3.9: The Anomeric Center
- Page ID
- 195893
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)When a sugar cyclizes via donation of a hydroxy lone pair to the carbonyl, it forms a "hemiacetal". We have already seen that hemiacetals are unstable with respect to further substitution. Pi donation from an oxygen in the hemiacetal can displace the other oxygen. A second nucleophile can then donate to the pseudo-carbonyl that results.
The hemiacetal position in the sugar is called the anomeric center. The anomeric center is special for two reasons. First, as you have already seen, the anomeric center is a chiral center. This new center can form with either of two configurations. The sugar, which is already chiral, can become either of two diastereomers when it cyclizes. Second, the anomeric center is a site of enhanced reactivity in the sugar, in terms of substitution of the carbonyl.
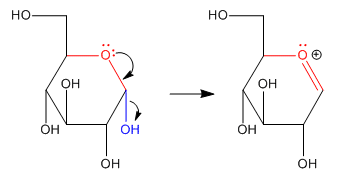
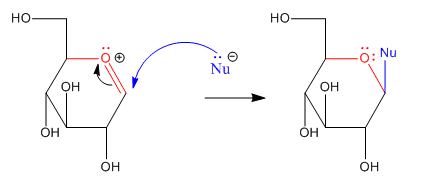
Anomeric reactivity involves pi donation from one oxygen to push off the other oxygen. This mode of reaction should be familiar. The C=O+ unit that forms resembles a carbonyl. Furthermore, the positive charge on the oxygen brings to mind an activated carbonyl. This position is especially attractive for nucleophiles.
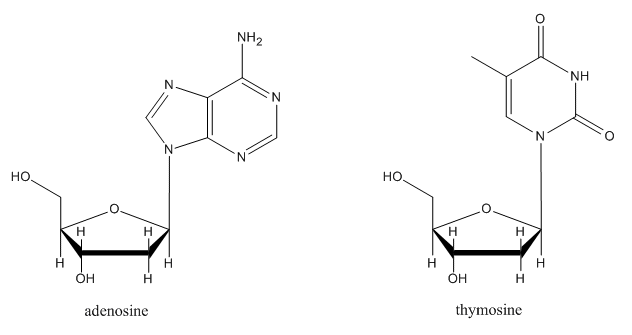
It isn't an accident that in many sugar-containing biomolecules, substituents are found at the anomeric center. For example, nucleosides sub-units found in DNA and RNA are all substituted at this position. A number of other biological agents contain this motif as well.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
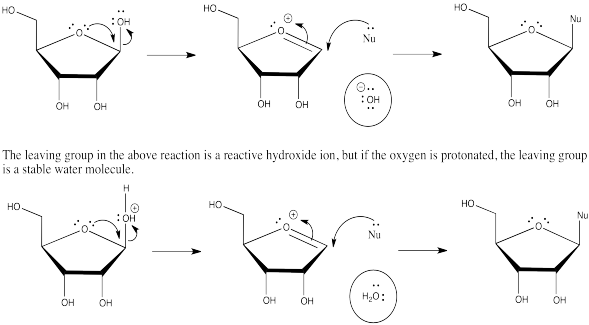
Substitution at the anomeric position can be accelerated if a proton source is available. Show why.
- Answer
-
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
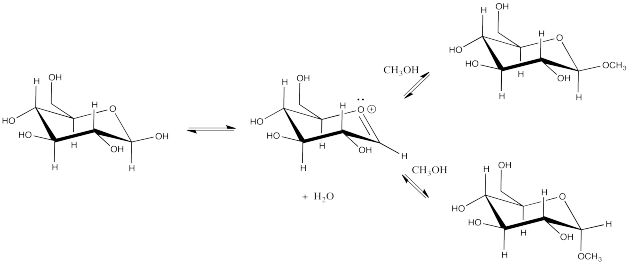
Show the stereochemical results of substitution at the anomeric center of glucose with methanol.
- Answer
-
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Nucleotides, which form DNA and RNA chains, are just like nucleosides, but they all have a phosphate at a specific position. Explain what is special about this position that could make it form a phosphate more easily than the other hydroxyl sites.
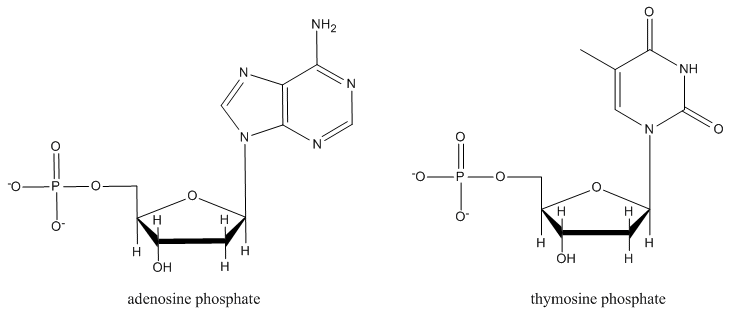
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
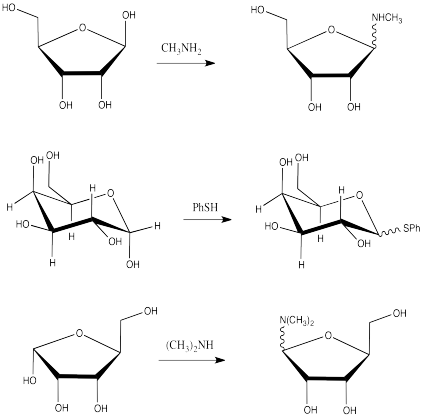
Show the products of the following substitution reactions.
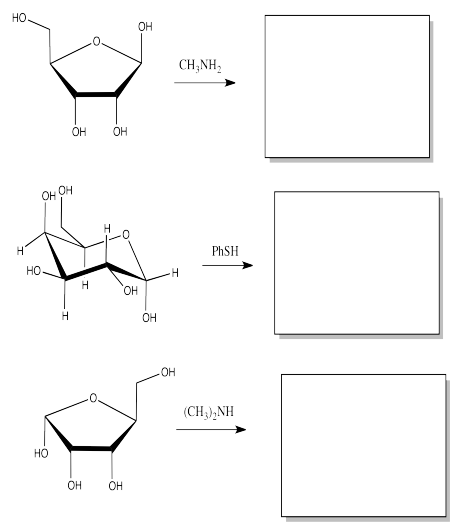
- Answer
-
Although sugars contain a number of chiral centers, characterizing them by polarimetry is complicated. Optical rotation measurements are done in solution, in a polarimetry cell. Polarimetry is always a little bit complicated, because the optical rotation varies with the concentration of the solution and the length of the polarimetry cell. When a pure enantiomer of a sugar such as alpha-D-glucose is dissolved, usually in water, its optical rotation also varies with time. In other words, the reading keeps changing, eventually settling out far from the initial value. That means care must be taken in measuring this information, and in interpreting the data.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Show why alpha-D-glucose would exhibit a changing optical rotation value after being dissolved.
- Answer
-
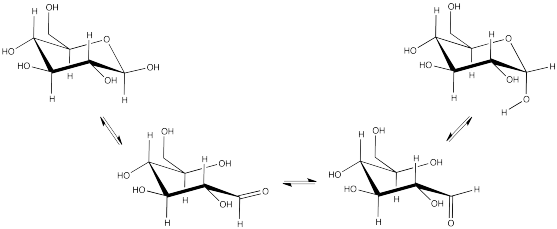
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Suppose a one gram sample of alpha-D-glucopyranose is dissolved in 1 mL of water and its optical rotation is measured in a a 1 dm cell. Initially, a value of 100 degrees is recorded. After several hours, the value has stopped changing, and is 48 degrees.
The experiment is repeated with beta-D-glucopyranose.
- What can you predict about the initial value with beta-D-glucopyranose?
- What can you predict after several hours?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
In water, alpha-D-glucopyranose predominates over the beta form in solution. Explain why.
- Answer
-
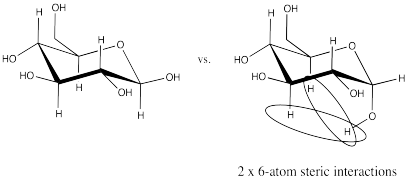
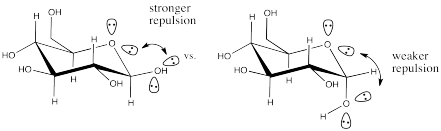
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
In less polar solvents (compared to water) such as dichloromethane, beta-D-glucopyranose predominates over the alpha form. This phenomenon is thought to result from the influence of lone pair-lone pair repulsion.
- Show why this factor might favor one isomer over the other.
- Show why this factor is less important in water.
- Answer
-