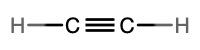5.12: Exercises
- Page ID
- 357321
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)5.2: Chemical Formulas
- Classify each of the following as an atomic element, a molecular element, an ionic compound, or a molecular compound. State how many atoms are in each formula unit or molecule.
- Fe
- PCl3
- P4
- CaBr2
- Answer
-
- atomic element
- molecular compound, 4 atoms
- molecular element, 4 atoms
- ionic compound, 3 atoms
- Classify each of the following as an atomic element, a molecular element, an ionic compound, or a molecular compound. State how many atoms are in each formula unit or molecule.
- I2
- Fe(NO3)2
- H2O
- Al
- Answer
-
- molecular element, 2 atoms
- ionic compound, 9 atoms
- molecular compound, 3 atoms
- atomic element
- What is the difference between CO and Co?
- Answer
-
CO is a molecular compound containing carbon and oxygen. Co is the atomic element cobalt.
- What is the difference between H2O and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)?
- Answer
-
H2O has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. H2O2 has two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms.
- Explain why the formula for an atom of the element oxygen and the formula for a molecule of oxygen differ.
- Answer
-
The symbol for the element oxygen, O, represents both the element and one atom of oxygen. A molecule of oxygen, O2, contains two oxygen atoms; the subscript 2 in the formula must be used to distinguish the diatomic molecule from two single oxygen atoms.
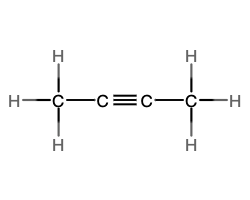
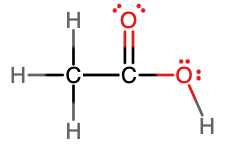
- Write the molecular and empirical formulas of the following compounds:
- Answer
-
- molecular = CO2, empirical = CO2
- molecular = C2H2, empirical = CH
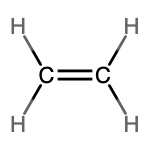
- molecular = C2H4, empirical = CH2
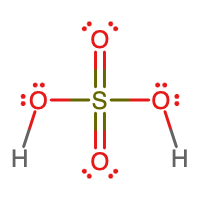
- molecular = H2SO4, empirical = H2SO4
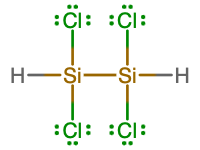
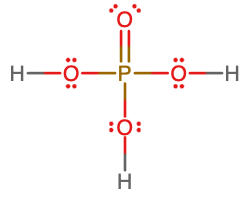
- Write the molecular and empirical formulas of the following compounds:
- Answer
-
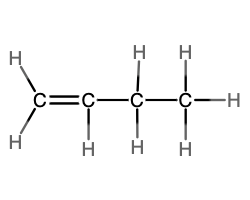
- molecular = C4H8; empirical = CH2
- molecular = C4H6; empirical = C2H3
- molecular = Si2H2Cl4; empirical = SiHCl2
- molecular = H3PO4; empirical = H3PO4
- Determine the empirical formulas for the following compounds:
- caffeine, C8H10N4O2
- sucrose, C12H22O11
- hydrogen peroxide, H2O2
- glucose, C6H12O6
- ascorbic acid (vitamin C), C6H8O6
- Answer
-
- C4H5N2O
- C12H22O11
- HO
- CH2O
- C3H4O3
- Write the empirical formulas for the following compounds:
- Answer
-
- CH2O
- C2H4O
- Determine the empirical formulas for the following compounds:
- acetic acid, C2H4O2
- citric acid, C6H8O7
- hydrazine, N2H4
- nicotine, C10H14N2
- butane, C4H10
- Answer
-
- CH2O
- C6H8O7
- NH2
- C5H7N
- C2H5
5.3: A Closer Look at Elements and Compounds
- From their positions on the periodic table, will Cu and I form a molecular compound or an ionic compound?
- Answer
-
ionic compound
- From their positions on the periodic table, will N and S form a molecular compound or an ionic compound?
- Answer
-
molecular compound
- Using the periodic table, predict whether the following chlorides are ionic or covalent: KCl, NCl3, ICl, MgCl2, PCl5, and CCl4.
- Answer
-
ionic = KCl, MgCl2; covalent = NCl3, ICl, PCl5, CCl4
- Using the periodic table, predict whether the following chlorides are ionic or covalent: SiCl4, PCl3, CaCl2, CsCl, CuCl2, and CrCl3.
- Answer
-
ionic = CaCl2, CsCl, CuCl2, CrCl3; covalent = SiCl4, PCl3
5.4: Chemical Nomenclature and the Classification of Compounds
- Classify each of the following compounds as binary ionic, ionic containing polyatomic ions, binary molecular, binary acid, or oxyacid.
- NF3
- HI
- (NH4)2CO3
- Sr3(PO4)2
- BaO
- H2SO4
- Answer
-
- binary molecular
- binary acid
- ionic containing polyatomic ions
- ionic containing polyatomic ions
- binary ionic
- oxyacid
- Classify each of the following compounds as binary ionic, ionic containing polyatomic ions, binary molecular, binary acid, or oxyacid.
- HClO3
- Mg(C2H3O2)2
- H2S
- Ag2S
- N2Cl4
- CoBr2
- Answer
-
- oxyacid
- ionic containing polyatomic ions
- binary acid
- binary ionic
- binary molecular
- binary ionic
5.5: Binary Ionic Compounds
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Mg2+ and Cl−
- Na+ and O2−
- Cd2+ and O2−
- Answer
-
- MgCl2, magnesium chloride
- Na2O, sodium oxide
- CdO, cadmium oxide
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- K+ and S2−
- Ag+ and Br−
- Sr2+ and N3−
- Answer
-
- K2S, potassium sulfide
- AgBr, silver bromide
- Sr3N2, strontium nitride
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Zn2+ and F−
- Ca2+ and O2−
- Li+ and P3−
- Answer
-
- ZnF2, zinc fluoride
- CaO, calcium oxide
- Li3P, lithium phosphide
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Na+ and N3−
- Sr2+ and I−
- Al3+ and S2−
- Answer
-
- Na3N, sodium nitride
- SrI2, strontium iodide
- Al2S3, aluminum sulfide
5.6: Ions With Variable Charges
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Ni2+ and Cl−
- Fe2+ and O2−
- Fe3+ and O2−
- Answer
-
- NiCl2, nickel(II) chloride
- FeO, iron(II) oxide
- Fe2O3, iron(III) oxide
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Cu+ and S2−
- Pt2+ and Br−
- Cr2+ and N3−
- Answer
-
- Cu2S, copper(I) sulfide
- PtBr2, platinum(II) bromide
- Cr3N2, chromium(II) nitride
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Cu2+ and F−
- U6+ and O2−
- Au+ and P3−
- Answer
-
- CuF2, copper(II) fluoride
- UO3, uranium(VI) oxide
- Au3P, gold(I) phosphide
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Sn2+ and N3−
- Co2+ and I−
- Au3+ and S2−
- Answer
-
- Sn3N2, tin(II) nitride
- CoI2, cobalt(II) iodide
- Au2S3, gold(III) sulfide
- Name each of the following compounds:
- Cr2O3
- FeCl2
- CrO3
- TiCl4
- CoO
- SnS2
- Answer
-
- chromium(III) oxide
- iron(II) chloride
- chromium(VI) oxide
- titanium(IV) chloride
- cobalt(II) oxide
- tin(IV) sulfide
- Name each of the following compounds:
- NiBr2
- WO3
- CoS
- V2O5
- MnO2
- Fe2O3
- Answer
-
- nickel(II) bromide
- tungsten(VI) oxide
- cobalt(II) sulfide
- vanadium(V) oxide
- manganese(IV) oxide
- iron(III) oxide
5.7: Ionic Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- K+ and SO42−
- NH4+ and S2−
- NH4+ and PO43−
- Answer
-
- K2SO4, potassium sulfate
- (NH4)2S, ammonium sulfide
- (NH4)3PO4, ammonium phosphate
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Ca2+ and NO3−
- Ca2+ and NO2−
- W3+ and C2H3O2−
- Answer
-
- Ca(NO3)2, calcium nitrate
- Ca(NO2)2, calcium nitrite
- W(C2H3O2)3, tungsten(III) acetate
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Pb4+ and SO42−
- Na+ and NO3−
- Li+ and CO32−
- Answer
-
- Pb(SO4)2, lead(IV) sulfate
- NaNO3, sodium nitrate
- Li2CO3, lithium carbonate
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- NH4+ and N3−
- Mg2+ and CN−
- Al3+ and OH−
- Answer
-
- (NH4)3N, ammonium nitride
- Mg(CN)2, magnesium cyanide
- Al(OH)3, aluminum hydroxide
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Ag+ and SO32−
- Na+ and HCO3−
- Fe3+ and ClO3−
- Answer
-
- Ag2SO3, silver sulfite
- NaHCO3, sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate
- Fe(ClO3)3, iron(III) chlorate
- Give the formula and name for each ionic compound formed between the two listed ions.
- Sn2+ and C2H3O2−
- Au3+ and SO32−
- Sr2+ and NO2−
- Answer
-
- Sn(C2H3O2)2, tin(II) acetate
- Au2(SO3)3, gold(III) sulfite
- Sr(NO2)2, strontium nitrite
- The uranyl cation has the formula UO22+. Propose formulas and names for the ionic compounds between the uranyl cation and F−, SO42−, and PO43−.
- Answer
-
UO2F2, uranyl fluoride; UO2SO4, uranyl sulfate; (UO2)3(PO4)2, uranyl phosphate
- The permanganate anion has the formula MnO4−. Propose formulas and names for the ionic compounds between the permanganate ion and K+, Ca2+, and Fe3+.
- Answer
-
KMnO4, potassium permangante; Ca(MnO4)2, calcium permanganate; Fe(MnO4)3, iron(III) permanganate
- For each of the following pairs of ions, write the formula of the compound they will form:
- Ca2+, S2−
- \(\ce{NH4+}\), \(\ce{SO4^2-}\)
- Al3+, Br−
- Na+, \(\ce{SO4^2-}\)
- Mg2+, \(\ce{PO4^3-}\)
- Answer
-
- CaS
- (NH4)2SO4
- AlBr3
- Na2SO4
- Mg3(PO4)2
- For each of the following pairs of ions, write the formula of the compound they will form:
- K+, O2−
- \(\ce{NH4+}\), \(\ce{PO4^3-}\)
- Al3+, O2−
- Li+, \(\ce{CO3^2-}\)
- Ba2+, \(\ce{PO4^3-}\)
- Answer
-
- K2O
- (NH4)3PO4
- Al2O3
- Li2CO3
- Ba3(PO4)2
- Write the formulas for each of the following compounds:
- potassium phosphate
- copper(II) sulfate
- calcium chloride
- titanium(IV) oxide
- ammonium nitrate
- Answer
-
- K3PO4
- CuSO4
- CaCl2
- TiO2
- NH4NO3
- Name each of the following compounds:
- Ca(ClO3)2
- FeSO4
- CaCO3
- AgNO2
- Ni(CN)3
- Answer
-
- calcium chlorate
- iron(II) sulfate
- calcium carbonate
- silver nitrite
- nickel(III) cyanide
5.8: Binary Molecular Compounds
- What is the stem of fluorine used in molecule names? CF4 is one example.
- Answer
-
fluor–
- What is the stem of bromine used in molecule names? SiBr4 is an example.
- Answer
-
brom–
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- PF3
- SCl2
- N2O3
- Answer
-
- phosphorus trifluoride
- sulfur dichloride
- dinitrogen trioxide
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- NO
- CS2
- As2O3
- Answer
-
- nitrogen monoxide
- carbon disulfide
- diarsenic trioxide
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- XeF2
- O2F2
- SF6
- Answer
-
- xenon difluoride
- dioxygen difluoride
- sulfur hexafluoride
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- P4O10
- B2O3
- P2S3
- Answer
-
- tetraphosphorus decoxide
- diboron trioxide
- diphosphorus trisulfide
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- N2O
- N2O4
- N2O5
- Answer
-
- dinitrogen monoxide
- dinitrogen tetroxide
- dinitrogen pentoxide
- Give the proper name for each molecule.
- SO2
- Cl2O
- XeF6
- Answer
-
- sulfur dioxide
- dichlorine monoxide
- xenon hexafluoride
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- dinitrogen pentoxide
- tetraboron tricarbide
- phosphorus pentachloride
- Answer
-
- N2O5
- B4C3
- PCl5
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- nitrogen triiodide
- diarsenic trisulfide
- iodine trichloride
- Answer
-
- NI3
- As2S3
- ICl3
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- dioxygen difluoride
- dinitrogen trisulfide
- xenon tetrafluoride
- Answer
-
- O2F2
- N2S3
- XeF4
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- chlorine dioxide
- sulfur dibromide
- dinitrogen trioxide
- Answer
-
- ClO2
- SBr2
- N2O3
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- iodine trifluoride
- xenon trioxide
- disulfur decafluoride
- Answer
-
- IF3
- XeO3
- S2F10
- Give the proper formula for each name.
- silicon dioxide
- carbon disulfide
- disulfur dibromide
- Answer
-
- SiO2
- CS2
- S2Br2
5.9: Acids
- Give the formula for each acid.
- chloric acid
- hydroiodic acid
- Answer
-
- HClO3
- HI
- Give the formula for each acid.
- hydrosulfuric acid
- phosphorous acid
- Answer
-
- H2S
- H3PO3
- Name each acid.
- HF(aq)
- HNO3(aq)
- HC2H3O2(aq)
- Answer
-
- hydrofluoric acid
- nitric acid
- acetic acid
- Name each acid.
- H2SO4(aq)
- H3PO4(aq)
- HCl(aq)
- Answer
-
- sulfuric acid
- phosphoric acid
- hydrochloric acid
5.10: Nomenclature Summary
- Name the following compounds:
- HClO2
- CuO
- K2SO4
- BrCl3
- HBr
- AlF3
- Answer
-
- chlorous acid
- copper(II) oxide
- potassium sulfate
- bromine trichloride
- hydrobromic acid
- aluminum fluoride
- Name the following compounds:
- NaF
- (NH4)2O
- MnCl3
- H2S
- P4O6
- HNO3
- Answer
-
- sodium fluoride
- ammonium oxide
- manganese(III) chloride
- hydrosulfuric acid
- tetraphosphorus hexoxide
- nitric acid
- Write the formulas of the following compounds:
- strontium bromide
- acetic acid
- lead(II) oxide
- gold(III) hydroxide
- hydrofluoric acid
- diphosphorus pentasulfide
- aluminum sulfite
- krypton tetrafluoride
- Answer
-
- SrBr2
- HC2H3O2
- PbO
- Au(OH)3
- HF
- P2S5
- Al2(SO3)3
- KrF4
- Write the formulas of the following compounds:
- lithium carbonate
- silver sulfide
- molybdenum(III) nitride
- diboron hexahydride
- sulfuric acid
- trisulfur heptachloride
- manganese(IV) chlorate
- hydrobromic acid
- Answer
-
- Li2CO3
- Ag2S
- MoN
- B2H6
- H2SO4
- S3Cl7
- Mn(ClO3)4
- HBr
- Write the formulas of the following compounds:
- chlorine dioxide
- carbonic acid
- potassium phosphide
- nickel(III) nitrite
- aluminum chlorite
- carbon disulfide
- Answer
-
- ClO2
- H2CO3
- K3P
- Ni(NO2)3
- Al(ClO2)3
- CS2
- Write the formulas of the following compounds:
- barium chloride
- xenon dioxide
- iron(III) nitrate
- acetic acid
- dinitrogen trioxide
- tin(IV) chloride
- Answer
-
- BaCl2
- XeO2
- Fe(NO3)3
- HC2H3O2
- N2O3
- SnCl4
This page was adapted from "Beginning Chemistry (Ball)" by LibreTexts and "Chemistry (OpenStax)" by LibreTexts and is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Vicki MacMurdo (Anoka-Ramsey Community College) and Lance S. Lund (Anoka-Ramsey Community College).