4.2: Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Page ID
- 239796
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The Citric Acid Cycle
In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are sites of cellular respiration. If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. In mitochondria, pyruvate will be transformed into a two-carbon acetyl group (by removing a molecule of carbon dioxide) that will be picked up by a carrier compound called coenzyme A (CoA), which is made from vitamin B5. The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA. (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Acetyl CoA can be used in a variety of ways by the cell, but its major function is to deliver the acetyl group derived from pyruvate to the next pathway in glucose catabolism.
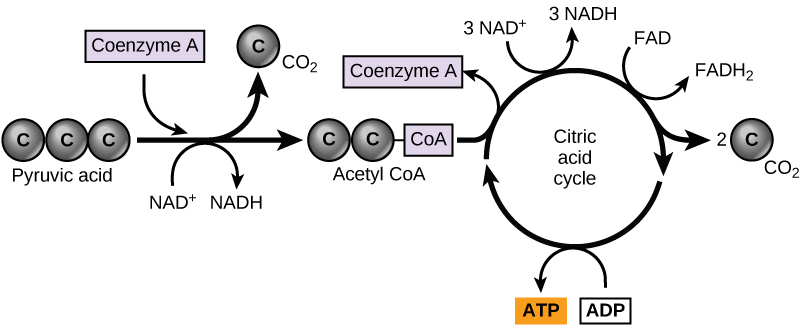
Like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the citric acid cycle in eukaryotic cells takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Unlike glycolysis, the citric acid cycle is a closed loop: The last part of the pathway regenerates the compound used in the first step. The eight steps of the cycle are a series of chemical reactions that produces two carbon dioxide molecules, one ATP molecule (or an equivalent), and reduced forms (NADH and FADH2) of NAD+ and FAD+, important coenzymes in the cell. Part of this is considered an aerobic pathway (oxygen-requiring) because the NADH and FADH2 produced must transfer their electrons to the next pathway in the system, which will use oxygen. If oxygen is not present, this transfer does not occur.
Two carbon atoms come into the citric acid cycle from each acetyl group. Two carbon dioxide molecules are released on each turn of the cycle; however, these do not contain the same carbon atoms contributed by the acetyl group on that turn of the pathway. The two acetyl-carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; in this way, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule will be eventually released as carbon dioxide. It takes two turns of the cycle to process the equivalent of one glucose molecule. Each turn of the cycle forms three high-energy NADH molecules and one high-energy FADH2 molecule. These high-energy carriers will connect with the last portion of aerobic respiration to produce ATP molecules. One ATP (or an equivalent) is also made in each cycle. Several of the intermediate compounds in the citric acid cycle can be used in synthesizing non-essential amino acids; therefore, the cycle is both anabolic and catabolic.
Steps of the Citric Acid Cycle
At first glance, the citric acid cycle appears rather complex (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). All the reactions, however, are familiar types in organic chemistry: hydration, oxidation, decarboxylation, and hydrolysis. Each reaction of the citric acid cycle is numbered, and in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), the two acetyl carbon atoms are highlighted in red. Each intermediate in the cycle is a carboxylic acid, existing as an anion at physiological pH. All the reactions occur within the mitochondria, which are small organelles within the cells of plants and animals.
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Reactions of the Citric Acid Cycle
- In the first step, acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, and the acetyl group is transferred onto oxaloacetate, yielding citrate. Note that this step releases coenzyme A. The reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase.
- In the next step, aconitase catalyzes the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate. In this reaction, a tertiary alcohol, which cannot be oxidized, is converted to a secondary alcohol, which can be oxidized in the next step.
- Isocitrate then undergoes a reaction known as oxidative decarboxylation because the alcohol is oxidized and the molecule is shortened by one carbon atom with the release of carbon dioxide (decarboxylation). The reaction is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase, and the product of the reaction is α-ketoglutarate. An important reaction linked to this is the reduction of the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. The NADH is ultimately reoxidized, and the energy released is used in the synthesis of ATP, as we shall see.
- The fourth step is another oxidative decarboxylation. This time α-ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl-CoA, and another molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH. The α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes this reaction. This is the only irreversible reaction in the citric acid cycle. As such, it prevents the cycle from operating in the reverse direction, in which acetyl-CoA would be synthesized from carbon dioxide.
So far, in the first four steps, two carbon atoms have entered the cycle as an acetyl group, and two carbon atoms have been released as molecules of carbon dioxide. The remaining reactions of the citric acid cycle use the four carbon atoms of the succinyl group to resynthesize a molecule of oxaloacetate, which is the compound needed to combine with an incoming acetyl group and begin another round of the cycle.
In the fifth reaction, the energy released by the hydrolysis of the high-energy thioester bond of succinyl-CoA is used to form guanosine triphosphate (GTP) from guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and inorganic phosphate in a reaction catalyzed by succinyl-CoA synthetase. This step is the only reaction in the citric acid cycle that directly forms a high-energy phosphate compound. GTP can readily transfer its terminal phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to generate ATP in the presence of nucleoside diphosphokinase.

Succinate dehydrogenase then catalyzes the removal of two hydrogen atoms from succinate, forming fumarate. This oxidation-reduction reaction uses flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), rather than NAD+, as the oxidizing agent. Succinate dehydrogenase is the only enzyme of the citric acid cycle located within the inner mitochondrial membrane. We will see soon the importance of this.
In the following step, a molecule of water is added to the double bond of fumarate to form L-malate in a reaction catalyzed by fumarase.
One revolution of the cycle is completed with the oxidation of L-malate to oxaloacetate, brought about by malate dehydrogenase. This is the third oxidation-reduction reaction that uses NAD+ as the oxidizing agent. Oxaloacetate can accept an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA, allowing the cycle to begin again.
Video: "The Citric Acid Cycle: An Overview". In the matrix of the mitochondrion, the Citric Acid Cycle uses Acetyl CoA molecules to produce energy through eight chemical reactions. This animation provides an overview of the pathway and its products. NDSU VCell Production's animation; for more information please see http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
You have just read about the citric acid cycle that generates ATP. Most of the ATP generated during the aerobic catabolism of glucose, however, is not generated directly from this pathway. Rather, it derives from a process that begins with passing electrons through a series of chemical reactions to a final electron acceptor, oxygen. These reactions take place in specialized protein complexes located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic organisms and on the inner part of the cell membrane of prokaryotic organisms. The energy of the electrons is harvested and used to generate a electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The potential energy of this gradient is used to generate ATP. The entirety of this process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
The electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)a) is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants for this purpose. In animals, oxygen enters the body through the respiratory system. Electron transport is a series of chemical reactions that resembles a bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the endpoint of the chain where oxygen is the final electron acceptor and water is produced. There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled I through IV in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)c, and the aggregation of these four complexes, together with associated mobile, accessory electron carriers, is called the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. In each transfer of an electron through the electron transport chain, the electron loses energy, but with some transfers, the energy is stored as potential energy by using it to pump hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient.
ART CONNECTION
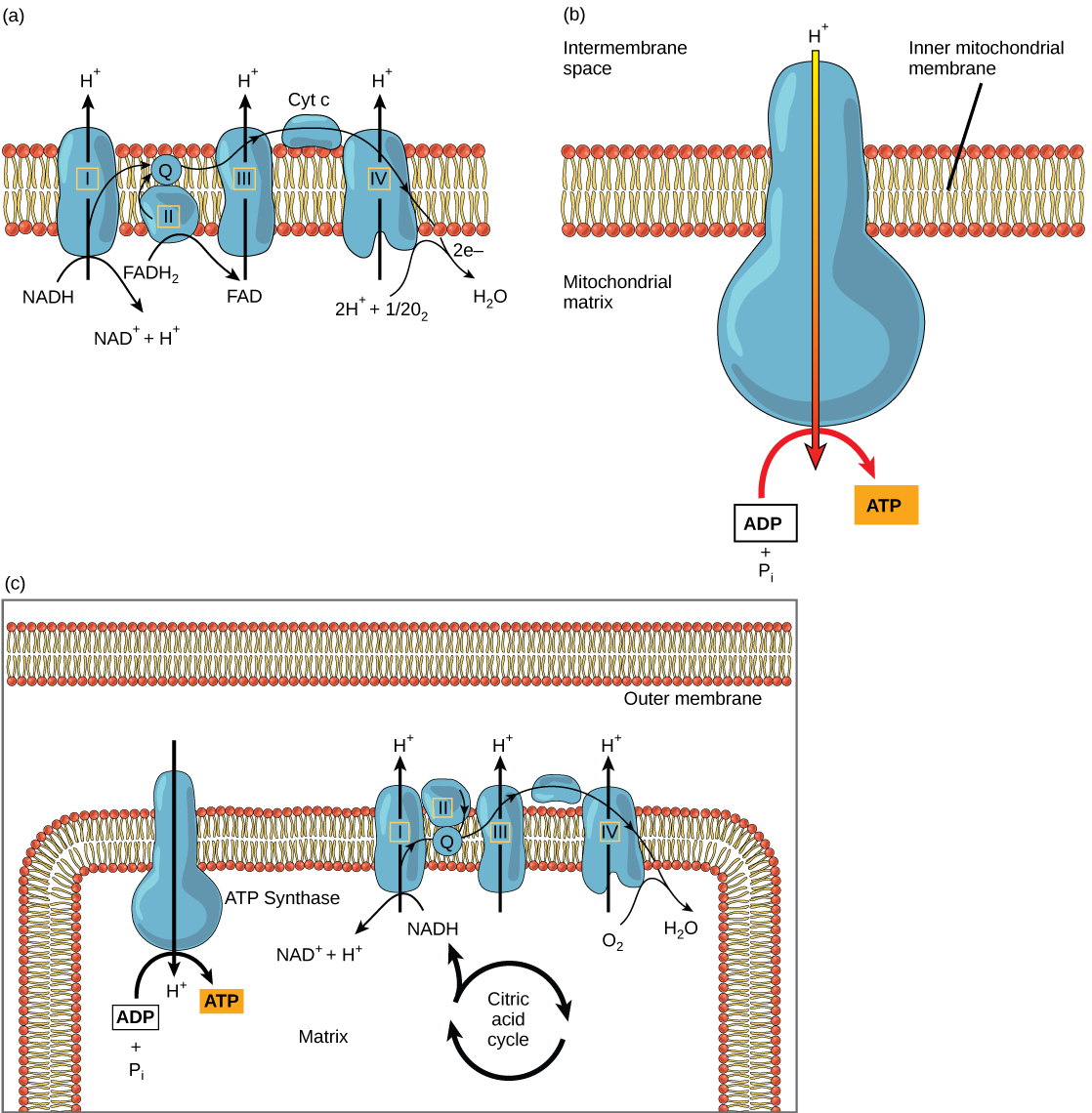
Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed to protein complexes in the electron transport chain. As they are passed from one complex to another (there are a total of four), the electrons lose energy, and some of that energy is used to pump hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space. In the fourth protein complex, the electrons are accepted by oxygen, the terminal acceptor. The oxygen with its extra electrons then combines with two hydrogen ions, further enhancing the electrochemical gradient, to form water. If there were no oxygen present in the mitochondrion, the electrons could not be removed from the system, and the entire electron transport chain would back up and stop. The mitochondria would be unable to generate new ATP in this way, and the cell would ultimately die from lack of energy. This is the reason we must breathe to draw in new oxygen.
In the electron transport chain, the free energy from the series of reactions just described is used to pump hydrogen ions across the membrane. The uneven distribution of H+ ions across the membrane establishes an electrochemical gradient, owing to the H+ ions’ positive charge and their higher concentration on one side of the membrane.
Hydrogen ions diffuse through the inner membrane through an integral membrane protein called ATP synthase (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)b). This complex protein acts as a tiny generator, turned by the force of the hydrogen ions diffusing through it, down their electrochemical gradient from the intermembrane space, where there are many mutually repelling hydrogen ions to the matrix, where there are few. The turning of the parts of this molecular machine regenerate ATP from ADP. This flow of hydrogen ions across the membrane through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)c) is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism. The result of the reactions is the production of ATP from the energy of the electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. These atoms were originally part of a glucose molecule. At the end of the electron transport system, the electrons are used to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen ions. The extra electrons on the oxygen ions attract hydrogen ions (protons) from the surrounding medium, and water is formed. The electron transport chain and the production of ATP through chemiosmosis are collectively called oxidative phosphorylation.
ATP Yield
The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. For example, the number of hydrogen ions that the electron transport chain complexes can pump through the membrane varies between species. Another source of variance stems from the shuttle of electrons across the mitochondrial membrane. The NADH generated from glycolysis cannot easily enter mitochondria. Thus, electrons are picked up on the inside of the mitochondria by either NAD+ or FAD+. Fewer ATP molecules are generated when FAD+ acts as a carrier. NAD+ is used as the electron transporter in the liver and FAD+ in the brain, so ATP yield depends on the tissue being considered.
Another factor that affects the yield of ATP molecules generated from glucose is that intermediate compounds in these pathways are used for other purposes. Glucose catabolism connects with the pathways that build or break down all other biochemical compounds in cells, and the result is somewhat messier than the ideal situations described thus far. For example, sugars other than glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction. Other molecules that would otherwise be used to harvest energy in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle may be removed to form nucleic acids, amino acids, lipids, or other compounds. Overall, in living systems, these pathways of glucose catabolism extract about 34 percent of the energy contained in glucose.
CAREERS IN ACTION: Mitochondrial Disease Physician
What happens when the critical reactions of cellular respiration do not proceed correctly? Mitochondrial diseases are genetic disorders of metabolism. Mitochondrial disorders can arise from mutations in nuclear or mitochondrial DNA, and they result in the production of less energy than is normal in body cells. Symptoms of mitochondrial diseases can include muscle weakness, lack of coordination, stroke-like episodes, and loss of vision and hearing. Most affected people are diagnosed in childhood, although there are some adult-onset diseases. Identifying and treating mitochondrial disorders is a specialized medical field. The educational preparation for this profession requires a college education, followed by medical school with a specialization in medical genetics. Medical geneticists can be board certified by the American Board of Medical Genetics and go on to become associated with professional organizations devoted to the study of mitochondrial disease, such as the Mitochondrial Medicine Society and the Society for Inherited Metabolic Disease.
Summary
The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions that removes high-energy electrons and uses them in the electron transport chain to generate ATP. One molecule of ATP (or an equivalent) is produced per each turn of the cycle.
The electron transport chain is the portion of aerobic respiration that uses free oxygen as the final electron acceptor for electrons removed from the intermediate compounds in glucose catabolism. The electrons are passed through a series of chemical reactions, with a small amount of free energy used at three points to transport hydrogen ions across the membrane. This contributes to the gradient used in chemiosmosis. As the electrons are passed from NADH or FADH2 down the electron transport chain, they lose energy. The products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP. A number of intermediate compounds can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nucleic acids, non-essential amino acids, sugars, and lipids. These same molecules, except nucleic acids, can serve as energy sources for the glucose pathway.
Art Connections
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
- Answer
-
After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. The pH of the intermembrane space would increase, and ATP synthesis would stop.
Glossary
- acetyl CoA
- the combination of an acetyl group derived from pyruvic acid and coenzyme A which is made from pantothenic acid (a B-group vitamin)
- ATP synthase
- a membrane-embedded protein complex that regenerates ATP from ADP with energy from protons diffusing through it
- chemiosmosis
- the movement of hydrogen ions down their electrochemical gradient across a membrane through ATP synthase to generate ATP
- citric acid cycle
- a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that harvests the energy in carbon-carbon bonds of sugar molecules to generate ATP; the citric acid cycle is an aerobic metabolic pathway because it requires oxygen in later reactions to proceed
- electron transport chain
- a series of four large, multi-protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accepts electrons from donor compounds and harvests energy from a series of chemical reactions to generate a hydrogen ion gradient across the membrane
- oxidative phosphorylation
- the production of ATP by the transfer of electrons down the electron transport chain to create a proton gradient that is used by ATP synthase to add phosphate groups to ADP molecules

