13.5: Water Properties
- Page ID
- 259382
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
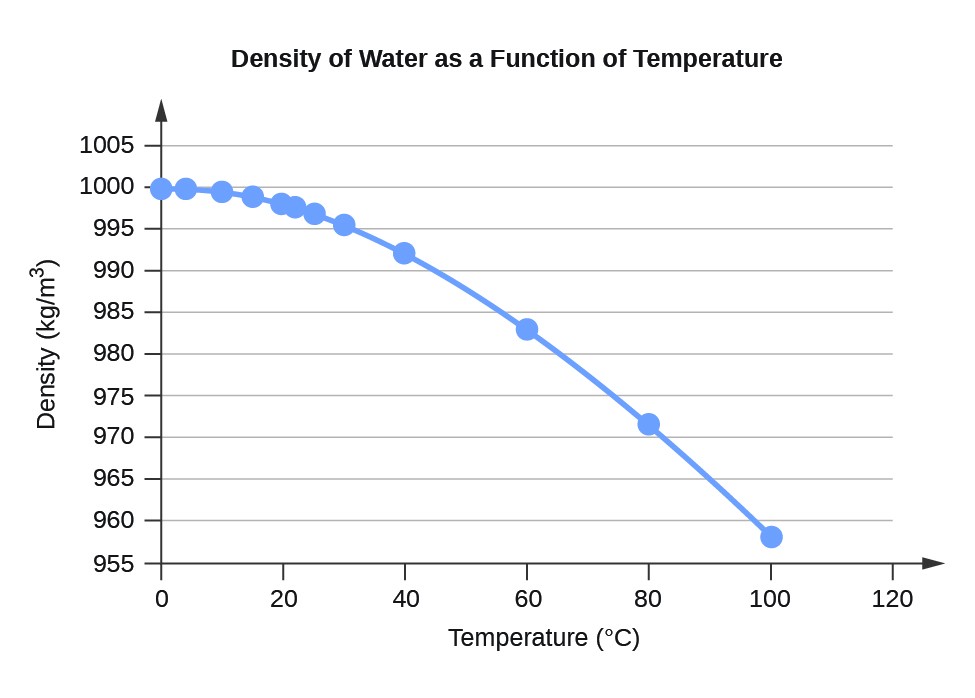
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)| Table 1. Water Density (kg/m3) at Different Temperatures (°C) | |
|---|---|
| Temperature[1] | Density |
| 0 | 999.8395 |
| 4 | 999.9720 (density maximum) |
| 10 | 999.7026 |
| 15 | 999.1026 |
| 20 | 998.2071 |
| 22 | 997.7735 |
| 25 | 997.0479 |
| 30 | 995.6502 |
| 40 | 992.2 |
| 60 | 983.2 |
| 80 | 971.8 |
| 100 | 958.4 |
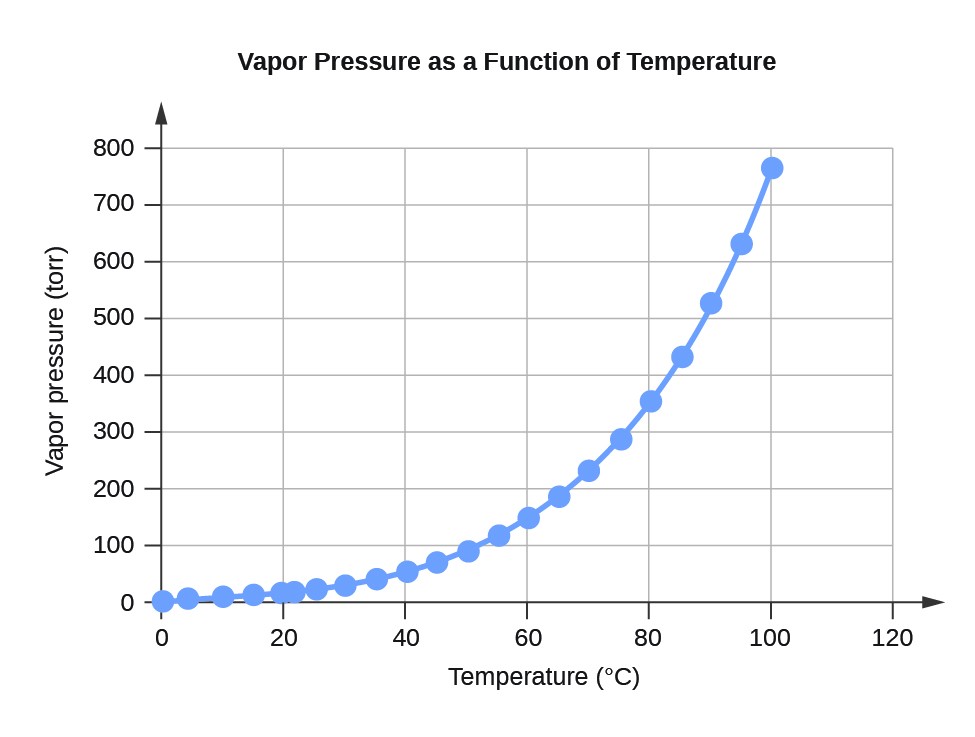
| Table 2. Water Vapor Pressure at Different Temperatures (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Vapor Pressure (torr) | Vapor Pressure (Pa) |
| 0 | 4.6 | 613.2812 |
| 4 | 6.1 | 813.2642 |
| 10 | 9.2 | 1226.562 |
| 15 | 12.8 | 1706.522 |
| 20 | 17.5 | 2333.135 |
| 22 | 19.8 | 2639.776 |
| 25 | 23.8 | 3173.064 |
| 30 | 31.8 | 4239.64 |
| 35 | 42.2 | 5626.188 |
| 40 | 55.3 | 7372.707 |
| 45 | 71.9 | 9585.852 |
| 50 | 92.5 | 12332.29 |
| 55 | 118.0 | 15732 |
| 60 | 149.4 | 19918.31 |
| 65 | 187.5 | 24997.88 |
| 70 | 233.7 | 31157.35 |
| 75 | 289.1 | 38543.39 |
| 80 | 355.1 | 47342.64 |
| 85 | 433.6 | 57808.42 |
| 90 | 525.8 | 70100.71 |
| 95 | 633.9 | 84512.82 |
| 100 | 760.0 | 101324.7 |
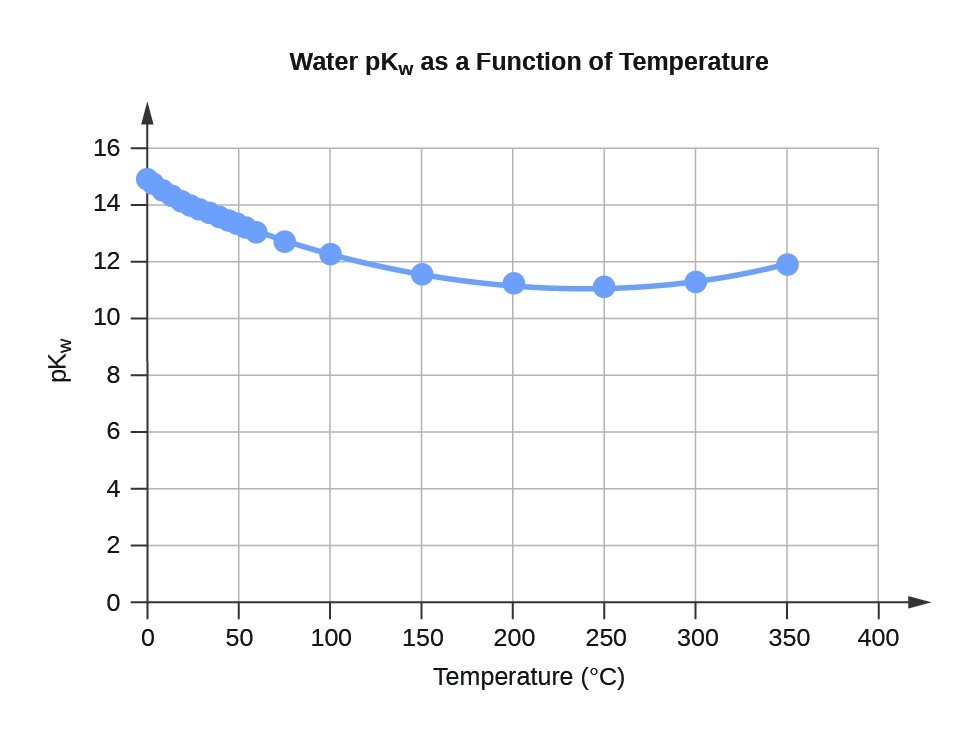
| Table 3. Water Kw and pKw at Different Temperatures (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Kw 10–14 | pKw[2] |
| 0 | 0.112 | 14.95 |
| 5 | 0.182 | 14.74 |
| 10 | 0.288 | 14.54 |
| 15 | 0.465 | 14.33 |
| 20 | 0.671 | 14.17 |
| 25 | 0.991 | 14.00 |
| 30 | 1.432 | 13.84 |
| 35 | 2.042 | 13.69 |
| 40 | 2.851 | 13.55 |
| 45 | 3.917 | 13.41 |
| 50 | 5.297 | 13.28 |
| 55 | 7.080 | 13.15 |
| 60 | 9.311 | 13.03 |
| 75 | 19.95 | 12.70 |
| 100 | 56.23 | 12.25 |
| Table 4. Specific Heat Capacity for Water |
|---|
| C°(H2O(l)) = 4179 J∙K-1∙kg-1 |
| C°(H2O(s)) = 1864 J∙K-1∙kg-1 |
| C°(H2O(g)) = 2093 J∙K-1∙kg-1 |
| Table 5. Standard Water Melting and Boiling Temperatures and Enthalpies of the Transitions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | ||
| melting | 273.15 | 6.088 |
| boiling | 373.15 | 40.656 (44.016 at 298 K) |
| Table 6. Water Cryoscopic (Freezing Point Depression) and Ebullioscopic (Boiling Point Elevation) Constants |
|---|
| Kf = 1.86 K∙mol-1∙kg-1 (cryoscopic constant) |
| Kb = 0.51 K∙mol-1∙kg-1 (cryoscopic constant) |

Water full-range spectral absorption curve. This curve shows the full-range spectral absorption for water. The y-axis signifies the absorption in 1/cm. If we divide 1 by this value, we will obtain the length of the path (in cm) after which the intensity of a light beam passing through water decays by a factor of the base of the natural logarithm e (e = 2.718281828).
- Chemistry. Provided by: OpenStax College. Located at: http://openstaxcollege.org. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/chemistry/get

