2.6: Ethers, Epoxides and Sulfides
- Page ID
- 16986
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Ethers
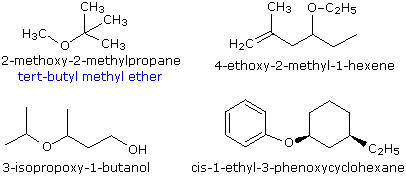
Ethers are compounds having two alkyl or aryl groups bonded to an oxygen atom, as in the formula R1–O–R2. The ether functional group does not have a characteristic IUPAC nomenclature suffix, so it is necessary to designate it as a substituent. To do so the common alkoxy substituents are given names derived from their alkyl component (below):
| Alkyl Group | Name | Alkoxy Group | Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3– | Methyl | CH3O– | Methoxy | |
| CH3CH2– | Ethyl | CH3CH2O– | Ethoxy | |
| (CH3)2CH– | Isopropyl | (CH3)2CHO– | Isopropoxy | |
| (CH3)3C– | tert-Butyl | (CH3)3CO– | tert-Butoxy | |
| C6H5– | Phenyl | C6H5O– | Phenoxy |
The smaller, shorter alkyl group becomes the alkoxy substituent. The larger, longer alkyl group side becomes the alkane base name. Each alkyl group on each side of the oxygen is numbered separately. The numbering priority is given to the carbon closest to the oxgen. The alkoxy side (shorter side) has an "-oxy" ending with its corresponding alkyl group. For example, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2CH3 is 1-propoxypentane. If there is cis or trans stereochemistry, the same rule still applies.
| Example |
|---|
| Examples are: CH3CH2OCH2CH3, diethyl ether (sometimes referred to as ether), and CH3OCH2CH2OCH3, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (glyme). |
Common names
Simple ethers are given common names in which the alkyl groups bonded to the oxygen are named in alphabetical order followed by the word "ether". The top left example shows the common name in blue under the IUPAC name. Many simple ethers are symmetrical, in that the two alkyl substituents are the same. These are named as "dialkyl ethers".
Epoxides
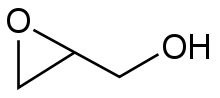
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. These rings approximately define an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in chloromethyloxirane. As a functional group, epoxides feature the epoxy prefix, such as in the compound 1,2-epoxycycloheptane, which can also be called cycloheptene epoxide, or simply cycloheptene oxide.
The chemical structure of the epoxide glycidol, a common chemical intermediate
A polymer formed by reacting epoxide units is called a polyepoxide or an epoxy. Epoxy resins are used as adhesives and structural materials. Polymerization of an epoxide gives a polyether, for example ethylene oxide polymerizes to give polyethylene glycol, also known as polyethylene oxide.
Sulfides (Thioethers)
A thioether is a functional group in organosulfur chemistry with the connectivity C-S-C as shown below. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile thioethers have foul odors.[1] A thioether is similar to an ether except that it contains a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen. The grouping of oxygen and sulfur in the periodic table suggests that the chemical properties of ethers and thioethers are somewhat similar.
General structure of a thioether with the blue marked functional group.
Nomenclature
Thioethers are sometimes called sulfides, especially in the older literature and this term remains in use for the names of specific thioethers. The two organic substituents are indicated by the prefixes. (CH3)2S is called dimethylsulfide. Some thioethers are named by modifying the common name for the corresponding ether. For example, C6H5SCH3 is methyl phenyl sulfide, but is more commonly called thioanisole, since its structure is related to that for anisole, C6H5OCH3.
Structure and properties
Thioether is an angular functional group, the C-S-C angle approaching 90°. The C-S bonds are about 180 pm.
Thioethers are characterized by their strong odors, which are similar to thiol odor. This odor limits the applications of volatile thioethers. In terms of their physical properties they resemble ethers but are less volatile, higher melting, and less hydrophilic. These properties follow from the polarizability of the divalent sulfur center, which is greater than that for oxygen in ethers.
Thiophenes
Thiophenes are a special class of thioether-containing heterocyclic compounds. Because of their aromatic character, they are non-nucleophilic. The nonbonding electrons on sulfur are delocalized into the π-system. As a consequence, thiophene exhibits few properties expected for a thioether - thiophene is non-nucleophilic at sulfur and, in fact, is sweet-smelling. Upon hydrogenation, thiophene gives tetrahydrothiophene, C4H8S, which indeed does behave as a typical thioether.
Contributors
- Wikipedia (used with permission)