10.S: Organohalides (Summary)
- Page ID
- 325345
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Concepts & Vocabulary
10.1 Introduction to Organohalides
- Alkyl halides (and allyl and benzyl halides) are more reactive than vinyl and aryl halides.
10.2 Names and Properties of Alkyl Halides
- Reactivity of alkyl halides is often related to the substitution of the carbon atom the halogen is attached to.
- Alkyl halides are categorized by the number of bonds to other alkyl groups (primary, secondary, and tertiary).
- Carbon-halogen bonds are polarized with partial positive charges on carbon and partial negative charges on the halogen.
- Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens while iodine is the least electronegative.
- Iodine is the largest of the halogens yielding the longest/weakest bonds to carbon of the halogens.
- Since haloalkanes have dipole-dipole interactions, they have greater intermolecular forces than similar sized alkanes and therefore higher boiling points.
- Alkyl halides are either slightly soluble or insoluble in water, but are soluble in organic solvents.
10.3 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alkanes - Radical Halogenation
- Halogenation of alkanes is exothermic, so it is energetically favorable.
- Radical chain mechanisms consist of three steps: initiation, propagation and termination.
- Hydrogens on more substituted carbon atoms are more reactive to radical halogenation.
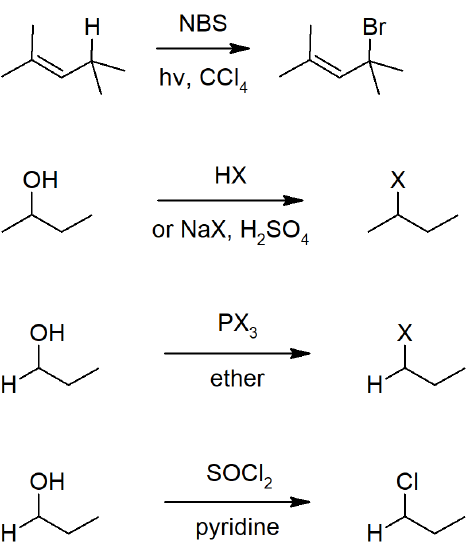
10.4 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alkenes - Allylic Bromination
- More substituted radicals and radicals with resonance structures are more stable than other radicals.
- Radical substitution can be carried out at the allylic or benzylic carbon by reacting with NBS.
10.5 Stability of the Allyl Radical - Resonance Revisited
- Allyl cations, anions and radicals have resonance structures. To draw these resonance structures non-bonded and pi-bond electrons can be moved.
- Resonance hybrids are used to show the combination of all resonance structures for a molecule or ion.
10.6 Preparing Alkyl Halides form Alcohols
- Alcohols can be reacted with hydrohalogen acids or a mixture of halogen salts and a stronger acid (to form hydrohalogen acids in situ).
- Alcohols will also react with thionyl chloride or with phosphorus halides to from haloalkanes.
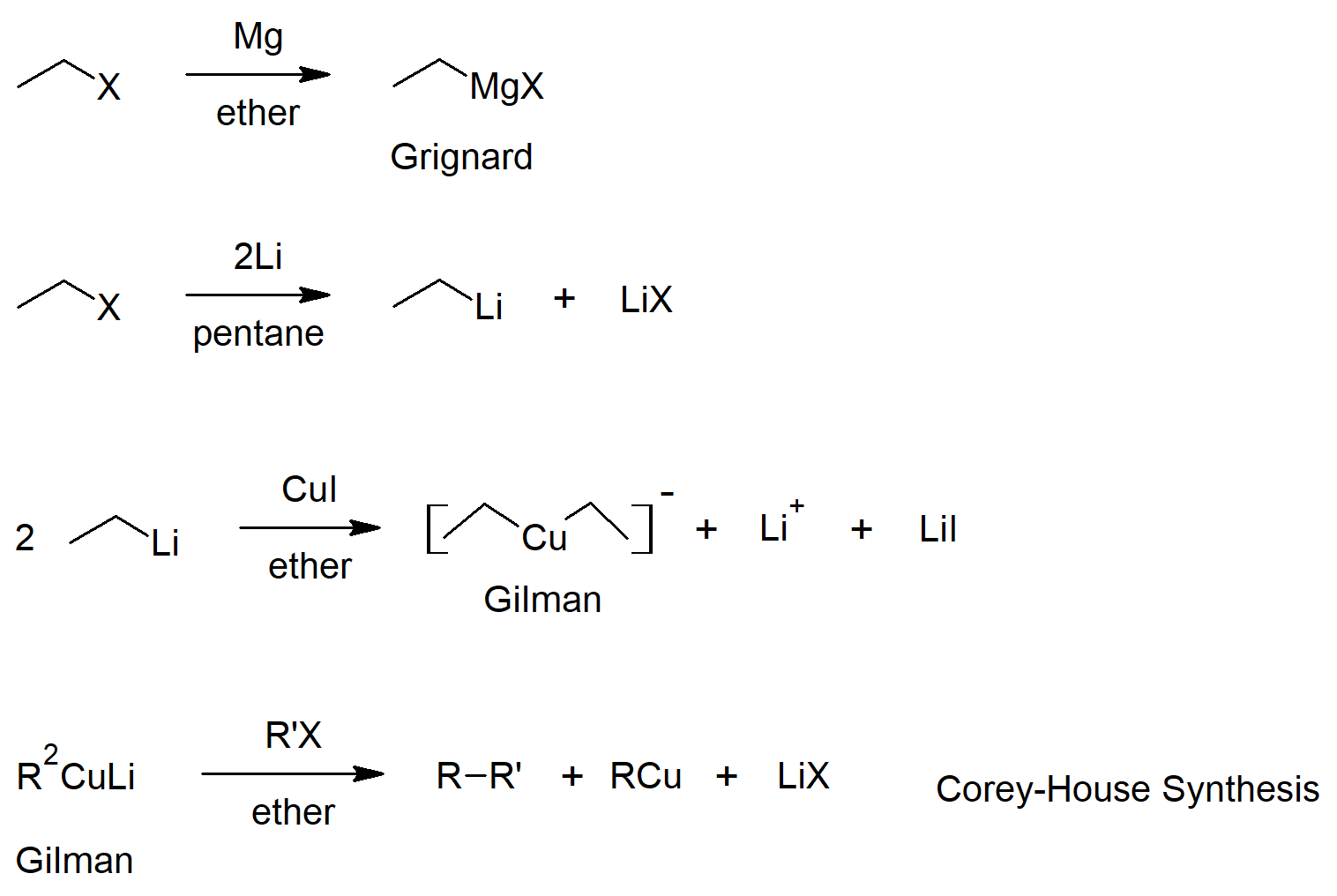
10.7 Reactions of Alkyl Halides - Grignard Reactions
- Organometallic reagents can be formed from alkyl halides and reactive metals (such as lithium and magnesium).
- Alkyl magnesium halide compounds are callled Grignard reagents.
- Grignard reagents react as bases where the alkyl group gets protonated and the metal complexes to the conjugate base of the reacting acid.
10.8 Organometallic Coupling Reactions
- Lithium dialkyl copper compounds are called Gilman reagents.
- Gilman reagents have different reactivity from the other organometallics (lithium and Grignard reagents).
- Organometallics can be reacted with alkyl halides to join to alkyl groups (coupling reactions).
10.9 Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Gaining bonds to hydrogen for organic molecules is reduction.
- Losing bonds to hydrogen for organic molecules is oxidation.
Skills to Master
- Skill 10.1 Differentiate between types of halides (alkyl, allyl, aryl, benzyl, and vinyl).
- Skill 10.2 Differentiate between substitution of alkyl halides (primary, secondary, and tertiary).
- Skill 10.3 Identify relative reactivity of carbon-hydrogen bonds to radical halogenation.
- Skill 10.4 Draw resonance structures for radical compounds.
- Skill 10.5 Draw mechanisms for radical halogenation of alkanes (initiation, propagation and termination).
- Skill 10.6 Calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using bond dissociation energies of reactants and products.
- Skill 10.7 Determine products for allylic bromination reactions.
- Skill 10.8 Draw resonance structures for allylic and other similar compounds and ions.
- Skill 10.9 Draw products of reactions of alcohols to form alkyl halides.
- Skill 10.10 Write equations to form Grignard reagents from alkyl halides.
- Skill 10.11 Draw reaction products for Grignard reagents acting as bases.
- Skill 10.12 Write equations for the formation of Gilman reagents.
- Skill 10.13 Draw reaction products of organometallic coupling reactions.
- Skill 10.14 Explain oxidation and reduction in organic molecules.
Summary of Reactions
Preparation of Alkyl Halides
Reactions Alkyl Halides
Contributors
- Layne Morsch (University of Illinois Springfield)
Dr. Dietmar Kennepohl FCIC (Professor of Chemistry, Athabasca University)