26.17: Additional Problems
- Page ID
- 459699
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
Visualizing Chemistry
(b)
(c)
Give the sequence of the following tetrapeptide (yellow = S):

Isoleucine and threonine are the only two amino acids with two chirality centers. Assign R or S configuration to the methyl-bearing carbon atom of isoleucine.
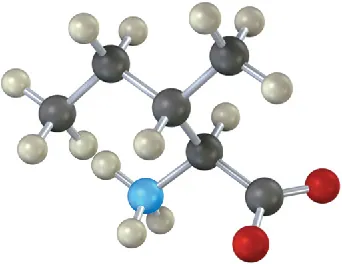
Isoleucine and threonine are the only two amino acids with two chirality centers. Assign R or S configuration to the methyl-bearing carbon atom of isoleucine.
Is the following structure a D amino acid or an L amino acid? Identify it.
Give the sequence of the following tetrapeptide:
Mechanism Problems
α-amino acid occurs in several steps. (a)
The first step is formation of an imine by reaction of the amino acid with ninhydrin. Show its structure and the mechanism of its formation.The final step is formation of the purple anion. Show the mechanism of the reaction.
The chloromethylated polystyrene resin originally used for Merrifield solid-phase peptide synthesis was prepared by treatment of polystyrene with chloromethyl methyl ether and a Lewis acid catalyst. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
An Fmoc protecting group can be removed from an amino acid by treatment with the amine base piperidine. Propose a mechanism.
Proteins can be cleaved specifically at the amide bond on the carboxyl side of methionine residues by reaction with cyanogen bromide, BrC≡N.
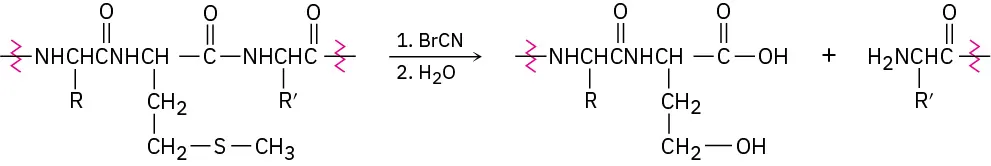
The reaction occurs in several steps:
(a)
The first step is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of the sulfur on the methionine side chain with BrCN to give a cyanosulfonium ion, [R2SCN]+. Show the structure of the product, and propose a mechanism for the reaction.
The second step is an internal SN2 reaction, with the carbonyl oxygen of the methionine residue displacing the positively charged sulfur leaving group and forming a five-membered ring product. Show the structure of the product and the mechanism of its formation.
(c)The third step is a hydrolysis reaction to split the peptide chain. The carboxyl group of the former methionine residue is now part of a lactone (cyclic ester) ring. Show the structure of the lactone product and the mechanism of its formation.
(d)The final step is a hydrolysis of the lactone to give the product shown. Show the mechanism of the reaction.
A clever recent method of peptide synthesis involves formation of an amide bond by reaction of an α-keto acid with an N-alkylhydroxylamine:
The reaction is thought to occur by nucleophilic addition of the N-alkylhydroxylamine to the keto acid as if forming an oxime (Section 19.8), followed by decarboxylation and elimination of water. Show the mechanism.
Amino Acid Structures and Chirality
Except for cysteine, only S amino acids occur in proteins. Several R amino acids are also found in nature, however. (R)-Serine is found in earthworms, and (R)-alanine is found in insect larvae. Draw Fischer projections of (R)-serine and (R)-alanine. Are these D or L amino acids?
Cysteine is the only amino acid that has L stereochemistry but an R configuration. Make up a structure for another L amino acid of your own creation that also has an R configuration.
Draw a Fischer projection of (S)-proline.
Trp
Proline has pKa1 = 1.99 and pKa2 = 10.60. Use the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation to calculate the ratio of protonated and neutral forms at pH = 2.50. Calculate the ratio of neutral and deprotonated forms at pH = 9.70.
Val, Ser, Leu
Look at the side chains of the 20 amino acids in Table 26.1, and then think about what is not present. None of the 20 contain either an aldehyde or a ketone carbonyl group, for instance. Is this just one of nature’s oversights, or is there a likely chemical reason? What complications might an aldehyde or ketone carbonyl group cause?
Amino Acid Synthesis and Reactions
Peptides and Enzymes
Which amide bonds in the following polypeptide are cleaved by trypsin? By chymotrypsin? Phe-Leu-Met-Lys-Tyr-Asp-Gly-Gly-Arg-Val-Ile-Pro-Tyr General Problems Arginine, the most basic of the 20 common amino acids, contains a guanidino functional group in its side chain. Explain, using resonance structures to show how the protonated guanidino group is stabilized. Evidence for restricted rotation around amide Propose a structure for an octapeptide that shows the composition Asp, Gly2, Leu, Phe, Pro2, Val on amino acid analysis. Edman analysis shows a glycine N-terminal group, and leucine is the C-terminal group. Acidic hydrolysis gives the following fragments: Val-Pro-Leu, Gly, Gly-Asp-Phe-Pro, Phe-Pro-Val Look at the structure of human insulin, and indicate where in each chain the molecule is cleaved by trypsin and chymotrypsin. What is the structure of a nonapeptide that gives the following fragments when cleaved? Trypsin cleavage: Val-Val-Pro-Tyr-Leu-Arg, Ser-Ile-Arg Chymotrypsin cleavage: Leu-Arg, Ser-Ile-Arg-Val-Val-Pro-Tyr Oxytocin, a nonapeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, functions by stimulating uterine contraction and lactation during childbirth. Its sequence was determined from the following evidence: 1. Oxytocin is a cyclic compound containing a disulfide bridge between two cysteine residues. 2. When the disulfide bridge is reduced, oxytocin has the constitution Asn, Cys2, Gln, Gly, Ile, Leu, Pro, Tyr. 3. Partial hydrolysis of reduced oxytocin yields seven fragments: Asp-Cys, Ile-Glu, Cys-Tyr, Leu-Gly, Tyr-Ile-Glu, Glu-Asp-Cys, and Cys-Pro-Leu. 4. Gly is the C-terminal group. 5. Both Glu and Asp are present as their side-chain amides (Gln and Asn) rather than as free side-chain acids. What is the amino acid sequence of reduced oxytocin? What is the structure of oxytocin itself? The first step in the biological degradation of histidine is formation of a 4-methylidene-5-imidazolone (MIO) by cyclization of a segment of the peptide chain in the histidine ammonia lyase enzyme. Propose a mechanism. The first step in the biological degradation of lysine is reductive amination with α-ketoglutarate to give saccharopine. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), a relative of NADH, is the reducing agent. Show the mechanism.Leucine
Methionine
Pro
Serine can be synthesized by a simple variation of the amidomalonate method using formaldehyde rather than an alkyl halide. How might this be done?
CH3CH2OH, acid
Draw resonance forms for the purple anion obtained by reaction of ninhydrin with an α-amino acid (see Problem 26-24).
C-H-E-M
Propose two structures for a tripeptide that gives Leu, Ala, and Phe on hydrolysis but does not react with phenyl isothiocyanate.
Show the steps involved in a synthesis of Phe-Ala-Val using the Merrifield procedure.
I-L-P-F
Hydrolases
Valine
Leuprolide is a synthetic nonapeptide used to treat both endometriosis in women and prostate cancer in men.
(a)
Both C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids in leuprolide have been structurally modified. Identify the modifications.
(b)
One of the nine amino acids in leuprolide has D stereochemistry rather than the usual L. Which one?
(c)
Write the structure of leuprolide using both one- and three-letter abbreviations.
(d)
What charge would you expect leuprolide to have at neutral pH?
The α-helical parts of myoglobin and other proteins stop whenever a proline residue is encountered in the chain. Why is proline never present in a protein α helix?
Cytochrome c is an enzyme found in the cells of all aerobic organisms. Elemental analysis of cytochrome c shows that it contains 0.43% iron. What is the minimum molecular weight of this enzyme?
Aspartame, a nonnutritive sweetener marketed under such trade names as Equal, NutraSweet, and Canderel, is the methyl ester of a simple dipeptide, Asp-Phe-OCH3.
(a)
Draw the structure of aspartame.Refer to Figure 26.5 and propose a mechanism for the final step in Edman degradation—the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of the ATZ derivative to the PTH derivative.
Amino acids are metabolized by a transamination reaction in which the −NH2 group of the amino acid changes places with the keto group of an α-keto acid. The products are a new amino acid and a new α-keto acid. Show the product from transamination of isoleucine.


