4.1: Organometallic Compounds of As(V) and Sb(V)
- Page ID
- 172738
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
In this section you will learn the following
- Organoaresnic and organoantimony compounds.
- Preparation and reactivity of pentavlent As and Sb compounds.
Organic chemistry of non-metal phosphorus, metalloids such as arsine and antimony along with metallic element bismuth is termed as organoelement chemistry. The importance given to organoarsenic compounds earlier due to their medicinal values was waded out after antibiotics were discovered and also their carcinogenic and toxic properties were revealed. Also, the synthetically important organometallic compounds of group 13 and 14 masked the growth of group 15 elements. However, the organoelement compounds of phosphorus, arsenic and antimony find usefulness as ligands in transition metal chemistry due to their σ-donor and π-acceptor abilities which can be readily tuned by simply changing the substituents. These donor properties are very useful in tuning them as ligands to make suitable metal complexes for metal mediated homogeneous catalysis. Although organoelement compounds can be formed in both +3 (trivalent and tricoordinated) and +5(pentavalent and tetra or pentacoordinated) oxidation states, trivalent compounds are important in coordination chemistry.
For organoelement compounds of group 15, the energy of E—C bond decreases in the order, E = P > As > Sb > Bi, and in the same sequence E—C bond polarity increases.
Organometallic compounds of As(V) and Sb(V)
Due to the strong oxidizing nature of pentahalides, the direct alkylation or arylation to generate ER5 is not feasible, but can be prepared in two steps.
A few representative methods of preparation are given below:
\[\ce{ Me3As ->[Cl2] Me3AsCl2 ->[MeLi][Et2O] Me5As} \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Ph3Sb + PhI -> Ph4SbI ->[PhLi][-LI] Ph5Sb} \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Ph3Bi ->[SO2Cl2][-SO2] Ph3BiCl2 ->[PhMgX][-MgXCl] Ph5Bi} \nonumber \]
Structures and properties
Pentaalkyl or pentaaryl derivatives are moderately thermally stable. On heating above 100°C, they form trivalent compounds as shown below:
\[\ce{Me5As ->[T>100°] Me3As + CH4 + CH2CH2} \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Ph5Sb ->[T>200°] Ph3Sb + Ph-Ph} \nonumber \]
Reaction with water,
\[\ce{Me5As+ H2O -> Me4AsOH + MeH} \nonumber \]
Pentavalent compounds readily form “tetrahedral onium” cations and “octahedral and hexacoordinatged ate” anions.
\[\ce{Ph5E + BPh3 -> [Ph4E][BPh4]} (E=As, Sb, Bi) \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Ph5E + LiPh -> Li[EPh6]} \nonumber \]
In solid state, Ph5As adopts trigonal bipyramidal geometry, whereas Ph5Sb prefers square based pyramidal geometry although the energy difference between the two is marginal.
The salts of the type [R4E]+ adopt tetrahedral geometry, whereas hexacoordinated anions [R6E]-assume octahedral geometry.
Mixed organo-halo compounds of the type RnEX5-n adopt often dimeric structures due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on X which can readily coordinate to the second molecule. The following structural types can be anticipated.
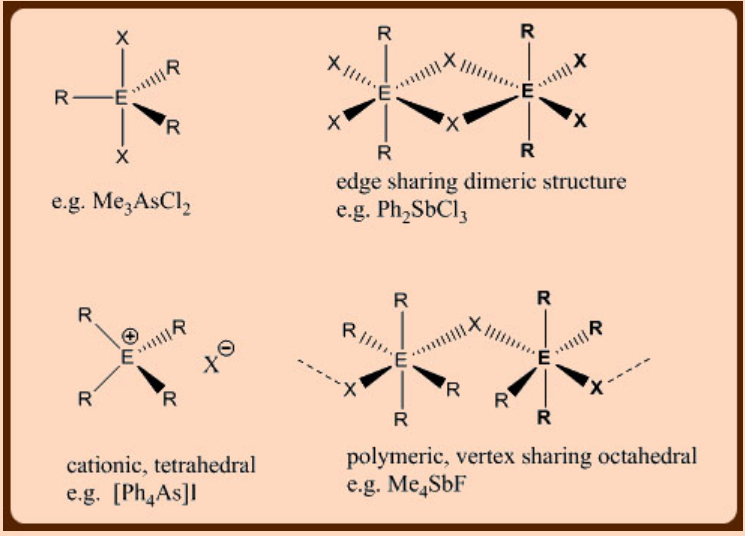
The thermal stability of RnEX5-n decreases with decreasing ‘n’. Thermal reactions are essentially the reverse reactions of addition reactions used in the preparation of R5E.
\[\ce{R3SbX2 ->[\Delta T] R2SbX + RX} \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Ph3AsCl2 ->[CO_{2}][100°C] Ph2AsCl + Cl2} \nonumber \]
\[\ce{Me2AsCl3 ->[50°C] MeAsCl2 + MeCl} \nonumber \]


