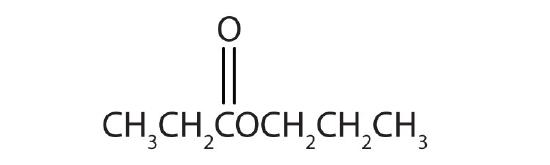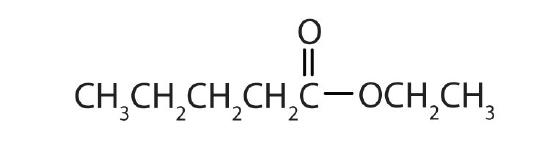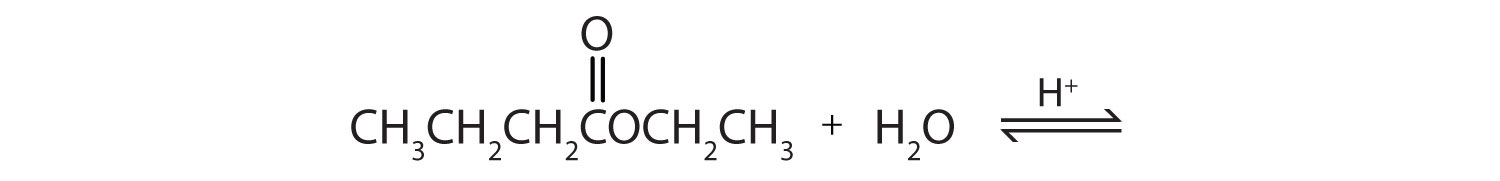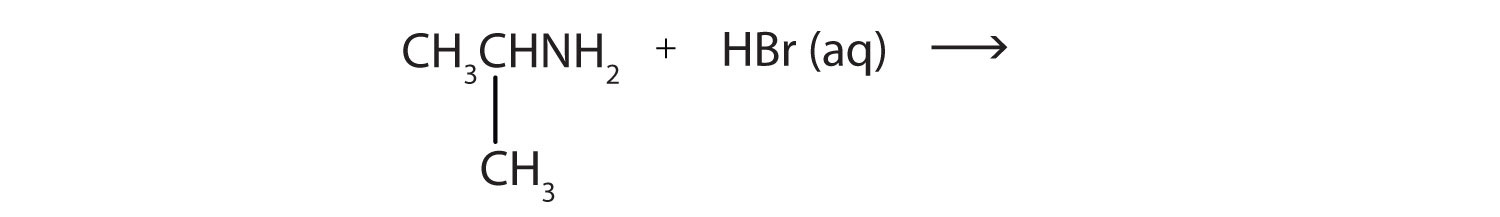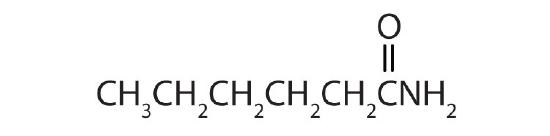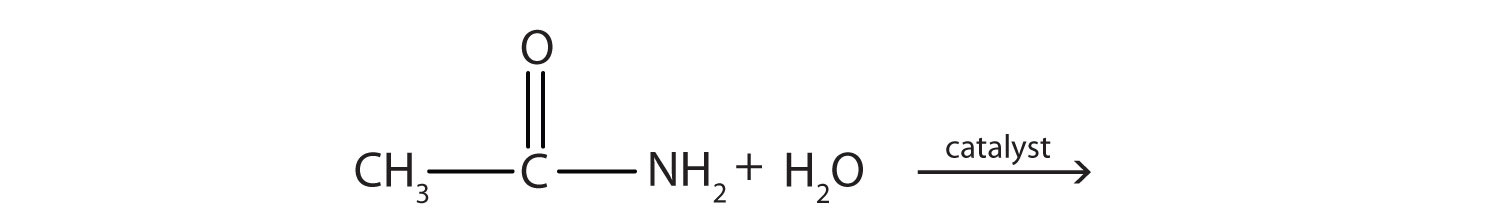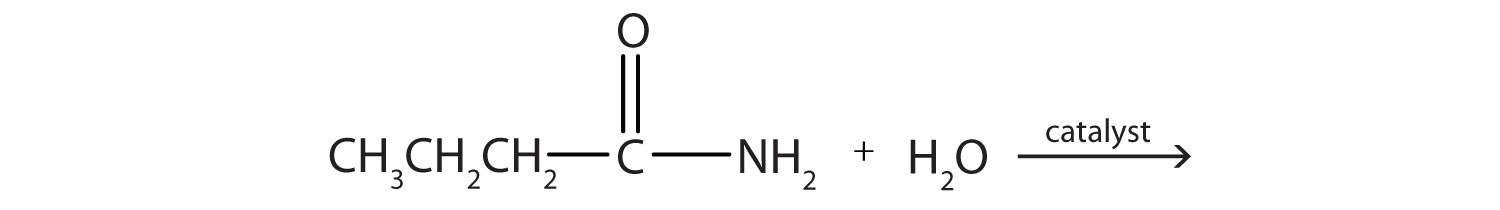15.E: Organic Acids and Bases and Some of Their Derivatives (Exercises)
- Page ID
- 73784
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Concept Review Exercises
- What is the IUPAC name for the straight-chain carboxylic acid with six carbon atoms?
- The straight-chain aldehyde with five carbon atoms has the common name valeraldehyde. What is the common name of the corresponding straight-chain carboxylic acid?
Answers
- hexanoic acid
- valeric acid
Exercises
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- heptanoic acid
- 3-methylbutanoic acid
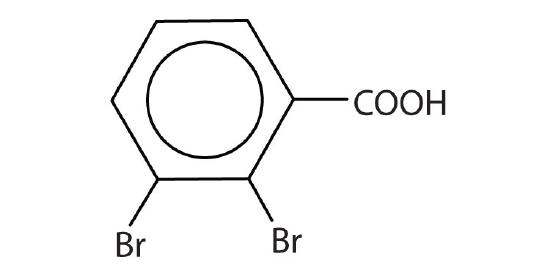
- 2,3-dibromobenzoic acid
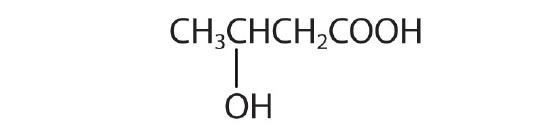
- β-hydroxybutyric acid
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- o-nitrobenzoic acid
- p-chlorobenzoic acid
- 3-chloropentanoic acid
- α-chloropropionic acid
- Name each compound with either the IUPAC name, the common name, or both.
- (CH3)2CHCH2COOH
- (CH3)3CCH(CH3)CH2COOH
- CH2OHCH2CH2COOH
- Name each compound with its IUPAC name.
- CH3(CH2)8COOH
- (CH3)2CHCCl2CH2CH2COOH
- CH3CHOHCH(CH2CH3)CHICOOH
Answers
-
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
-
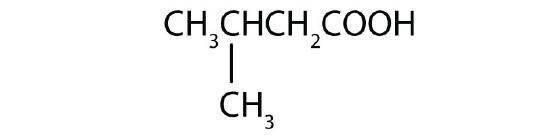
-
-
-
- 3-methylbutanoic acid; β-methylbutyric acid
- 3,4,4-trimethylpentanoic acid
- 4-hydroxybutanoic acid; γ- hydroxybutyric acid
Concept Review Exercises
- Caproic acid (hexanoic acid) can be prepared in an oxidation reaction from
- what alcohol?
- what aldehyde?
- Give the structures of the aldehyde and the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of isobutyl alcohol [(CH3)2CHCH2OH].
Answers
-
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
-
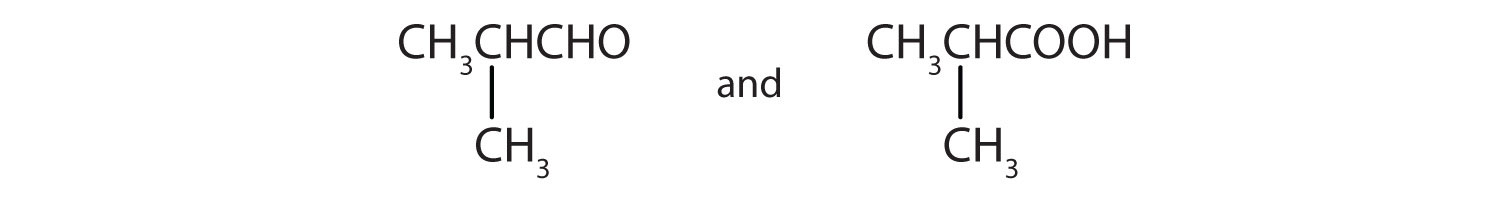
Exercises
- Caprylic acid (octanoic acid) can be prepared in an oxidation reaction from
- what alcohol?
- what aldehyde?
- Give the structures of the aldehyde and the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of 1,4-butanediol (HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH).
Answer
-
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
Concept Review Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—butanoic acid (molar mass 88) or 2-pentanone (molar mass 86)? Explain.
- Would you expect butyric acid (butanoic acid) to be more or less soluble than 1-butanol in water? Explain.
Answers
- butyric acid because of hydrogen bonding (There is no intermolecular hydrogen bonding in 2-pentanone.)
- more soluble because there is more extensive hydrogen bonding
Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2COOH? Explain.
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2CH2COOH? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—CH3COOH or CH3CH2CH2CH3? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—CH3CH2COOH or CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH? Explain.
Answers
- CH3CH2CH2COOH because of hydrogen bonding (There is no intermolecular hydrogen bonding with CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH3.)
- CH3COOH because it engages in hydrogen bonding with water (There is no intermolecular hydrogen bonding with CH3CH2CH2CH3.)
Concept Review Exercises
- How does the neutralization of a carboxylic acid differ from that of an inorganic acid? How are they similar?
- What products are formed when a carboxylic acid is neutralized with a strong base? What additional product is formed when a carboxylic acid is neutralized with a carbonate or a bicarbonate?
Answers
- Insoluble carboxylic acids often form soluble carboxylate salts. Both form a salt and water.
- a carboxylate salt and water; carbon dioxide
Exercises
- Write the equation for the ionization of CH3CH2CH2COOH in water.
- Write the equation for the neutralization of CH3CH2CH2COOH with sodium hydroxide [NaOH(aq)].
- Write the equation for the reaction of CH3COOH with sodium carbonate [Na2CO3(aq)].
- Write the equation for the reaction of CH3CH2COOH with sodium bicarbonate [NaHCO3(aq)].
- Write the equation for the ionization of propionic acid in water.
- Write the equation for the ionization of γ-chloropentanoic acid in water.
- Write an equation for the reaction of butyric acid with each compound.
- aqueous NaOH
- aqueous NaHCO3
- Write the condensed structural formula for each compound.
- potassium acetate
- calcium propanoate
- Name each compound.
- CH3CH2CH2COO−Li+
- CH3CH2CH2COO−NH4+
Answers
- CH3CH2CH2COOH(aq) + H2O(ℓ) → CH3CH2CH2COO−(aq) + H3O+(aq)
- 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3(aq) → 2CH3COO−Na+(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + CO2(g)
- CH3CH2COOH(aq) + H2O(ℓ) → CH3CH2COO−(aq) + H3O+(aq)
-
- CH3CH2CH2COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3CH2CH2COO−Na+(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
- CH3(CH2)2COOH + NaHCO3(aq) → CH3(CH2)COO−Na+(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + CO2(g)
-
- lithium butyrate (lithium butanoate)
- ammonium butanoate or ammonium butyrate
Concept Review Exercises
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can isopropyl hexanoate be made?
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can cyclobutyl butyrate be made?
Answers
- hexanoic acid and isopropyl alcohol
- butyric acid and cyclobutyl alcohol
Exercises
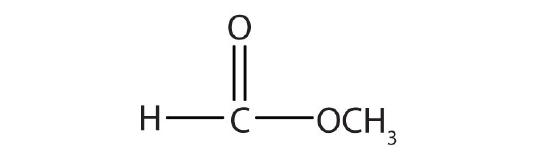
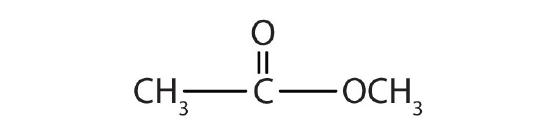
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- methyl acetate
- ethyl pentanoate
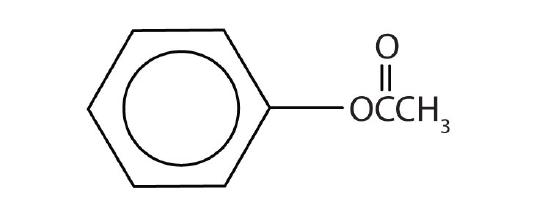
- phenyl acetate
- isopropyl propionate
- Draw the structure for each compound.
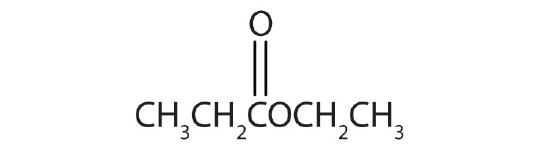
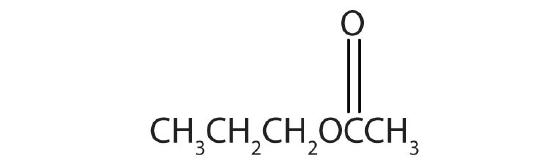
- ethyl hexanoate
- ethyl benzoate
- phenyl benzoate
- ethyl 3-methylhexanoate
- Name each compound with both the common name and the IUPAC name.
-
- Name each compound with both the common name and the IUPAC name.
-
Answers
-
- methyl formate; methyl methanoate
- ethyl propionate; ethyl propanoate
Concept Review Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—CH3CH2CH2CH2OH or CH3COOCH3? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—methyl butyrate or butyric acid? Explain.
Answers
- CH3CH2CH2CH2OH because there is intermolecular hydrogen bonding (There is no intermolecular hydrogen bonding in CH3COOCH3.)
- butyric acid because of hydrogen bonding with water
Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—CH3CH2CH2COOH or CH3CH2CH2COOCH3? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—methyl acetate or octyl acetate? Explain.
Answer
- CH3CH2CH2COOH because there is intermolecular hydrogen bonding (There is no intermolecular hydrogen bonding in CH3CH2COOCH3.)
Concept Review Exercises
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester isopropyl nonanoate be made?
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester cyclobutyl butyrate be made?
Answers
- nonanoic acid and isopropyl alcohol
- butyric acid and cyclobutyl alcohol
Exercises
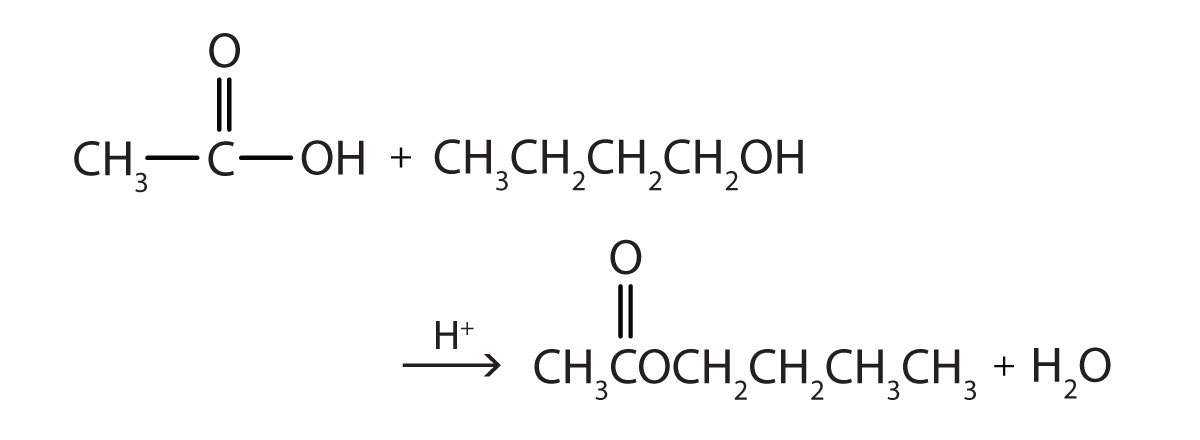
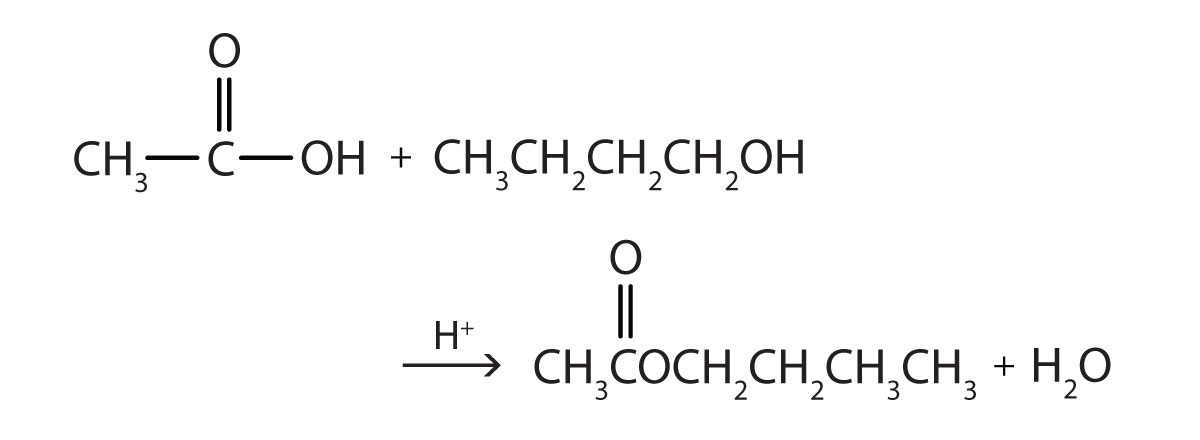
- Write the equation for the reaction of acetic acid with each compound.
- ethanol
- 1-butanol in the presence of a mineral acid catalyst
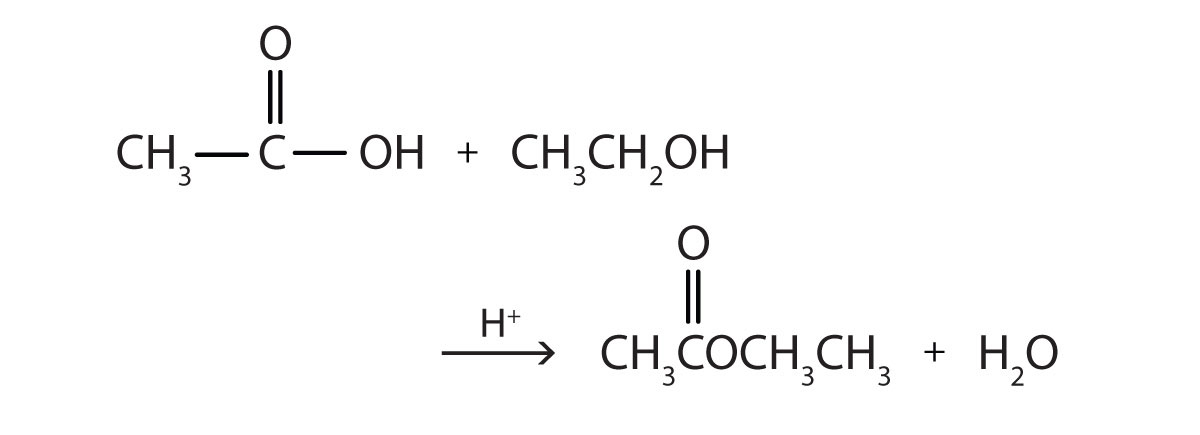
- Write the equation for the reaction of benzoic acid with each compound.
- methanol
- 1-propanol in the presence of a mineral acid catalyst
Answer
Concept Review Exercises
- How do acidic hydrolysis and basic hydrolysis of an ester differ in terms of
- products obtained?
- the extent of reaction?
- What is saponification?
Answers
-
- acidic hydrolysis: carboxylic acid + alcohol; basic hydrolysis: carboxylate salt + alcohol
- basic hydrolysis: completion; acidic hydrolysis: incomplete reaction
- the basic hydrolysis of an ester
Exercises
- Write an equation for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl acetate.
- Write an equation for the base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl acetate.
- Complete each equation.
-
- Complete each equation.
- \(\mathrm{(CH_3)_2CHCOOCH_2CH_3 + H_2O \overset{H^+}{\rightleftharpoons}}\)
- CH3COOCH(CH3)2 + KOH(aq) →
Answers
- \(\mathrm{CH_3COOCH_2CH_3 + H_2O \xrightarrow{H^+} CH_3COOH + CH_3CH_2OH}\)
-
- CH3COONa(aq) + CH3CH2CH2OH
- CH3CH2CH2COOH + CH3CH2OH
Exercises
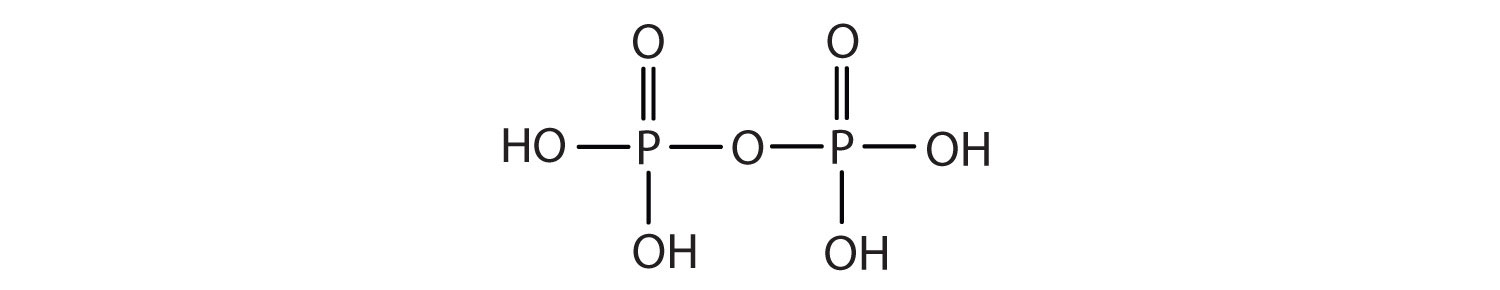
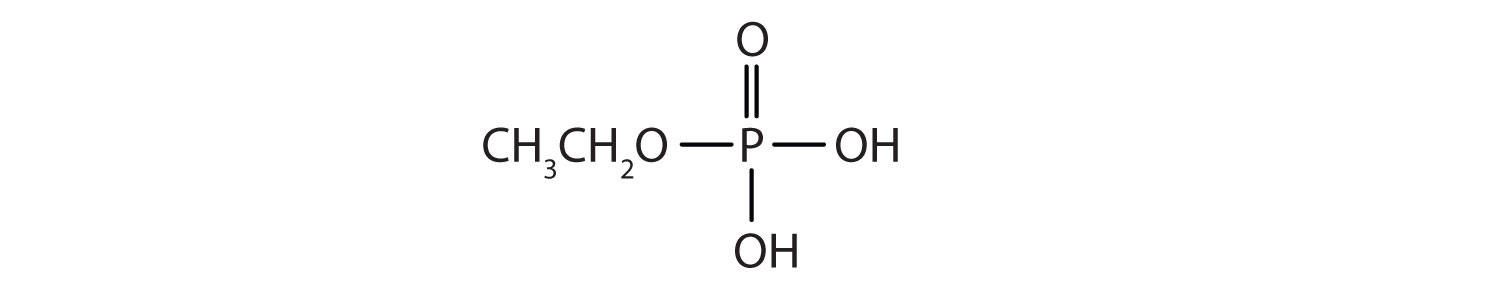
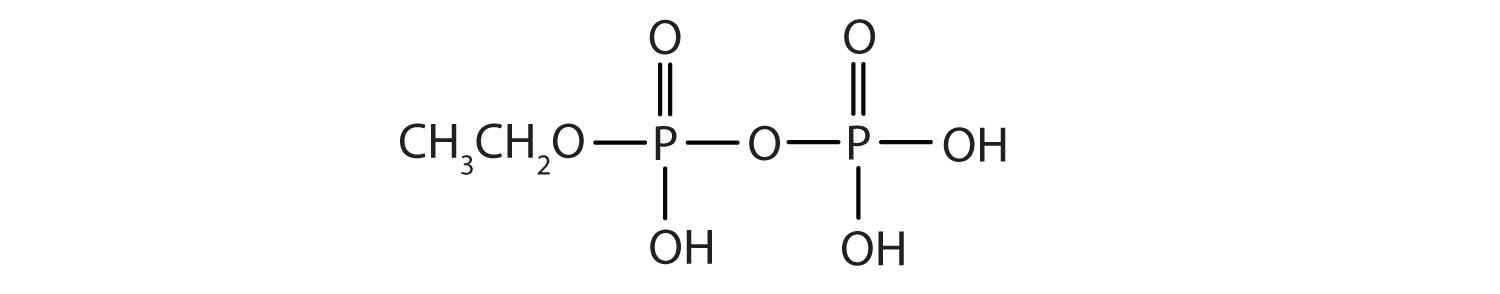
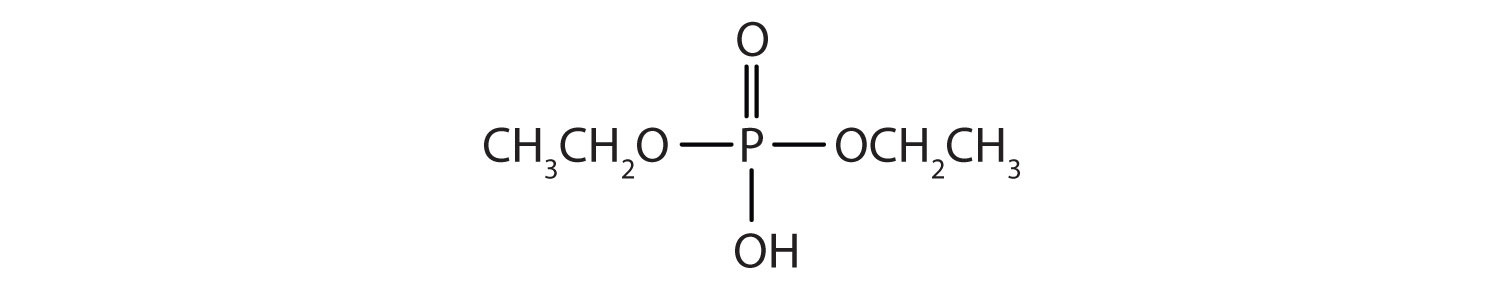
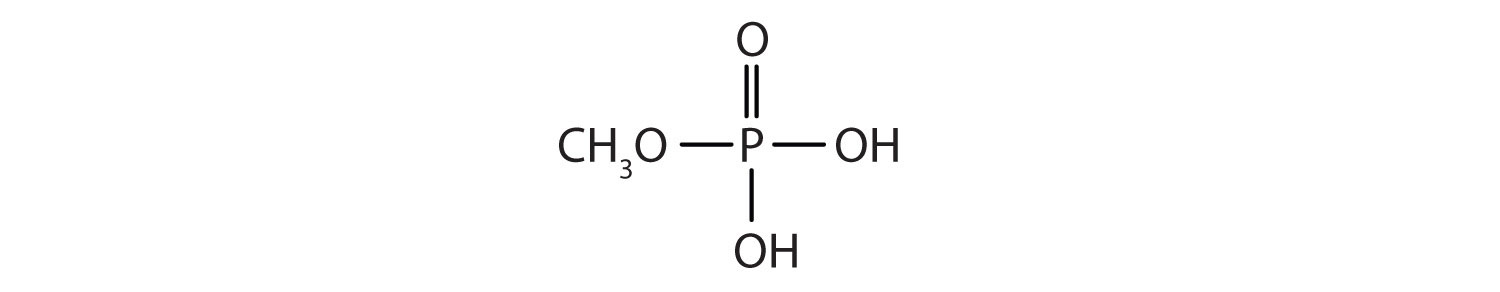
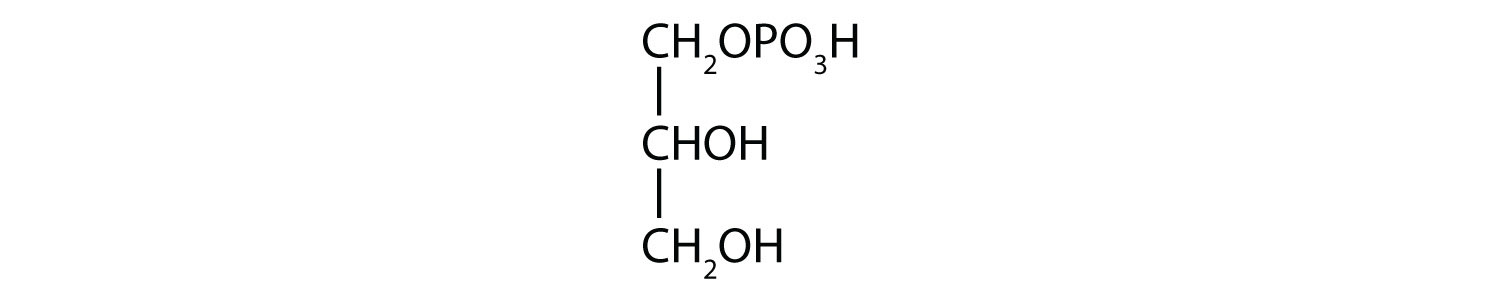
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- diethyl hydrogen phosphate
- methyl dihydrogen phosphate
- 1-glycerol phosphate
- Name each compound.
-
Answer
Concept Review Exercises
- To what inorganic compound are the amines related?
- How are amines classified?
Answers
- ammonia
- by the number of hydrocarbon groups on the nitrogen atom: primary amine, one group; secondary amine, two groups; tertiary amine, three groups
Exercises
- Draw the structure for each compound and classify the amine as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
- dimethylamine
- diethylmethylamine
- 2-aminoethanol
- Draw the structure for each compound and classify the amine as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
- 3-aminopentane
- 1,6-diaminohexane
- ethylphenylamine
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- aniline
- m-bromoaniline
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- 2-chloroaniline
- 3,5-dichloroaniline
- Name each compound.
- CH3CH2CH2NH2
-

-
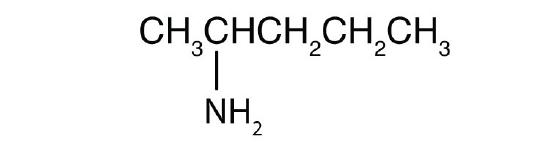
- Name each compound.
- (CH3CH2)3N
- (CH3CH2)2NCH3
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- dimethylammonium chloride
- anilinium chloride
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- ethylmethylammonium chloride
- anilinium nitrate
- Name each compound.
- [CH3CH2NH2CH2CH3]+Br−
- [(CH3CH2)3NH]+I−
- Name each compound.
- [(CH3)3NH]+NO3−
- [(CH3CH2)2NH2]+Cl−
Answers
-
- CH3NHCH3; secondary
- tertiary
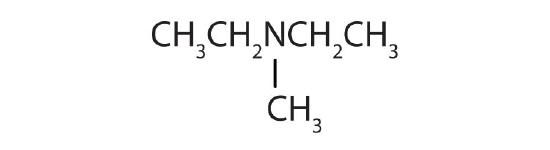
- HOCH2CH2NH2; primary
-
- propylamine
- isopropylmethylamine
- 2-aminopentane
-
- [(CH3)2NH2+]Cl–
-

-
- diethylammonium bromide
- triethylammonium iodide
Concept Review Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2 or CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 or CH3CH2NHCH2CH3? Explain.
Answers
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2 because the nitrogen-to-hydrogen (N–H) bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding; CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
- CH3CH2NHCH2CH3 because amines can engage in hydrogen bonding with water; alkanes cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
Exercises
- Which compound of each pair has the higher boiling point? Explain.
- butylamine or pentane
- CH3NH2 or CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2
- Which compound of each pair has the higher boiling point? Explain.
- butylamine or butyl alcohol
- trimethylamine or propylamine
- Which compound is more soluble in water—CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH2NH2? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—CH3CH2CH2NH2 or CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2? Explain.
Answers
-
- butylamine because the N–H bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding; pentane cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2 because it has a greater molar mass than CH3NH2
- CH3CH2NH2 because amines can engage in hydrogen bonding with water; alkanes cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
Concept Review Exercises
- Explain the basicity of amines.
- Contrast the physical properties of amines with those of alcohols and alkanes.
- What is a heterocyclic compound?
Answers
- Amines have a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom and can thus act as proton acceptors (bases).
- The solubilities of amines are similar to those of alcohols; the boiling points of primary and secondary amines are similar to those of alcohols; the boiling points of tertiary amines, which cannot engage in hydrogen bonding because they do not have a hydrogen atom on the nitrogen atom, are comparable to those of alkanes.
- Heterocyclic compounds are ring compounds with atoms other than carbon atoms in the ring.
Exercises
- What salt is formed in each reaction? Write its condensed structural formula.
- CH3NH2(aq) + HBr(aq) →
- CH3NHCH3(aq) + HNO3(aq) →
- What salt is formed in each reaction? Draw its structure.
-
Answer
-
- CH3NH3+Br−(aq)
- [CH3NH2CH3]+NO3−(aq)
Concept Review Exercises
- Name this compound with the common name and the IUPAC name.
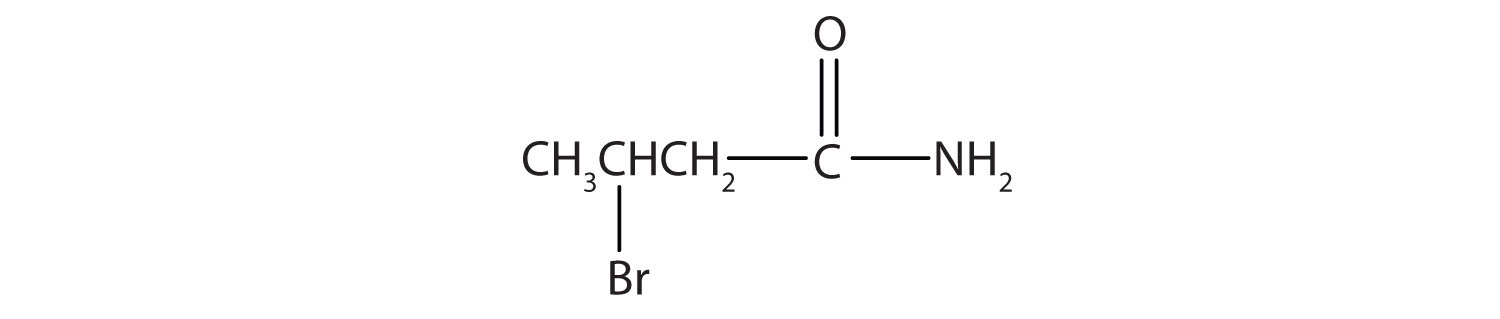
- Draw a the structural formulae for pentanamide.
Answers
- β-bromobutyramide (3-bromobutanamide)
-
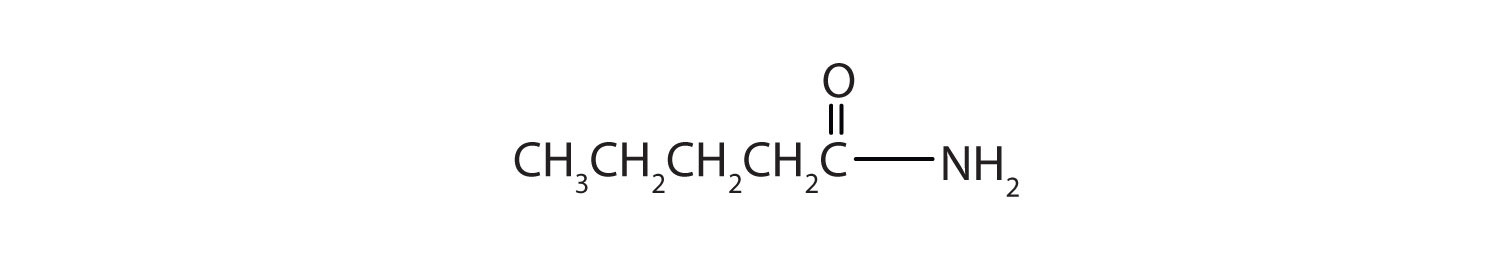
Exercises
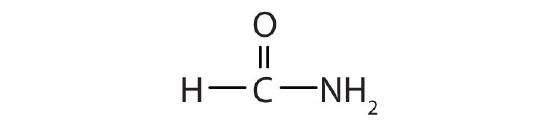
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- formamide
- hexanamide
- Draw the structure for each compound.
- propionamide
- butanamide
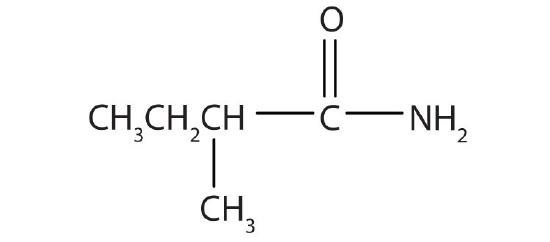
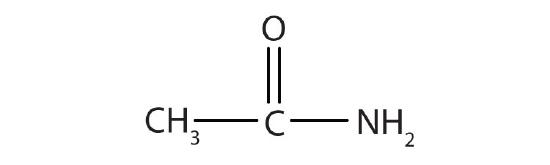
- Name each compound with the common name, the IUPAC name, or both.
-
- Name the compound.
Answers
-
- propionamide (propanamide)
- α-methylbutyramide (2-methylbutanamide)
Concept Review Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—pentanamide (CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2) or propyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH2CH3)? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—propanamide (CH3CH2CONH2) or 1-pentene (CH2=CHCH2CH2CH3)? Explain.
Answers
- pentanamide because the nitrogen-to-hydrogen (N–H) and the carbon-to-oxygen double (C=O) bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding; propyl acetate cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
- propanamide because the N–H and C=O bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding with water; 1-pentene cannot engage in hydrogen bonding with water
Exercises
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—butyramide (CH3CH2CH2CONH2) or ethyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH3)? Explain.
- Which compound has the higher boiling point—butyramide or dimethylacetamide [CH3CON(CH3)2]? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—acetamide (CH3CONH2) or 1-butene (CH2=CHCH2CH3)? Explain.
- Which compound is more soluble in water—CH3CONHCH3 or 2-methylbutane [CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3)]? Explain.
Answers
- butyramide because the nitrogen-to-hydrogen (N–H) and the carbon-to-oxygen double (C=O) bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding; ethyl acetate cannot engage in hydrogen bonding
- acetamide because the N–H and C=O bonds can engage in hydrogen bonding with water; 1-butene cannot engage in hydrogen bonding with water
Concept Review Exercises
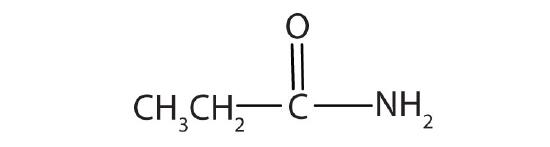
- Write the condensed structural formulas and give names of the two compounds from which butanamide (CH3CH2CH2CONH2) is formed.
- Write the condensed structural formulas and names of the two compounds from which CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CONHCH2CH2CH3 is formed.
Answers
- CH3CH2CH2COOH (butanoic acid) and NH3 (ammonia)
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH (hexanoic acid) and CH3CH2CH2NH2 (propylamine)
Exercises
- Write the condensed structural formulas and names of the two compounds from which pentanamide (CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2) is formed.
- Write the condensed structural formulas and names of the two compounds from which CH3CONHCH3 is formed.
Answer
- CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH (pentanoic acid) and NH3 (ammonia)
Concept Review Exercises
- What are the products of the hydrolysis of an amide?
- When the amide CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2 is hydrolyzed in an NaOH solution, the products are CH3CH2CH2CH2COO−Na+ and NH3. What products are obtained when CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2 is hydrolyzed in an hydrochloric acid solution?
Answers
- a carboxylic acid and ammonia or an amine
- CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH and NH4Cl
Exercises
- Complete each equation.
-
- Complete each equation.
-
Answer
-
- CH3COOH + NH3
-

Concept Review Exercises
- What are the products of the hydrolysis of an amide?
- When the amide CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2 is hydrolyzed in an NaOH solution, the products are CH3CH2CH2CH2COO−Na+ and NH3. What products are obtained when CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2 is hydrolyzed in an hydrochloric acid solution?
ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
-
Of the families of organic compounds discussed in this chapter, which are known for their typically unpleasant odors? Which for their characteristically pleasant aromas?
-
What is esterification of a carboxylic acid? How does it differ from neutralization?
-
Like alcohols, phenols form esters with carboxylic acids. The hydrocarbon group from phenol is called phenyl. Draw the structure of phenyl acetate.
-
Describe the hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acids, both acid-acid and acid-water. How does this influence their physical properties?
-
Which compound is more soluble in water—benzoic acid or sodium benzoate? Explain.
-
Dicarboxylic acids have two carboxyl groups and are named with the ending -dioic acid. Give the equation for the reaction of 1,5-pentanedioic acid (HOOCCH2CH2CH2COOH; common name, glutaric acid) with each of the following:
- 1 mol of NaOH
- 2 mol of NaOH
-
Without consulting tables, arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point: butyl alcohol, methyl acetate, pentane, and propionic acid.
-
From which alcohol might each acid be prepared via oxidation with acidic dichromate?
- CH3CH2COOH
- HCOOH
- HOOCH2COOH
- (CH3)2CHCH2COOH
-
The distinctive aroma and flavor of oranges are due in part to octyl acetate, an ester formed from 1-octanol (octyl alcohol) and acetic acid. Write the condensed structural formula for octyl acetate.
-
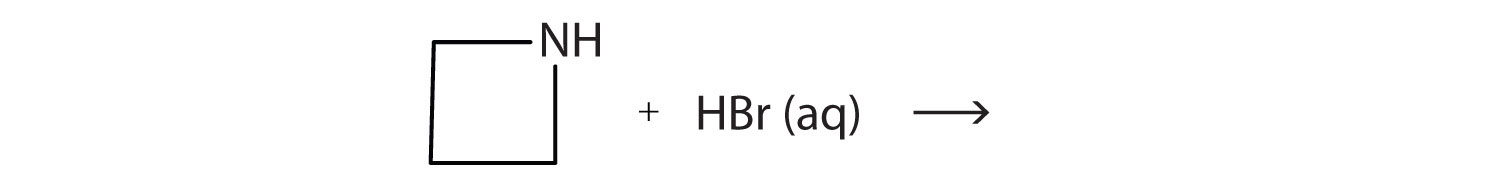
A lactone is a cyclic ester. What product is formed in following reaction?
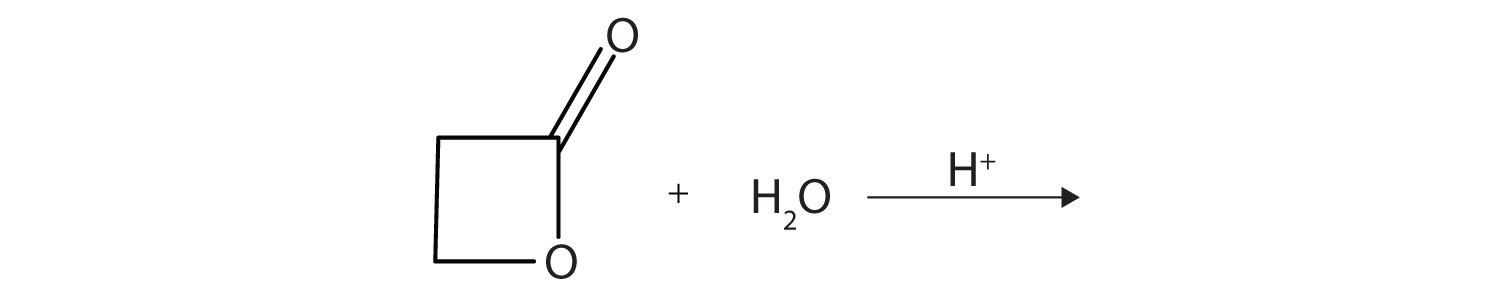
-
A lactam is a cyclic amide. What product is formed in the following reaction?
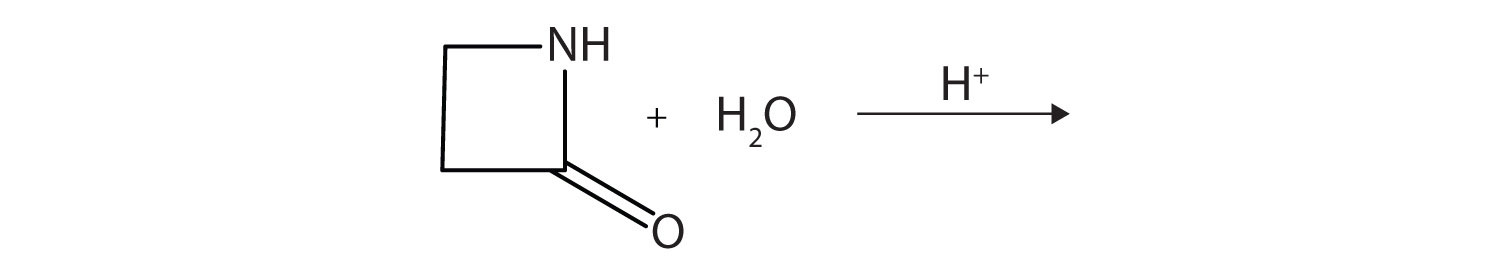
-
Draw the structures for the eight isomeric amines that have the molecular formula C4H11N. Give each a common name and classify it as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
-
Draw the structures for the five isomeric amines that have the molecular formula C7H9N and contain a benzene ring. Classify each compound as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
-
Cocaine is usually used in the form of the salt cocaine hydrochloride and sniffed up the nose. Some prefer to ingest their cocaine by smoking it (mixed with tobacco, for example). Before smoking, the cocaine hydrochloride must be converted back to the free base (that is, to the molecular form). Explain the choice of dosage form for each route of administration.
-
Draw the structures all the isomeric amides that have the molecular formula C4H9NO.
-
An ester with the molecular formula C6H12O2 was hydrolyzed in aqueous acid to yield an acid Y and an alcohol Z. Oxidation of the alcohol with potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) gave the identical acid Y. What is the condensed structural formula of the ester?
-
The neutralization of 125 mL of a 0.400 M NaOH solution requires 5.10 g of a monocarboxylic acid. Draw all the possible structures for the acid.
-
If 3.00 g of acetic acid reacts with excess methanol, how many grams of methyl acetate are formed?
-
How many milliliters of a 0.100 M barium hydroxide solution are required to neutralize 0.500 g of dichloroacetic acid?
ANSWERS
-
unpleasant: carboxylic acids; pleasant: esters
-
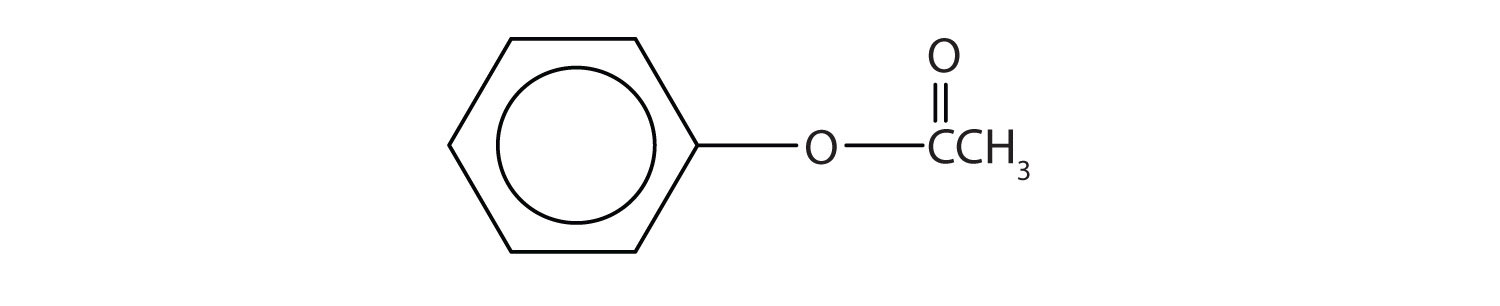
-
sodium benzoate because it is ionic and forms ion-dipole forces with water; benzoic acid can engage in hydrogen bonding only with water
-
pentane < methyl acetate < butyl alcohol < propionic acid
-
CH3COOCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
-
H3N+CH2CH2COOH
-
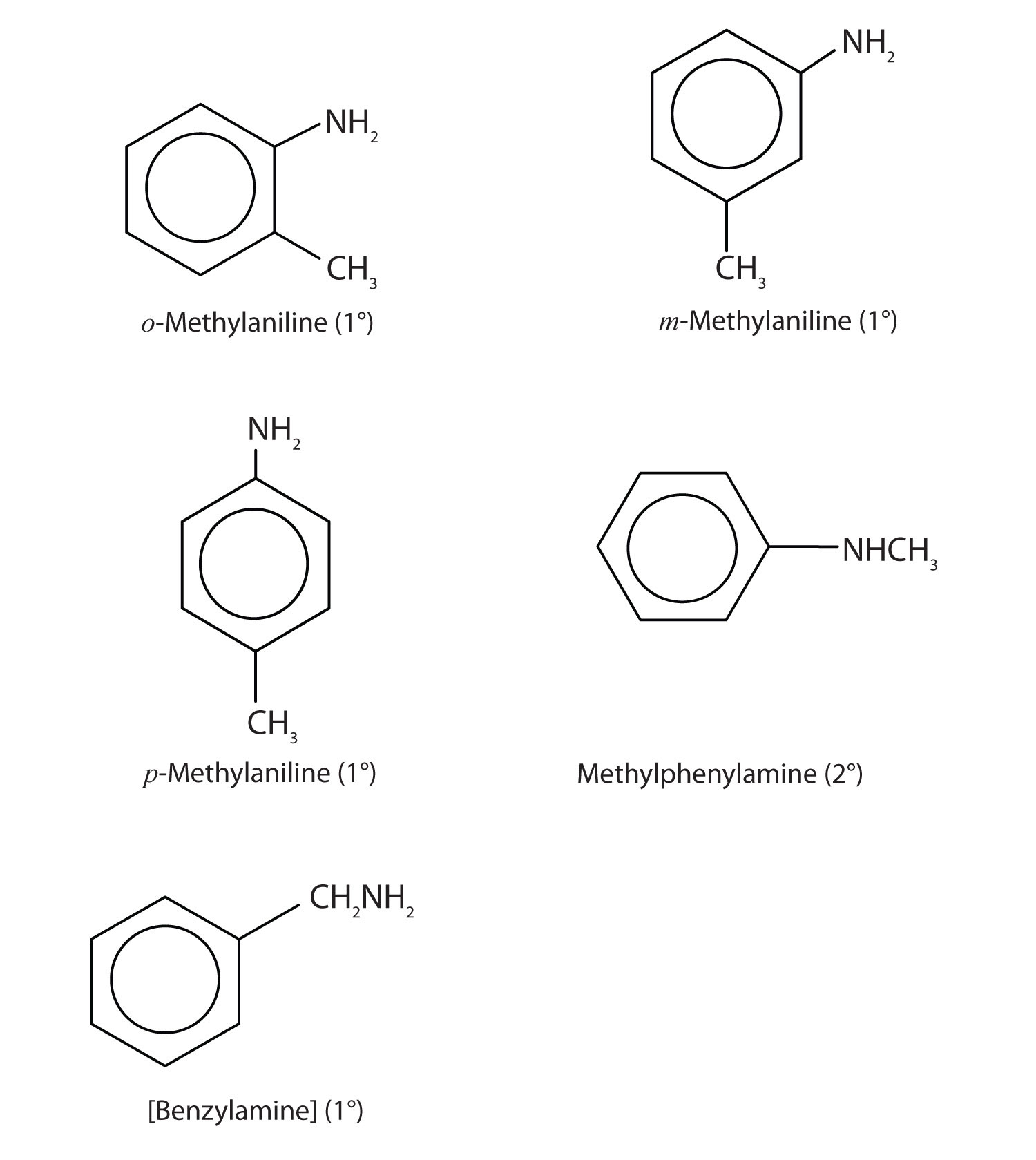
-
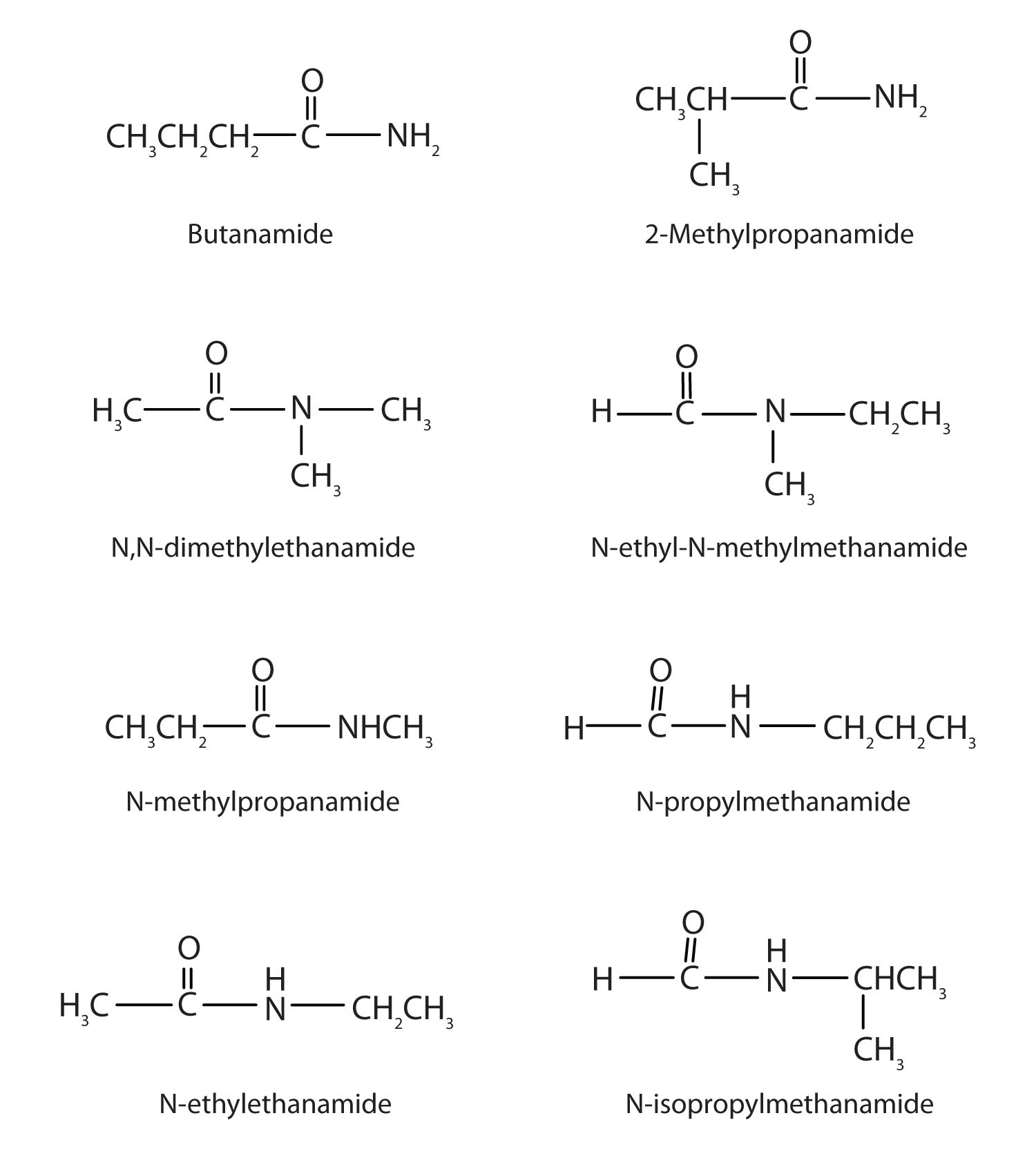
-
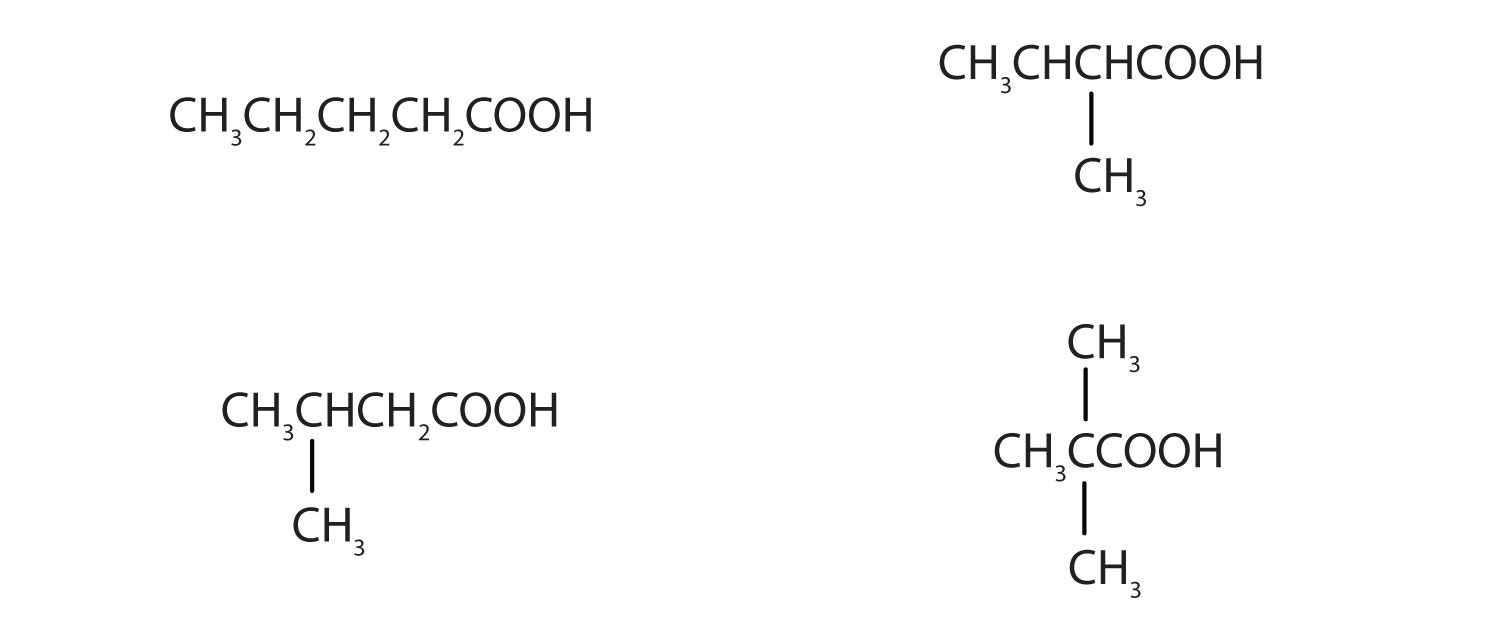
-
20.0 mL