13.3: The Combined Gas Law
- Page ID
- 288515
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- To predict the properties of gases using the gas laws.
In the previous section you read about the ideal gas law which can be used to determine a missing property of a gas when the other three properties are known. This is helpful when one variable cannot be easily measured, such as the pressure inside a container that does not have a pressure gauge.
In this section we will turn our focus to making predictions about gases that are changing. For instance, what is the new pressure of a gas when the temperature is increased? What is the new volume of a gas when the pressure is decreased?
A systematic way to learn relationships between properties of gases is to control as many variables as possible and to study how one variable is affected when another changes. For instance, study how the pressure of a gas changes when the temperature is increased or decreased (and other variables such as the amount of gas and volume are kept constant). With four different possible variables (pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas) there are several possible relationships to study. Each can be represented by a mathematical equation.
A more realistic scenario in which multiple properties are changing simultaneously can be represented by a mathematical equation that includes all of the variables that describe a gas. Such an equation is called the combined gas law because it is constructed from a combination of the individual gas laws (mathematical equations) that describe pairs of properties.
In this section you will learn to use the combined gas law equation, including how to use it as a replacement for all of the individual gas laws that describe how different pairs of properties change individually.
If the units of similar quantities are not the same, one of them must be converted to the other quantity’s units for the calculation to work out properly. It does not matter which quantity is converted to a different unit; the only thing that matters is that the conversion and subsequent algebra are performed properly. The following example illustrates this process.
Combined Gas Law
Other gas laws can be constructed, but we will focus on one in this section, the combined gas law.
\[\mathrm{\dfrac{P_1V_1}{n_1T_1}=\dfrac{P_2V_2}{n_2T_2}}\]
Notice that this equation contains copies of each variable (i.e two pressures, two volumes, etc.). The subscript 1 indicates an initial value (before a change); a subscript 2 indicates a final value (after a change). As with the ideal gas law, the temperature must be expressed in Kelvin. For the other variables any relevant unit may be used, but the units must be paired. In other words, both pressures must have the same unit, both volumes must have the same unit, etc.
A sample of gas has P1 = 1.50 atm, V1 = 10.5 L, and T1 = 300 K. What is the final volume if P2 = 0.750 atm and T2 = 350 K?
SolutionUsing the combined gas law, substitute for five of the quantities. Since the amount of gas is not changing, n1 and n2 are the same and cancel out.
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{(1.50\: atm)(10.5\: L)}{300\: K}=\dfrac{(0.750\: atm)(V_2)}{350\: K}}\)
We algebraically rearrange this expression to isolate V2 on one side of the equation:
\(\mathrm{V_2=\dfrac{(1.50\: atm)(10.5\: L)(350\: K)}{(300\: K)(0.750\: atm)}=24.5\: L}\)
Note how all the units cancel except the unit for volume.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
A sample of gas has P1 = 0.768 atm, V1 = 10.5 L, and T1 = 300 K. What is the final pressure if V2 = 7.85 L and T2 = 250 K?
- Answer
-
0.856 atm
A balloon containing a sample of gas has a temperature of 22°C and a pressure of 1.09 atm in an airport in Cleveland. The balloon has a volume of 1,070 mL. The balloon is transported by plane to Denver, where the temperature is 11°C and the pressure is 655 torr. What is the new volume of the balloon?
Solution
The first task is to convert all quantities to the proper and consistent units. The temperatures must be expressed in kelvins, and the pressure units are different so one of the quantities must be converted. Let us convert the atmospheres to torr:
22°C + 273 = 295 K = T1
11°C + 273 = 284 K = T2
\(\mathrm{1.09\: atm\times\dfrac{760\: torr}{1\: atm}=828\: torr = P_1}\)
Now we can substitute the quantities into the combined has law:
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{(828\: torr)(1,070\: mL)}{295\: K}=\dfrac{(655\: torr)\times V_f}{284\: K}}\)
To solve for V2, we multiply the 284 K in the denominator of the right side into the numerator on the left, and we divide 655 torr in the numerator of the right side into the denominator on the left:
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{(828\: torr)(1,070\: mL)(284\: K)}{(295\: K)(655\: torr)}=V_2}\)
Notice that torr and kelvins cancel, as they are found in both the numerator and denominator. The only unit that remains is milliliters, which is a unit of volume. So V2 = 1,300 mL. The overall change is that the volume of the balloon has increased by 230 mL.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
A balloon used to lift weather instruments into the atmosphere contains gas having a volume of 1,150 L on the ground, where the pressure is 0.977 atm and the temperature is 18°C. Aloft, this gas has a pressure of 6.88 torr and a temperature of −15°C. What is the new volume of the gas?
- Answer
-
110,038 L
Direct vs. Inverse Relationships
If only two properties of a gas are changing, it is usually possible to make a qualitative prediction about the size of the unknown variable. This can be very helpful when checking your work!
Direct Relationships
Experiments indicate that as the temperature of a gas sample is increased, its volume increases as long as the pressure and the amount of gas remain constant. Because volume increases as temperature increases, these two properties are directly proportional. If you are solving a problem in which only temperature and volume are changing, then you can check your work to make sure that volume increases when temperature increases and vice versa.
What happens to the volume of a gas if its temperature is decreased? Assume that all other conditions remain constant.
SolutionIf the temperature of a gas sample is decreased, the volume decreases as well.
What happens to the temperature of a gas if its volume is increased? Assume that all other conditions remain constant.
- Answer
-
The temperature increases.
A gas sample at 20°C has an initial volume of 20.0 L. What is its volume if the temperature is changed to 60°C? Does the answer make sense? Assume that the pressure and the amount of the gas remain constant.
Solution
Although the temperatures are given in degrees Celsius, we must convert them to the kelvins before we can use Charles’s law. Thus,
20°C + 273 = 293 K = T1 60°C + 273 = 333 K = T2
Now we can substitute these values into Charles’s law, along with the initial volume of 20.0 L:
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{20.0\: L}{293\: K}=\dfrac{V_2}{333\: K}}\)
Multiplying the 333 K to the other side of the equation, we see that our temperature units will cancel:
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{(333\: K)(20.0\: L)}{293\: K}=V_2}\)
Solving for the final volume, V2 = 22.7 L. So, as the temperature is increased, the volume increases. This makes sense because volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (as long as the pressure and the amount of the remain constant).
A gas sample at 35°C has an initial volume of 5.06 L. What is its volume if the temperature is changed to −35°C? First make a prediction: will the new volume be higher or lower than 5.06 L? Then calculate the answer. Assume that the pressure and the amount of the gas remain constant.
- Answer
-
The final volume should be lower than 5.06 L because when temperature decreases volume also decreases. The final volume is 3.91 L.
Inverse Relationships
If the amount of gas in a sample and its temperature are kept constant, then as the pressure of a gas is increased, the volume of the gas decreases proportionately. Because volume decreases as pressure increases, these two properties are inversely proportional. If you are solving a problem in which only pressure and volume are changing, then you can check your work to make sure that volume decreases when pressure increases and vice versa.
What happens to the volume of a gas if its pressure is increased? Assume all other conditions remain the same.
Solution
If the pressure of a gas is increased, the volume decreases in response.
What happens to the pressure of a gas if its volume is increased? Assume all other conditions remain the same.
- Answer
-
If the volume of a gas is increased, the pressure decreases.
If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 1.56 atm and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final volume if the pressure is reduced to 0.987 atm? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant. First predict whether the answer will be larger or smaller than 7.02 L, then perform the calculation to see if you were correct.
Solution
The key in problems like this is to be able to identify which quantities represent which variables from the relevant equation. The way the question is worded, you should be able to tell that 1.56 atm is P1, 7.02 L is V1, and 0.987 atm is P2. What we are looking for is the final volume—V2. Therefore, substituting these values into P1V1 = P2V2: (Because the amount of gas and temperature are not changing n1 and n2 cancel out and T1 and T2 cancel out)
(1.56 atm)(7.02 L) = (0.987 atm) × V2
The expression has atmospheres on both sides of the equation, so they cancel algebraically:
(1.56)(7.02 L) = (0.987) × V2
Now we divide both sides of the expression by 0.987 to isolate V2, the quantity we are seeking:
\(\mathrm{\dfrac{(1.56)(7.02\: L)}{0.987}=V_2}\)
Performing the multiplication and division, we get the value of V2, which is 11.1 L. The volume increases. This should make sense because the pressure decreases, so pressure and volume are inversely related.
If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 3.66 atm and an initial volume of 11.8 L, what is the final pressure if the volume is reduced to 5.09 L? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant.
- Answer
-
8.48 atm
If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 1.56 atm and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final volume if the pressure is changed to 1,775 mm Hg? Does the answer make sense? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant.
Solution
This example is similar to Example \(\PageIndex{2}\), except now the final pressure is expressed in mm Hg. For the math to work out properly, one of the pressure values must be converted to the other unit. Let us change the initial pressure to mm Hg:
\(\mathrm{1.56\: atm\times\dfrac{760\: mm\:Hg}{1\: atm}=1,190\: mm \:Hg}\)
Now we can use Boyle’s law:
(1,190 mm Hg)(7.02 L) = (1,775 mm Hg) × V2
Torr cancels algebraically from both sides of the equation, leaving
(1,190)(7.02 L) = (1,775) × V2
Now we divide both sides of the equation by 1,775 to isolate V2 on one side. Solving for the final volume,
\(\mathrm{V_2=\dfrac{(1,190)(7.02\: L)}{1,775}=4.71\: L}\)
Because the pressure increases, it makes sense that the volume decreases.
The answer for the final volume is essentially the same if we converted the 1,775 mm Hg to atmospheres: \(\mathrm{1,775\: mm\:\times\dfrac{1\: atm}{760\: mm \:Hg}=2.336\: atm}\). Using Boyle’s law: (1.56 atm)(7.02 L) = (2.335 atm) × V2; \(\mathrm{V_f=\dfrac{(1.56\: atm)(7.02\: L)}{2.336\: atm}=4.69\: L}\).
If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 375 torr and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final pressure if the volume is changed to 4,577 mL? Does the answer make sense? Assume that amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant.
- Answer
-
575 torr. Since the volume decreased, it makes sense that the pressure increased because pressure and volume are inversely related.
Breathing certainly is a major contribution to your health! Without breathing, we could not survive. Curiously, the act of breathing itself is little more than an application of the inverse relationship between volume and pressure (called Boyle’s law).
The lungs are a series of ever-narrowing tubes that end in a myriad of tiny sacs called alveoli. It is in the alveoli that oxygen from the air transfers to the bloodstream and carbon dioxide from the bloodstream transfers to the lungs for exhalation. For air to move in and out of the lungs, the pressure inside the lungs must change, forcing the lungs to change volume—just as predicted by Boyle’s law.
The pressure change is caused by the diaphragm, a muscle that covers the bottom of the lungs. When the diaphragm moves down, it expands the size of our lungs. When this happens, the air pressure inside our lungs decreases slightly. This causes new air to rush in, and we inhale. The pressure decrease is slight—only 3 torr, or about 0.4% of an atmosphere. We inhale only 0.5–1.0 L of air per normal breath.
Exhaling air requires that we relax the diaphragm, which pushes against the lungs and slightly decreases the volume of the lungs. This slightly increases the pressure of the air in the lungs, and air is forced out; we exhale. Only 1–2 torr of extra pressure is needed to exhale. So with every breath, our own bodies are performing an experimental test of Boyle’s law.
Determining Relationships
Think about the two relationships that were just discussed:
- Volume and temperature are directly related: when one increases, the other also increases
- Pressure and volume are inversely related: when one increases, the other decreases
Now take a look at the combined gas law and see if you can figure out whether relationships between other variables (e.g. pressure and temperature) will be direct or inverse.
\[\mathrm{\dfrac{P_1V_1}{n_1T_1}=\dfrac{P_2V_2}{n_2T_2}}\]
You can determine whether a pair of properties are directly or inversely related by looking at their relative positions in the mathematical equation. If two variables must be multiplied to obtain a constant, like P1 and V1, then they are inversely proportional. If two variables must be divided to obtain a constant, like V1 and T1, then they are directly proportional.
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
The ideal gas equation of state applies to mixtures just as to pure gases. It was in fact with a gas mixture, ordinary air, that Boyle, Gay-Lussac and Charles did their early experiments. The only new concept we need in order to deal with gas mixtures is the partial pressure, a concept invented by the famous English chemist John Dalton (1766-1844). Dalton reasoned that the low density and high compressibility of gases indicates that they consist mostly of empty space; from this it follows that when two or more different gases occupy the same volume, they behave entirely independently. The contribution that each component of a gaseous mixture makes to the total pressure of the gas is known as the partial pressure of that gas.
The definition of Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures that address this is:
The total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of its components
which is expressed algebraically as
\[P_{total}=P_1+P_2+P_3 ... = \sum_i P_i\]
or, equivalently
\[ P_{total} = \dfrac{RT}{V} \sum_i n_i\]
There is also a similar relationship based on volume fractions, known as Amagat's law of partial volumes. It is exactly analogous to Dalton's law, in that it states that the total volume of a mixture is just the sum of the partial volumes of its components. But there are two important differences: Amagat's law holds only for ideal gases which must all be at the same temperature and pressure. Dalton's law has neither of these restrictions. Although Amagat's law seems intuitively obvious, it sometimes proves useful in chemical engineering applications. We will make no use of it in this course.
Three flasks having different volumes and containing different gases at various pressures are connected by stopcocks as shown. When the stopcocks are opened,
- What will be the pressure in the system?
- Which gas will be most abundant in the mixture?
Assume that the temperature is uniform and that the volume of the connecting tubes is negligible.
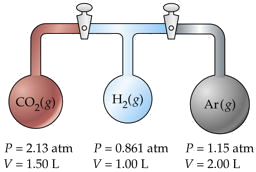
Solution
The trick here is to note that the total number of moles nT and the temperature remain unchanged, so we can make use of Boyle's law PV = constant. We will work out the details for CO2 only, denoted by subscripts a.
For CO2,
\[P_aV_a = (2.13\; atm)(1.50\; L) = 3.19\; L \cdot atm\]
Adding the PV products for each separate container, we obtain
\[\sum_i P_iV_i = 6.36\; L \cdot atm = n_T RT\]
We will call this sum P1V1. After the stopcocks have been opened and the gases mix, the new conditions are denoted by P2V2.
From Boyle's law (\(\ref{Eq1}\),
\[P_1V_1 = P_2V_2 = 6.36\; L \cdot atm\]
\[V_2 = \sum_i V_i = 4.50\; L\]
Solving for the final pressure P2 we obtain (6.36 L-atm)/(4.50 L) = 1.41 atm.
For part (b), note that the number of moles of each gas is n = PV/RT. The mole fraction of any one gas is Xi = ni /nT . For CO2, this works out to (3.19/RT) / (6.36/RT) = 0.501. Because this exceeds 0.5, we know that this is the most abundant gas in the final mixture.
Dalton’s law states that in a gas mixture (\(P_{total}\)) each gas will exert a pressure independent of the other gases (\(P_n\)) and each gas will behave as if it alone occupies the total volume. By extension, the partial pressure of each gas can be calculated by multiplying the total pressure (\(P_{total}\)) by the gas percentage (%).
\[P_{Total} = P_1 + P_2 + P_3 + P_4 + ... + P_n\]
or
\[P_n = \dfrac{\text{% of individual gas}_n}{P_{Total}}\]
| Gas | Partial Pressure (mm Hg) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen, (N_2\) | \(P_{N_2}\) = 594 | 78 |
| Oxygen, \(O_2\) | \(P_{O_2}\)= 160 | 21 |
| Carbon Dioxide, \(CO_2\) | \(P_{CO_2}\) = 0.25 | 0.033 |
| Water Vapor, \(H_2O\) | \(P_{H_2O}\) = 5.7 | 0.75 |
| Other trace gases | \(P_{Other}\) = 0.05 | 0.22 |
| Total air | \(P_{Total}\) = 760 | 1 |
Application of Dalton's Law: Collecting Gases over Water
A common laboratory method of collecting the gaseous product of a chemical reaction is to conduct it into an inverted tube or bottle filled with water, the opening of which is immersed in a larger container of water. This arrangement is called a pneumatic trough, and was widely used in the early days of chemistry. As the gas enters the bottle it displaces the water and becomes trapped in the upper part.
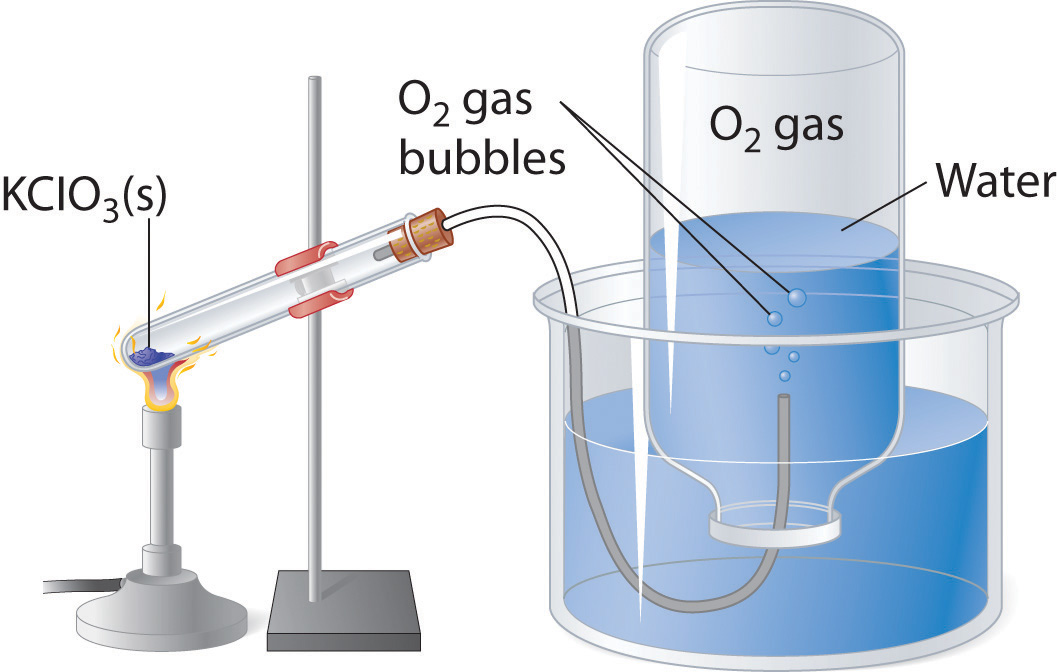
The volume of the gas can be observed by means of a calibrated scale on the bottle, but what about its pressure? The total pressure confining the gas is just that of the atmosphere transmitting its force through the water. (An exact calculation would also have to take into account the height of the water column in the inverted tube.) But liquid water itself is always in equilibrium with its vapor, so the space in the top of the tube is a mixture of two gases: the gas being collected, and gaseous H2O. The partial pressure of H2O is known as the vapor pressure of water and it depends on the temperature. In order to determine the quantity of gas we have collected, we must use Dalton's Law to find the partial pressure of that gas.
Oxygen gas was collected over water as shown above. The atmospheric pressure was 754 torr, the temperature was 22°C, and the volume of the gas was 155 mL. The vapor pressure of water at 22°C is 19.8 torr. Use this information to estimate the number of moles of \(O_2\) produced.
Solution
From Dalton's law,
\[P_{O_2} = P_{total} – P_{H_2O} = 754 – 19.8 = 734 \; torr = 0.966\; atm \nonumber\]
Now use the Ideal Gas Law to convert to moles
\[ n =\dfrac{PV}{RT} = \dfrac{(0.966\; atm)(0.155\;L)}{(0.082\; L atm mol^{-1} K^{-1})(295\; K)}= 0.00619 \; mol \nonumber\]
Henry’s Law
Henry's law is one of the gas laws formulated by William Henry in 1803. It states: "At a constant temperature, the amount of a given gas that dissolves in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid." An equivalent way of stating the law is that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid.
To explain this law, Henry derived the equation:
\[ C =k P_{gas} \]
where
Henry’s Law tells us that the greater the pressure of gas above the surface of a liquid, the higher the concentration of the gas in the liquid. Also, Henry’s law tells us that gases diffuse from areas of high gas concentration to areas of low gas concentration.
- Henry's law only works if the molecules are at equilibrium.
- Henry's law does not work for gases at high pressures (e.g., \(N_{2\;(g)}\) at high pressure becomes very soluble and harmful when in the blood supply).
- Henry's law does not work if there is a chemical reaction between the solute and solvent (e.g., \(HCl_{(g)}\) reacts with water by a dissociation reaction to generate \(H_3O^+\) and \(Cl^-\) ions).
Application of Henry's Law: Scuba diving
Our respiratory systems are designed to maintain the proper oxygen concentration in the blood when the partial pressure of O2 is 0.21 atm, its normal sea-level value. Below the water surface, the pressure increases by 1 atm for each 10.3 m increase in depth; thus a scuba diver at 10.3 m experiences a total of 2 atm pressure pressing on the body. In order to prevent the lungs from collapsing, the air the diver breathes should also be at about the same pressure.

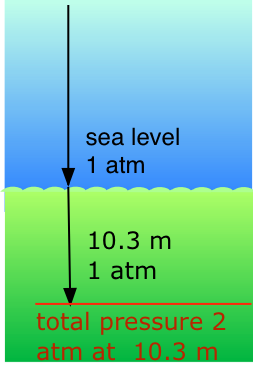
But at a total pressure of 2 atm, the partial pressure of \(O_2\) in ordinary air would be 0.42 atm; at a depth of 100 ft (about 30 m), the \(O_2\) pressure of 0.8 atm would be far too high for health. For this reason, the air mixture in the pressurized tanks that scuba divers wear must contain a smaller fraction of \(O_2\). This can be achieved most simply by raising the nitrogen content, but high partial pressures of N2 can also be dangerous, resulting in a condition known as nitrogen narcosis. The preferred diluting agent for sustained deep diving is helium, which has very little tendency to dissolve in the blood even at high pressures.
Certain diseases—such as emphysema, lung cancer, and severe asthma—primarily affect the lungs. Respiratory therapists help patients with breathing-related problems. They can evaluate, help diagnose, and treat breathing disorders and even help provide emergency assistance in acute illness where breathing is compromised.
Most respiratory therapists must complete at least two years of college and earn an associate’s degree, although therapists can assume more responsibility if they have a college degree. Therapists must also pass state or national certification exams. Once certified, respiratory therapists can work in hospitals, doctor’s offices, nursing homes, or patient’s homes. Therapists work with equipment such as oxygen tanks and respirators, may sometimes dispense medication to aid in breathing, perform tests, and educate patients in breathing exercises and other therapy.
Because respiratory therapists work directly with patients, the ability to work well with others is a must for this career. It is an important job because it deals with one of the most crucial functions of the body.
Concept Review Exercises
- What properties do the gas laws help us predict?
- What makes the ideal gas law different from the other gas laws?
Answers
- Gas laws relate four properties: pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles.
- The ideal gas law does not require that the properties of a gas change.
Key Takeaway
- The physical properties of gases are predictable using mathematical formulas known as gas laws.
- \(C\) is the solubility of a gas at a fixed temperature in a particular solvent (in units of M or mL gas/L)
- \(k\) is Henry's law constant (often in units of M/atm)
- \(P_{gas}\) is the partial pressure of the gas (often in units of Atm)
Exercises
-
What conditions of a gas sample should remain constant for Boyle’s law to be used?
-
What conditions of a gas sample should remain constant for Charles’s law to be used?
-
Does the identity of a gas matter when using Boyle’s law? Why or why not?
-
Does the identity of a gas matter when using Charles’s law? Why or why not?
-
A sample of nitrogen gas is confined to a balloon that has a volume of 1.88 L and a pressure of 1.334 atm. What will be the volume of the balloon if the pressure is changed to 0.662 atm? Assume that the temperature and the amount of the gas remain constant.
-
A sample of helium gas in a piston has a volume of 86.4 mL under a pressure of 447 torr. What will be the volume of the helium if the pressure on the piston is increased to 1,240 torr? Assume that the temperature and the amount of the gas remain constant.
-
If a gas has an initial pressure of 24,650 Pa and an initial volume of 376 mL, what is the final volume if the pressure of the gas is changed to 775 torr? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant.
-
A gas sample has an initial volume of 0.9550 L and an initial pressure of 564.5 torr. What would the final pressure of the gas be if the volume is changed to 587.0 mL? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant.
-
A person draws a normal breath of about 1.00 L. If the initial temperature of the air is 18°C and the air warms to 37°C, what is the new volume of the air? Assume that the pressure and amount of the gas remain constant.
-
A person draws a normal breath of about 1.00 L. If the initial temperature of the air is −10°C and the air warms to 37°C, what is the new volume of the air? Assume that the pressure and the amount of the gas remain constant.
-
An air/gas vapor mix in an automobile cylinder has an initial temperature of 450 K and a volume of 12.7 cm3. The gas mix is heated to 565°C. If pressure and amount are held constant, what is the final volume of the gas in cubic centimeters?
-
Given the following conditions for a gas: Vi = 0.665 L, Ti = 23.6°C, Vf = 1.034 L. What is Tf in degrees Celsius and kelvins?
-
Assuming the amount remains the same, what must be the final volume of a gas that has an initial volume of 387 mL, an initial pressure of 456 torr, an initial temperature of 65.0°C, a final pressure of 1.00 atm, and a final temperature of 300 K?
-
When the nozzle of a spray can is depressed, 0.15 mL of gas expands to 0.44 mL, and its pressure drops from 788 torr to 1.00 atm. If the initial temperature of the gas is 22.0°C, what is the final temperature of the gas?
-
Use the ideal gas law to show that 1 mol of a gas at STP has a volume of about 22.4 L.
-
Use a standard conversion factor to determine a value of the ideal gas law constant R that has units of L•torr/mol•K.
-
How many moles of gas are there in a 27.6 L sample at 298 K and a pressure of 1.44 atm?
-
How many moles of gas are there in a 0.066 L sample at 298 K and a pressure of 0.154 atm?
-
A 0.334 mol sample of carbon dioxide gas is confined to a volume of 20.0 L and has a pressure of 0.555 atm. What is the temperature of the carbon dioxide in kelvins and degrees Celsius?
-
What must V be for a gas sample if n = 4.55 mol, P = 7.32 atm, and T = 285 K?
21. What is the pressure of 0.0456 mol of Ne gas contained in a 7.50 L volume at 29°C?
22. What is the pressure of 1.00 mol of Ar gas that has a volume of 843.0 mL and a temperature of −86.0°C?
23. A mixture of the gases \(N_2\), \(O_2\), and \(Ar\) has a total pressure of 760 mm Hg. If the partial pressure of \(N_2\) is 220 mm Hg and of \(O_2\) is 470 mm Hg, What is the partial pressure of \(Ar\)?
24. What percent of the gas above is Ar?
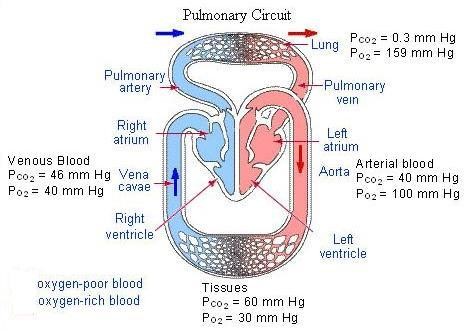
25. Apply Henry’s Law to the diagram below to explain:
why oxygen diffuses from the alveoli of the lungs into the blood and from the blood into the tissues of the body. why carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissues into the blood and from the blood into the alveoli and then finally out into the atmosphere.
Answers
-
temperature and amount of the gas
6. 31.1 mL
7. 92.1 mL
8. 918.4 torr
9. 1.07 L
10. 1.18 L
11. 23.7 cm3
12. 461 K; 1880C
13. 206 mL
14. 835 K; 5620C
15. The ideal gas law confirms that 22.4 L equals 1 mol.
16. \(\dfrac{760\: torr}{1\: atm}\)
17. 1.63 mol
18. 4.2 x 10-4 mol
19. 405 K; 132°C
20. 14.5 L
21. 0.151 atm
22. 18.2 atm
23. 70 mm Hg
24. 9.2%
25. Gases diffuse from high concentration to low concentration (Henry's Law). The partial pressure of oxygen is high in the alveoli and low in the blood of the pulmonary capillaries. As a result, oxygen diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the alveoli into the blood. It's also higher partial pressure in the blood than in the tissues, hence it transfers to the tissues. On the other hand, carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissues (highest CO2 partial pressure) and across the respiratory membrane from the blood into the alveoli and out to the atmosphere.

