10.2: DEA Drug Schedules
- Page ID
- 85181
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Explain the purpose of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention, and Control Act of 1970.
- Name the two govermental agencies that regulate highly abused substances.
- Explain DEA controlled substances scheduling.
- List examples of susbstances found in the five schedules.
- Provide legal and illegal applications of GHB.
- Compare and contrast the chemical structures of CBD and THC.
- Know basic uses (legal and illegal) of CBD and THC.
Controlled Substances
Under the Nixon administration, the United States passed the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention,and Control Act of 1970. This law enabled the federal government to regulate the manufacturing and distribution of narcotics, depressants, hallucinogens, anabolic steroids, and amphetamines. In 1973, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) was created to assist the Food and Drug Administration with regulating addiction medications and illicit substances.

Within Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970, the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was embedded to provide criteria as to how a drug is declared to be illegal. This particular legislation was amended in 1986 to include analogs (similar chemicals) of the already defined illegal substances.
https://youtu.be/aBKrrWGpOEM
In the United States, legal and illegal drugs that could be potentially abused are classified (scheduled) and defined as being controlled substances by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). According to this federal agency, there are five levels of scheduled substances. Substances listed in the first tier of DEA scheduling have the highest potential for abuse and are defined as having no legal medical use. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Congress do assist the DEA in altering the scheduling of drugs and illicit substances.
| Schedule | Examples of Substances |
|---|---|
| 1 | Heroin, Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), Marijuana (cannabis), Ecstasy/MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine), Phencyclidine (PCP), and Peyote. |
| 2 | Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Methadone, Hydromorphone (Dilaudid®), Meperidine (Demerol®), Oxycodone (Oxycontin ®), Amphetamine stimulants (Adderall®, Ritalin®, Vivance®, and Concerta®), Hydrocodone, Fentanyl, and Morphine. |
| 3 | Codeine (less than 90 mg dose), anabolic steroids, Ketamine, and Testosterone. |
| 4 | Alprazolam (Xanax®), Clonazepam (Klonopin®), Diazepam (Valium®), Lorazepam (Ativan®), Zolpidem (Ambien®), and Eszopiclone (Lunesta®). |
| 5 | Codeine cough syrup (less than 200 mg per dose), Lomotil ®, Promothezine (Phenergan®), and Ondansetron hydrochloride dihydrate (Zofran®). |
Scheduling of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB)
In the late 1980s, Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (other chemical names include 4-Hydroxybutanoic acid) was sold at many health food stores in the United States. GHB was marketed and sold as a natural sleep aid and a weight-loss supplement. Also, GHB manufacturers claimed that this substance could increase muscle mass. Dieters and bodybuilders stocked-piled GHB supplements. Unfortunately, no scientific study has ever proven that GHB is capable of reducing weight or gaining muscle mass.
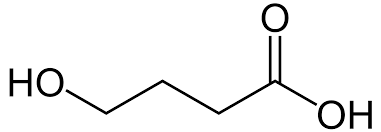
Immediately, consumers of this substance noticed the euphoric and hallucinogenic properties after use. In lower concentrations, GHB can reduce anxiety and inhibition. In larger concentrations, GHB can increase libido, cause extreme nausea, and render users unconscious. Quickly, GHB became known as a date-rape drug due to its ability to subdue a victim. Also, this water-soluble chemical can cause amnesia and will be metabolized and excreted by the body quite quickly. GHB acts within 15-30 minutes of ingestion and the effects can last 3 to 6 hours.
On November 8, 1990, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stopped all manufacturing and sales of GHB due to an increase in overdoses and death. For years, GHB and its analogs remained off the DEA scheduling of controlled substances. On November 11, 1999, Congress passed the Hillory J. Farias and Samantha Reid-Date-Rape Drug Prohibition Act of 1999. This legislation amended the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) to include GHB, GHB salts, and GHB isomers. On March 13, 2000, GHB was officially listed as being a scheduled 1 substance. In 2002, the FDA approved GHB for the treatment of narcolepsy. Sold under the name Xyrem, this compound can be prescribed legally and is a scheduled 3 substance.
As of November 2020, the DEA and FDA still rank Marijuana as being a scheduled 1 controlled substance. Both of these agencies have deemed marijuana to have no federally approved medication applications. However, synthetic forms of Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive ingredient in marijuana, have been approved for various medical uses. For example, Marinol is a scheduled III substance used to treat extreme nausea and vomiting in AIDS and cancer patients. Also, the scheduled IV substance, Epidoloex, can be prescribed for individuals who have been diagnosed with certain forms of epilepsy.
Looking at the DEA scheduling of controlled substances, why do you think cocaine and methamphetamine are scheduled II substances? Access the dea.gov website to see reasoning as to why these two chemicals are not listing scheduled I.
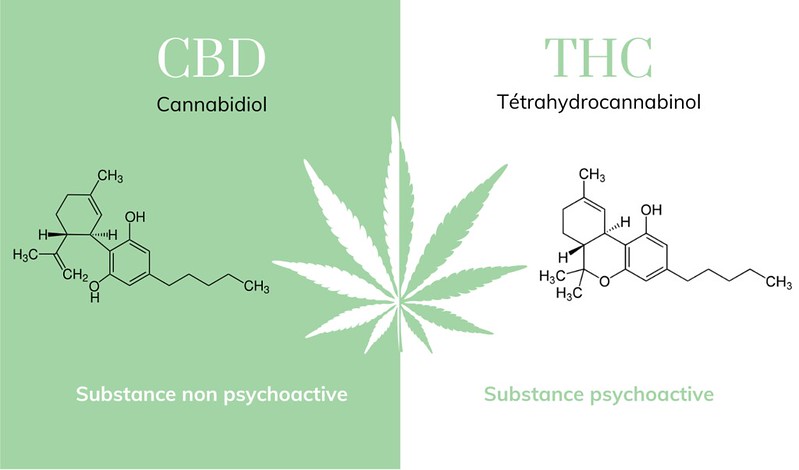
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Visual CBD: Molecules thc et cbd. (Copyright, molecules thc et cbd | Comparatif des molecules entre CBD et… | Flickr, )
Individual states have enacted their own laws regarding the legalization of tetrahydrocannabinol-based products. By accessing this link, you can view the current status of each state.



