. Mass (40.53 g), Volume (2.1 mL), density (19 g/mL)
b. Mass (40.53 g), Volume (2.340 mL), density (19 g/mL)
c. Mass (35.53 g), Volume (2.1 mL), density (19 g/mL)
d. Mass (40.53 g), Volume (2.1 mL), density (19.208 g/mL)
The specific gravity of household bleach is 1.168. What is the mass, in grams, of 750 mL of bleach? __________
Determine the volume of an object that has a mass of 455.6 g and a density of 19.3 g/cm\(^3\).
If an object has a density of 8.65 g/cm\(^3\), what is its density in units of kg/m\(^3\)?
Determine the volume of an object that has a mass of 44.3 g and a density of 10.55 g/mL.
What apparatus do you use to determine density of irregular shape of gold?
a. meter stick and balance
b. volumetric flask and Bunsen burner
c. graduate cylinder and balance
d. beaker and desiccator
Which one has the highest density?
a. Ice, 0.92 g/mL
b. Sugar, 1.59 g/mL
c. Bone, 1.80 g/mL
d. \(\ce{CO2}\), 1.96 g/L

