6.8: Connecting Gas Properties to Kinetic Molecular Theory
- Page ID
- 37011
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- To understand the significance of the kinetic molecular theory of gases
We now describe how the kinetic molecular theory of gases explains some of the important relationships we have discussed previously.
Diffusion and Effusion
As you have learned, the molecules of a gas are not stationary but in constant and random motion. If someone opens a bottle of perfume in the next room, for example, you are likely to be aware of it soon. Your sense of smell relies on molecules of the aromatic substance coming into contact with specialized olfactory cells in your nasal passages, which contain specific receptors (protein molecules) that recognize the substance. How do the molecules responsible for the aroma get from the perfume bottle to your nose? You might think that they are blown by drafts, but, in fact, molecules can move from one place to another even in a draft-free environment.
Diffusion is the gradual mixing of gases due to the motion of their component particles even in the absence of mechanical agitation such as stirring. The result is a gas mixture with uniform composition. Diffusion is also a property of the particles in liquids and liquid solutions and, to a lesser extent, of solids and solid solutions. The related process, effusion, is the escape of gaseous molecules through a small (usually microscopic) hole, such as a hole in a balloon, into an evacuated space.
The phenomenon of effusion had been known for thousands of years, but it was not until the early 19th century that quantitative experiments related the rate of effusion to molecular properties. The rate of effusion of a gaseous substance is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. This relationship is referred to as Graham’s law, after the Scottish chemist Thomas Graham (1805–1869). The ratio of the effusion rates of two gases is the square root of the inverse ratio of their molar masses:
\[\dfrac{\text{rate of effusion A}}{\text{rate of effusion B}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{M_B}{M_A}} \label{6.8.1}\]
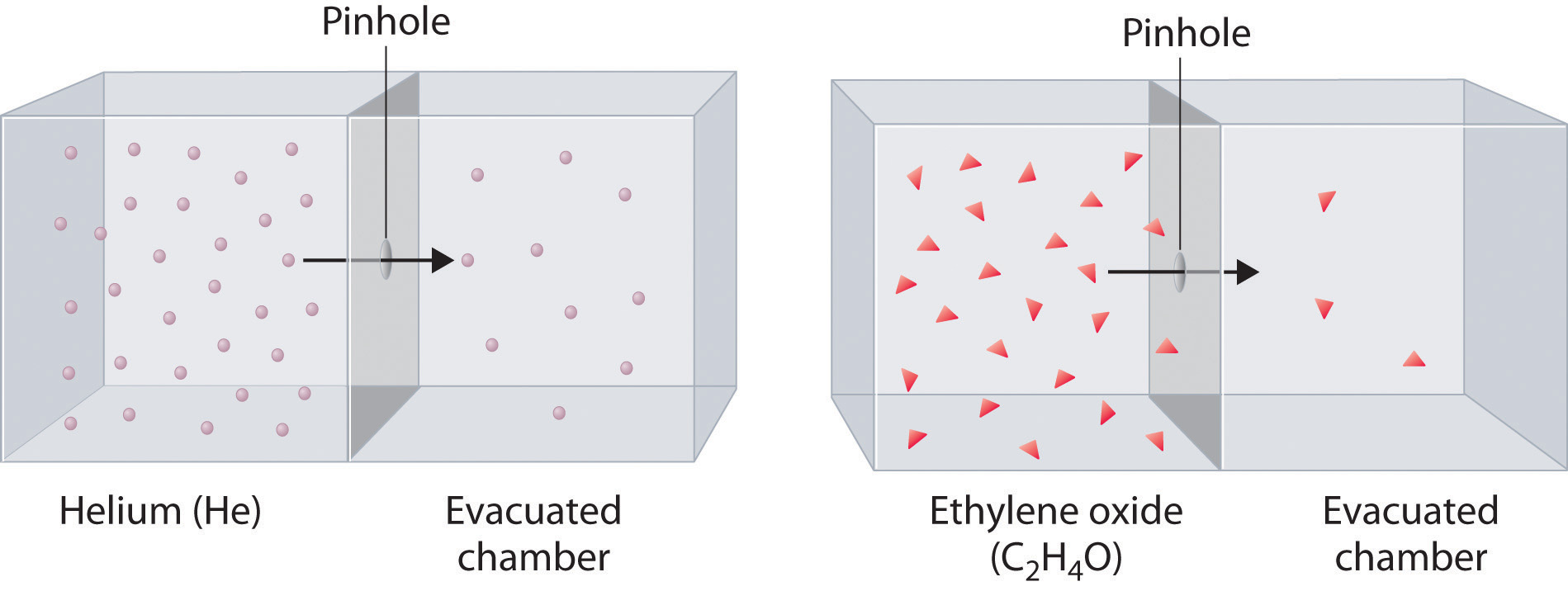
At a given temperature, heavier molecules move more slowly than lighter molecules.
During World War II, scientists working on the first atomic bomb were faced with the challenge of finding a way to obtain large amounts of \(\ce{^{235}U}\). Naturally occurring uranium is only 0.720% \(\ce{^{235}U}\), whereas most of the rest (99.275%) is \(\ce{^{238}U}\), which is not fissionable (i.e., it will not break apart to release nuclear energy) and also actually poisons the fission process. Because both isotopes of uranium have the same reactivity, they cannot be separated chemically. Instead, a process of gaseous effusion was developed using the volatile compound \(UF_6\) (boiling point = 56°C).
- Calculate the ratio of the rates of effusion of 235UF6 and 238UF6 for a single step in which UF6 is allowed to pass through a porous barrier. (The atomic mass of 235U is 235.04, and the atomic mass of 238U is 238.05.)
- If n identical successive separation steps are used, the overall separation is given by the separation in a single step (in this case, the ratio of effusion rates) raised to the nth power. How many effusion steps are needed to obtain 99.0% pure 235UF6?
Given: isotopic content of naturally occurring uranium and atomic masses of 235U and 238U
Asked for: ratio of rates of effusion and number of effusion steps needed to obtain 99.0% pure 235UF6
Strategy:
- Calculate the molar masses of 235UF6 and 238UF6, and then use Graham’s law to determine the ratio of the effusion rates. Use this value to determine the isotopic content of 235UF6 after a single effusion step.
- Divide the final purity by the initial purity to obtain a value for the number of separation steps needed to achieve the desired purity. Use a logarithmic expression to compute the number of separation steps required.
Solution:
- The molar mass of 238UF6 is
238.05 + (6)(18.998) = 352.04 g/mol
The difference is only 3.01 g/mol (less than 1%). The ratio of the effusion rates can be calculated from Graham’s law using Equation 6.8.1:
\[\rm\dfrac{\text{rate }^{235}UF_6}{\text{rate }^{238}UF_6}=\sqrt{\dfrac{352.04\;g/mol}{349.03\;g/mol}}=1.0043\] -
rate U235F6rate U238F6=352.04349.03−−−−−−√=1.0043
Thus passing UF6 containing a mixture of the two isotopes through a single porous barrier gives an enrichment of 1.0043, so after one step the isotopic content is (0.720%)(1.0043) = 0.723% 235UF6.
- B To obtain 99.0% pure 235UF6 requires many steps. We can set up an equation that relates the initial and final purity to the number of times the separation process is repeated: final purity = (initial purity)(separation)n
In this case, 0.990 = (0.00720)(1.0043)n, which can be rearranged to give
\[1.0043^n=\dfrac{0.990}{0.00720}=137.50\] - Taking the logarithm of both sides gives
\[n\ln(1.0043)=\ln(137.50)\]
\[n=\dfrac{\ln(137.50)}{\ln(1.0043)}=1148\]Thus at least a thousand effusion steps are necessary to obtain highly enriched 235U. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows a small part of a system that is used to prepare enriched uranium on a large scale.

Helium consists of two isotopes: 3He (natural abundance = 0.000134%) and 4He (natural abundance = 99.999866%). Their atomic masses are 3.01603 and 4.00260, respectively. Helium-3 has unique physical properties and is used in the study of ultralow temperatures. It is separated from the more abundant 4He by a process of gaseous effusion.
- Calculate the ratio of the effusion rates of 3He and 4He and thus the enrichment possible in a single effusion step.
- How many effusion steps are necessary to yield 99.0% pure 3He?
Answer: a. ratio of effusion rates = 1.15200; one step gives 0.000154% 3He; b. 96 steps
Rates of Diffusion or Effusion
Graham’s law is an empirical relationship that states that the ratio of the rates of diffusion or effusion of two gases is the square root of the inverse ratio of their molar masses. The relationship is based on the postulate that all gases at the same temperature have the same average kinetic energy. We can write the expression for the average kinetic energy of two gases with different molar masses:
\[KE=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{M_{\rm A}}{N_A}v_{\rm rms,A}^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{M_{\rm B}}{N_A}v_{\rm rms,B}^2\label{6.8.2}\]
Multiplying both sides by 2 and rearranging give
\[\dfrac{v_{\rm rms, B}^2}{v_{\rm rms,A}^2}=\dfrac{M_{\rm A}}{M_{\rm B}}\label{6.8.3}\]
Taking the square root of both sides gives
\[\dfrac{v_{\rm rms, B}}{v_{\rm rms,A}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{M_{\rm A}}{M_{\rm B}}}\label{6.8.4}\]
Thus the rate at which a molecule, or a mole of molecules, diffuses or effuses is directly related to the speed at which it moves. Equation 6.8.4 shows that Graham’s law is a direct consequence of the fact that gaseous molecules at the same temperature have the same average kinetic energy.
Typically, gaseous molecules have a speed of hundreds of meters per second (hundreds of miles per hour). The effect of molar mass on these speeds is dramatic, as illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) for some common gases. Because all gases have the same average kinetic energy, according to the Boltzmann distribution, molecules with lower masses, such as hydrogen and helium, have a wider distribution of speeds.

The lightest gases have a wider distribution of speeds and the highest average speeds.
Molecules with lower masses have a wider distribution of speeds and a higher average speed.
Gas molecules do not diffuse nearly as rapidly as their very high speeds might suggest. If molecules actually moved through a room at hundreds of miles per hour, we would detect odors faster than we hear sound. Instead, it can take several minutes for us to detect an aroma because molecules are traveling in a medium with other gas molecules. Because gas molecules collide as often as 1010 times per second, changing direction and speed with each collision, they do not diffuse across a room in a straight line, as illustrated schematically in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).
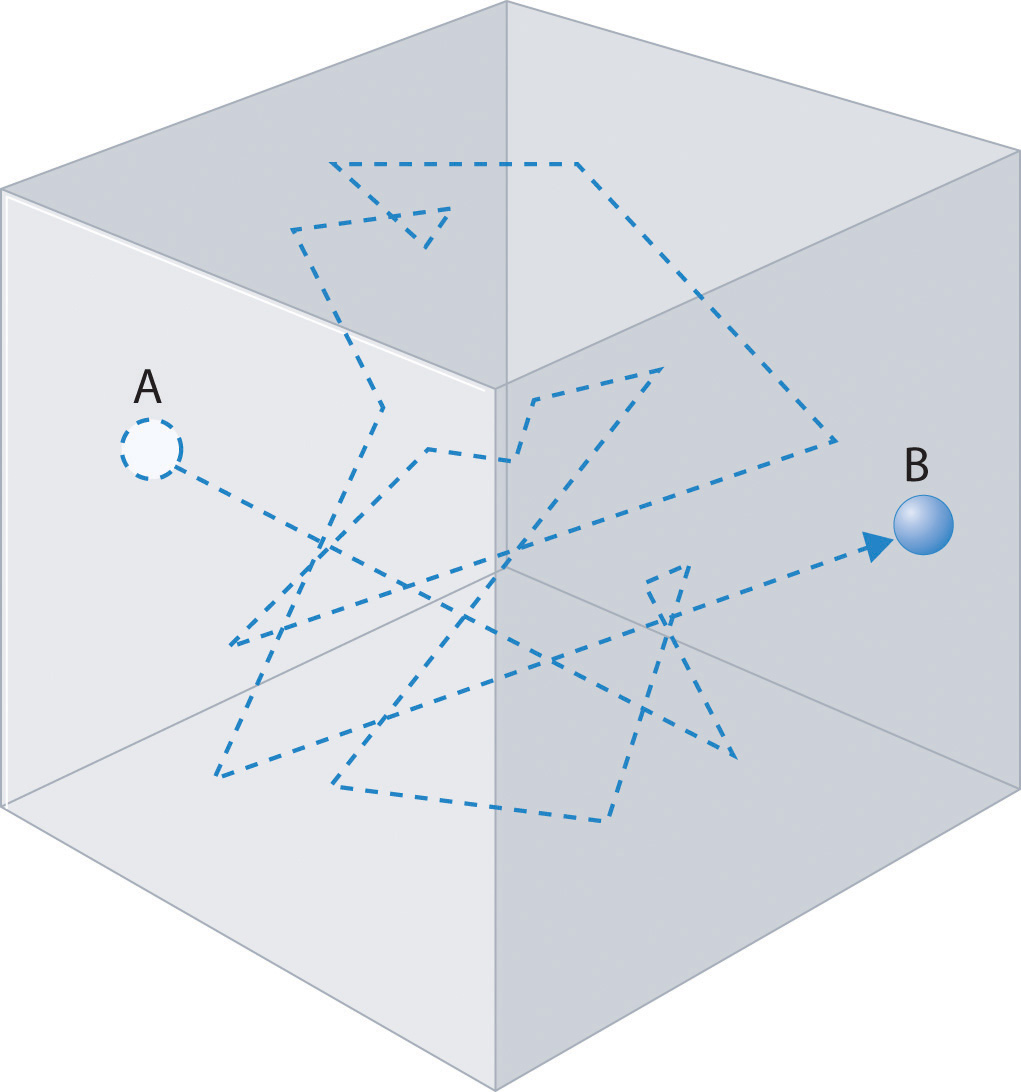
The average distance traveled by a molecule between collisions is the mean free path. The denser the gas, the shorter the mean free path; conversely, as density decreases, the mean free path becomes longer because collisions occur less frequently. At 1 atm pressure and 25°C, for example, an oxygen or nitrogen molecule in the atmosphere travels only about 6.0 × 10−8 m (60 nm) between collisions. In the upper atmosphere at about 100 km altitude, where gas density is much lower, the mean free path is about 10 cm; in space between galaxies, it can be as long as 1 × 1010 m (about 6 million miles).
The denser the gas, the shorter the mean free path.
Calculate the rms speed of a sample of cis-2-butene (C4H8) at 20°C.
Given: compound and temperature
Asked for: rms speed
Strategy:
Calculate the molar mass of cis-2-butene. Be certain that all quantities are expressed in the appropriate units and then use Equation 6.8.5 to calculate the rms speed of the gas.
Solution:
To use Equation 6.8.4, we need to calculate the molar mass of cis-2-butene and make sure that each quantity is expressed in the appropriate units. Butene is C4H8, so its molar mass is 56.11 g/mol. Thus
\[u_{\rm rms}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}}=\rm\sqrt{\dfrac{3\times8.3145\;\dfrac{J}{K\cdot mol}\times(20+273)\;K}{56.11\times10^{-3}\;kg}}=361\;m/s\]
or approximately 810 mi/h.Calculate the rms speed of a sample of radon gas at 23°C.
Answer: 1.82 × 102 m/s (about 410 mi/h)
The kinetic molecular theory of gases demonstrates how a successful theory can explain previously observed empirical relationships (laws) in an intuitively satisfying way. Unfortunately, the actual gases that we encounter are not “ideal,” although their behavior usually approximates that of an ideal gas. In Section 10.8, we explore how the behavior of real gases differs from that of ideal gases.
Graham’s law of Diffusion and Effusion: https://youtu.be/9HO-qgh-iGI
Summary
- The kinetic molecular theory of gases provides a molecular explanation for the observations that led to the development of the ideal gas law.
- Average kinetic energy:\[\overline{e_K}=\dfrac{1}{2}m{u_{\rm rms}}^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\dfrac{R}{N_A}T,\]
- Root mean square speed: \[u_{\rm rms}=\sqrt{\dfrac{u_1^2+u_2^2+\cdots u_N^2}{N}},\]
- Kinetic molecular theory of gases: \[u_{\rm rms}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}}.\]
- Graham’s law for effusion: \[\dfrac{v_{\rm rms, B}}{v_{\rm rms,A}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{M_{\rm A}}{M_{\rm B}}}\]
Diffusion is the gradual mixing of gases to form a sample of uniform composition even in the absence of mechanical agitation. In contrast, effusion is the escape of a gas from a container through a tiny opening into an evacuated space. The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass (Graham’s law), a relationship that closely approximates the rate of diffusion. As a result, light gases tend to diffuse and effuse much more rapidly than heavier gases. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions.

