7.5: Steroids
- Page ID
- 342700
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Recognize the structural features of lipids.
One major class of lipids is the steroids, which have structures totally different from the other classes of lipids. The main feature of steroids is the steroid nucleus, a fused ring system of three cyclohexanes and one cyclopentane (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). There are a variety of functional groups that may be attached. The main feature, as in all lipids, is the large number of carbon and hydrogen which make steroids non-polar.
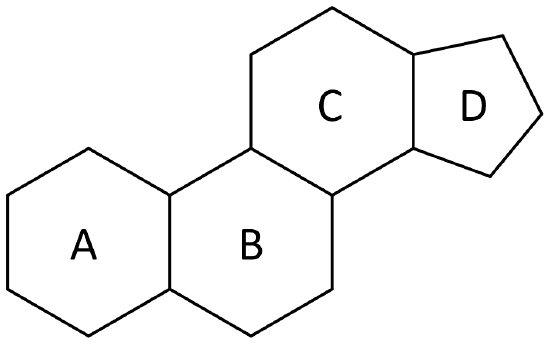
Steroids include such well known compounds as cholesterol, sex hormones, birth control pills, cortisone, and anabolic steroids.
Cholesterol
The best known and most abundant steroid in the body is cholesterol. Cholesterol is formed in brain tissue, nerve tissue, and the blood stream. It is the major compound found in gallstones and bile salts.
Cholesterol also contributes to the formation of deposits on the inner walls of blood vessels. These deposits harden and obstruct the flow of blood. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, results in various heart diseases, strokes, and high blood pressure.
Structures of Sex Hormones
Sex hormones are also steroids. The primary male hormone, testosterone, is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics. Two female sex hormones, progesterone and estrogen (or estradiol) control the ovulation cycle. Notice that the male and female hormones have only slight differences in structures, but yet have very different physiological effects.
Testosterone promotes the normal development of male genital organs ans is synthesized from cholesterol in the testes. It also promotes secondary male sexual characteristics such as deep voice, facial and body hair. Estrogen, along with progesterone regulates changes occurring in the uterus and ovaries known as the menstrual cycle. For more details see Birth Control. Estrogen is synthesized from testosterone by making the first ring aromatic which results in mole double bonds, the loss of a methyl group and formation of an alcohol group.
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Structures of sex hormones.
Adrenocorticoid Hormones
The adrenocorticoid hormones are products of the adrenal glands ("adrenal" means adjacent to the renal (kidney)). The most important mineralocrticoid is aldosterone, which regulates the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the kidney tubules and increases the loss of potassium ions. Aldosterone is secreted when blood sodium ion levels are too low to cause the kidney to retain sodium ions. If sodium levels are elevated, aldosterone is not secreted, so that some sodium will be lost in the urine. Aldosterone also controls swelling in the tissues.
Cortisol, the most important glucocortinoid, has the function of increasing glucose and glycogen concentrations in the body. These reactions are completed in the liver by taking fatty acids from lipid storage cells and amino acids from body proteins to make glucose and glycogen.
In addition, cortisol and its ketone derivative, cortisone, have the ability to inflammatory effects. Cortisone or similar synthetic derivatives such as prednisolone are used to treat inflammatory diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, and bronchial asthma. There are many side effects with the use of cortisone drugs, so there use must be monitored carefully.
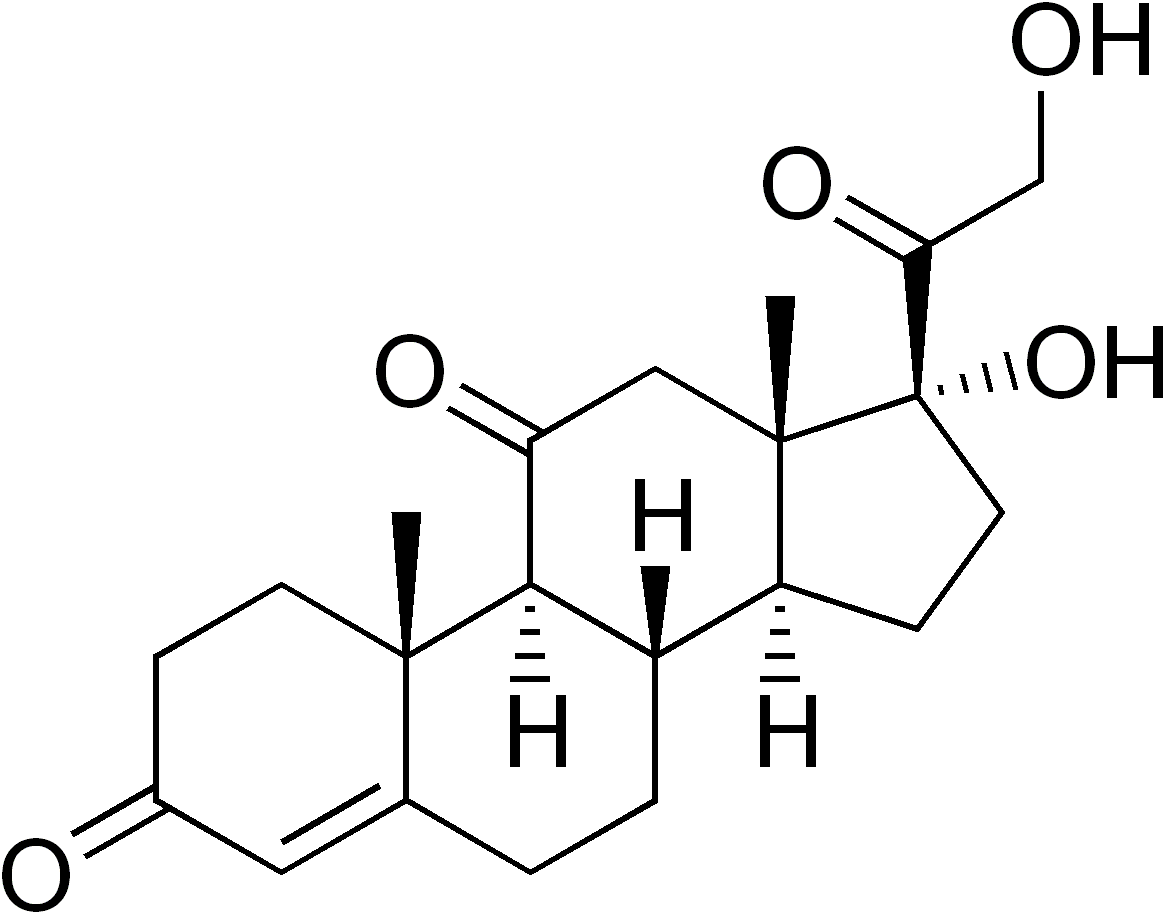
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): Structures of adrenocorticoid hormones.
Contributors
- Charles Ophardt, Professor Emeritus, Elmhurst College; Virtual Chembook
Thumbnail: Ball-and-stick model of the cholesterol molecule, a compound essential for animal life that forms the membranes of animal cells. (Public Domain; Jynto).

