6.4: Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Page ID
- 347439
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Source: BiochemFFA_5_2.pdf. The entire textbook is available for free from the authors at http://biochem.science.oregonstate.edu/content/biochemistry-free-and-easy

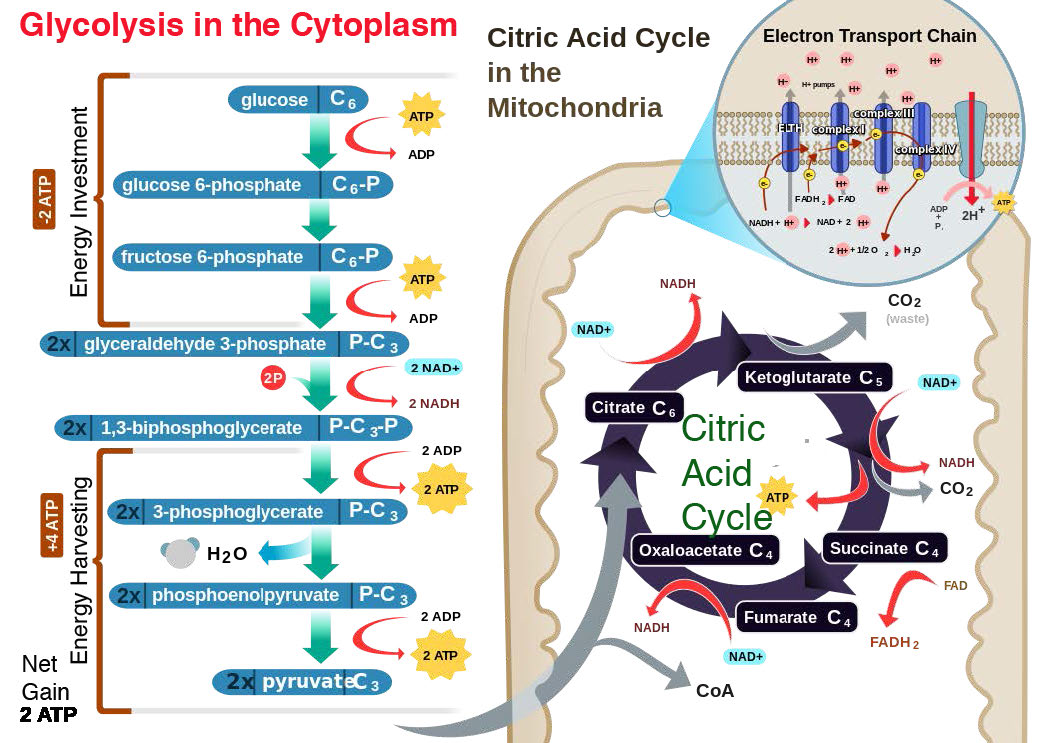
In eukaryotic cells, the vast majority of ATP synthesis occurs in the mitochondria in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Even plants, which generate ATP by photophosphorylation in chloroplasts, contain mitochondria for the synthesis of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
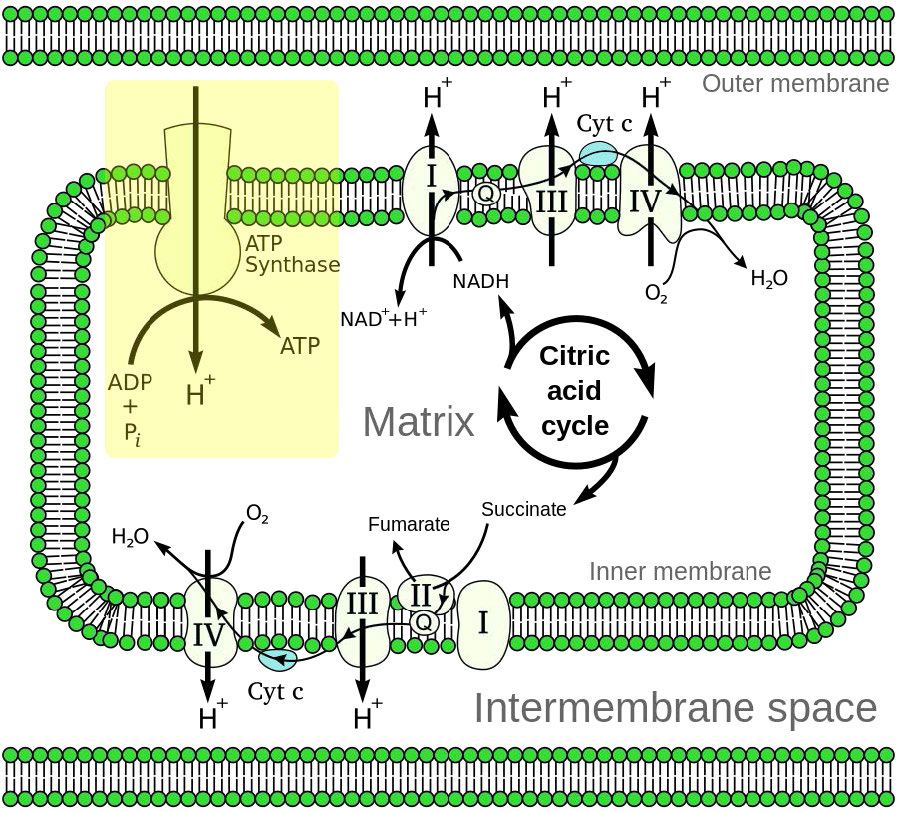
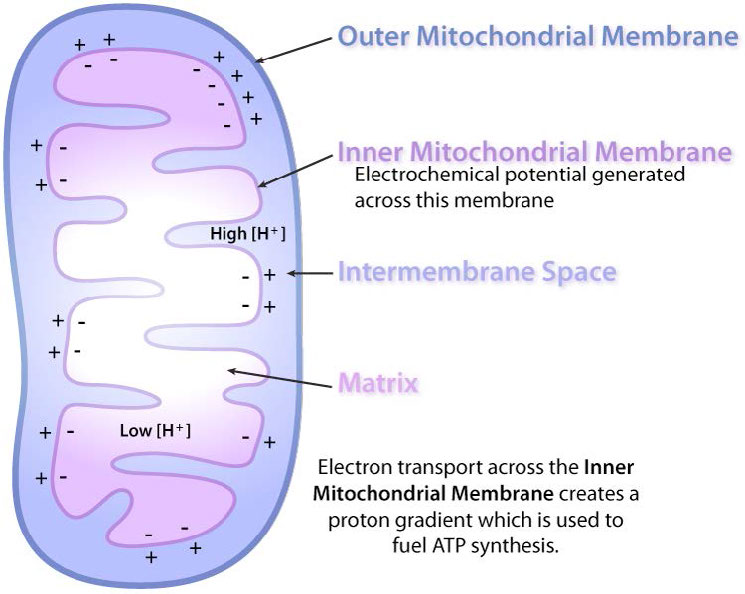
Oxidative phosphorylation is linked to a process known as electron transport (Figure 5.14). The electron transport system, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, transfers electrons donated by the reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH2 (obtained from glycolysis, the citric acid cycle or fatty acid oxidation) through a series of electrons acceptors, to oxygen. As we shall see, movement of electrons through complexes of the electron transport system essentially “charges” a battery that is used to make ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. In this way, the oxidation of sugars and fatty acids is coupled to the synthesis of ATP, effectively extracting energy from food.
Chemiosmotic model
Dr. Peter Mitchell introduced a radical proposal in 1961 to explain the mechanism by which mitochondria make ATP. It is known as the chemiosmotic hypothesis and has been shown over the years to be correct. Mitchell proposed that synthesis of ATP in mitochondria depends on an electrochemical gradient, across the mitochondrial inner membrane, that arises ultimately from the energy of reduced electron carriers, NADH and FADH2.
Electron transport
Further, the proposal states that the gradient is created when NADH and FADH2 transfer their electrons to an electron transport system (ETS) located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Movement of electrons through a series of of electron carriers is coupled to the pumping of protons out of the mitochondrial matrix across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the space between the inner and outer membranes. The result is creation of a gradient of protons whose potential energy can be used to make ATP. Electrons combine with oxygen and protons at the end of the ETS to make water.
ATP synthase
In oxidative phosphorylation, ATP synthesis is accomplished as a result of protons re-entering the mitochondrial matrix via the transmembrane ATP synthase complex, which combines ADP with inorganic phosphate to make ATP. Central to the proper functioning of mitochondria through this process is the presence of an intact mitochondrial inner membrane impermeable to protons.
Tight coupling
When this is the case, tight coupling is said to exist between electron transport and the synthesis of ATP (called oxidative phosphorylation). Chemicals which permeabilize the inner mitochondrial membrane to protons cause uncoupling, that is, they allow the protons to leak back into the mitochondrial matrix, rather than through the ATP synthase, so that the movement of electrons through the ETS is no longer linked to the synthesis of ATP.
Power plants
Mitochondria are called the power plants of the cell because most of a cell’s ATP is produced there in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. The mechanism by which ATP is made in oxidative phosphorylation is one of the most interesting in all of biology.
Considerations
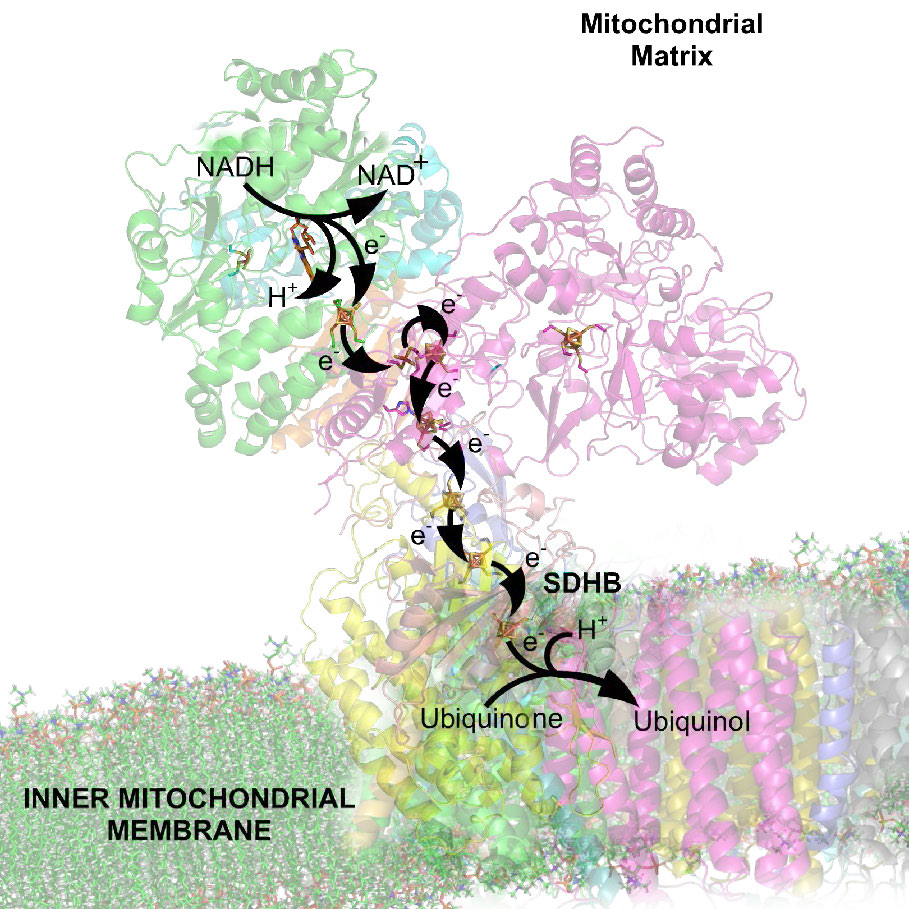
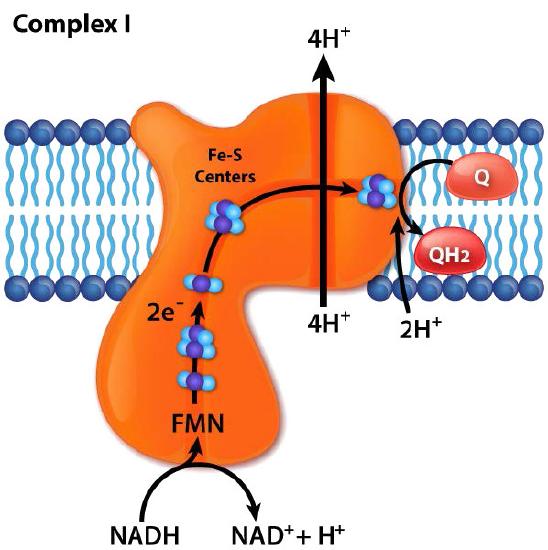
The process has three primary considerations. The first is electrical – electrons from reduced electron carriers, such as NADH and FADH2, enter the electron transport system via Complex I and II, respectively. As seen in Figure 5.16 and Figure 5.17, electrons move from one complex to the next, not unlike the way they move through an electrical circuit. Such movement occurs a a result of a set of reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions with electrons moving from a more negative reduction potential to a more positive one.
One can think of this occurring as a process where carriers “take” electrons away from complexes with lower reduction potential, much the way a bully takes lunch money from a smaller child. In this scheme, the biggest “bully” is oxygen in Complex IV. Electrons gained by a carrier cause it to be reduced, whereas the carrier giving up the electrons is oxidized.
Entry of electrons to system
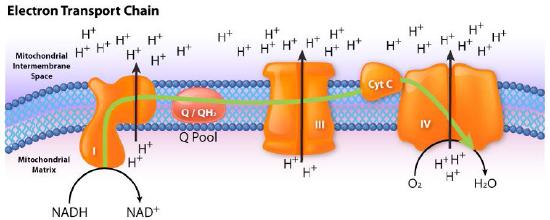
Movement of electrons through the chain begins either by 1) transfer from NADH to Complex I (Figure 5.16) or 2) movement of electrons through a covalently bound FADH2 (Figure 5.17) in the membrane-bound succinate dehydrogenase (Complex II). (An alternate entry point for electrons from FADH2 is the Electron Transferring Flavoprotein via the electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase, not shown).
Traffic cop
Both Complex I and II pass electrons to the inner membrane’s coenzyme Q (CoQ - Figures 5.18 & 5.19). In each case, coenzyme Q accepts electrons in pairs and passes them off to Complex III (CoQH2-cytochrome c reductase) singly. Coenzyme Q thus acts as a traffic cop, regulating the flow of electrons through the ETS.
Docking station
Complex III is a docking station or interchange for the incoming electron carrier (coenzyme Q) and the outgoing carrier (cytochrome c). Movement of electrons from Coenzyme Q to Complex III and then to cytochrome C occurs as a result of what is referred to as the Q-cycle (see below).
Complex III acts to ferry electrons from CoQ to cytochrome c. Cytochrome c takes one electron from Complex III and passes it to Complex IV (cytochrome oxidase). Complex IV is the final protein recipient of the electrons. It passes them to molecular oxygen (O2) to make two molecules of water. Making two water molecules requires four electrons, so Complex IV must accept, handle, and pass to molecular oxygen four separate electrons, causing the oxidation state of oxygen to be sequentially changed with addition of each electron.
Proton pumping
As electrons pass through complexes I, III, and IV, there is a release of a small amount of energy at each step, which is used to pump protons from the mitochondrial matrix (inside of mitochondrion) and deposit them in the intermembrane space (between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondrion). The effect of this redistribution is to increase the electrical and chemical potential across the membrane.
Potential energy
As discussed earlier, electrochemical gradients have potential energy. Students may think of the process as “charging the battery.” Just like a charged battery, the potential arising from the proton differential across the membrane can be used to do things. In the mitochondrion, what the proton gradient does is facilitate the production of ATP from ADP and Pi. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation, because the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP is dependent on the oxidative reactions occurring in the mitochondria.
Having understood the overall picture of the synthesis of ATP linked to the movement of electrons through the ETS, we will take a closer look at the individual components of the ETS.
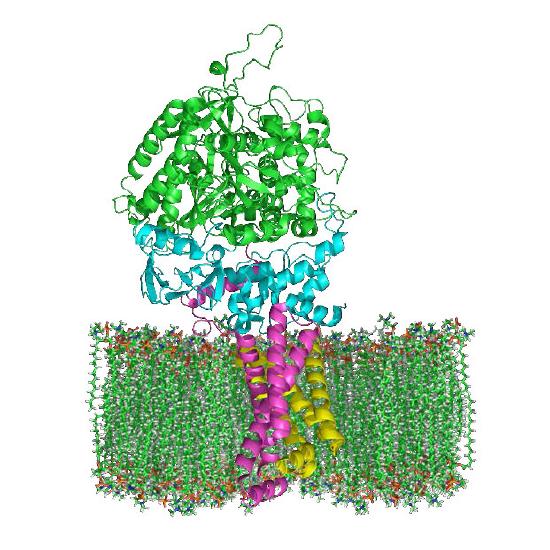
Complex I
Complex I (also called NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase or NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone)) is the electron acceptor from NADH in the electron transport chain and the largest complex found in it.
Complex I contains 44 individual polypeptide chains, numerous iron-sulfur centers, a molecule of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and has an L shape with about 60 transmembrane domains. In the process of electron transport through it, four protons are pumped across the inner membrane into the intermembrane space and electrons move from NADH to coenzyme Q, converting it from ubiquinone (no electrons) to ubiquinol (gain of two electrons). An intermediate form, ubisemiquinone (gain of one electron), is found in the Q-cycle.
Electrons travel through the complex via seven primary iron sulfur centers. The best known inhibitor of the complex, rotenone, works by binding to the CoQ binding site. Other inhibitors include ADP-ribose (binds to the NADH site) and piericidin A (rotenone analog). The process of electron transfer through complex I is reversible and when this occurs, superoxide (a reactive oxygen species) may be readily generated.
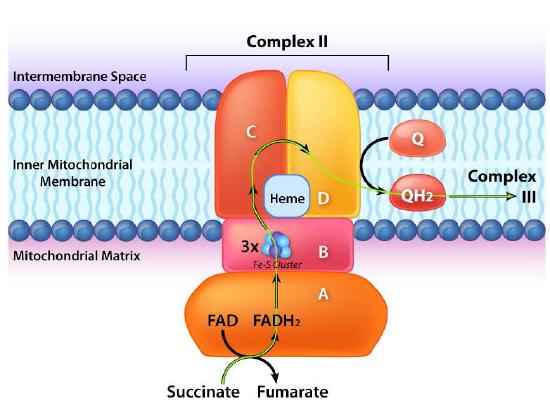
Complex II
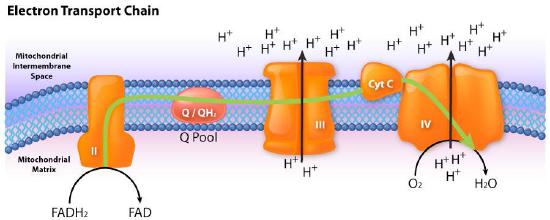
Complex II (also called succinate dehydrogenase or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase ) is a membrane bound enzyme of the citric acid cycle that plays a role in the electron transport process, transferring electrons from its covalently bound FADH2 to coenzyme Q. The process occurs, as shown in Figure 5.20 and Figure 5.21, with transfer of electrons from succinate to FAD to form FADH2 and fumarate. FADH2, in turn, donates electrons to a relay system of iron-sulfur groups and they ultimately reduce ubiquinone (CoQ) along with two protons from the matrix to ubiquinol. The role of the heme group in the process is not clear. Inhibitors of the process include carboxin, malonate, malate, and oxaloacetate. The role of citric acid cycle intermediates as inhibitors is thought to be due to inhibition of the reversal of the transfer process which can produce superoxide.
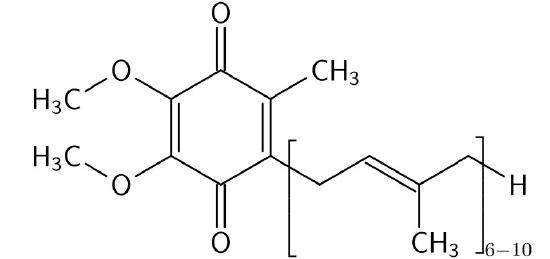
Coenzyme Q
Coenzyme Q (Figure 5.23) is a 1,4 benzoquinone whose name is often given as Coenzyme Q10, CoQ, or Q10. The 10 in the name refers to the number of isoprenyl units it contains that anchor it to the mitochondrial inner membrane. CoQ is a vitamin-like lipid substance found in most eukaryotic cells as a component of the electron transport system. The requirement for CoQ increases with increasing energy needs of cells, so the highest concentrations of CoQ in the body are found in tissues that are the most metabolically active - heart, liver, and kidney.
Three forms
CoQ is useful because of its ability to carry and donate electrons and particularly because it can exist in forms with two extra electrons (fully reduced - ubiquinol), one extra electron (semi-reduced - ubisemiquinone), or no extra electrons (fully oxidized - ubiquinone). This ability allows CoQ to provide transition between the first part of the electron transport system that moves electrons in pairs and the last part of the system that moves electrons one at a time.
Complex III
Complex III (also known as coenzyme Q : cytochrome c — oxidoreductase or the cytochrome bc1 complex - Figure 5.24) is the third electron accepting complex of the electron transport system. It is a transmembrane protein with multiple subunits present in the mitochondria of all aerobic eukaryotic organisms and and the cell membrane of almost all bacteria. The complex contains 11 subunits, a 2-iron ferredoxin, cytochromes b and c1 and belongs to the family of oxidoreductase enzymes.
It accepts electrons from coenzyme Q in electron transport and passes them off to cytochrome c. In this cycle, known as the Q cycle, electrons arrive from CoQ in pairs, but get passed to cytochrome c individually. In the overall process, two protons are consumed from the matrix and four protons are pumped into the intermembrane space. Movement of electrons through the complex can be inhibited by antimycin A, myxothiazol, and stigmatellin. Complex III is also implicated in creation of superoxide (a reactive oxygen species) when electrons from it leak out of the chain of transfer. The phenomenon is more pronounced when antimycin A is present.
Q-cycle
In the Q-cycle, electrons are passed from ubiquinol (QH2) to cytochrome c using Complex III as an intermediary docking station for the transfer. Two pair of electrons enter from QH2 and one pair is returned to another CoQ to re-make QH2. The other pair is donated singly to two different cytochrome c molecules.
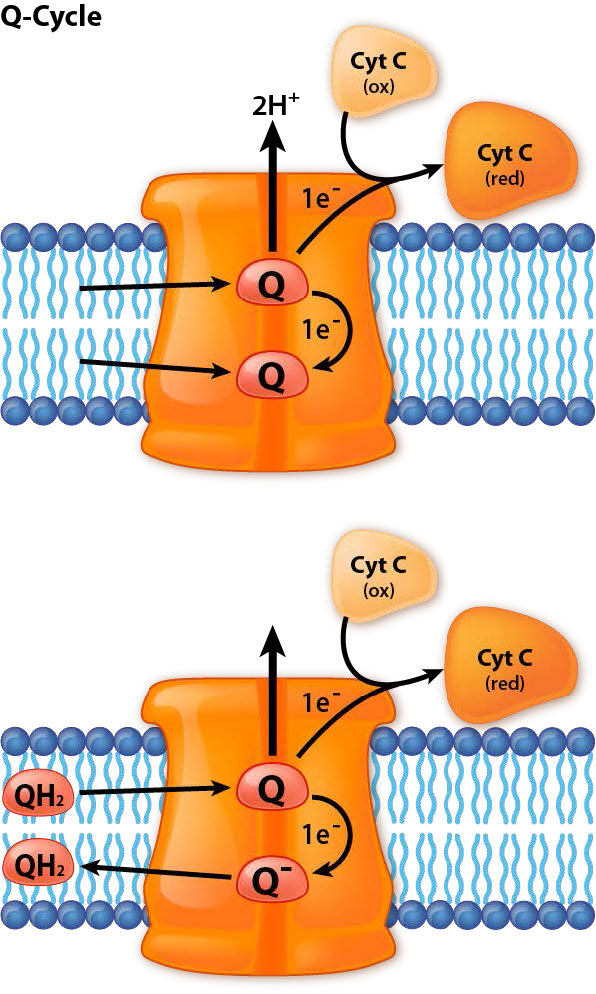
Step one
The Q-cycle happens in a two step process. First, a ubiquinol (CoQH2) and a ubiquinone (CoQ) dock at Complex III. Ubiquinol transfers two electrons to Complex III. One electron goes to a docked cytochrome c, reducing it and it exits (replaced by an oxidized cytochrome c). The other goes to the docked uniquinone to create the semi-reduced semiubiquinone (CoQ.-) and leaving behind a ubiquinone, which exits. This is the end of step 1.
Step two
The gap left behind by the ubiquinone (Q) that departed is replaced by another ubiquinol (QH2). It too donates two electrons to Complex III, which splits them. One goes to the newly docked oxidized cytochrome c, which is reduced and exits. The other goes to the ubisemiquinone. Two protons from the matrix combine with it to make another ubiquinol. It and the ubiquinone created by the electron donation exit Complex III and the process starts again. In the overall process, two protons are consumed from the matrix and four protons are pumped into the intermembrane space.
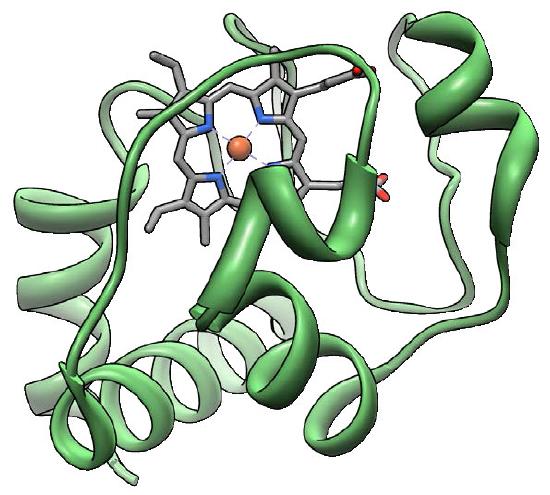
Cytochrome c
Cytochrome c (Figure 5.26) is a small (12,000 Daltons), highly conserved protein, from unicellular species to animals, that is loosely associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane where it functions in electron transport. It contains a heme group which is used to carry a single electron from Complex III to Complex IV. Cytochrome c also plays an important role in apoptosis in higher organisms. Damage to the mitochondrion that results in release of cytochrome c can stimulate assembly of the apoptosome and activation of the caspase cascade that leads to programmed cell death.
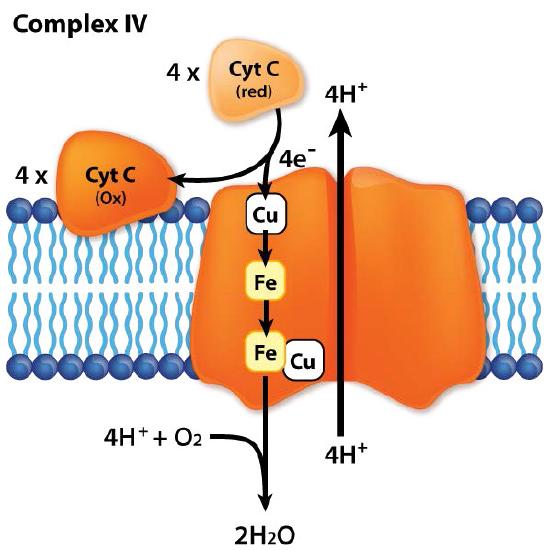
Complex IV
Complex IV, also known as cytochrome c oxidase is a 14 subunit integral membrane protein at the end of the electron transport chain (Figure 5.27). It is responsible for accepting one electron each from four cytochrome c proteins and adding them to molecular oxygen (O2) along with four protons from the mitochondrial matrix to make two molecules of water. Four protons from the matrix are also pumped into the intermembrane space in the process. The complex has two molecules of heme, two cytochromes (a and a3), and two copper centers (called CuA ad CuB). Cytochrome c docks near the CuA and donates an electron to it. The reduced CuA passes the electron to cytochrome a, which turns it over to the a3-CuB center where the oxygen is reduced. The four electrons are thought to pass through the complex rapidly resulting in complete reduction of the oxygen-oxygen molecule without formation of a peroxide intermediate or superoxide, in contrast to previous predictions.
Respirasome
There has been speculation for many years that a supercomplex of electron carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion may exist in cells with individual carriers making physical contact with each other. This would make for more efficient transfer reactions, minimize the production of reactive oxygen species and be similar to metabolons of metabolic pathway enzymes, for which there is some evidence. Now, evidence appears to be accumulating that complexes I, III, and IV form a supercomplex, which has been dubbed the respirasome1.
Oxidative phosphorylation
The process of oxidative phosphorylation uses the energy of the proton gradient established by the electron transport system as a means of phosphorylating ADP to make ATP. The establishment of the proton gradient is dependent upon electron transport. If electron transport stops or if the inner mitochondrial membrane’s impermeability to protons is compromised, oxidative phosphorylation will not occur because without the proton gradient to drive the ATP synthase, there will be no synthesis of ATP.
ATP synthase
The protein complex harvesting energy from the proton gradient and using it to make ATP from ADP is an enzyme that has several names - Complex V, PTAS (Proton Translocating ATP Synthase), and ATP synthase (Figure 5.29). Central to its function is the movement of protons through it (from the intermembrane space back into the matrix). Protons will only provide energy to make ATP if their concentration is greater in the intermembrane space than in the matrix and if ADP is available.
It is possible, in some cases, for the concentration of protons to be greater inside the matrix than outside of it. When this happens, the ATP synthase can run backwards, with protons moving from inside to out, accompanied by conversion of ATP to ADP + Pi. This is usually not a desirable circumstance and there are some controls to reduce its occurrence.
Normally, ATP concentration will be higher inside of the mitochondrion and ADP concentration be higher outside the mitochondrion. However, when the rate of ATP synthesis exceeds the rate of ATP usage, then ATP concentrations rise outside the mitochondrion and ADP concentrations fall everywhere.
This may happen, for example, during periods of rest. It has the overall effect of reducing transport and thus lowering the concentration of ADP inside the matrix. Reducing ADP concentration in the matrix reduces oxidative phosphorylation and has effects on respiratory control (see HERE).
Another important consideration is that when ATP is made in oxidative phosphorylation, it is released into the mitochondrial matrix, but must be transported into the cytosol to meet the energy needs of the rest of the cell. This is accomplished by action of the adenine nucleotide translocase, an antiport that moves ATP out of the matrix in exchange for ADP moving into the matrix. This transport system is driven by the concentrations of ADP and ATP and ensures that levels of ADP are maintained within the mitochondrion, permitting continued ATP synthesis.
One last requirement for synthesis of ATP from ADP is that phosphate must also be imported into the matrix. This is accomplished by action of the phosphate translocase, which is a symport that moves phosphate into the mitochondrial matrix along with a proton.
There is evidence that the two translocases and ATP synthase may exist in a complex, which has been dubbed the ATP synthasome.
In summary, the electron transport system charges the battery for oxidative phosphorylation by pumping protons out of the mitochondrion. The intact inner membrane of the mitochondrion keeps the protons out, except for those that re-enter through ATP Synthase. The ATP Synthase allows protons to re-enter the mitochondrial matrix and harvests their energy to make ATP.
ATP synthase mechanism
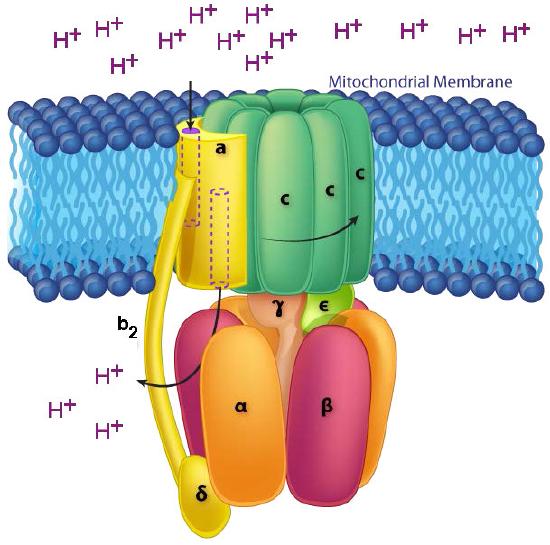
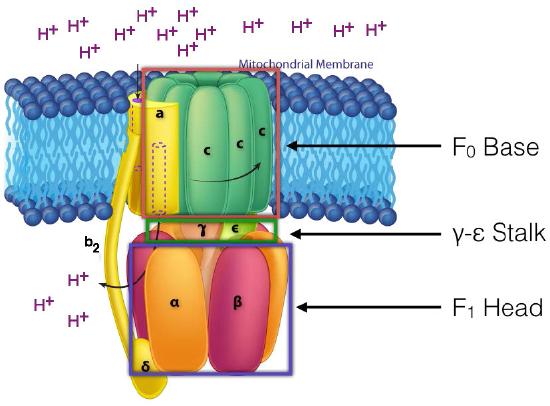
In ATP Synthase, the spinning components, or rotor, are the membrane portion (c ring) of the F0 base and the γ-ε stalk, which is connected to it. The γ-ε stalk projects into the F1 head of the mushroom structure. The F1 head contains the catalytic ability to make ATP. The F1 head is hexameric in structure with paired α and β proteins arranged in a trimer of dimers. ATP synthesis occurs within the β subunits.
Rotation of γ unit
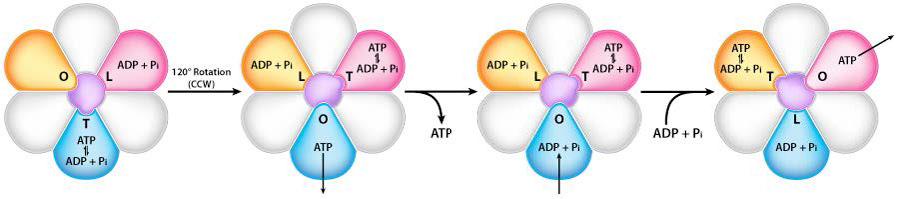
Turning of the γ shaft (caused by proton flow) inside the α-β trimer of the F1 head causes each set of β proteins to change structure slightly into three different forms called Loose, Tight, and Open (L,T,O - Figure 5.31). Each of these forms has a function.
The Loose form binds ADP + Pi. The Tight form “squeezes” them together to form the ATP. The Open form releases the ATP into the mitochondrial matrix. Thus, as a result of the proton flow through the ATP synthase, from the intermembrane space into the matrix, ATP is made from ADP and Pi.
Respiratory control
When a mitochondrion has an intact inner membrane and protons can only return to the matrix by passing through the ATP synthase, the processes of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are said to be tightly coupled.
Interdependence
In simple terms, tight coupling means that the processes of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are interdependent. Without electron transport going on in the cell, oxidative phosphorylation will soon stop.
The reverse is also true, because if oxidative phosphorylation stops, the proton gradient will not be dissipated as it is being built by the electron transport system and will grow larger and larger. The greater the gradient, the greater the energy needed to pump protons out of the mitochondrion. Eventually, if nothing relieves the gradient, it becomes too large and the energy of electron transport is insufficient to perform the pumping. When pumping stops, so too does electron transport.
ADP dependence
Another relevant point is that ATP synthase is totally dependent upon a supply of ADP. In the absence of ADP, the ATP synthase stops functioning and when it stops, so too does movement of protons back into the mitochondrion. With this information, it is possible to understand the link between energy usage and metabolism. The root of this, as noted, is respiratory control.
At rest
To illustrate these links, let us first consider a person, initially at rest, who then suddenly jumps up and runs away. At first, the person’s ATP levels are high and ADP levels are low (no exercise to burn ATP), so little oxidative phosphorylation is occurring and thus the proton gradient is high. Electron transport is moving slowly, if at all, so it is not using oxygen and the person’s breathing is slow, as a result.
Exercise
When running starts, muscular contraction, which uses energy, causes ATP to be converted to ADP. Increasing ADP in muscle cells favors oxidative phosphorylation to attempt to make up for the ATP being burned. ATP synthase begins working and protons begin to come back into the mitochondrial matrix. The proton gradient decreases, so electron transport re-starts.
Electron transport needs an electron acceptor, so oxygen use increases and when oxygen use increases, the person starts breathing more heavily to supply it. When the person stops running, ATP concentrations get rebuilt by ATP synthase. Eventually, when ATP levels are completely restored, ADP levels fall and ATP synthase stops or slows considerably. With little or no proton movement, electron transport stops because the proton gradient is too large. When electron transport stops, oxygen use decreases and the rate of breathing slows down.
Electron transport critical
The really interesting links to metabolism occur relative to whether or not electron transport is occurring. From the examples, we can see that electron transport will be relatively slowed when not exercising and more rapid when exercise (or other ATP usage) is occurring. Remember that electron transport is the way in which reduced electron carriers, NADH and FADH2, donate their electrons to the ETS , becoming oxidized to NAD+ and FAD, respectively.
Oxidized carriers, such as NAD+ and FAD are needed by catabolic pathways, like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and fatty acid oxidation. Anabolic pathways, such as fatty acid/fat synthesis and gluconeogenesis rely on reduced electron carriers, such as FADH2, NADH, and the related carrier, NADPH.
Links to exercise
High levels of NADH and FADH2 prevent catabolic pathways from operating, since NAD+ and FAD levels will be low and these are needed to accept the electrons released during catabolism by the oxidative processes.
Thanks to respiratory control, when one is exercising, NAD+ and FAD levels increase (because electron transport is running), so catabolic pathways that need NAD+ and FAD can function. The electrons lost in the oxidation reactions of catabolism are captured by NAD+ and FAD to yield NADH and FADH2, which then supply electrons to the electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation to make more needed ATP.
Thus, during exercise, cells move to a mode of quickly cycling between reduced electron carriers (NADH/FADH2) and oxidized electron carriers (NAD+/FAD). This allows rapidly metabolizing tissues to transfer electrons to NAD+/FAD and it allows the reduced electron carriers to rapidly become oxidized, allowing the cell to produce ATP.
Rest
When exercise stops, NADH and FADH2 levels rise (because electron transport is slowing) causing catabolic pathways to slow/stop. If one does not have the proper amount of exercise, reduced carriers remain high in concentration for long periods of time. This means we have an excess of energy and then anabolic pathways, particularly fatty acid synthesis, are favored, so we get fatter.
Altering respiratory control
One might suspect that altering respiratory control could have some very dire consequences and that would be correct. Alterations can take the form of either inhibiting electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation or uncoupling the two . These alterations can be achieved using compounds with specific effects on particular components of the system.
All of the chemicals described here are laboratory tools and should never be used by people. The first group for discussion are the inhibitors. In tightly coupled mitochondria, inhibiting either electron transport or oxidative phosphorylation has the effect of inhibiting the other one as well.
Electron transport inhibitors
Common inhibitors of electron transport include rotenone and amytal, which stop movement of electrons past Complex I, malonate, malate, and oxaloacetate, which inhibit movement of electrons through Complex II, antimycin A which stops movement of electrons past Complex III, and cyanide, carbon monoxide, azide, and hydrogen sulfide, which inhibit electron movement through Complex IV (Figure 5.33). All of these compounds can stop electron transport directly (no movement of electrons) and oxidative phosphorylation indirectly (proton gradient will dissipate). While some of these compounds are not commonly known, almost everyone is aware of the hazards of carbon monoxide and cyanide, both of which can be lethal.
ATP synthase inhibitor
It is also possible to use an inhibitor of ATP synthase to stop oxidative phosphorylation directly (no ATP production) and electron transport indirectly (proton gradient not relieved so it becomes increasingly difficult to pump protons out of matrix). Oligomycin A (Figure 5.34) is an inhibitor of ATP synthase.
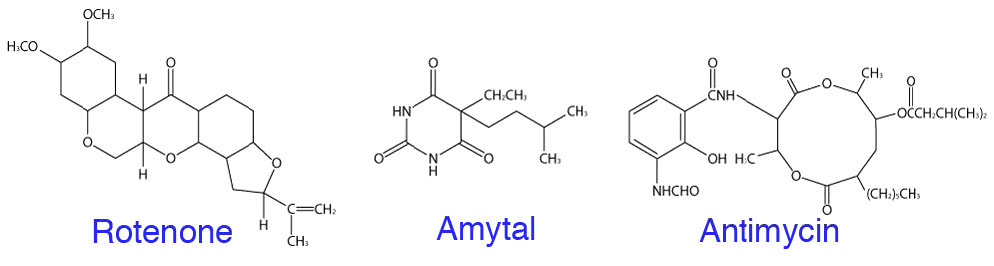
Rotenone
Rotenone, which is a plant product, is used as a natural insecticide that is permitted for organic farming. When mitochondria are treated with this, electron transport will stop at Complex I and so, too, will the pumping of protons out of the matrix. When this occurs, the proton gradient rapidly dissipates, stopping oxidative phosphorylation as a consequence. There are other entry points for electrons than Complex I, so this type of inhibition is not as serious as using inhibitors of Complex IV, since no alternative route for electrons is available. It is for this reason that cyanide, for example, is so poisonous.
2,4-DNP
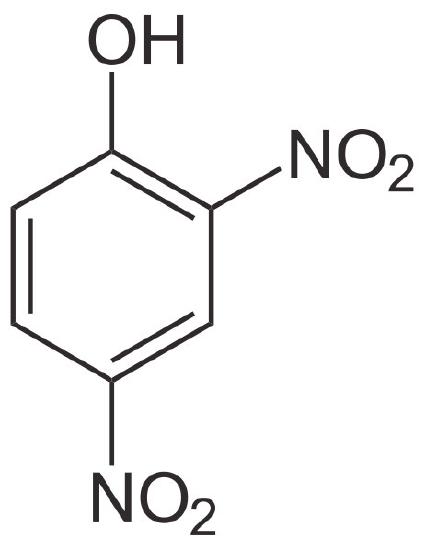
Imagine a dam holding back water with a turbine generating electricity through which water must flow. When all water flows through the turbine, the maximum amount of electricity can be generated. If one pokes a hole in the dam, though, water will flow through the hole and less electricity will be created. The generation of electricity will thus be uncoupled from the flow of water. If the hole is big enough, the water will all drain out through the hole and no electricity will be made.
Bypassing ATP synthase
Imagine, now, that the proton gradient is the equivalent of the water, the inner membrane is the equivalent of the dam and the ATP synthase is the turbine. When protons have an alternate route, little or no ATP will be made because protons will pass through the membrane’s holes instead of spinning the turbine of ATP synthase.
It is important to recognize, though, that uncoupling by 2,4 DNP works differently from the electron transport inhibitors or the ATP synthase inhibitor. In those situations, stopping oxidative phosphorylation resulted in indirectly stopping electron transport, since the two processes were coupled and the inhibitors did not uncouple them. Similarly, stopping electron transport indirectly stopped oxidative phosphorylation for the same reason.
Such is not the case with 2,4 DNP. Stopping oxidative phosphorylation by destroying the proton gradient allows electron transport to continue unabated (it actually stimulates it), since the proton gradient cannot build no matter how much electron transport runs. Consequently, electron transport runs like crazy but oxidative phosphorylation stops. When that happens, NAD+ and FAD levels rise, and catabolic pathways run unabated with abundant supplies of these electron acceptors. The reason such a scenario is dangerous is because the body is using all of its nutrient resources, but no ATP is being made. Lack of ATP leads to cellular (and organismal) death. In addition, the large amounts of heat generated can raise the temperature of the body to unsafe levels.

Thermogenin
One of the byproducts of uncoupling electron transport is the production of heat. The faster metabolic pathways run, the more heat is generated as a byproduct. Since 2,4 DNP causes metabolism to speed up, a considerable amount of heat can be produced. Controlled uncoupling is actually used by the body in special tissues called brown fat. In this case, brown fat cells use the heat created to help thermoregulate the temperature of newborn children.
Permeabilization of the inner membrane is accomplished in brown fat by the synthesis of a protein called thermogenin (also known as uncoupling protein). Thermogenin binds to the inner membrane and allows protons to pass through it, thus bypassing the ATP synthase. As noted for 2,4 DNP, this results in activation of catabolic pathways and the more catabolism occurs, the more heat is generated.
Dangerous drug
In uncoupling, whether through the action of an endogenous uncoupling protein or DNP, the energy that would have normally been captured in ATP is lost as heat. In the case of uncoupling by thermogenin, this serves the important purpose of keeping newborn infants warm. But in adults, uncoupling merely wastes the energy that would have been harvested as ATP. In other words, it mimics starvation, even though there is plenty of food, because the energy is dissipated as heat.
This fact, and the associated increase in metabolic rate, led to DNP being used as a weight loss drug in the 1930s. Touted as an effortless way to lose weight without having to eat less or exercise more, it was hailed as a magic weight loss pill. It quickly became apparent, however, that this was very dangerous. Many people died from using this drug before laws were passed to ban the use of DNP as a weight loss aid.
Alternative oxidase
Another approach to generating heat that doesn’t involve breaking respiratory control is taken by some fungi, plants, and protozoa. They use an alternative electron transport. In these organisms, there is an enzyme called alternative oxidase (Figure 5.36). Alternative oxidase is able to accept electrons from CoQ and pass them directly to oxygen.
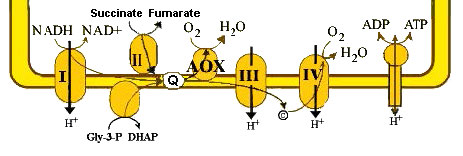
The process occurs in coupled mitochondria. Its mechanism of action is to reduce the yield of ATP, since fewer protons are being pumped per reduced electron carrier. Thus NAD+ concentrations increase, oxygen consumption increases, and the efficiency of ATP production decreases.
Organisms using this method must activate catabolic pathways by the increase in NAD+ concentration. This, in turn produces quantities of NADH and FADH2 necessary to make sufficient amounts of ATP. The byproduct of this increased catabolism is more heat. Not surprisingly, the alternative oxidase pathway can be activated by cold temperatures.
Energy efficiency
Cells are not 100% efficient in energy use. Nothing we know is. Consequently, cells do not get as much energy out of catabolic processes as they put into anabolic processes. A good example is the synthesis and breakdown of glucose, something liver cells are frequently doing. The complete conversion of glucose to pyruvate in glycolysis (catabolism) yields two pyruvates plus 2 NADH plus 2 ATPs. Conversely, the complete conversion of two pyruvates into glucose by gluconeogenesis (anabolism) requires 4 ATPs, 2 NADH, and 2 GTPs. Since the energy of GTP is essentially equal to that of ATP, gluconeogenesis requires a net of 4 ATPs more than glycolysis yields. This difference must be made up in order for the organism to meet its energy needs. It is for this reason that we eat. In addition, the inefficiency of our capture of energy in reactions results in the production of heat and helps to keep us warm, as noted. You can read more about glycolysis (HERE) and gluconeogenesis (HERE).
Metabolic controls of energy
It is also noteworthy that cells do not usually have both catabolic and anabolic processes for the same molecules occurring simultaneously inside of them (for example, breakdown of glucose and synthesis of glucose) because the cell would see no net production of anything but heat and a loss of ATPs with each turn of the cycle. Such cycles are called futile cycles and cells have controls in place to limit the extent to which they occur. Since futile cycles can, in fact, yield heat, they are used as sources of heat in some types of tissue. Brown adipose tissue of mammals uses this strategy, as described earlier. See also HERE for more on heat generation with a futile cycle.
Reactive oxygen species
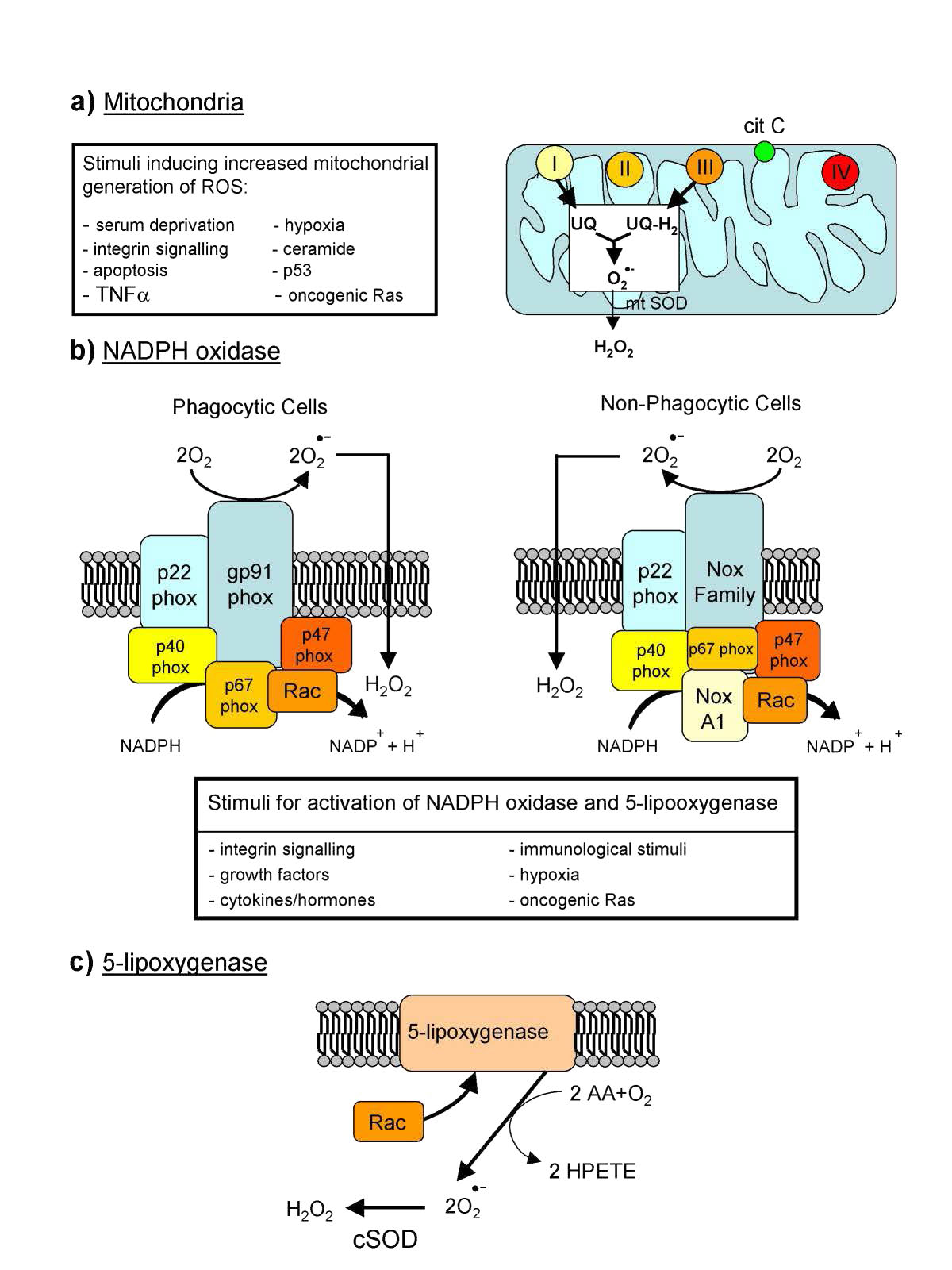
Endogenous production of ROS is directed towards intracellular signaling (H2O2 and nitric oxide, for example) and defense. Many cells, for example, have NADPH oxidase (Figure 5.38) embedded in the exterior portion of the plasma membranes, in peroxisomes, and endoplasmic reticulum. It produces superoxides in the reaction below to kill bacteria .
In the immune system, cells called phagocytes engulf foreign cells and then use ROS to kill them. ROS can serve as signals for action. In zebrafish, damaged tissues have increased levels of H2O2 and this is thought to be a signal for white blood cells to converge on the site. In fish lacking the genes to produce hydrogen peroxide, white blood cells do not converge at the damage site. Sources of hydrogen peroxide include peroxisomes, which generate it as a byproduct of oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
Aging
Reactive oxygen species are at the heart of the free radical theory of aging, which states that organisms age due to the accumulation of damage from free radicals in their cells. In yeast and Drosophila, there is evidence that reducing oxidative damage can increase lifespan. In mice, increasing oxidative damage decreases life span, though in Caenorhabditis, blocking production of superoxide dismutase actually increases lifespan, so the role of ROS in aging is not completely clear.
It is clear, though, that accumulation of mitochondrial damage is problematic for individual cells. Bcl-2 proteins on the surface of mitochondria monitor damage and if they detect it, will activate proteins called Bax to stimulate the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondrial membrane, stimulating apoptosis (programmed cell death). Eventually the dead cell will be phagocytosed.
A common endogenous source of superoxide is the electron transport chain. Superoxide can be produced when movement of electrons into and out of the chain don’t match well. Under these circumstances, semi-reduced CoQ can donate an electron to O2 to form superoxide (O2-). Superoxide can react with many molecules, including DNA where it can cause damage leading to mutation. If it reacts with the aconitase enzyme, ferrous iron (Fe++) can be released which, in turn, can react in the Fenton reaction to produce another reactive oxygen species, the hydroxyl radical (Figure 5.39) .
Countering the effects of ROS are enzymes, such as catalase, superoxide dismutase, and anti-oxidants, such as glutathione and vitamins C and E.
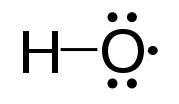
Glutathione protects against oxidative damage by being a substrate for the enzyme glutathione peroxidase. Glutathione peroxidase catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water (next page).
Catalase
2 H2O2 <=> 2 H2O + O2
The enzyme, which employs four heme groups in its catalysis, works extremely rapidly, converting up to 40,000,000 molecules of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen per enzyme per second. It is abundantly found in peroxisomes.
In addition to catalase’s ability to break down hydrogen peroxide, the enzyme can also use hydrogen peroxide to oxidize a wide variety organic compounds, including phenols, formic acid, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and alcohols, but with much lower efficiency.
Health
The importance of catalase for health is uncertain. Mice deficient in the enzyme appear healthy and humans with low levels of the enzyme display few problems. On the other hand, mice engineered to produce higher levels of catalase, in at least one study, lived longer. The ability of organisms to live with lower levels or no catalase may arise from another group of enzymes, the peroxiredoxins, which also act on hydrogen peroxide and may make up for lower quantities of catalase. Last, there is evidence that reduced levels of catalase with aging may be responsible for the graying of hair. Higher levels of H2O2 with reduced catalase results in a bleaching of hair follicles.
Superoxide dismutase
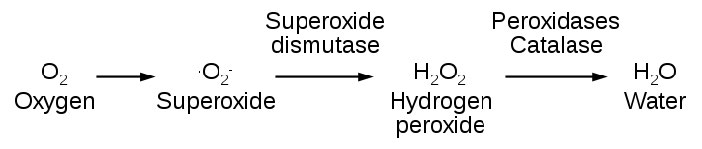
Another important enzyme for protection against reactive oxygen species is superoxide dismutase (SOD), which is found, like catalase, in virtually all organisms living in an oxygen environment. Superoxide dismutase, also like catalase, has a very high Kcat value and, in fact, has the highest Kcat/Km known for any known enzyme. It catalyzes the reactions at the top of the next column (superoxides shown in red):
The enzyme thus works by a ping-pong (double displacement) mechanism (see HERE), being converted between two different forms.
The hydrogen peroxide produced in the second reaction is easily handled by catalase and is also less harmful than superoxide, which can react with nitric oxide (NO) to form very toxic peroxynitrite ions (Figure 5.43). Peroxynitrite has negative effects on cells, as shown in Figure 5.45.
In addition to copper, an ion of Zn++ is also bound by the enzyme and likely plays a role in the catalysis. Forms of superoxide dismutase that use manganese, nickel, or iron are also known and are mostly found in prokaryotes and protists, though a manganese SOD is found in most mitochondria. Copper/zinc enzymes are common in eukaryotes.
Three forms of superoxide dismutase are found in humans and localized to the cytoplasm (SOD1 - Figure 5.45), mitochondria (SOD2 - Figure 5.46), and extracellular areas (SOD3 - Figure 5.47). Mice lacking any of the three forms of the enzyme are more sensitive to drugs, such as paraquat. Deficiency of SOD1 in mice leads to hepatocellular carcinoma and early loss of muscle tissue related to aging. Drosophila lacking SOD2 die before birth and those lacking SOD1 prematurely age.
In humans, superoxide dismutase mutations are associated with the genetically-linked form of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and over-expression of the gene is linked to neural disorders associated with Down syndrome.
Mixed function oxidases
Other enzymes catalyzing reactions involving oxygen include the mixed function oxidases. These enzymes use molecular oxygen for two different purposes in one reaction. The mixed function part of the name is used to indicate reactions in which two different substrates are being oxidized simultaneously. Monooxygenases are examples of mixed function oxidases. An example of a mixed function oxidase reaction is shown below.
AH + BH2 + O2 <=> AOH + B + H2O
In this case, the oxygen molecule has one atom serve as an electron acceptor and the other atom is added to the AH, creating an alcohol.
Cytochrome P450 enzymes
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (called CYPs) are family of heme-containing mixed function oxidase enzymes found in all domains of life. Over 21,000 CYP enzymes are known. The most characteristic reaction catalyzed by these enzymes follows
Monooxygenase reactions such as this are relatively rare in the cell due to their use of molecular oxygen. CYPs require an electron donor for reactions like the one shown here and frequently require a protein to assist in transferring electrons to reduce the heme iron. There are six different classes of P450 enzymes based on how they get electrons
1. Bacterial P450 - electrons from ferredoxin reductase and ferredoxin
2. Mitochondrial P450 - electrons from adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin
3. CYB5R/cyb5 - electrons come from cytochrome b5
4. FMN/Fd - use a fused FMN reductase
5. Microsomal P450 - NADPH electrons come via cytochrome P450 reductase or from cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase
6. P450 only systems - do not require external reducing power
The CYP genes are abundant in humans and catalyze thousand of reactions on both cellular and extracellular chemicals. There are 57 human genes categorized into 18 different families of enzymes. Some CYPs are specific for one or a few substrates, but others can act on many different substrates.
CYP enzymes are found in most body tissues and perform important functions in synthesis of steroids (cholesterol, estrogen, testoterone, Vitamin D, e.g.), breakdown of endogenous compounds (bilirubin), and in detoxification of toxic compounds including drugs. Because they act on many drugs, changes in CYP activity can produce unexpected results and cause problems with drug interactions.
Bioactive compounds, for example, in grapefruit juice, can inhibit CYP3A4 activity, leading to increased circulating concentrations of drugs that would normally have been acted upon by CYP3A4. This is the reason that patients prescribed drugs that are known to be CYP3A4 substrates are advised to avoid drinking grapefruit juice while under treatment. St. Johns Wort, an herbal treatment, on the other hand, induces CYP3A4 activity, but inhibits CYP1A1, CYP1B1, and CYP2D6. Tobacco smoke induces CYP1A2 and watercress inhibits CYP2E1.
Cytochromes
Cytochromes are heme-containing proteins that play major roles in the process of electron transport in the mitochondrion and in photosynthesis in the chloroplast. They exist either as monomers (cytochrome c) or as subunits within large redox complexes (Complex III and Complex IV of electron transport. An atom of iron at the center of the heme group plays a central role in the process, flipping between the ferrous (Fe++) and ferric (Fe+++) states as a result of the movement of electrons through it.
There are several different cytochromes. Cytochrome c (Figure 5.47) is a soluble protein loosely associated with the mitochondrion. Cytochromes a and a3 are found in Complex IV. Complex III has cytochromes b and c1 and the plastoquinol-plastocyanin reductase of the chloroplast contains cytochromes b6 and f. Another important class of enzymes containing cytochromes is the cytochrome P450 oxidase group (see above). They get their name from the fact that they absorb light at 450 nm when their heme iron is reduced.
Iron-Sulfur Proteins
Iron-sulfur proteins contain iron-sulfur clusters in a variety of formats, including sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers existing in different oxidation states (Figures 5.48 & 5.49). The clusters play a variety of roles, but the best known ones are in electron transport where they function in the redox reactions involved in the movement of electrons.
Complexes I and Complex II contain multiple Fe-S centers. Iron-sulfur proteins, though, have many other roles in cells. Aconitase uses an iron-sulfur center in its catalytic action and the ability of the enzyme to bind iron allows it to function as a barometer of iron concentration in cells. Iron-sulfur centers help to generate radicals in enzymes using S-Adenosyl Methionine (SAM) and can serve as a source of sulfur in the synthesis of biotin and lipoic acid. Some iron-sulfur proteins even help to regulate gene expression.
Ferredoxin
Ferredoxins are iron-sulfur containing proteins performing electron transfer in a wide variety of biological systems and processes. They include roles in photosynthesis in chloroplasts. Ferredoxins are classified structurally by the iron-sulfur clustered centers they contain. Fe2S2 clusters (Figure 5.50) are found in chloroplast membranes and can donate electrons to glutamate synthase, nitrate reductase, and sulfite reductase and serve as electron carriers between reductase flavoproteins and bacterial dioxygenase systems. Adrenodoxin is a soluble human Fe2S2 ferredoxin (also called ferredoxin 1) serving as an electron carrier (to cytochrome P450) in mitochondrial monooxygenase systems. Fe4S4 ferredoxins are subdivided as low and high potential ferredoxins, with the latter ones functioning in anaerobic electron transport chains.
Ferritin
Ferritin is an intracellular iron-storage protein found in almost all living organisms, from bacteria to higher plants and animals. It is a globular protein complex with 24 subunits and is the primary intracellular iron-storage protein in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Ferritin functions to keep iron in a soluble and non-toxic form. Its ability to safely store iron and release it in a controlled fashion allow it to act like the prime iron buffer and solubilizer in cells - keeping the concentration of free iron from going to high or falling too low. Ferritin is located in the cytoplasm in most tissues, but it is also found in the serum acting as an iron carrier. Ferritin that doesn’t contain any iron is known as apoferritin.
Monoamine oxidases
Monoamine oxidases are enzymes that catalyze the oxidative deamination of monoamines, such as serotonin, epinephrine, and dopamine. Removal of the amine with oxygen results in the production of an aldehyde and ammonia. The enzymes are found inside and outside of the central nervous system.
There are two types of monoamine oxidase enzymes - MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A is particularly important for oxidizing monoamines consumed in the diet. Both MAO-A and MAO-B play important roles in inactivating monoaminergic neurotransmitters. Both enzymes act on dopamine, tyramine (Figure 5.50), and tryptamine. MAO-A is the primary enzyme for metabolizing melatonin, serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, while MAO-B is the primary enzyme for phenethylamine (Figure 5.51) and benzylamine. MAO-B levels have been reported to be considerably reduced with tobacco usage.
Actions of monoamine oxidases thus affects levels of neurotransmitters and consequently are thought to play roles in neurological and/or psychiatric disorders. Aberrant levels of MAOs have been linked to numerous psychological problems, including depression, attention deficit disorder (ADD), migraines, schizophrenia, and substance abuse. Medications targeting MAOs are sometimes used to treat depression as a last resort - due to potential side effects. Excess levels of catecholamines, such as epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine, can result in dangerous hypertension events.
DNA damage theory of aging
The DNA Damage Theory of Aging is based on the observation that, over time, cells are subject to extensive oxidative events. As already noted, these afford opportunities for the formation of ROS that can damage cellular molecules, and it follows that accumulation of such damage, especially to the DNA would be deleterious to the cell. The build-up of DNA damage could, thus, be responsible for the changes in gene expression that we associate with aging.
Numerous damage events
The amount of DNA damage that can occur is considerable. In mice, for example, it is estimated that each cell experiences 40,000 to 150,000 damage events per day. The damage, which happens to nuclear as well as to mitochondrial DNA, can result in apoptosis and/or cellular senescence. DNA repair systems, of course, protect against damage to DNA, but over time, unrepairable damage may accumulate.
Oxidative damage
DNA damage can occur in several ways. Oxidation can damage nucleotides and alter their base-pairing tendencies. Oxidation of guanine by reactive oxygen species, for example, can produce 8-oxo-guanine (Figures 5.52 and 5.53). This oxidized nucleobase commonly produced lesion in DNA arising from action of reactive oxygen species like superoxides. 8-oxoguanine is capable of forming a stable base pairing interaction within a DNA duplex with adenine, potentially giving rise to a mutation when DNA replication proceeds. 8-oxoguanine can be repaired if recognized in time by a DNA glycosylase, which acts to clip out the damaged base and it can then be replaced by the proper one. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from cigarette smoke, diesel exhaust, or overcooked meat can covalently bind to DNA and, if unrepaired, lead to mutation. Chemical damage to DNA can result in broken or cross-linked DNAs.
Diseases of DNA repair
The importance of DNA repair in the aging process is made clear by diseases affecting DNA repair that lead to premature aging. These include Werner syndrome, for whom the life expectancy is 47 years. It arises as a result of loss of two enzymes in base excision repair. People suffering from Cockayne syndrome have a life expectancy of 13 years due to mutations that alter transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair, which is an important system for fixing oxidative damage.
Further, the life expectancies of 13 species of mammalian organisms correlates with the level of expression of the PARP DNA repair-inducing protein. Interestingly, people who lived past the age of 100 had a higher level of PARP than younger people in the population.
Antioxidants
There is a growing interest in the subject of antioxidants because of health concerns raised by our knowledge of problems created as a result of spontaneous oxidation of biomolecules by Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), such as superoxide. Antioxidants have the chemical property of protecting against oxidative damage by being readily oxidized themselves, preferentially to other biomolecules.
Biologically, cells have several lines of antioxidant defense. They include molecules, such as vitamins C, A, and E, glutathione, and enzymes that destroy ROS such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidases.

Health effects
Oxidation by ROS is mutagenic and has been linked to atherosclerosis. Nonetheless, randomized studies of oral supplementation of various vitamin combinations have shown no protective effect against cancer and supplementation of Vitamin E and selenium has revealed no decrease in the risk of cardiovascular disease. Further, no reduction in mortality rates as a result of supplementation with these materials has been found, so the protective effects, if any, of antioxidants on ROS in human health remain poorly understood.
Glutathione
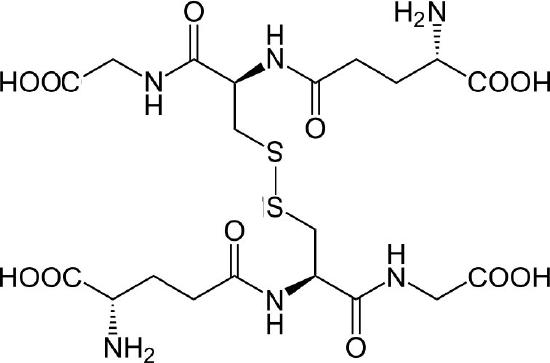
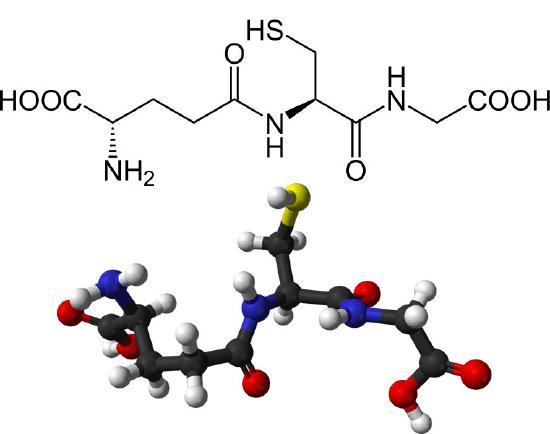
The thiol group of cysteine is a reducing agent that reduces disulfide bonds to sulfhydryls in cytoplasmic proteins. This, in turn, is the bridge when two glutathiones get oxidized and form a disulfide bond with each other (Figure 5.56). Glutathione’s two oxidative states are abbreviated as follows: GSH (reduced) and GSSG (oxidized).
Disulfide-joined glutathiones can be separated by reduction of their bonds with glutathione reductase, using electrons from NADPH for the reduction.
Non-ribosomal synthesis
Glutathione is not made by ribosomes. Rather, two enzymes catalyze its synthesis. The enzyme γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase catalyzes the joining of the glutamate to the cysteine and then glutathione synthetase catalyzes the peptide bond formation between the cysteine and the glycine. Each step requires energy from ATP.
Essential for life
Glutathione is important for life. Mice lacking the first enzyme involved in its synthesis in the liver die in the first month after birth. In healthy cells, 90% of glutathione is in the GSH state. Higher levels of GSSG correspond to cells that are oxidatively stressed.
Besides reducing disulfide bonds in cells, glutathione is also important for the following:
• Neutralization of free radicals and reactive oxygen species.
• Maintenance of exogenous antioxidants such as vitamins C and E in their reduced forms.
Regulation of the nitric oxide cycle
Resveratrol
Some data indicates resveratrol may improve the functioning of mitochondria. It also acts as an antioxidant and causes concentration of another anti-oxidant, glutathione, to increase. The compound appears to induce expression of manganese superoxide dismutase (protects against reactive oxygen species) and inhibits several phosphodiesterases. This causes an increase in cAMP which results in increases in oxidation of fatty acids, mitochondria formation, gluconeogenesis, and glycogen breakdown. It has been claimed to be the cause of the French Paradox in which drinking of red wine is supposed to give protection for the cardiovascular system. Research data is lacking in support of the claim, however. Resveratrol is known to activate Sirtuin proteins, which play roles in gene inactivation.
Summary
In summary, energy is needed for cells to perform the functions that they must carry out in order to stay alive. At its most basic level, this means fighting a continual battle with entropy, but it is not the only need for energy that cells have.
References
1. Winge, D.R., Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul; 32(14): 2647–2652. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00573-12
Energy: Electron Transport & Oxidative Phosphorylation
429
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
430
Figure 5.14 - Overview of electron transport (bottom left and top right) and oxidative phosphorylation (top left - yellow box) in the mitochondrion
431
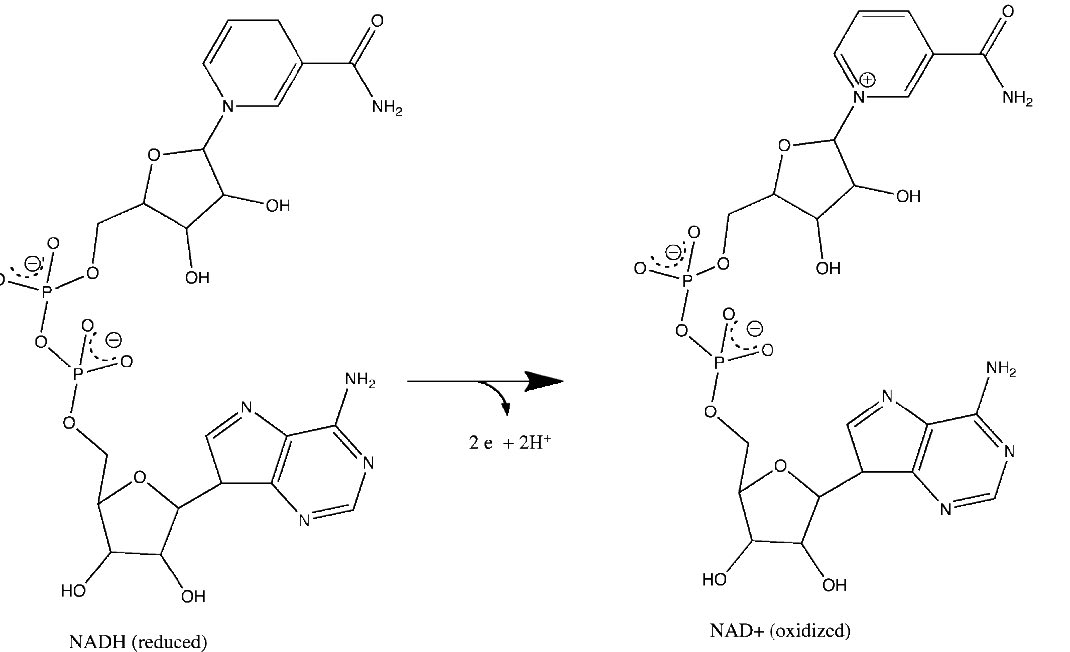
Figure 5.15 - Loss of electrons by NADH to form NAD+. Relevant reactions occur in the top ring of the molecule.
432
Figure 5.16 - Flow of electrons from NADH into the electron transport system. Entry is through complex I
Image by Aleia Kim
Figure 5.17 - Flow of electrons from FADH2 into the electron transport chain. Entry is through complex II.
Image by Aleia Kim
Interactive Learning
Module
HERE
433
Figure 5.18 - Complex I embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The mitochondrial matrix at at the top
Wikipedia
434
Figure 5.19 - Complex II embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane. Matrix is up.
Wikipedia
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
435
Figure 5.20 - Movement of electrons through complex I from NADH to coenzyme Q. The mitochondrial matrix is at the bottom
Image by Aleia Kim
Figure 5.21 - Movement of electrons from succinate through complex II (A->B->C->D->Q). Mitochondrial matrix on bottom.
Image by Aleia Kim
436
Figure 5.22 - Complex II in inner mitochondrial membrane showing electron flow. Matrix is up.
Wikipedia
Figure 5.23 - Coenzyme Q
437
Movie 5.2 - The Q-cycle
Wikipedia
Figure 5.24 - The Q-Cycle Image by Aleia Kim
Figure 5.24 - Complex III
Wikipedia
438
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
Figure 5.25 - The Q-cycle. Matrix is down.
Image by Aleia Kim
439
Figure 5.26 - Movement of electrons and protons through complex IV. Matrix is down
Image by Aleia Kim
Figure 5.25 - Cytochrome c with bound heme Group
Wikipedia
440
Figure 5.27 - Mitochondrial anatomy. Electron transport complexes and ATP synthase are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Image by Aleia Kim
441
Figure 5.28 - ATP synthase. Protons pass from intermembrane space (top) through the complex and exit in the matrix (bottom).
Image by Aleia Kim
Interactive Learning
Module
HERE
442
Movie 5.3 - ATP Synthase - ADP + Pi (pink) and ATP (red). The view is end-on from the cytoplasmic side viewing the β subunits
Movie 5.3 - ATP Synthase - ADP + Pi (pink) and ATP (red). The view is end-on from the cytoplasmic side viewing the β subunits
443
Figure 5.29 - Important structural features of the ATP synthase
Image by Aleia Kim
444
Figure 5.30 - Loose (L), Tight (T), and Open (O) structures of the F1 head of ATP synthase. Change of structure occurs by rotation of γ-protein (purple) in center as a result of proton movement. Individual α and β units do not rotate
Image by Aleia Kim
445
Figure 5.31 - Respiration overview in eukaryotic cells
Wikipedia
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
446
Rest
ATP High / ADP Low
Oxidative Phosphorylation Low
Electron Transport Low
Oxygen Use Low
NADH High / NAD+ Low
Citric Acid Cycle Slow
Exercise
ATP Low / ADP High
Oxidative Phosphorylation High
Electron Transport High
Oxygen Use High
NADH Low / NAD+ High
Citric Acid Cycle Fast
Interactive Learning
Module
HERE
447
Figure 5.32 - Three inhibitors of electron transport
Image by Aleia Kim
448
Figure 5.33 - Oligomycin A - An inhibitor of ATP synthase
Figure 5.34 - 2,4 DNP - an uncoupler of respiratory control
449
In Cells With Tight Coupling
O2 use depends on metabolism
NAD+ levels vary with exercise
Proton gradient high with no exercise
Catabolism depends on energy needs
ETS runs when OxPhos runs and vice versa
In Cells That Are Uncoupled
O2 use high
NAD+ Levels high
Little or no proton gradient
Catabolism high
OxPhos does not run, but ETS runs rapidly
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
450
451
Figure 5.35 - Alternative oxidase (AOX) of fungi, plants, and protozoa bypasses part of electron transport by taking electrons from CoQ and passing them to oxygen.
452
Figure 5.36 - Structure of an oxygen free radical
Wikipedia
NADPH + 2O2
NADP+ + 2O2− + H+
Figure 5.37 - Three sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells
Wikipedia
453
454
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
Figure 5.38 A hydroxyl radical
Wikipedia
455
Reduced Glutathione (GSH) + H2O2
Oxidized Glutathione (GSSG) + H2O
Figure 5.40 - Detoxifying reactive oxygen species
Figure 5.39 - Catalase
456
1. O2- + Enzyme-Cu++
O2 + Enzyme-Cu+
2. O2- + Enzyme-Cu+ + 2H+
H2O2 + Enzyme-Cu++
Figure 5.41 - SOD2 of humans
Figure 5.42 3 - Peroxynitrite Ion
Figure 5.44 - SOD1 of humans
Wikipedia
Figure 5.45 - SOD3 of humans
457
Figure 5.43 - Peroxynitrite’s effects on cells lead to necrosis or apoptosis
Wikipedia
458
RH + O2 + NADPH + H+
ROH + H2O + NADP+
459
Figure 5.46 - Cytochrome c with its heme group
460
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
Figure 5.47 - Fe2S2 Cluster
Figure 5.48 - Redox reactions for Fe4S4 clusters
461
Figure 5.49 - Tyramine
Figure 5.50 - Phenethylamine
462
Figure 5.51 - Guanine and 8-oxo-guanine
Figure 5.52 - Adenine-8-oxo-guanine base pair. dR = deoxyribose
463
Figure 5.53 - Good antioxidant sources
464
Figure 5.55 - Oxidized glutathiones (GSSG) joined by a disulfide bond
Wikipedia
Figure 5.54 - Structure of reduced glutathione (GSH)
465
Figure 5.56 - Resveratrol
YouTube Lectures
by Kevin
HERE & HERE
466
Graphic images in this book were products of the work of several talented students. Links to their Web pages are below
Click HERE for
Martha Baker’s
Web Page
Click HERE for
Pehr Jacobson’s
Web Page
Click HERE for
Aleia Kim’s
Web Page
Click HERE for
Penelope Irving’s
Web Page
Problem set related to this section HERE
Point by Point summary of this section HERE
To get a certificate for mastering this section of the book, click HERE
Kevin Ahern’s free iTunes U Courses - Basic / Med School / Advanced
Biochemistry Free & Easy (our other book) HERE / Facebook Page
Kevin and Indira’s Guide to Getting into Medical School - iTunes U Course / Book
To see Kevin Ahern’s OSU ecampus courses - BB 350 / BB 450 / BB 451
To register for Kevin Ahern’s OSU ecampus courses - BB 350 / BB 450 / BB 451
Biochemistry Free For All Facebook Page (please like us)
Kevin Ahern’s Web Page / Facebook Page / Taralyn Tan’s Web Page
Kevin Ahern’s free downloads HERE
OSU’s Biochemistry/Biophysics program HERE
OSU’s College of Science HERE
Oregon State University HERE
Email Kevin Ahern / Indira Rajagopal / Taralyn Tan
I'm a little mitochondrion
Who gives you energy
I use my proton gradient
To make the ATPs
He's a little mitochondrion
Who gives us energy
He uses proton gradients
To make some ATPs
Electrons flow through Complex II
To traffic cop Co-Q
Whenever they arrive there in
An FADH-two
Electrons flow through Complex II
To traffic cop Co-Q
Whenever they arrive there in
An FADH-two
Tightly coupled is my state
Unless I get a hole
Created in my membrane by
Some di-ni-tro-phe-nol
Yes tightly coupled is his state
Unless he gets a hole
Created in his membrane by
Some di-ni-tro-phenol
Both rotenone and cyanide
Stop my electron flow
And halt the calculation of
My "P" to "O" ratio
Recording by Tim Karplus
Lyrics by Kevin Ahern
Recording by Tim Karplus Lyrics by Kevin Ahern
I’m a Little Mitochondrion
To the tune of “I’m a Lumberjack”
Metabolic Melodies Website HERE
In the catabolic pathways that our cells employ
Oxidations help create the ATP
While they lower Gibbs free energy
Thanks to enthalpy
If a substrate is converted from an alcohol
To an aldehyde or ketone it is clear
Those electrons do not disappear
They just rearrange – very strange
N-A-D is in my ears and in my eyes
Help-ing mol-e-cules get oxidized
Making N-A-D-H then
And the latter is a problem anaerobically
‘Cuz accumulations of it muscles hate
They respond by using pyruvate
To produce lactate
Catalyzing is essential for the cells to live
So the enzymes grab their substrates eagerly
If they bind with high affinity
Low Km you see, just as me
N-A-D is in my ears and in my eyes
Help-ing mol-e-cules get oxidized
Making N-A-D-H then
N-A-D
To the tune of “Penny Lane”
Metabolic Melodies Website HERE
Recorded by Tim Karplus
Lyrics by Kevin Ahern
Recorded by Tim Karplus Lyrics by Kevin Ahern
When oxygen’s electrons all are in the balanced state
There’s twelve of them for oh-two. The molecule is great
But problems sometimes happen on the route to complex IV
Making reactive species that the cell cannot ignore
Oh superoxide dismutase is super catalytic
Keeping cells from getting very peroxynitritic
Faster than a radical, its actions are terrific
Superoxide dismutase is super catalytic
Enzyme, enzyme deep inside
Blocking all the bad oxides
The enzyme’s main advantage is it doesn’t have to wait
By binding superoxide in a near-transition state
It turns it to an oxygen in mechanism one
Producing “h two oh two” when the cycle is all done
Oh superoxide dismutase you’re faster than all them
You’ve got the highest ratio of kcat over KM
This means that superoxide cannot cause too much mayhem
Superoxide dismutase is faster than all them
Superoxide dismutase
Stopping superoxide’s ways
The enzyme’s like a ping-pong ball that mechanistic-ly
Bounces between two copper states, plus one and two you see
So S-O-D behaves just like an anti-oxidant
Giving as much protection as a cell could ever want
Oh superoxide dismutase, the cell’s in love with you
Because you let electron transport do what it must do
Without accumulation of a radical oh two
Superoxide dismutase - that’s why a cell loves you
Superoxide Dismutase
To the tune of “Supercalifragilistiexpialidocious”
Metabolic Melodies Website HERE
Lyrics by Kevin Ahern
No Recording Yet For This Song


