6.4.6: Lewis base strength may also be estimated by measuring structural or energy changes upon formation of a Lewis acid-base complex, as illustrated by efforts to spectroscopically assess the strengths of halogen bonds
- Page ID
- 162910
When a Lewis acid and base form an adduct, it shifts the bond lengths, and strengths in the acid and base also shift.
According to the frontier orbital description of Lewis acid-base interactions, adduct formation results in a net transfer of electron density from the base HOMO to the acid LUMO. This transfer
- increases the electron density between the acid (A) and base (D)
- alters the strength of the bonding within the base as the base LUMO becomes partially populated.
These changes result in structural and spectroscopic shifts on adduct formation that can be taken as a measure of the strength of the Lewis acid-base interaction. Since these shifts depend on the nature of the bonding in the acid and base, in practice structural and spectroscopic measurements of Lewis basicity are applied to a few classes of Lewis acid-base interactions, most notably hydrogen bonding and halogen bonding. Since hydrogen bonds will be discussed in section 6.5.1. the remainder of this subsection will focus on halogen bonds.
Halogen bonds are coordinate covalent bonds formed between a Lewis base and an organohalogen.
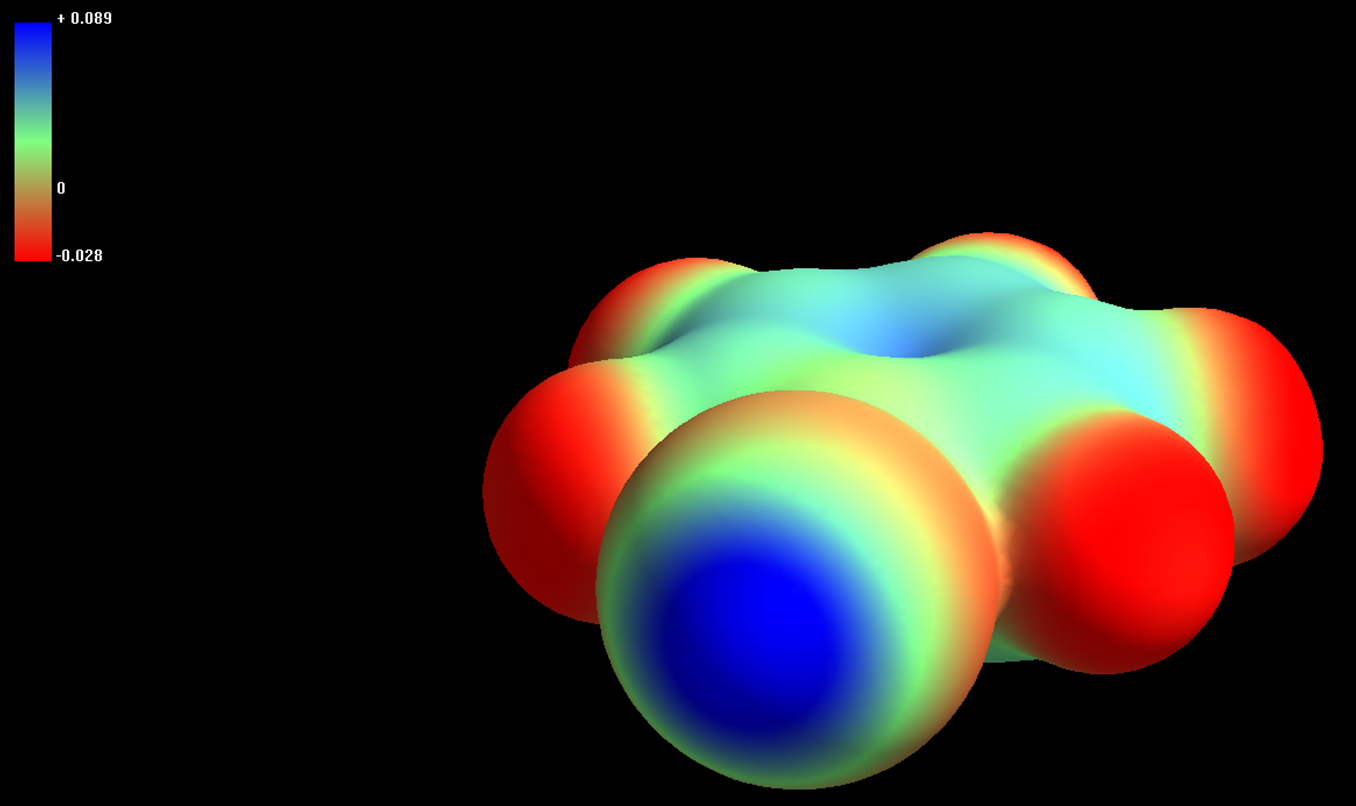
The halogens in compounds containing a singly-bonded halogen can engage in a special type of intermolecular interaction called halogen bonding, since the bonded halogens are electrophilic on the opposite side of the bond. This electrophilicity is apparent from the charge distribution in \(CF_5I\) shown in Figure 4.5.1, in which the charge is distributed on the I such that the I is Lewis basic perpendicular to the C-I bond and Lewis acidic opposite to it. This region of diminished electron density on the halogen opposite the existing sigma bond is called a \(\sigma\)-hole.*
Schematically,

Since the halogen can act as a Lewis acid in the direction opposite the R-X bond it can form adducts with Lewis bases in that direction.
 \[ \nonumber \]
\[ \nonumber \]
The bonds holding these adducts together are called halogen bonds, often abbreviated XB.
The halogen is said to act as a halogen bond donor when it forms a halogen bond with a base along that direction, with the base acting as the halogen bond acceptor. Consequently, the two previous schemes may also be given as:

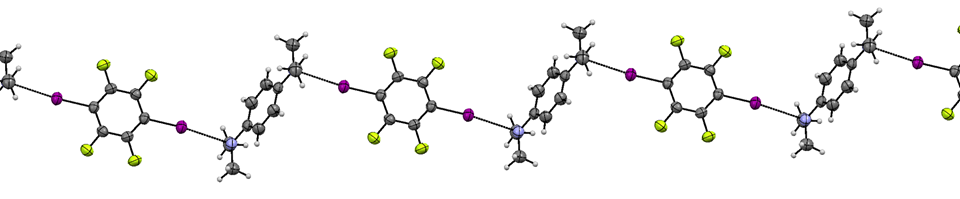
The ability of singly-bonded halogen atoms to form halogen bonds forms the basis of many efforts to engineer structures in which halogen-containing compounds are held together into chains, sheets, or 3D structures using halogen bonds. One easy-to-see example involves 1D chains formed between p-diiodotetrafluorobenzene and p-bis(dimethylamino)benzene.3
Trends in halogen bond strength in a closely-related series of compounds may be assessed by examining how the vibrational stretching frequency of I2 and the I2 \(\pi^*\) to \( \sigma^*\) transition energy change upon formation of the adduct.
From the description of halogen bonding above it should be apparent that the iodine charge transfer complexes described in section 6.4.2 are held together by halogen bonds. This means that the description of the bonding in \(I_2\) charge transfer complexes given in that section illustrate how vibrational and electronic transitions shift when a halogen-bonded adduct is formed between a halogen bond donor and acceptor.
The orbital interactions involved in halogen bond formation are shown in Figure 6.4.5.3. As can be seen from that figure, the formation of an adduct between \(I_2\) and a Lewis base is expected to result in weakening of the I-I bond and a shift in the \( I_2~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) transition energy to higher energy/shorter wavelengths (i.e., a blueshift). Further, both the weakening of the I-I bond and the \(I_2~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) blueshift are expected to increase with the HOMO energy of the Lewis base.
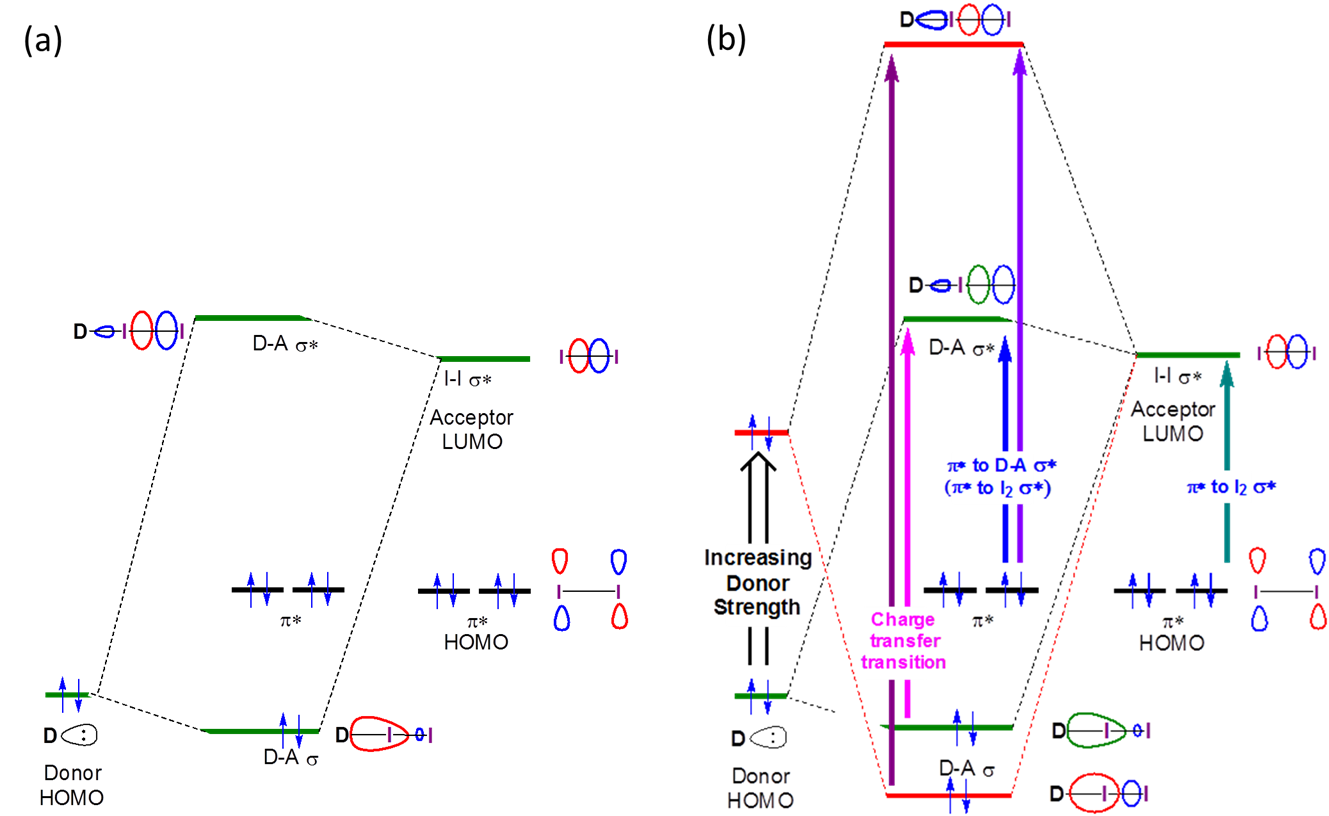
Because the I-I bond strength and \(I_2~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) blueshift increase with the Lewis basicity of the donor, the blueshift and the I-I vibrational stretching frequency are sometimes used as measures of donor's halogen bond affinity. However, the data obtained from such spectroscopic measurements should be interpreted with a degree of caution. As seen in Table 6.4.5.1, the extent to which the I-I bond is weakened (indicated by \(\Delta \nu_{I-I}\)) and the \(I_2's~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) band is blue shifted are imperfectly correlated overall. However, a careful comparison of the data in 6.4.5.1. reveals that the I-I bond weakening and \(I_2's~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) blue shift correlate well for Lewis bases of a given type. Consequently, shifts in the I-I stretching frequency and \(I_2~ \pi^*~\rightarrow~\sigma^*\) absorption band are not useful as an absolute measure of Lewis basicity but can be used to rank the halogen bond affinity of a closely-related set of donors.**
| Base (type) | \(\Delta \nu_{I-I}~cm^{-1}\) | Blue shift of \(I_2's~ \pi *~\rightarrow ~\sigma*\) |
|---|---|---|
| 4-methylpyridine (pyridines) | 29.1 | 4730 |
| pyridine (pyridines) | 27.4 | 4560 |
| tetrahydrothiophene (thioethers) | 44.5 | 3640 |
| tetrahydrofuran, THF (ethers) | 6.4 | 2280 |
| diethyl ether (ethers) | 5.5 | 1950 |
| acetone (ketone) | 5.0 | 1850 |
| acetophenone (ketone) | 4.6 | 1650 |
| acetonitrile (nitrile) | 4.1 | 1610 |
| hexamethylbenzene (aromatic) | 10.4 | 1070 |
| benzene (aromatic) | 4.3 | 450 |
References and Further Reading
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G., The Halogen Bond. Chemical Reviews 2016, 116 (4), 2478-2601.
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. σ-Hole Interactions: Perspectives and Misconceptions. Crystals 2017, 7, 212.
- R.Liantonio, S.Luzzati, P.Metrangolo, T.Pilati, G.Resnati, Tetrahedron, 2002, 58, 4023, DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00264-8
- Laurence, C.; Gal, J.-F. o., Lewis Basicity and Affinity scales: Data and Measurement. John Wiley: Chichester, West Sussex, U.K., 2010.
Notes
* Other compounds also exhibit \(\sigma\)-holes (and \(\pi\)-holes) that can be used in crystal engineering. For details see reference 2.
** for more details consult reference 4, pp. 286-309.
Contributors and Attributions
Consistent with the policy for original artwork made as part of this project, all unlabeled drawings of chemical structures are by Stephen Contakes and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

