Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy
- Page ID
- 15741
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)While interaction with infrared light causes molecules to undergo vibrational transitions, the shorter wavelength, higher energy radiation in the UV (200-400 nm) and visible (400-700 nm) range of the electromagnetic spectrum causes many organic molecules to undergo electronic transitions. What this means is that when the energy from UV or visible light is absorbed by a molecule, one of its electrons jumps from a lower energy to a higher energy molecular orbital.
Electronic transitions
Let’s take as our first example the simple case of molecular hydrogen, H2. As you may recall from section 2.1A, the molecular orbital picture for the hydrogen molecule consists of one bonding σ MO, and a higher energy antibonding σ* MO. When the molecule is in the ground state, both electrons are paired in the lower-energy bonding orbital – this is the Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO). The antibonding σ* orbital, in turn, is the Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO).

If the molecule is exposed to light of a wavelength with energy equal to ΔE, the HOMO-LUMO energy gap, this wavelength will be absorbed and the energy used to bump one of the electrons from the HOMO to the LUMO – in other words, from the σ to the σ* orbital. This is referred to as a σ - σ* transition. ΔE for this electronic transition is 258 kcal/mol, corresponding to light with a wavelength of 111 nm.
When a double-bonded molecule such as ethene (common name ethylene) absorbs light, it undergoes a π - π* transition. Because π- π* energy gaps are narrower than σ - σ* gaps, ethene absorbs light at 165 nm - a longer wavelength than molecular hydrogen.

The electronic transitions of both molecular hydrogen and ethene are too energetic to be accurately recorded by standard UV spectrophotometers, which generally have a range of 220 – 700 nm. Where UV-vis spectroscopy becomes useful to most organic and biological chemists is in the study of molecules with conjugated pi systems. In these groups, the energy gap for π -π* transitions is smaller than for isolated double bonds, and thus the wavelength absorbed is longer. Molecules or parts of molecules that absorb light strongly in the UV-vis region are called chromophores.
Let’s revisit the MO picture for 1,3-butadiene, the simplest conjugated system . Recall that we can draw a diagram showing the four pi MO’s that result from combining the four 2pz atomic orbitals. The lower two orbitals are bonding, while the upper two are antibonding.
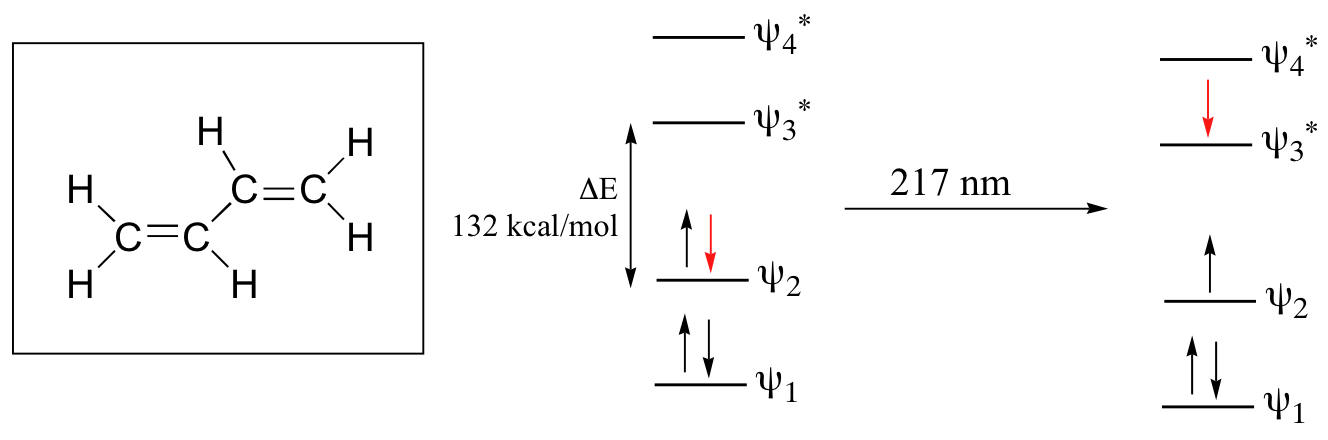
Comparing this MO picture to that of ethene, our isolated pi-bond example, we see that the HOMO-LUMO energy gap is indeed smaller for the conjugated system. 1,3-butadiene absorbs UV light with a wavelength of 217 nm.
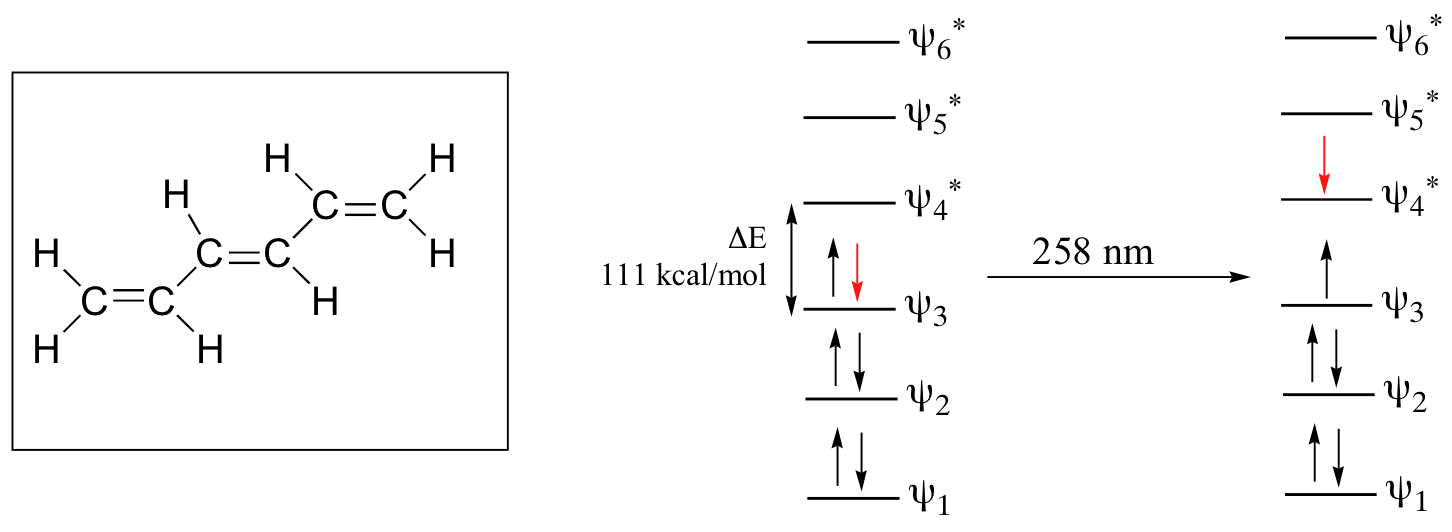
As conjugated pi systems become larger, the energy gap for a π - π* transition becomes increasingly narrow, and the wavelength of light absorbed correspondingly becomes longer. The absorbance due to the π - π* transition in 1,3,5-hexatriene, for example, occurs at 258 nm, corresponding to a ΔE of 111 kcal/mol.
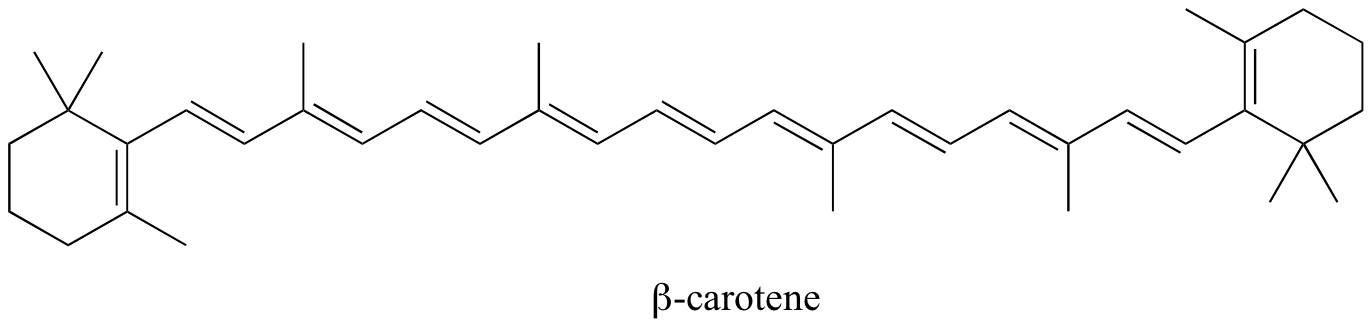
In molecules with extended pi systems, the HOMO-LUMO energy gap becomes so small that absorption occurs in the visible rather then the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Beta-carotene, with its system of 11 conjugated double bonds, absorbs light with wavelengths in the blue region of the visible spectrum while allowing other visible wavelengths – mainly those in the red-yellow region - to be transmitted. This is why carrots are orange.
The conjugated pi system in 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one gives rise to a strong UV absorbance at 236 nm due to a π - π* transition. However, this molecule also absorbs at 314 nm. This second absorbance is due to the transition of a non-bonding (lone pair) electron on the oxygen up to a π* antibonding MO:
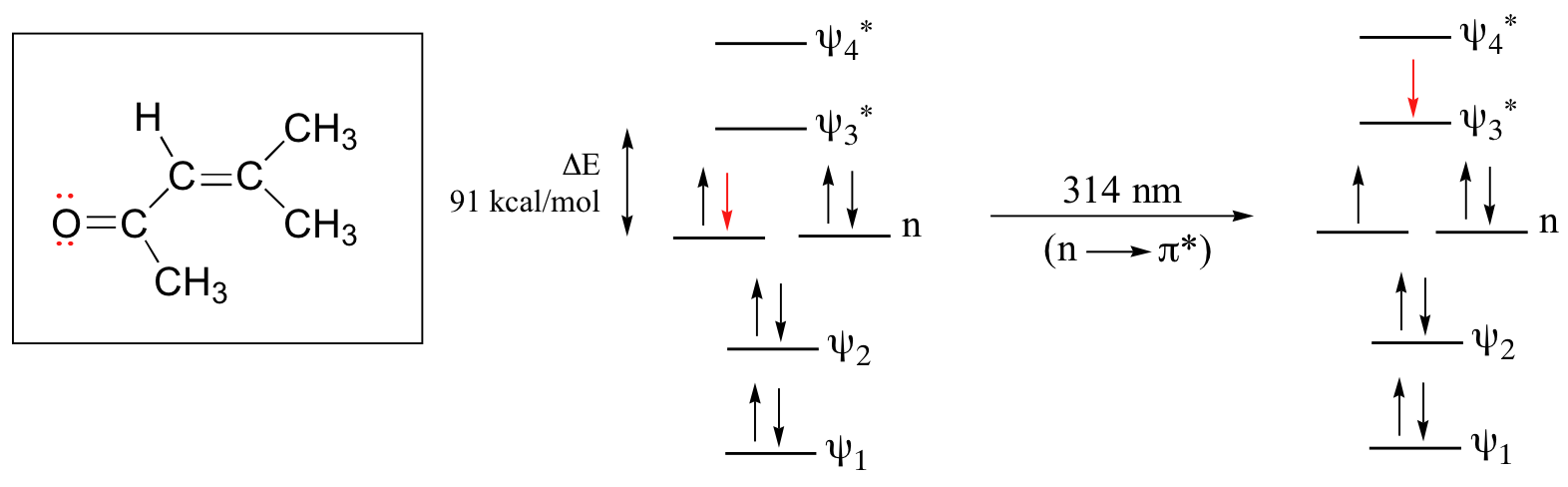
This is referred to as an n - π* transition. The nonbonding (n) MO’s are higher in energy than the highest bonding p orbitals, so the energy gap for an n - π* transition is smaller that that of a π - π* transition – and thus the n - π* peak is at a longer wavelength. In general, n - π* transitions are weaker (less light absorbed) than those due to π - π* transitions.
Express A = 1.0 in terms of percent transmittance (%T, the unit usually used in IR spectroscopy (and sometimes in UV-vis as well).
Template:ExampleEndHere is the absorbance spectrum of the common food coloring Red #3:
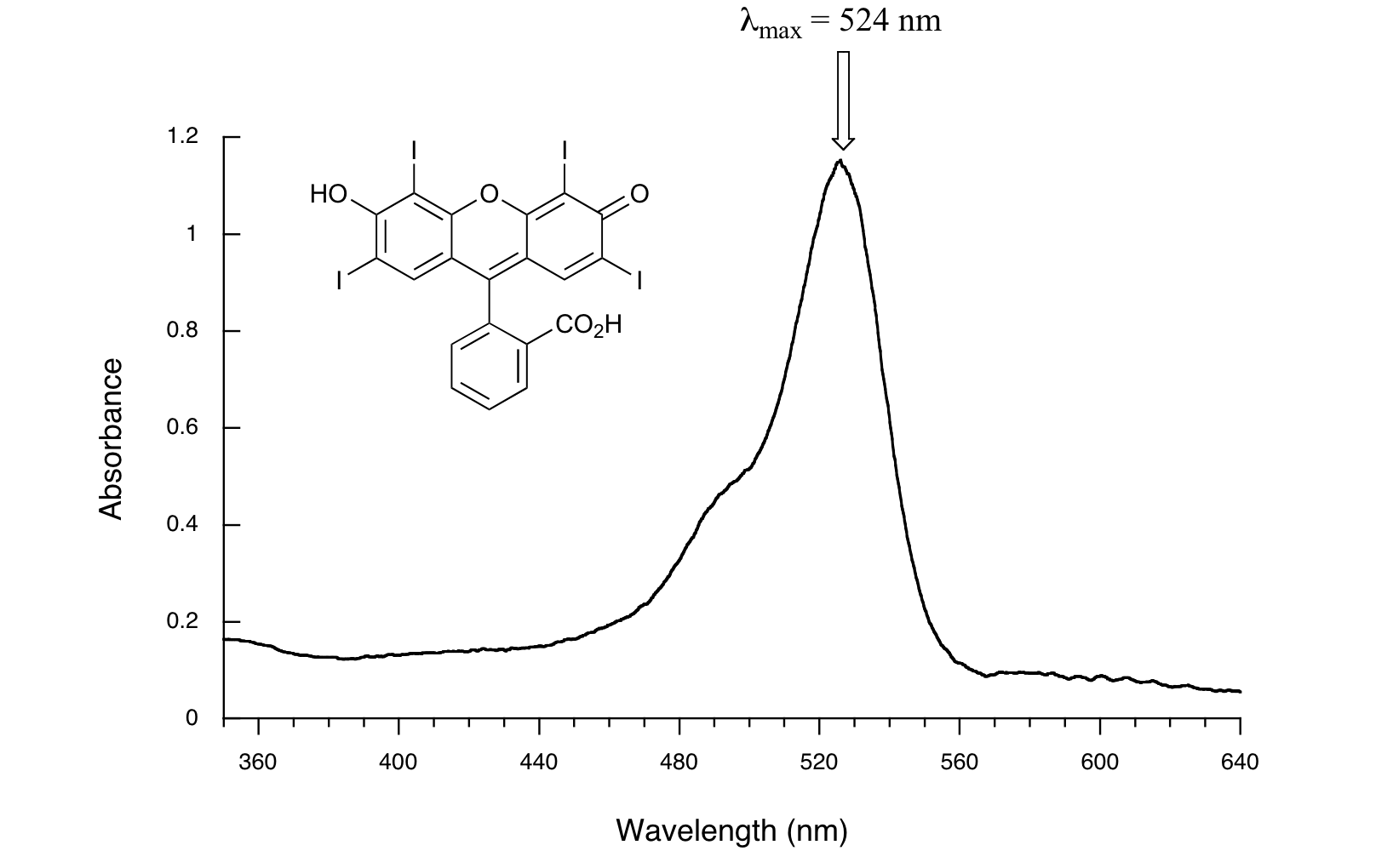
Here, we see that the extended system of conjugated pi bonds causes the molecule to absorb light in the visible range. Because the λmax of 524 nm falls within the green region of the spectrum, the compound appears red to our eyes.
Now, take a look at the spectrum of another food coloring, Blue #1:
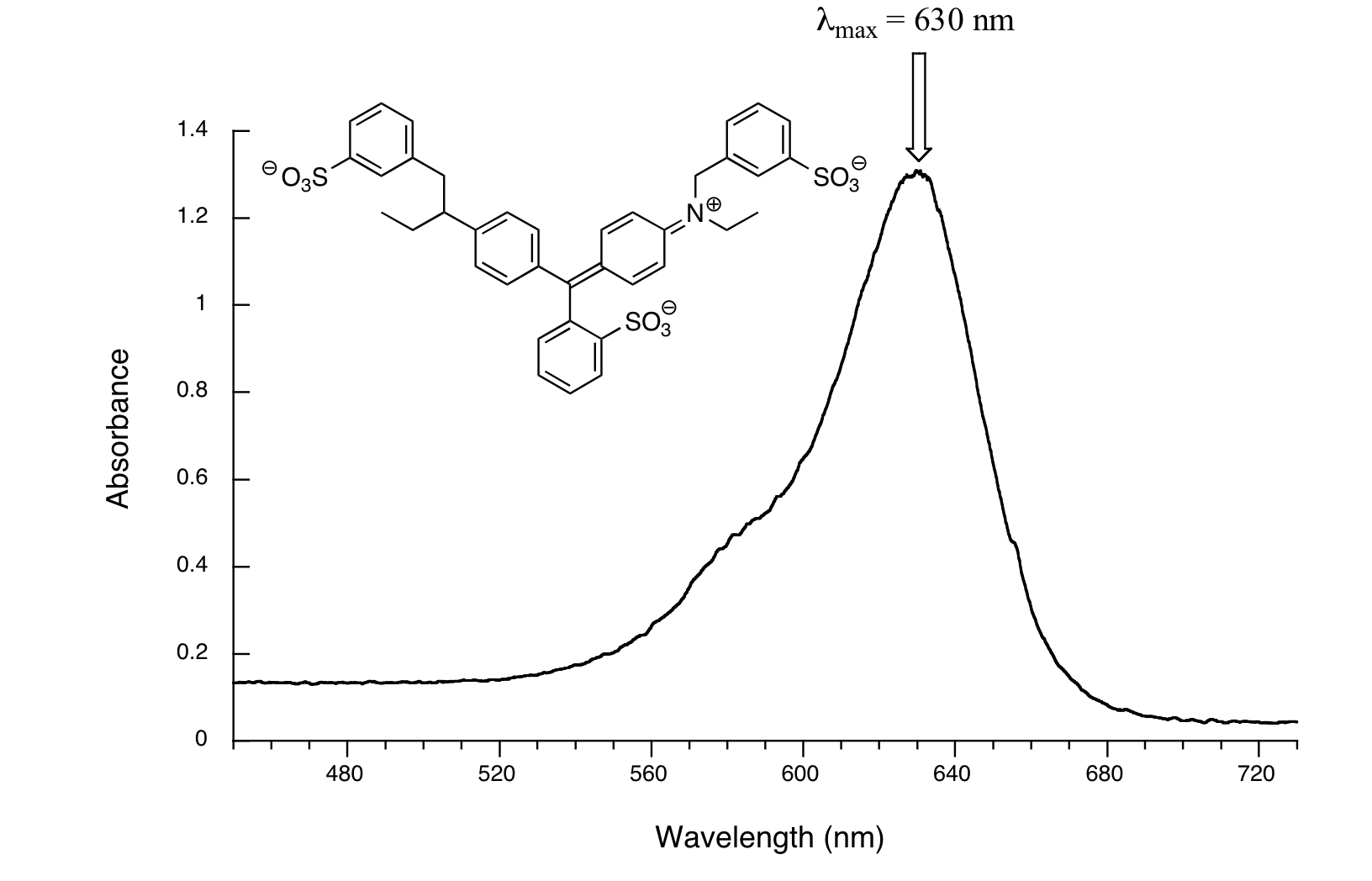
Here, maximum absorbance is at 630 nm, in the orange range of the visible spectrum, and the compound appears blue.
Applications of UV spectroscopy in organic and biological chemistry
UV-vis spectroscopy has many different applications in organic and biological chemistry. One of the most basic of these applications is the use of the Beer - Lambert Law to determine the concentration of a chromophore. You most likely have performed a Beer – Lambert experiment in a previous chemistry lab. The law is simply an application of the observation that, within certain ranges, the absorbance of a chromophore at a given wavelength varies in a linear fashion with its concentration: the higher the concentration of the molecule, the greater its absorbance. If we divide the observed value of A at λmax by the concentration of the sample (c, in mol/L), we obtain the molar absorptivity, or extinction coefficient (ε), which is a characteristic value for a given compound.
ε = A/c
The absorbance will also depend, of course, on the path length - in other words, the distance that the beam of light travels though the sample. In most cases, sample holders are designed so that the path length is equal to 1 cm, so the units for molar absorptivity are mol * L-1cm-1. If we look up the value of e for our compound at λmax, and we measure absorbance at this wavelength, we can easily calculate the concentration of our sample. As an example, for NAD+ the literature value of ε at 260 nm is 18,000 mol * L-1cm-1. In our NAD+ spectrum we observed A260 = 1.0, so using equation 4.4 and solving for concentration we find that our sample is 5.6 x 10-5 M.
Template:ExampleStartThe literature value of ε for 1,3-pentadiene in hexane is 26,000 mol * L-1cm-1 at its maximum absorbance at 224 nm. You prepare a sample and take a UV spectrum, finding that A224 = 0.850. What is the concentration of your sample?
Template:ExampleEndThe bases of DNA and RNA are good chromophores:

Biochemists and molecular biologists often determine the concentration of a DNA sample by assuming an average value of ε = 0.020 ng-1×mL for double-stranded DNA at its λmax of 260 nm (notice that concentration in this application is expressed in mass/volume rather than molarity: ng/mL is often a convenient unit for DNA concentration when doing molecular biology).
Template:ExampleStart50 mL of an aqueous sample of double stranded DNA is dissolved in 950 mL of water. This diluted solution has a maximal absorbance of 0.326 at 260 nm. What is the concentration of the original (more concentrated) DNA sample, expressed in mg/mL?
Because the extinction coefficient of double stranded DNA is slightly lower than that of single stranded DNA, we can use UV spectroscopy to monitor a process known as DNA melting. If a short stretch of double stranded DNA is gradually heated up, it will begin to ‘melt’, or break apart, as the temperature increases (recall that two strands of DNA are held together by a specific pattern of hydrogen bonds formed by ‘base-pairing’).
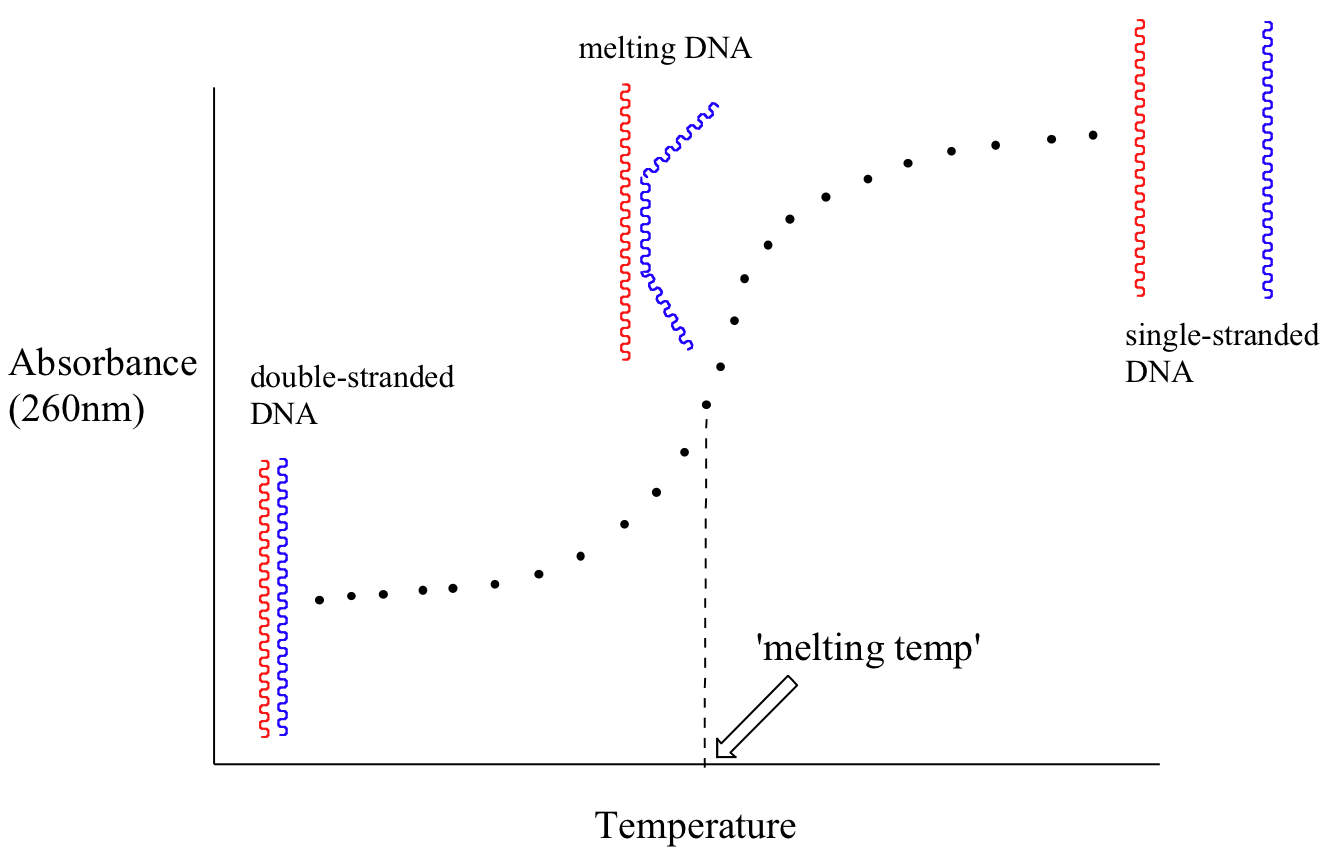
As melting proceeds, the absorbance value for the sample increases, eventually reaching a high plateau as all of the double-stranded DNA breaks apart, or ‘melts’. The mid-point of this process, called the ‘melting temperature’, provides a good indication of how tightly the two strands of DNA are able to bind to each other.
Proteins absorb light in the UV range due to the presence of the aromatic amino acids tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine, all of which are chromophores.
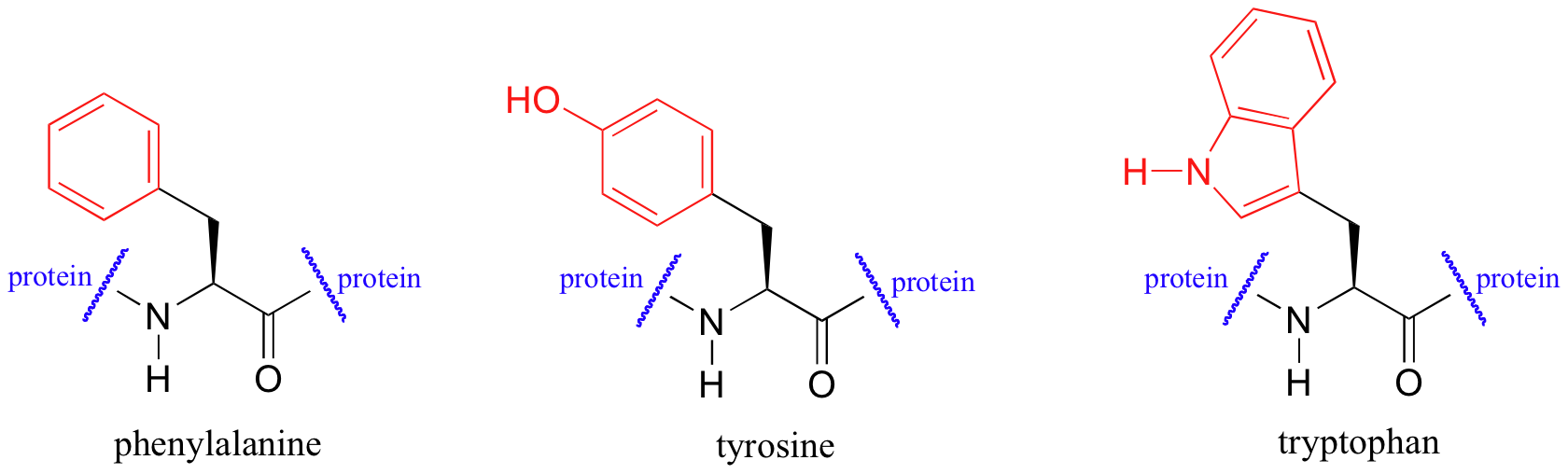
Biochemists frequently use UV spectroscopy to study conformational changes in proteins - how they change shape in response to different conditions. When a protein undergoes a conformational shift (partial unfolding, for example), the resulting change in the environment around an aromatic amino acid chromophore can cause its UV spectrum to be altered.

