7.19: The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
- Page ID
- 253522
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objective
- Analyze, broadly, the causes of the fall of the Roman Empire
Key Points
- Throughout the 5th century, the empire’s territories in western Europe and northwestern Africa, including Italy, fell to various invading or indigenous peoples, in what is sometimes called the Migration Period.
- By the late 3rd century, the city of Rome no longer served as an effective capital for the emperor, and various cities were used as new administrative capitals. Successive emperors, starting with Constantine, privileged the eastern city of Byzantium, which he had entirely rebuilt after a siege.
- In 476, after being refused lands in Italy, Odacer and his Germanic mercenaries took Ravenna, the Western Roman capital at the time, and deposed Western Emperor Romulus Augustus. The whole of Italy was quickly conquered, and Odoacer’s rule became recognized in the Eastern Empire.
- Four broad schools of thought exist on the decline and fall of the Roman Empire: decay owing to general malaise, monocausal decay, catastrophic collapse, and transformation.
Terms
Migration Period
Also known as the period of the Barbarian Invasions, it was a period of intensified human migration in Europe from about 400 to 800 CE, during the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages.
Odoacer
A soldier, who came to power in the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE. His reign is commonly seen as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire.
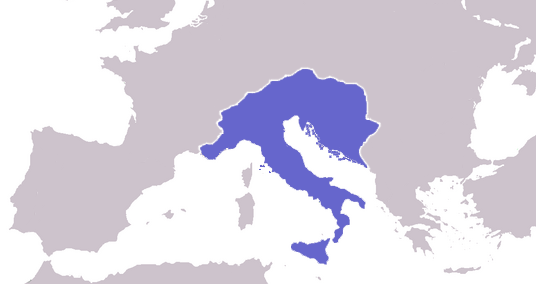
The Fall of the Western Roman Empire was the process of decline during which the empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control; modern historians mention factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperor, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the historiography of the ancient world, and they inform much modern discourse on state failure.
By 476 CE, when Odoacer deposed Emperor Romulus, the Western Roman Empire wielded negligible military, political, or financial power and had no effective control over the scattered western domains that could still be described as Roman. Invading “barbarians” had established their own polities on most of the area of the Western Empire. While its legitimacy lasted for centuries longer and its cultural influence remains today, the Western Empire never had the strength to rise again.
It is important to note, however, that the so-called fall of the Roman Empire specifically refers to the fall of the Western Roman Empire, since the Eastern Roman Empire, or what became known as the Byzantine Empire, whose capital was founded by Constantine, remained for another 1,000 years. Theodosius was the last emperor who ruled over the whole empire. After his death in 395, he gave the two halves of the empire to his two sons, Arcadius and Honorius; Arcadius became ruler in the east, with his capital in Constantinople, and Honorius became ruler in the west, with his capital in Milan, and later Ravenna.
Rome in the 5th Century CE
Throughout the 5th century, the empire’s territories in western Europe and northwestern Africa, including Italy, fell to various invading or indigenous peoples in what is sometimes called the Migration Period, also known as the Barbarian Invasions, from the Roman and South European perspective. The first migrations of peoples were made by Germanic tribes, such as the Goths, Vandals, Angles, Saxons, Lombards, Suebi, Frisii, Jutes and Franks; they were later pushed westwards by the Huns, Avars, Slavs, and Bulgars.
Although the eastern half still survived with borders essentially intact for several centuries (until the Muslim conquests), the Empire as a whole had initiated major cultural and political transformations since the Crisis of the Third Century, with the shift towards a more openly autocratic and ritualized form of government, the adoption of Christianity as the state religion, and a general rejection of the traditions and values of Classical Antiquity.
The reasons for the decline of the Empire are still debated today, and are likely multiple. Historians infer that the population appears to have diminished in many provinces (especially western Europe), judging from the diminishing size of fortifications built to protect the cities from barbarian incursions from the 3rd century on. Some historians even have suggested that parts of the periphery were no longer inhabited, because these fortifications were restricted to the center of the city only. By the late 3rd century, the city of Rome no longer served as an effective capital for the emperor, and various cities were used as new administrative capitals. Successive emperors, starting with Constantine, privileged the eastern city of Byzantium, which he had entirely rebuilt after a siege. Later renamed Constantinople, and protected by formidable walls in the late 4th and early 5th centuries, it was to become the largest and most powerful city of Christian Europe in the Early Middle Ages. Since the Crisis of the Third Century, the empire was intermittently ruled by more than one emperor at once (usually two), presiding over different regions.
The Latin-speaking west, under dreadful demographic crisis, and the wealthier Greek-speaking east, also began to diverge politically and culturally. Although this was a gradual process, still incomplete when Italy came under the rule of barbarian chieftains in the last quarter of the 5th century, it deepened further afterward, and had lasting consequences for the medieval history of Europe.
In 476, after being refused lands in Italy, Orestes’ Germanic mercenaries, under the leadership of the chieftain Odoacer, captured and executed Orestes and took Ravenna, the Western Roman capital at the time, deposing Western Emperor Romulus Augustus. The whole of Italy was quickly conquered, and Odoacer’s rule became recognized in the Eastern Empire. Meanwhile, much of the rest of the Western provinces were conquered by waves of Germanic invasions, most of them being disconnected politically from the east altogether, and continuing a slow decline. Although Roman political authority in the west was lost, Roman culture would last in most parts of the former western provinces into the 6th century and beyond.
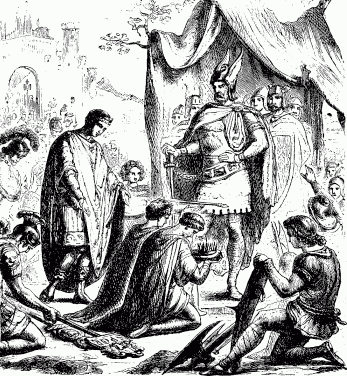
Theories on the Decline and Fall
The various theories and explanations for the fall of the Roman Empire in the west may be very broadly classified into four schools of thought (although the classification is not without overlap):
- Decay owing to general malaise
- Monocausal decay
- Catastrophic collapse
- Transformation
The tradition positing general malaise goes back to the historian, Edward Gibbon, who argued that the edifice of the Roman Empire had been built on unsound foundations from the beginning. According to Gibbon, the fall was—in the final analysis—inevitable. On the other hand, Gibbon had assigned a major portion of the responsibility for the decay to the influence of Christianity, and is often, though perhaps unjustly, seen as the founding father of the school of monocausal explanation. On the other hand, the school of catastrophic collapse holds that the fall of the empire had not been a pre-determined event and need not be taken for granted. Rather, it was due to the combined effect of a number of adverse processes, many of them set in motion by the Migration Period, that together applied too much stress to the empire’s basically sound structure. Finally, the transformation school challenges the whole notion of the ‘fall’ of the empire, asking instead to distinguish between the fall into disuse of a particular political dispensation, anyway unworkable towards its end; and the fate of the Roman civilization that under-girded the empire. According to this school, drawing its basic premise from the Pirenne thesis, the Roman world underwent a gradual (though often violent) series of transformations, morphing into the medieval world. The historians belonging to this school often prefer to speak of Late Antiquity, instead of the Fall of the Roman Empire.
Sources
- Boundless World History. Authored by: Boundless. Located at: https://www.boundless.com/world-history/textbooks/boundless-world-history-textbook/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

