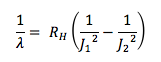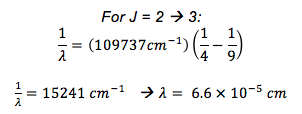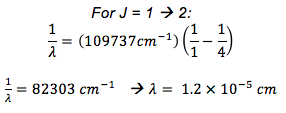Extra Credit 56
- Page ID
- 49896
Q2.60
Explain the Maxwell distribution plot and what two factors contribute to a molecule having a different distribution.
The Maxwell distribution is a plot that shows the velocity distribution of all the molecules. The two factors that influence it are temperature and mass. As temperature increases, kinetic energy will increase as well as velocity. As the number of molecules in a system does not change with an increase in temperature, the bell curve velocity distribution flattens out as the most probable velocity (the peak of the curve) increases. Mass also influences the distribution curve because the lighter the molecule, the higher its velocity will be. This is due to the fact that since all molecules at the same temperature will have the same kinetic energy, the equation KE = 1/2mv2 shows that heavier molecules will thus have slower velocities, and vice versa.
Q2.71
If you put 10 marbles (each 2 cm in diameter) in a 1000 cm3 bag and shake it around, what is the mean free path of the of the marbles.
Relavant Information:
- N = 10 marbles
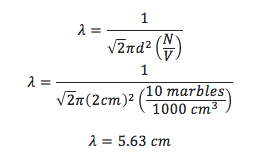
Q9.3
Find the units of the rate constant for a second-order reaction.
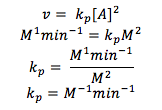
Q9.10
Assuming a first order reaction, find the rate constant on the reaction below. Use the data table providing pressures and time at a constant 500K.
N2O4(g) à 2NO2(g)
|
Time (min-1) |
Pressure of N2O4 (mmHg-1) |
|
0 |
350 |
|
1 |
400 |
|
2 |
450 |
|
3 |
500 |
|
4 |
550 |
|
5 |
600 |
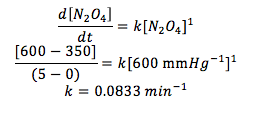
Q9.27
If a reaction takes place at 273K and 283K, assuming that the rate doubles with every 10° rise in temperature, find the activation energies that would correspond.
Relavant Information:
- R = 8.314 J/mol K
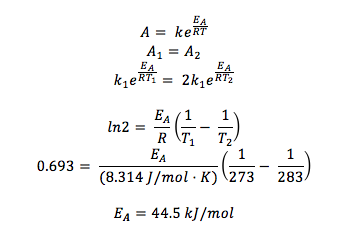
Q10.2
Explain the differences between how an enzyme-substrate complex would behave when follow a rapid equilibrium or steady-state scheme using the below formula.
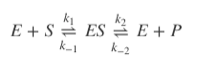
Rapid equilibrium would mean that the 1st step in the above reaction would be fast, and the second step slow. Steady-state on the other hand would mean a slow 1st step, and a fast second step. Therefore, given that 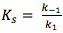 and ,
and ,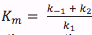 when
when
Ks = Km then the reaction is at rapid equilibrium, but when 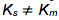 then the reaction is most likely at steady-state.
then the reaction is most likely at steady-state.
Q11.17
A laser causes a 400g sample of water to absorb IR radiation with a wavelength of 5.40 x 104 nm. If all the radiation is converted to heat, what is the amount of photons required to raise the temperature of water by 7°C?
Relevant information:
- specific heat of water = 4.186 J/gC
Energy per photon:
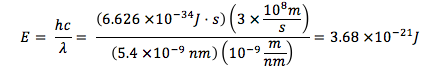
Total energy needed:
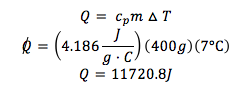
Amount of photons:
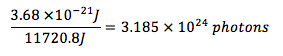
Q12.9
Write the general wave function equations for a molecules that is (a) entirely covalent, (b) entirely ionic, (c) a mix of covalent and ionic.
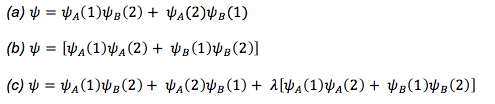
Q13.12
Given that for an Argon molecule, ε = 0.997 kJ/mol and σ = 3.4Å, find the potential energy of an argon molecule with a radius of 5Å.
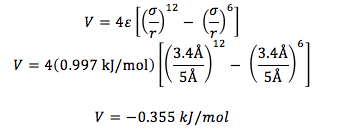
Q14.15
Assuming you have a rigid rotor molecule, what is the wavenumber for a J = 1 à 2 and J = 2 à 3 transition?
Relevant Information:
- RH = 109737 cm-1