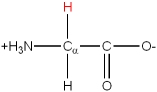
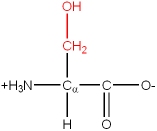
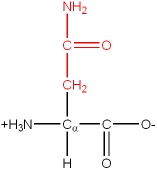
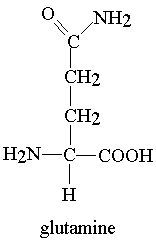
Nomenclature of Amino acids
- Page ID
- 490
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Common amino acids
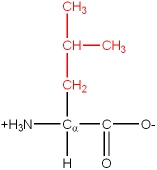
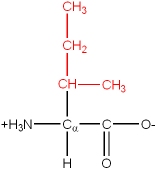
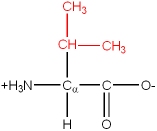
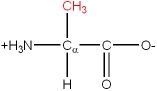
There are 20 common amino acids. They are composed of C, H, O, N and S atoms. They are structurally and chemically different, and also differ in size and volume. Some are branched structures, some are linear, some have ring structures. One of the 20 common amino acids is actually an imino acid. A typical grouping of their chemical nature is as follows:
- Nonpolar (hydrocarbons and one sulfur-containing amino acid). Dispersion forces and hydrophobic effects predominate in their interactions. They cannot H-bond with water and these side chains have a characteristic hydrophobic effect in water.
- Polar uncharged. Contain functional groups that can H-bond with water and other amino acids. Include C, H, O, N and S atoms.
- Acidic. Contain a carboxylic acid functional group with a negative charge at neutral pH. Can H-bond with water, can form ionic interactions, and can also serve as nucleophiles or participate in acid-base chemistry.
- Basic. Nitrogen containing bases (e.g. guanidino, imidazole or amino groups) with a net positive charge at neutral pH. Can serve as proton donors in chemical reactions, and form ionic interactions.
The amino acids have a name, as well as a three letter or single letter mnemonic code:
|
Type |
Name |
R-group Structure |
|---|---|---|
|
Nonpolar |
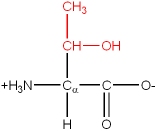
Leu, L |
|
|
Ile, I |
|
|
|
Val, V |
|
|
|
Ala, A |
|
|
|
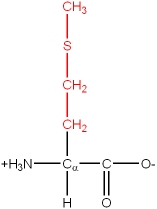
Met, M |
|
|
|
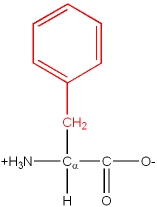
Phe, F |
|
|
|
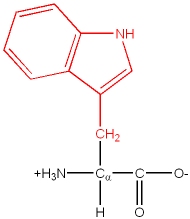
Trp, W |
|
|
|
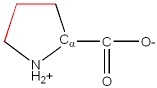
Pro, P |
|
|
|
Gly, G (note: sometimes included in polar group) |
|
|
|
Polar, uncharged |
Ser, S |
|
|
Asn, N |
|
|
|
Gln, Q |
|
|
|
Thr, T |
|
|
|
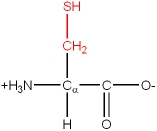
Cys, C |
|
|
|
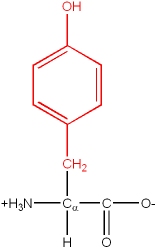
Tyr, Y |
|
|
|
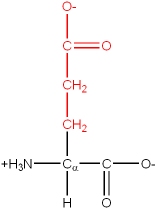
Acidic |
Asp, D |
|
|
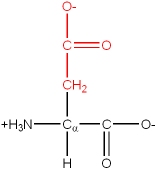
Glu, E |
|
|
|
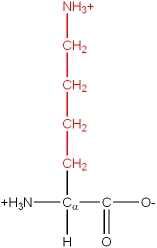
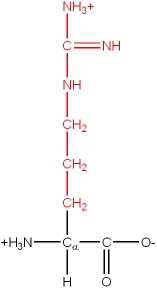
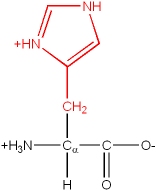
Basic |
Lys, K |
|
|
Arg, R |
|
|
|
His, H |
|
Uncommon amino acids
In addition to the 20 common amino acids, there are several uncommon ones found:
- Hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline. These are found in the protein collagen. Collagen is a fibrous protein made up of three polypeptides that form a stable assembly, but only if the proline and lysine residues are hydroxylated. (requires vitamin C for reduction of these amino acids to hydroxy form)
- Thyroxine, an iodinated derivative of tyrosine, found in thyroglobulin (produced by thyroid gland; requires iodine in diet)
- g-carboxyglutamic acid (i.e. glutamic acid with two carboxyl groups) found in certain blood clotting enzymes (requires vitamin K for production)
- N-methyl arginine and n-acetyl lysine. Found in some DNA binding proteins known as histones
Amino acid derivatives not found in proteins
Some amino acids are made that are not intended for incorporation into proteins, rather they have important functionalities on their own
- Serotonin (derivative of tryptophan) and g-amino butyric acid (a derivative of glutamic acid) are both neurotransmitters
- Histamine (derivative of histidine) involved in allergic response
- Adrenaline (derivative of tyrosine) a hormone
- Various antibiotics are amino acid derivatives (penicillin)
Contributors and Attributions
Thumbnail: 3D model of L-tryptophan. (Public Domain; Benjah-bmm27).