16.6: The Diels-Alder (4 + 2) Cycloaddition Reaction
- Page ID
- 111057
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The Diels-Alder (4+2) Cycloaddition Reaction
A cycloaddition reaction is the concerted bonding together of two independent pi-electron systems to form a new ring of atoms. When this occurs, two pi-bonds are converted to two sigma-bonds, the simplest example being the hypothetical combination of two ethene molecules to give cyclobutane. This does not occur under normal conditions, but the cycloaddition of 1,3-butadiene to cyanoethene (acrylonitrile) does, and this is an example of the Diels-Alder reaction. The following diagram illustrates two cycloadditions, and introduces several terms that are useful in discussing reactions of this kind.
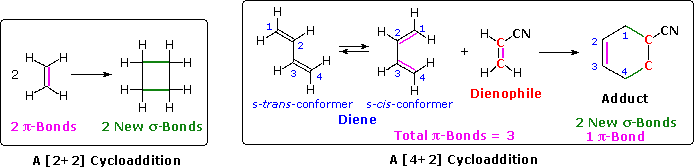
In the hypothetical ethylene dimerization on the left, each reactant molecule has a pi-bond (colored orange) occupied by two electrons. The cycloaddition converts these pi-bonds into new sigma-bonds (colored green), and this transformation is then designated a [2+2] cycloaddition, to enumerate the reactant pi-electrons that change their bonding location.
The Diels-Alder reaction is an important and widely used method for making six-membered rings, as shown on the right. The reactants used in such reactions are a conjugated diene, simply referred to as the diene, and a double or triple bond co-reactant called the dienophile, because it combines with (has an affinity for) the diene. The Diels-Alder cycloaddition is classified as a [4+2] process because the diene has four pi-electrons that shift position in the reaction and the dienophile has two.
Diels-Alder Mechanism
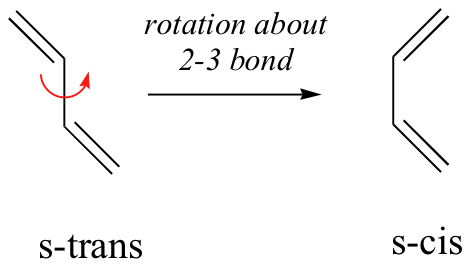
The Diels-Alder reaction is a single step process, so the diene component must adopt an s-cisconformation in order for the end carbon atoms (#1 & #4) to bond simultaneously to the dienophile. For many acyclic dienes the s-trans conformer is more stable than the s-cis conformer (due to steric crowding of the end groups), but the two are generally in rapid equilibrium, permitting the use of all but the most hindered dienes as reactants in Diels-Alder reactions. In order for a Diels-Alder reaction to occur, the diene molecule must adopt what is called the s-cis conformation:
In its usual form, the diene component is electron rich, and the best dienophiles are electron poor due to electron withdrawing substituents such as CN, C=O & NO2. The initial bonding interaction reflects this electron imbalance, with the two new sigma-bonds being formed simultaneously, but not necessarily at equal rates. Essentially, this process involves overlap of the 2p orbitals on carbons 1 and 4 of the diene with the two 2p orbitals on the sp2-hybridized carbons of the dienophile. Both of these new overlaps form new sigma bonds, and a new pi bond is formed between carbon 2 and 3 of the diene.
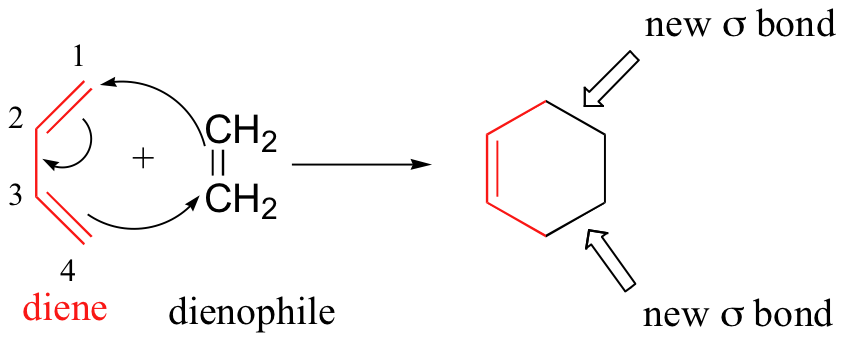
One of the most important things to understand about this process is that it is concerted – all of the electron rearrangement takes place at once, with no carbocation intermediates.
Since the diene takes the role of the nucleophile, electron donating group increase the reactivity of the diene. While the dienophile takes the role of the electrophile, electronwithdrawing groups increase the reactivity of the dienophile. The reactions below are examples of the Diels-Alder reaction.
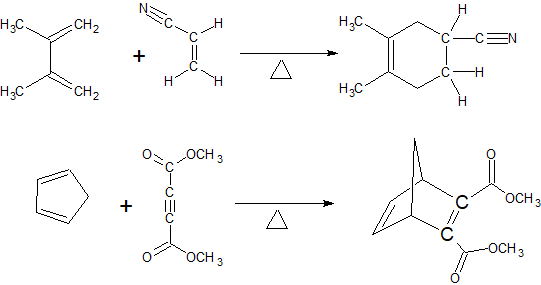
Exercise
7. Draw the bond-line structures for the reactions below.
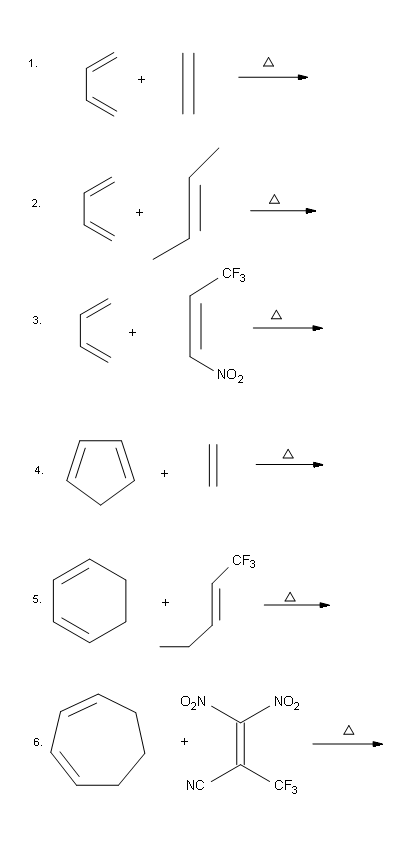
- Answer
-
7.
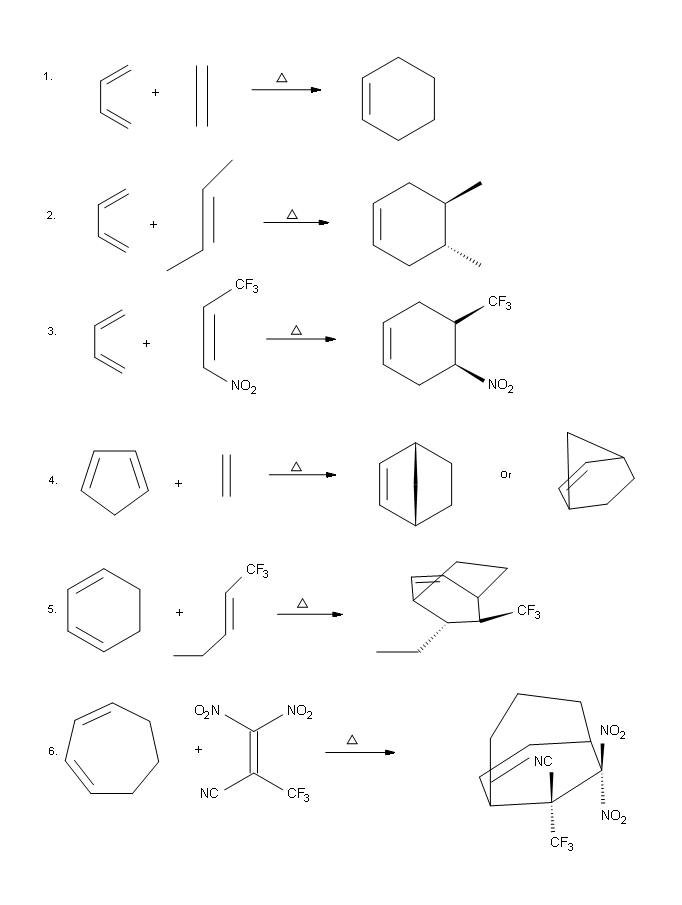.png?revision=1)
Contributors and Attributions
Dr. Dietmar Kennepohl FCIC (Professor of Chemistry, Athabasca University)
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)
William Reusch, Professor Emeritus (Michigan State U.), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry With a Biological Emphasis by Tim Soderberg (University of Minnesota, Morris)
- Amar Patel (UCD)

