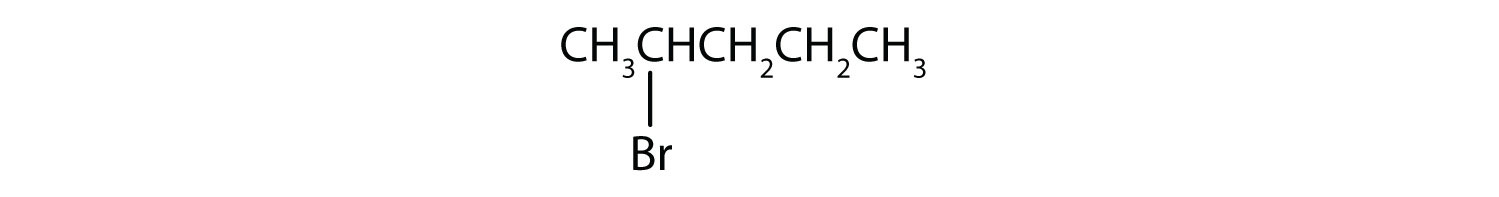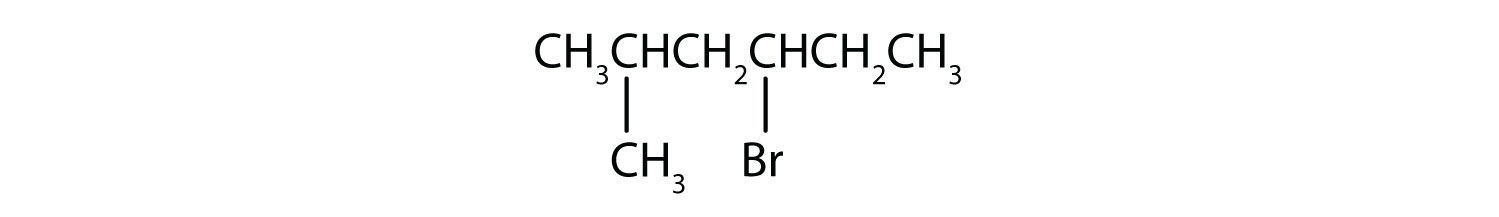1.8: Halogenated Hydrocarbons
- Page ID
- 288533
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
- To name halogenated hydrocarbons when given formulas and write formulas for these compounds when given names.
Many organic compounds are closely related to the alkanes. As we noted previously, alkanes react with halogens to produce halogenated hydrocarbons, the simplest of which have a single halogen atom substituted for a hydrogen atom of the alkane. Even more closely related are the cycloalkanes, compounds in which the carbon atoms are joined in a ring, or cyclic fashion.
The reactions of alkanes with halogens produce halogenated hydrocarbons, compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon have been replaced by halogen atoms:

The replacement of only one hydrogen atom gives an alkyl halide (or haloalkane). The IUPAC system uses the name of the parent alkane with a prefix indicating the halogen substituents, preceded by number indicating the substituent’s location. The prefixes are fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, and iodo-. Thus CH3CH2Cl has IUPAC name chloroethane. Note: Alkyl halides with simple alkyl groups (one to four carbon atoms) are often called by common names. Those with a larger number of carbon atoms are usually given IUPAC names.
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
- CH3CH2CH2Br

Solution
- The prefix for bromine (bromo) is combined with the name for a three-carbon chain (propane), preceded by a number identifying the carbon atom to which the Br atom is attached, so the IUPAC name is 1-bromopropane.
- The Cl atom (prefix chloro-) attached to the middle (second) carbon atom of a propane chain results in 2-chloropropane.
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
- CH3CH2I
- CH3CH2CH2CH2F
- Answer
-
- Iodoethane. A number is not needed because wherever the iodine atom is on the two carbon chain will be position 1.
- 1-fluorobutane. Here a number is needed because the fluorine could be on either the first or second carbon atom.
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Solution
- The parent alkane has five carbon atoms in the longest continuous chain; it is pentane. A bromo (Br) group is attached to the second carbon atom of the chain. The IUPAC name is 2-bromopentane.
- The parent alkane is hexane. Methyl (CH3) and bromo (Br) groups are attached to the second and fourth carbon atoms, respectively. Listing the substituents in alphabetical order gives the name 4-bromo-2-methylhexane.
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
- Answer
-
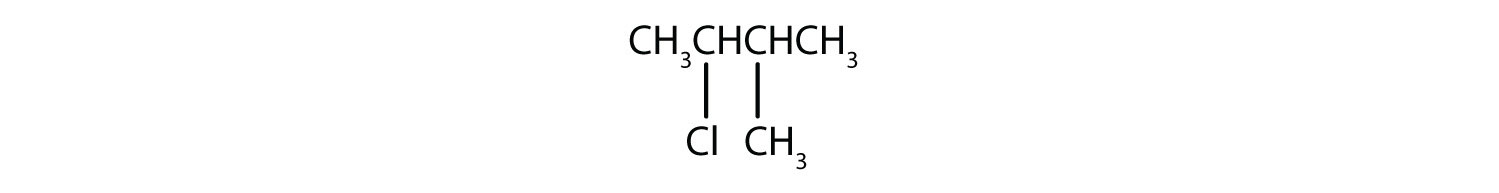
- 2-chloro-3-methylbutane.
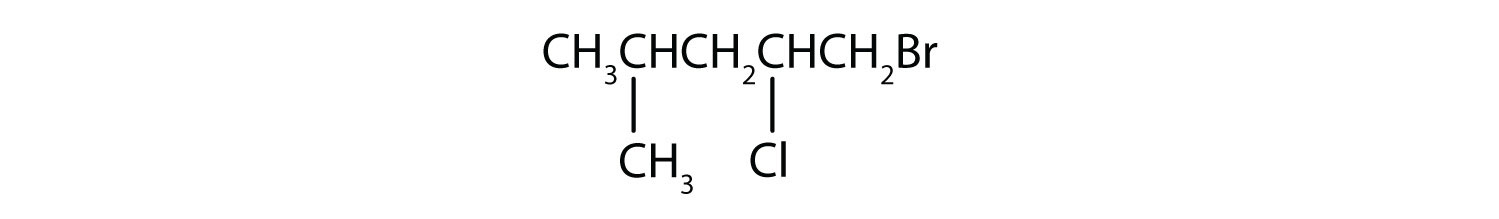
- 1-bromo-2-chloro-4-methylpentane.
To Your Health: Halogenated Hydrocarbons
Once widely used in consumer products, many chlorinated hydrocarbons are suspected carcinogens (cancer-causing substances) and also are known to cause severe liver damage. An example is carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), once used as a dry-cleaning solvent and in fire extinguishers but no longer recommended for either use. Even in small amounts, its vapor can cause serious illness if exposure is prolonged. Moreover, it reacts with water at high temperatures to form deadly phosgene (COCl2) gas, which makes the use of CCl4 in fire extinguishers particularly dangerous. Can you figure out the IUPAC name for carbon tetrachloride? It's tetrachloromethane.
Chloroethane, in contrast, is used as an external local anesthetic. When sprayed on the skin, it evaporates quickly, cooling the area enough to make it insensitive to pain. It can also be used as an emergency general anesthetic.
Bromine-containing compounds are widely used in fire extinguishers and as fire retardants on clothing and other materials. Because they too are toxic and have adverse effects on the environment, scientists are engaged in designing safer substitutes for them, as for many other halogenated compounds.
Key Takeaway
- The replacement of an hydrogen atom on an alkane by a halogen atom—F, Cl, Br, or I—forms a halogenated compound.