27.5: Chemically Induced Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (CIDNP)
- Page ID
- 22380
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)One of the most startling developments in NMR spectroscopy since its inception has been the discovery of chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization or CIDNP. An especially dramatic example is provided by irradiation of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone with ultraviolet light.
The CIDNP effect is a complicated one and we will not attempt to explain it in detail. It is observed exclusively for radical reactions. However, it is not expected for chain-propagation steps, but only for termination steps. Furthermore, chemically dissimilar radicals have to be involved at some stage in the reaction sequence. Let us now consider how these considerations apply to the irradiation of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone.
Absorption of light by a ketone can give several reactions, but an especially important one, which will be discussed in more detail in Chapter 28, is cleavage of \(\ce{C-C=O}\) bonds to give radical pairs. For 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone there are two possible cleavage reactions of this type:
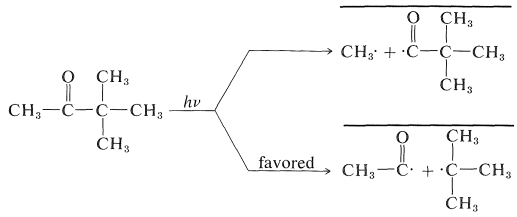
The heavy lines drawn over the radical pairs indicate that the radicals in the pairs are in close proximity to one another. Combination of the radicals in the pairs regenerates the ketone, whereas separation of the radicals can lead to formation of other products. The radicals in a pair can combine with each other only if the odd electron on one radical has its spin opposite to the spin of the odd electron on the other radical. This is necessary for formation of an electron-pair bond.
CIDNP arises because the radical combination products have nonequilibrium distributions of their proton magnetic states. How can nonequilibrium distributions arise? First, we must recognize that the radicals formed by irradiation of the ketone can have different proton magnetic states. For example, the methyl protons of any given \(\ce{CH_3CO} \cdot\) radical will be in one of the proton states: \(+\frac{1}{2}, \: +\frac{1}{2}, \: +\frac{1}{2}; \: -\frac{1}{2}, \: +\frac{1}{2}, \: +\frac{1}{2}; \cdots ; -\frac{1}{2}, \: -\frac{1}{2}, \: -\frac{1}{2}\) states (8 in all; see Section 27-3).
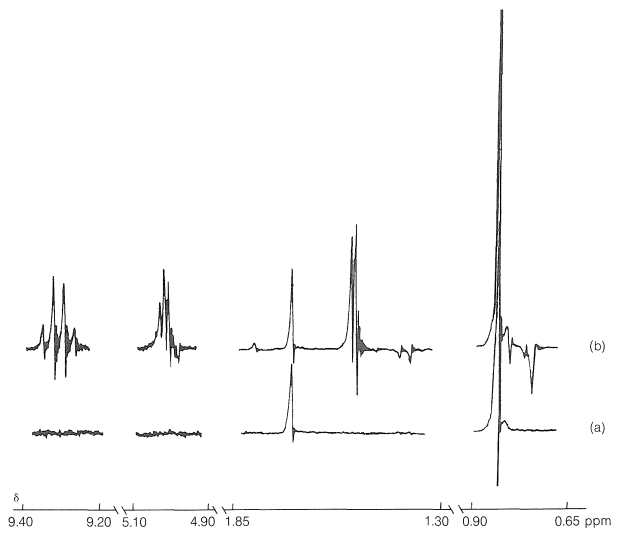
The effect of the different proton magnetic states is to cause the two unpaired electrons of the radical pairs to become unpaired at different rates. In other words, \(\overline{\ce{R} \uparrow + \ce{R'} \downarrow}\) pairs produced by irradiation are converted to \(\overline{\ce{R} \uparrow + \ce{R'} \uparrow}\) at different rates, depending on the proton magnetic states of \(\ce{R} \uparrow\) and \(\ce{R'} \downarrow\). Thus, a particular pair of proton magnetic states for \(\ce{R} \uparrow\) and \(\ce{R'} \downarrow\) can favor radical-pair recombination over radical-pair separation while another pair of proton magnetic states for \(\ce{R} \uparrow\) and \(\ce{R'} \downarrow\) can favor separation over combination. The result is a "sorting" of proton magnetic states, some appearing preferentially in particular products and others appearing in other products. Thus one product may have more than the normal equilibrium value of a higher-energy magnetic state and hence will emit radio-frequency energy to get back to equilibrium, while another product may have an abnormally low concentration of the higher-energy magnetic states and hence exhibit an enhanced absorption intensity. Figure 27-9 shows that recombination of the radical pairs produced in photolysis of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone forms ketone with a higher-than-normal magnetic energy in the protons of the methyl group (reduced absorption) and lower-than-normal magnetic energy in the protons of the tert-butyl group (enhanced absorption).
The other CIDNP peaks in Figure 27-9b arise from reactions of the separated radicals first formed, and show both enhanced absorption and enhanced emission. You should try to identify the origin of each of the CIDNP resonances with the expected reaction products:
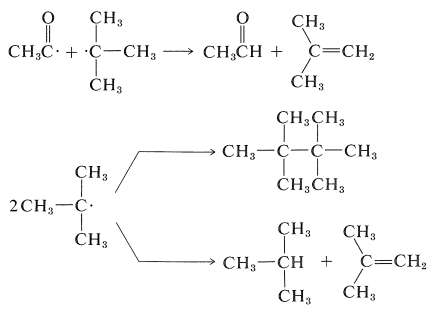
Because thermodynamic equilibrium usually is established between magnetic states of protons in a few seconds, the enhanced-absorption and enhanced-emission resonances disappear quickly when irradiation is stopped.
Contributors and Attributions
John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and performance of this work in any format."


