18.2: Functional Group Order of Precedence For Organic Nomenclature
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
In the IUPAC nomenclature system, organic molecules are grouped into specific classes of compounds determined by the main functional group present in the structure. A system of priorities is used to determine the main functional group, which determines the identity of the compound. All other functional groups are treated as substituents. The following order of precedence refers to functional groups containing carbon as the central atom. As a rule of thumb, the higher the oxidation state of the central carbon, the higher the priority of the functional group. Thus, carboxylic acids have higher priority than alcohols, and so on (See also table 21-1 in your textbook).
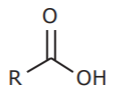
1. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (highest priority among carbon-containing functional groups).
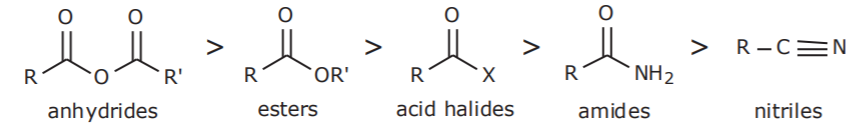
2. CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
3. OTHER GROUPS CONTAINING OXYGEN OR NITROGEN
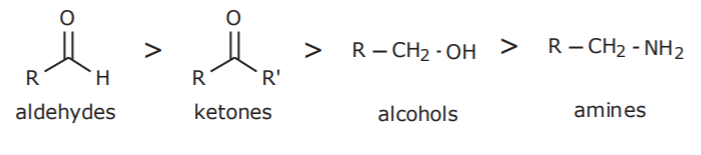
4. ALKENES AND ALKYNES
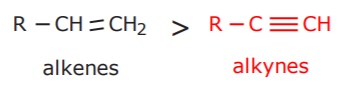
Note: substances containing double and triple bonds are called alkenynes. (notice that the name ends in yne). Chain numbering starts from the end closest to either group, unless they’re both equidistant from the chain ends, in which case the double bond takes priority and is given the lower number. See examples in the textbook.
5. LOWEST PRIORITY. These groups are usually considered substituents in the main chain.