Density and Lava Lamps
- Page ID
- 49962
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Lava Lamps were a craze in the 1960s and later[1][2], and have been reproduced for retro parties and nostalgia buffs.

An original Mathmos Astro lava lamp
Hobbyists have recreated Lava Lamps using everyday materials, which must be immiscible and of just the right density so that the heat of the lamp causes irregular floating and sinking. Walker's U.S. patent mentions additives such as dye, mineral oil, carbon tetrachloride, and polyethylene glycol (PEG), but the exact formula of commercial lamps is a trade secret. Spain tells C&EN that only five or six staff chemists know the formula and are in charge of occasional reformulations. Densities must be recorded for each batch of wax that Haggerty makes, which is mixed in 5-foot-tall vats in factories in China[4].
Density Values Density values for virtually any substance or material can be found on the web. For example, [5]
1. A typical wax has a density of 0.77 g/cm3. What is the weight in pounds of wax in one of the 5 foot high by 3 foot diameter vats used in LavaLamp production? The terms heavy and light are commonly used in two different ways. We refer to weight when we say that an adult is heavier than a child. On the other hand, something else is alluded to when we say that oak is heavier than balsa wood. A small shaving of oak would obviously weigh less than a roomful of balsa wood, but oak is heavier in the sense that a piece of given size weighs more than the same-size piece of balsa.
What we are actually comparing is the mass per unit volume, that is, the density. In order to determine these densities, we might weigh a cubic centimeter of each type of wood. If the oak sample weighed 0.71 g and the balsa 0.15 g, we could describe the density of oak as 0.71 g cm–3 and that of balsa as 0.15 g cm–3. (Note that the negative exponent in the units cubic centimeters indicates a reciprocal. Thus 1 cm–3 = 1/cm3 and the units for our densities could be written as 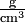 , g/cm3, or g cm–3. In each case the units are read as grams per cubic centimeter, the per indicating division.) We often abbreviate "cm3" as "cc", and 1 cm3 = 1 mL exactly, by definition.
, g/cm3, or g cm–3. In each case the units are read as grams per cubic centimeter, the per indicating division.) We often abbreviate "cm3" as "cc", and 1 cm3 = 1 mL exactly, by definition.
In general it is not necessary to weigh exactly 1 cm3 of a material in order to determine its density. We simply measure mass and volume and divide volume into mass:
\[\text{Density} = \dfrac{\text{mass}} {\text{volume}}\]
or
\[\rho = \dfrac{\text{m}} {\text{V}}\]
where ρ = density m = mass V = volume
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Density Calculation
Calculate the density of (a) a piece of aluminum whose mass is 37.42 g and which, when submerged, increases the water level in a graduated cylinder by 13.9 ml; (b) an aluminum cylinder of mass 25.07 g, radius 0.750 cm, and height 5.25 cm.
Solution
a) Since the submerged metal displaces its own volume,
\(\text{Density} =\rho = \dfrac{\text{m}} {\text{V}} = \dfrac{37.42 g} {13.9 mL} = \text {2.69 g/mL or 2.69 g mL}^{-1}\)
b) The volume of the cylinder must be calculated first, using the formula
\(\text{V} = {\pi} r^{2} h = 3.142 × \text{(0.750 cm)}^{2} * 5.25 \text{cm} = \text{9.278 718 8 cm}^{3}\)
Then \(\rho = \dfrac{\text{m}} {\text{V}} = \dfrac{25.07g} {9.278 718 8cm^{3}}\)
\(= \text{2.70} \dfrac{\text{g}}{\text{cm}^3}\)
Note
Note that unlike mass or volume, the density of a substance is independent of the size of the sample. Thus density is a property by which one substance can be distinguished from another. A sample of pure aluminum can be trimmed to any desired volume or adjusted to have any mass we choose, but its density will always be 2.70 g/cm3 at 20°C. The densities of some common pure substances are listed in Table 1.4.
Tables and graphs are designed to provide a maximum of information in a minimum of space. When a physical quantity (number × units) is involved, it is wasteful to keep repeating the same units. Therefore it is conventional to use pure numbers in a table or along the axes of a graph. A pure number can be obtained from a quantity if we divide by appropriate units. For example, when divided by the units gram per cubic centimeter, the density of aluminum becomes a pure number 2.70:
\[\dfrac{\text{Density of aluminum}} {\text{1 g cm}^{-3}} = \dfrac{\text{2.70 g cm}^{-3}} {\text{1 g cm}^{-3}} = 2.70\]
TABLE \(\PageIndex{1}\) Density of Several Substances at 20°C.
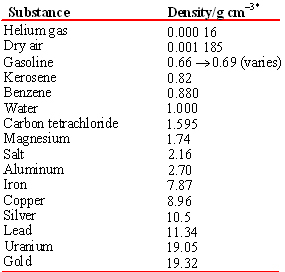
Densities of many more materials are easily found.
Therefore, a column in a table or the axis of a graph is conveniently labeled in the following form:
\[\dfrac{\text{Quantity}}{\text{units}}\]
This indicates the units that must be divided into the quantity to yield the pure number in the table or on the axis. This has been done in the second column of Table 1.4.
Converting Densities
In our exploration of Density, notice that chemists may express densities differently depending on the subject. The density of pure substances may be expressed in kg/m3 in some journals which insist on strict compliance with SI units; densities of soils may be expressed in lb/ft3 in some agricultural or geological tables; the density of a cell may be expressed in mg/µL; and other units are in common use. It is easy to transform densities from one set of units to another, by multiplying the original quantity by one or more unity factors:
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\): Density Conversion
Convert the density of water, 1 g/cm3 to (a) lb/cm3 and (b) lb/ft3
a. The equality 454 g = 1 lb can be used to write two unity factors,
\(\dfrac{\text{454g}} {\text{1lb}}\) or \(\dfrac{\text{1lb}} {\text{454}}\)
The given density can be multiplied by one of the unity factors to get the desired result. The correct conversion factor is chosen so that the units cancel:
\(\dfrac{\text{1 g}} {\text{cm}^{3}}* \dfrac{\text{1 lb}} {\text{454 g}} = 0.002203 \dfrac{\text{lb}} {\text{cm}^{3}}\)
b. Similarly, the equalities 2.54 cm = 1 inch, and 12 inches = 1 ft can be use to write the unity factors:
\(\dfrac{\text{2.54 cm}} {\text{1 in}}\), \(\dfrac{\text{1 in}} {\text{2.54 cm}}\), \(\dfrac{\text{12 in}} {\text{1 ft}}\) and \(\dfrac{\text{1ft}} {\text{12 in}}\)
In order to convert the cm3 in the denominator of 0.002203 \(\dfrac{lb} {cm^{3}}\) to in3, we need to multiply by the appropriate unity factor three times, or by the cube of the unity factor:
\(\text{0.002203} \dfrac{\text{g}} {\text{cm}^{3}}\) x \(\dfrac{\text{2.54 cm}} {\text{1 in}}\) x \(\dfrac{\text{2.54 cm}} {\text{1 in}}\) x \(\dfrac{\text{2.54 cm}} {\text{1 in}}\)
or \(\text{0.002203} \dfrac{\text{g}} {\text{cm}^{3}}\) x \((\dfrac{\text{2.54 cm}} {\text{1 in}})^{3} = \text{0.0361} \dfrac{\text{lb}}{\text{in}^3}\)
This can then be converted to lb/ft3:
\(\text{0.0361} \dfrac{\text{lb}} {\text{in}^{3}}\) x \((\dfrac{\text{12 in}} {\text{1 ft}})^{3} = \text{62.4} \dfrac{\text{lb}}{\text{ft}^3}\)
Note
It is important to notice that we have used conversion factors to convert from one unit to another unit of the same parameter
From ChemPRIME: 1.8: Density
References
Contributors and Attributions
Ed Vitz (Kutztown University), John W. Moore (UW-Madison), Justin Shorb (Hope College), Xavier Prat-Resina (University of Minnesota Rochester), Tim Wendorff, and Adam Hahn.


