Questions and Problems
- Page ID
- 296469
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Access to and use of the internet is assumed in answering all questions including general information, statistics, constants, and mathematical formulas required to solve problems. These questions are designed to promote inquiry and thought rather than just finding material in the text. So in some cases there may be several “right” answers. Therefore, if your answer reflects intellectual effort and a search for information from available sources, your answer can be considered to be “right."
1. What distinguishes the molecules of chemical compounds from those of elements, such as N2?
2. Several “characteristics of compounds that meet the criteria of being green” were mentioned at the beginning of this chapter. Near the end of the chapter, acetic acid was mentioned as a “green acid.” In what respects does it meet the criteria of green compounds?
3. What is sodium stearate? Why is it regarded as being green?
4. Which of the following is not usually regarded as a characteristic of green chemical compounds? Why is it not so regarded?
A. Preparation from renewable resources
B. Low tendency to undergo sudden, violent, unpredictable reactions
C. Readily biodegradable
D. Extremely high stability
5. What are valence electrons? Why are they particularly important?
6. What is the octet rule? Why is it particularly important in chemistry?
7. What does the structure representing CH4 below say about bonding and octets of electrons around the central C atom?
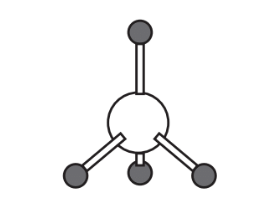
8. Considering that the central nitrogen atom in ammonia, NH3, has an unshared pair of valence electrons and 3 pairs shared between N and H, propose a structure for the ammonia molecule based upon the structure of the methane molecule in the preceding question. Use a pair of dots to represent the unshared pair of electrons.
9. What is an ionic bond? Why is it not regarded as being between one specific cation and a specific anion in an ionic compound?
10. Do ionic compounds such as NaCl obey the octet rule? Explain.
11. Why is NaCl referred to as a formula unit of the ionic compound rather than a molecule of sodium chloride?
12. Energy is involved in several steps of the process by which an elemental metal and an elemental nonmetal are converted to an ionic compound (salt). Of these, which has the largest energy?
13. Place the following ions in decreasing order of size: Na+, Cl-, Al3+, K+
14. What is a major disadvantage of calcium chloride as a road de-icing agent? Why is calcium acetate a good substitute?
15. List some important characteristics of a covalent bond.
16. What is the major characteristic of ions in ionic liquids that enable these materials to be liquid at around room temperature?
17. Can the atoms in NO2 obey the octet rule? Suggest the structural formula for this molecule inwhich the 2 O atoms are bonded to an N atom.
18. Coordinate covalent bonds are normally regarded as those in which each of two atoms contributes electrons to be shared in the bond. Are there any circumstances in which this is not true? If so, give an example.
19. What are three major ways in which covalent bonds are characterized?
20. What are some of the ways in which the characteristics of covalent bonds are related to green chemistry?
21. Why are elements in the middle of periods of the periodic table less likely to form ionic compounds and more likely to form covalent compounds than those near either end of each period?
22. Predict the formula of the compound formed when H reacts with P and explain.
23. Although hydrogen chloride, HCl, exists as a gas, the contest for the two shared electrons in the bond between H and Cl is unequal, with the Cl nucleus having the greater attraction. Suggest the nature of the H-Cl bond and suggest what may happen when HCl gas dissolves in water to produce hydrochloric acid.
24. Using Lewis formulas, show the bonding in the SO2 molecule in which two O atoms are bonded to a central O atom. Can another equivalent structure be drawn? Considering the bonding in NO discussed in this chapter, what are these structures called.
25. Summarize the information shown in the formula Ca3(PO4)2.


