8.5: Effusion and Diffusion of Gases
- Page ID
- 233040
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define and explain effusion and diffusion
- State Graham’s law and use it to compute relevant gas properties
If you have ever been in a room when a piping hot pizza was delivered, you have been made aware of the fact that gaseous molecules can quickly spread throughout a room, as evidenced by the pleasant aroma that soon reaches your nose. Although gaseous molecules travel at tremendous speeds (hundreds of meters per second), they collide with other gaseous molecules and travel in many different directions before reaching the desired target. At room temperature, a gaseous molecule will experience billions of collisions per second. The mean free path is the average distance a molecule travels between collisions. The mean free path increases with decreasing pressure; in general, the mean free path for a gaseous molecule will be hundreds of times the diameter of the molecule.
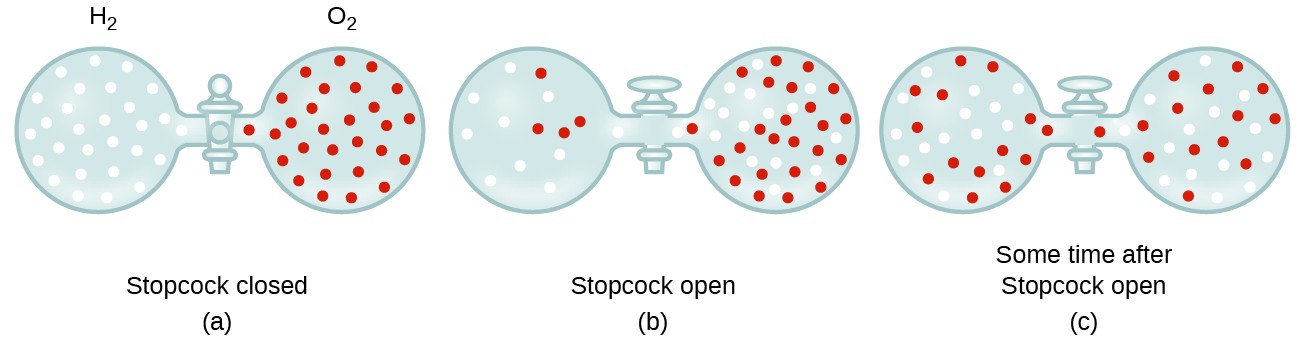
In general, we know that when a sample of gas is introduced to one part of a closed container, its molecules very quickly disperse throughout the container; this process by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration is called diffusion (shown in Figure 1). The gaseous atoms or molecules are, of course, unaware of any concentration gradient, they simply move randomly—regions of higher concentration have more particles than regions of lower concentrations, and so a net movement of species from high to low concentration areas takes place. In a closed environment, diffusion will ultimately result in equal concentrations of gas throughout, as depicted in Figure 1. The gaseous atoms and molecules continue to move, but since their concentrations are the same in both bulbs, the rates of transfer between the bulbs are equal (no net transfer of molecules occurs).
We are often interested in the rate of diffusion, the amount of gas passing through some area per unit time:
The diffusion rate depends on several factors: the concentration gradient (the increase or decrease in concentration from one point to another); the amount of surface area available for diffusion; and the distance the gas particles must travel. Note also that the time required for diffusion to occur is inversely proportional to the rate of diffusion, as shown in the rate of diffusion equation.
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion, the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum (Figure 2). Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same.
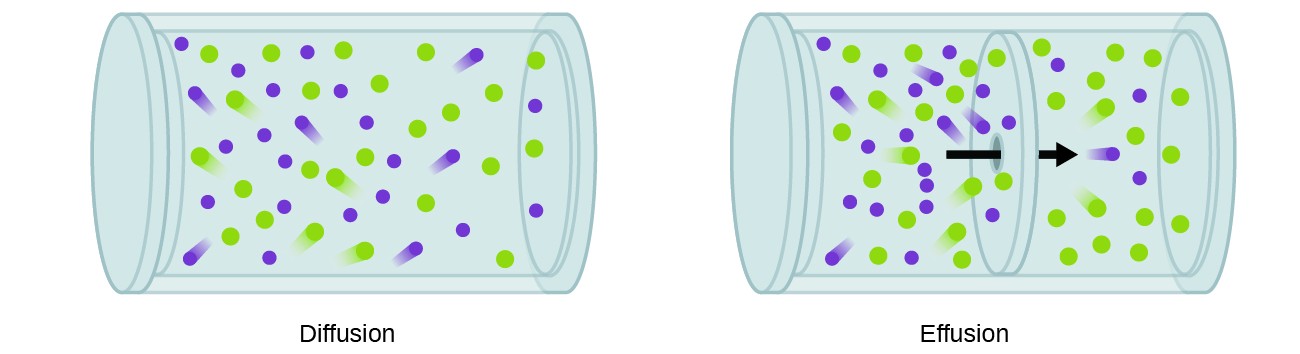
If a mixture of gases is placed in a container with porous walls, the gases effuse through the small openings in the walls. The lighter gases pass through the small openings more rapidly (at a higher rate) than the heavier ones (Figure 3). In 1832, Thomas Graham studied the rates of effusion of different gases and formulated Graham’s law of effusion: The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles:
This means that if two gases A and B are at the same temperature and pressure, the ratio of their effusion rates is inversely proportional to the ratio of the square roots of the masses of their particles:
Example 1: Applying Graham’s Law to Rates of Effusion
Calculate the ratio of the rate of effusion of hydrogen to the rate of effusion of oxygen.
[reveal-answer q=”190867″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”190867″]
From Graham’s law, we have:
Using molar masses:
Hydrogen effuses four times as rapidly as oxygen.
[/hidden-answer]
Check Your Learning
At a particular pressure and temperature, nitrogen gas effuses at the rate of 79 mL/s. Using the same apparatus at the same temperature and pressure, at what rate will sulfur dioxide effuse?
[reveal-answer q=”337487″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”337487″]52 mL/s[/hidden-answer]
Here’s another example, making the point about how determining times differs from determining rates.
Example 2: Effusion Time Calculations
It takes 243 s for 4.46 × 10-5 mol Xe to effuse through a tiny hole. Under the same conditions, how long will it take 4.46 × 10–5 mol Ne to effuse?
[reveal-answer q=”844226″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”844226″]It is important to resist the temptation to use the times directly, and to remember how rate relates to time as well as how it relates to mass. Recall the definition of rate of effusion: and combine it with Graham’s law:
To get:
Noting that amount of A = amount of B, and solving for time for Ne:
and substitute values:
Finally, solve for the desired quantity:
Note that this answer is reasonable: Since Ne is lighter than Xe, the effusion rate for Ne will be larger than that for Xe, which means the time of effusion for Ne will be smaller than that for Xe.
[/hidden-answer]
Check Your Learning
A party balloon filled with helium deflates to of its original volume in 8.0 hours. How long will it take an identical balloon filled with the same number of moles of air (ℳ = 28.2 g/mol) to deflate to
of its original volume?
[reveal-answer q=”192191″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”192191″]32 h[/hidden-answer]
Finally, here is one more example showing how to calculate molar mass from effusion rate data.
Example 3: Determining Molar Mass Using Graham’s Law
An unknown gas effuses 1.66 times more rapidly than CO2. What is the molar mass of the unknown gas? Can you make a reasonable guess as to its identity?
[reveal-answer q=”422479″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”422479″]
From Graham’s law, we have:
Plug in known data:
Solve:
The gas could well be CH4, the only gas with this molar mass.
[/hidden-answer]
Check Your Learning
Hydrogen gas effuses through a porous container 8.97-times faster than an unknown gas. Estimate the molar mass of the unknown gas.
[reveal-answer q=”844180″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”844180″]163 g/mol[/hidden-answer]
Use of Diffusion for Nuclear Energy Applications: Uranium Enrichment
Gaseous diffusion has been used to produce enriched uranium for use in nuclear power plants and weapons. Naturally occurring uranium contains only 0.72% of 235U, the kind of uranium that is “fissile,” that is, capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. Nuclear reactors require fuel that is 2–5% 235U, and nuclear bombs need even higher concentrations. One way to enrich uranium to the desired levels is to take advantage of Graham’s law. In a gaseous diffusion enrichment plant, uranium hexafluoride (UF6, the only uranium compound that is volatile enough to work) is slowly pumped through large cylindrical vessels called diffusers, which contain porous barriers with microscopic openings. The process is one of diffusion because the other side of the barrier is not evacuated. The molecules have a higher average speed and diffuse through the barrier a little faster than the heavier
molecules. The gas that has passed through the barrier is slightly enriched in
and the residual gas is slightly depleted. The small difference in molecular weights between
and
only about 0.4% enrichment, is achieved in one diffuser (Figure 4). But by connecting many diffusers in a sequence of stages (called a cascade), the desired level of enrichment can be attained.
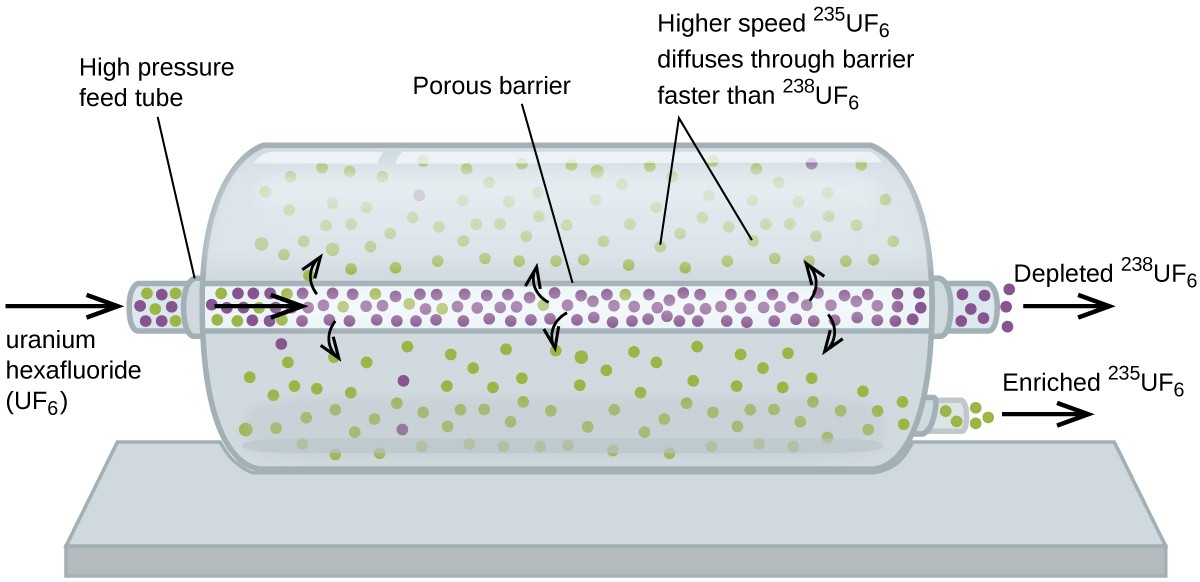
The large scale separation of gaseous from
was first done during the World War II, at the atomic energy installation in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, as part of the Manhattan Project (the development of the first atomic bomb). Although the theory is simple, this required surmounting many daunting technical challenges to make it work in practice. The barrier must have tiny, uniform holes (about 10–6 cm in diameter) and be porous enough to produce high flow rates. All materials (the barrier, tubing, surface coatings, lubricants, and gaskets) need to be able to contain, but not react with, the highly reactive and corrosive UF6.
Because gaseous diffusion plants require very large amounts of energy (to compress the gas to the high pressures required and drive it through the diffuser cascade, to remove the heat produced during compression, and so on), it is now being replaced by gas centrifuge technology, which requires far less energy. A current hot political issue is how to deny this technology to Iran, to prevent it from producing enough enriched uranium for them to use to make nuclear weapons.
Key Concepts and Summary
Gaseous atoms and molecules move freely and randomly through space. Diffusion is the process whereby gaseous atoms and molecules are transferred from regions of relatively high concentration to regions of relatively low concentration. Effusion is a similar process in which gaseous species pass from a container to a vacuum through very small orifices. The rates of effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their densities or to the square roots of their atoms/molecules’ masses (Graham’s law).
Key Equations
Exercises
- A balloon filled with helium gas is found to take 6 hours to deflate to 50% of its original volume. How long will it take for an identical balloon filled with the same volume of hydrogen gas (instead of helium) to decrease its volume by 50%?
- Explain why the numbers of molecules are not identical in the left- and right-hand bulbs shown in the center illustration of Figure 1.
- Starting with the definition of rate of effusion and Graham’s finding relating rate and molar mass, show how to derive the Graham’s law equation, relating the relative rates of effusion for two gases to their molecular masses.
- Heavy water, D2O (molar mass = 20.03 g mol–1), can be separated from ordinary water, H2O (molar mass = 18.01), as a result of the difference in the relative rates of diffusion of the molecules in the gas phase. Calculate the relative rates of diffusion of H2O and D2O.
- Which of the following gases diffuse more slowly than oxygen? F2, Ne, N2O, C2H2, NO, Cl2, H2S
- During the discussion of gaseous diffusion for enriching uranium, it was claimed that
diffuses 0.4\% faster than
Show the calculation that supports this value. The molar mass of
= 235.043930 + 6 × 18.998403 = 349.034348 g/mol, and the molar mass of
= 238.050788 + 6 × 18.998403 = 352.041206 g/mol.
- Calculate the relative rate of diffusion of
(molar mass 2.0 g/mol) compared to that of
(molar mass 4.0 g/mol) and the relative rate of diffusion of O2 (molar mass 32 g/mol) compared to that of O3 (molar mass 48 g/mol).
- A gas of unknown identity diffuses at a rate of 83.3 mL/s in a diffusion apparatus in which carbon dioxide diffuses at the rate of 102 mL/s. Calculate the molecular mass of the unknown gas.
- When two cotton plugs, one moistened with ammonia and the other with hydrochloric acid, are simultaneously inserted into opposite ends of a glass tube that is 87.0 cm long, a white ring of NH4Cl forms where gaseous NH3 and gaseous HCl first come into contact. (Hint: Calculate the rates of diffusion for both NH3 and HCl, and find out how much faster NH3 diffuses than HCl.)
At approximately what distance from the ammonia moistened plug does this occur?
[reveal-answer q=”693396″]Selected Answers[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”693396″]
1. Use the rate of effusion equation:
3. Effusion can be defined as the process by which a gas escapes through a pinhole into a vacuum. Graham’s law states that with a mixture of two gases A and B: Both A and B are in the same container at the same temperature, and therefore will have the same kinetic energy:
Therefore,
5. Gases with molecular masses greater than that of oxygen (31.9988 g/mol) will diffuse more slowly than O2. These gases are F2 (37.9968 g/mol), N2O (44.0128 g/mol ), Cl2 (70.906 g/mol), and H2S (34.082 g/mol).
7.
9. Rate of diffusion for NH3 is proportional to Rate of diffusion for HCl is proportional to
[/hidden-answer]
Glossary
diffusion: movement of an atom or molecule from a region of relatively high concentration to one of relatively low concentration (discussed in this chapter with regard to gaseous species, but applicable to species in any phase)
effusion: transfer of gaseous atoms or molecules from a container to a vacuum through very small openings
Graham’s law of effusion: rates of diffusion and effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molecular masses
mean free path: average distance a molecule travels between collisions
rate of diffusion: amount of gas diffusing through a given area over a given time
- Chemistry. Provided by: OpenStax College. Located at: http://openstaxcollege.org. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/chemistry/get

