4.3: Conformation Analysis of Cyclohexane
- Page ID
- 359583
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Chair conformation of cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is the most stable cycloalkane. It is strain-free, meaning neither angle strains nor torsional strains apply, and it shows the same stability as chain alkanes. This special stability is due to a unique conformation that it adopts. The most stable conformation of cyclohexane is called “chair“ conformation, since it somewhat resembles a chair.
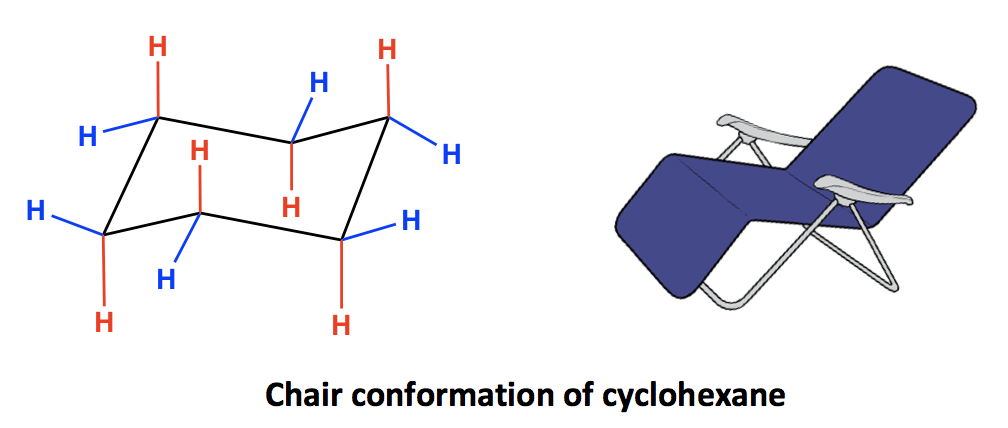
In the chair conformation of cyclohexane, all the carbons are at 109.5º bond angles, so no angle strain applies. The hydrogens on adjacent carbons are also arranged in a perfect staggered conformation that makes the ring free of torsional strain as well. This will be illustrated more clearly later when we learn about the Newman projection of the chair conformation.
Properties of the chair conformation
In the chair conformation of cyclohexane, the total twelve C-H bonds can be divided into two categories based on the orientations, which are axial (“a”) and equatorial (“e”). In the structure below, the six red coloured bonds are axial and the six blue coloured bonds are equatorial. Axial bonds are vertical and perpendicular to the average plane of the ring, while the equatorial bonds are more “flat” and extend from the perimeter of the ring. For both “a” and “e”, they can either point up ↑(above the ring), or point down ↓(below the ring). The trending of “a” and “e” bonds in the chair conformation can be summarized as:
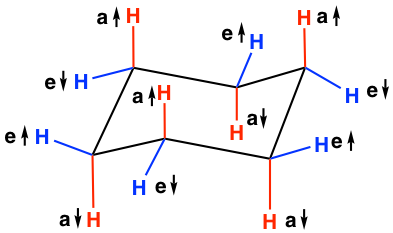
- Each carbon has one “a” bond and one “e” bond; if one bond points up ↑(above the ring), the other has to point down ↓(below the ring);
- For the same type of bonds, the orientation up ↑ and down ↓ alternates from one carbons to the adjacent carbon, meaning if a certain carbon has a ↑, then the adjacent carbon must has a ↓;
- For the total twelve C-H bonds: 3a↑ , 3 a↓, 3 e↑ , 3 e↓.
How to draw chair conformation
It is important to be able to understand and recognize all the bonds in the chair conformation, and you are also expected to be able to draw the conformation correctly and quickly. The procedure is:
- Draw two parallel lines of the same length both point slightly down (if connected, they would form a parallelogram with an internal angle of about 60°/120°).
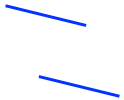
- Connect the right ending points of the two lines with a “V” shape, so that the vertex of the V points to the upper right

- Connect the left starting points of the two lines with another “V” shape, so that the vertex of the V points to the bottom left
 Add up all of the “a” bonds on each carbon as the vertical lines, follow the alternating trend on adjacent carbons
Add up all of the “a” bonds on each carbon as the vertical lines, follow the alternating trend on adjacent carbons
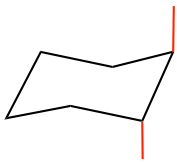
- Add all of the “e” bonds by following the trend in which on a certain carbon, if an “a” bond points up, then an “e” bond must point down, and vice versa. Also notice that the “e” bond is parallel to the C-C bond which is one bond away, as shown below. The “green e” is parallel to the “green C-C bond”, and the “blue e” is parallel to the “blue C-C bond”. (It is more challenging to draw “e” bonds, and following the above trend makes it easier).

It is highly recommended that a molecular model set is used as a study tool in this section. Assemble a cyclohexane ring with the model, and get familiar with all the bonds in chair conformation.
Practice makes perfect! A lot of practice is required to become skilled in drawing and understanding the chair conformation.
Ring flipping
When a cyclohexane ring undergoes a chair-chair conformation conversion, that is known as ring flipping. Ring flipping comes from C-C bond rotation, but since all of the bonds are limited within the ring, the rotation can only occur partially, which leads to the ring “flipping”. Cyclohexane rapidly interconverts between two stable chair conformations because of the ease of bond rotation. The energy barrier is about 45 kJ/mol, and the thermal energies of the molecules at room temperature are great enough to cause about 1 million interconversions to occur per second.
For cyclohexane, the ring after flipping still appears somewhat identical to the original ring, however there are some changes happening on the C-H bonds. Specifically, all the “a” bonds become “e” bonds and all the “e” bonds become “a” bonds, however their relative positions in terms of the ring, up or down, remain the same. The ring flipping is shown in the equation below. Compare the carbon with the same numbering in the two structures to see what happened to the bonds due to ring flipping.
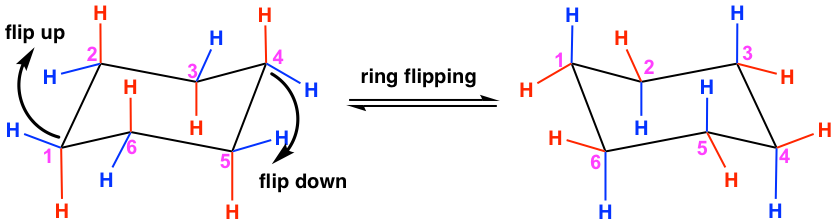
Taking C #1 as an example, you will notice that the red a↓ converted to a red e↓, and the blue e↑converted to a blue a↑ after ring flipping.
Summary of ring flipping for chair conformation:
- This is NOT rotation, but ring flipping
- The two structures are conformation isomers (or conformers)
- all “a” bonds become “e” bonds and all “e” bonds become “a” bonds
- These two conformations are equivalent for the cyclohexane ring itself (without any substituents), with the same energy level
A molecular model is very useful in understanding ring flipping.
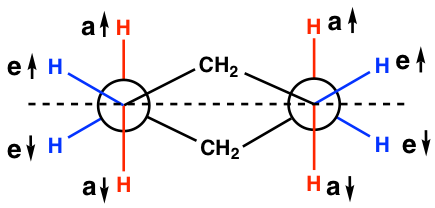
Newman projection of chair conformation
The chair conformation is strain free, with all the C-H bonds in staggered position. However, it is not that easy to see the staggered conformation in the drawings we have so far, and Newman projection help for this purpose.
To draw Newman projections for the chair conformation of cyclohexane, we also need to pick up the C-C bond to view along, just as we did for alkanes. Since there are a total of six C-C bonds, we will pick two of them, and these two need to be parallel to each other.
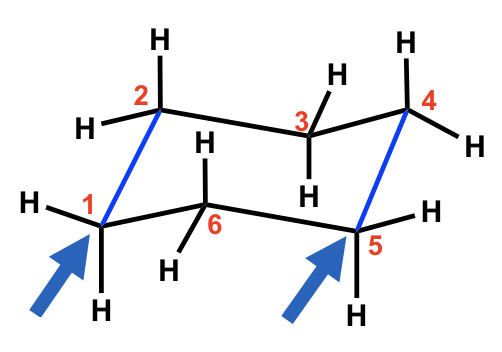
For the chair conformation example here, the two blue parallel C-C bonds are picked up for viewing, which are C1-C2 and C5-C4. (There are 3 pairs of parallel bonds in the chair conformation, any pair can be picked with the resulting Newman projection looking the same).
For the C1-C2 bond, C1 is the ‘front” carbon and C2 is the “rear” carbon; for the C5-C4 bond, C5 is the ‘front” carbon and C4 is the “rear” carbon. These two bonds will be represented by two “Newman projections” that we are familiar with (two circle things) and each represents two carbons, as shown below:
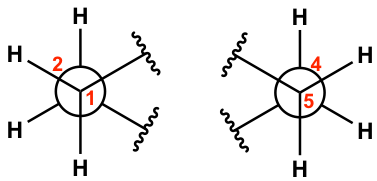
Keep in mind that there are a total of six carbons in the ring, and the the drawing above only shows four of them with C3 and C6 being left out. Additionally, the two “separated” Newman projections above are actually connected to both C3 and C6, so the overall Newman projection of the chair conformation of cyclohexane looks like this:
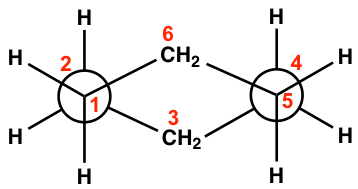
The staggered conformation of hydrogens are shown clearly in the Newman projection here!
Notes for Newman projections of the chair conformation (refer to the drawing below):
- The “a” or “e” bonds on four carbons (C1, C2, C4 and C5) are shown explicitly, while the bonds on C3 and C6 are just shown as CH2.
- The vertical red C-H bonds are the “a” bonds, the “flat” blue C-H bonds are the “e” bonds.
- The dashed line in the drawing below can be regarded as the average plane of the ring. Those above the line are the bonds point up ↑, those below the line are the bonds point down ↓.
Other conformation of cyclohexane
The chair conformation is the most stable one with the lowest energy, but it is not the only conformation for cyclohexane. During the ring flipping from one chair conformation to another chair conformation, the ring goes through several other conformations, and we will only talk briefly about the boat conformation here.
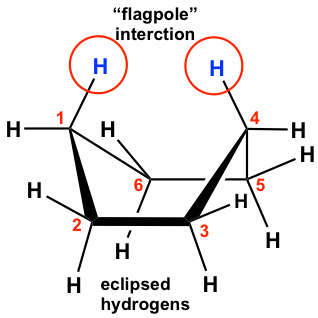
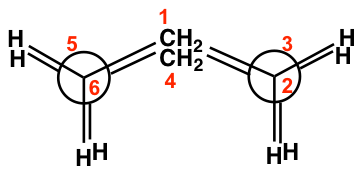
The boat conformation comes from partial C-C bond rotations (only flipping one carbon up to convert the chair to a boat) of the chair conformation, and all the carbons still have 109.5º bond angles, so there are no angle strains. However, the hydrogens on the base of the boat are all in eclipsed positions, so there are torsional strains. This can be illustrated by the Newman projection below. The Newman projection is drawn by viewing along C6-C5 and C2-C3 bonds of the above boat conformation.
Other than that, the two hydrogen atoms on C1 and C4 are very close to each other and causes steric strain. This is also called the “flagpole” interaction of the boat conformation. The two types of strains make the boat conformation have considerably higher energy (about 30 kJ/mol) than the chair conformation.


