5.7: Naming Ionic Compounds
- Page ID
- 369342
Learning Objectives
- To use the rules for naming ionic compounds.
After learning a few more details about the names of individual ions, you will be one step away from knowing how to name ionic compounds. This section begins the formal study of nomenclature, the systematic naming of chemical compounds.
Naming Ions
The name of a monatomic cation is simply the name of the element followed by the word ion. Thus, Na+ is the sodium ion, Al3+ is the aluminum ion, Ca2+ is the calcium ion, and so forth.
We have seen that some elements lose different numbers of electrons, producing ions of different charges (Figure 3.3). Iron, for example, can form two cations, each of which, when combined with the same anion, makes a different compound with unique physical and chemical properties. Thus, we need a different name for each iron ion to distinguish Fe2+ from Fe3+. The same issue arises for other ions with more than one possible charge.
There are two ways to make this distinction. In the simpler, more modern approach, called the Stock system, an ion’s positive charge is indicated by a roman numeral in parentheses after the element name, followed by the word ion. Thus, Fe2+ is called the iron(II) ion, while Fe3+ is called the iron(III) ion. This system is used only for elements that form more than one common positive ion. We do not call the Na+ ion the sodium(I) ion because (I) is unnecessary. Sodium forms only a 1+ ion, so there is no ambiguity about the name sodium ion.
| Element | Stem | Charge | Modern Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iron | ferr- | 2+ | iron(II) ion | ferrous ion |
| 3+ | iron(III) ion | ferric ion | ||
| copper | cupr- | 1+ | copper(I) ion | cuprous ion |
| 2+ | copper(II) ion | cupric ion | ||
| tin | stann- | 2+ | tin(II) ion | stannous ion |
| 4+ | tin(IV) ion | stannic ion | ||
| lead | plumb- | 2+ | lead(II) ion | plumbous ion |
| 4+ | lead(IV) ion | plumbic ion | ||
| chromium | chrom- | 2+ | chromium(II) ion | chromous ion |
| 3+ | chromium(III) ion | chromic ion | ||
| gold | aur- | 1+ | gold(I) ion | aurous ion |
| 3+ | gold(III) ion | auric ion |
The second system, called the common system, is not conventional but is still prevalent and used in the health sciences. This system recognizes that many metals have two common cations. The common system uses two suffixes (-ic and -ous) that are appended to the stem of the element name. The -ic suffix represents the greater of the two cation charges, and the -ous suffix represents the lower one. In many cases, the stem of the element name comes from the Latin name of the element. Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) lists the elements that use the common system, along with their respective cation names.
| Ion | Name |
|---|---|
| F− | fluoride ion |
| Cl− | chloride ion |
| Br− | bromide ion |
| I− | iodide ion |
| O2− | oxide ion |
| S2− | sulfide ion |
| P3− | phosphide ion |
| N3− | nitride ion |
The name of a monatomic anion consists of the stem of the element name, the suffix -ide, and then the word ion. Thus, as we have already seen, Cl− is “chlor-” + “-ide ion,” or the chloride ion. Similarly, O2− is the oxide ion, Se2− is the selenide ion, and so forth. Table \(\PageIndex{2}\) lists the names of some common monatomic ions. The polyatomic ions have their own characteristic names, as discussed earlier.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Name each ion.
- Ca2+
- S2−
- SO32−
- NH4+
- Cu+
Solution
- the calcium ion
- the sulfide ion
- the sulfite ion
- the ammonium ion
- the copper(I) ion or the cuprous ion
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Name each ion.
- Fe2+
- Fe3+
- SO42−
- Ba2+
- HCO3−
- Answer a:
- iron(II) ion
- Answer b:
- iron(III) ion
- Answer c:
- sulfate ion
- Answer d:
- barium ion
- Answer e:
- hydrogen carbonate ion or bicarbonate ion
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Write the formula for each ion.
- the bromide ion
- the phosphate ion
- the cupric ion
- the magnesium ion
Solution
- Br−
- PO43−
- Cu2+
- Mg2+
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Write the formula for each ion.
- the fluoride ion
- the carbonate ion
- the stannous ion
- the potassium ion
- Answer a:
- F-
- Answer b:
- CO32-
- Answer c:
- Sn 2+
- Answer d:
- K+
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds with a Metal that Forms Only One Type of Cation
A binary ionic compound is a compound composed of a monatomic metal cation and a monatomic nonmetal anion. The metal cation is named first, followed by the nonmetal anion as illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) for the compound BaCl2. The word ion is dropped from both parts.
Subscripts in the formula do not affect the name.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): Naming Ionic Compounds
Name each ionic compound.
- CaCl2
- AlF3
- KCl
Solution
- Using the names of the ions, this ionic compound is named calcium chloride.
- The name of this ionic compound is aluminum fluoride.
- The name of this ionic compound is potassium chloride
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Name each ionic compound.
- AgI
- MgO
- Ca3P2
- Answer a:
- silver iodide
- Answer b:
- magnesium oxide
- Answer c:
- calcium phosphide
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds with a Metal That Forms More Than One Type of Cation
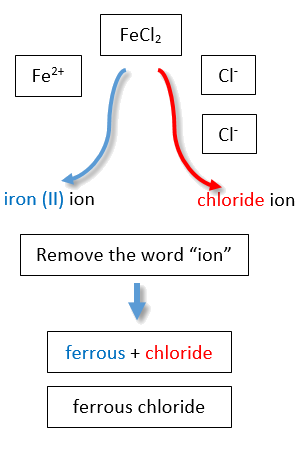
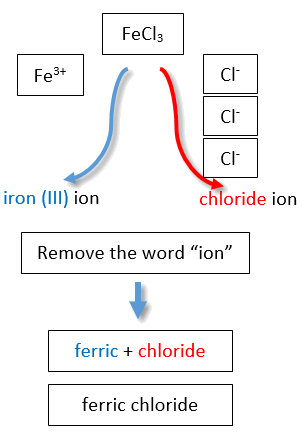
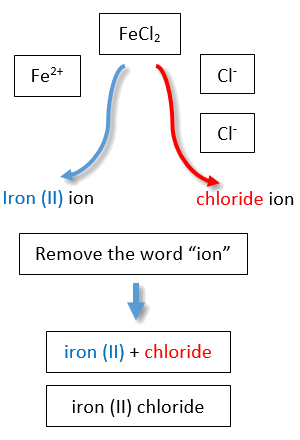
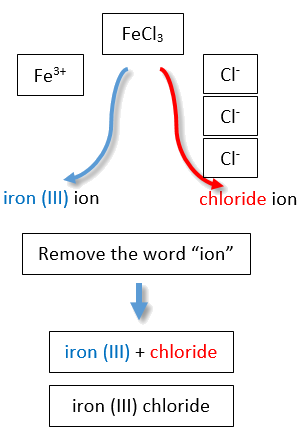
If you are given a formula for an ionic compound whose cation can have more than one possible charge, you must first determine the charge on the cation before identifying its correct name. For example, consider FeCl2 and FeCl3 . In the first compound, the iron ion has a 2+ charge because there are two Cl− ions in the formula (1− charge on each chloride ion). In the second compound, the iron ion has a 3+ charge, as indicated by the three Cl− ions in the formula. These are two different compounds that need two different names. By the Stock system, the names are iron(II) chloride and iron(III) chloride (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).
| Name of cation (metal) + (Roman Numeral in parenthesis) + Base name of anion (nonmetal) and -ide | |
 |
 |
If we were to use the stems and suffixes of the common system, the names would be ferrous chloride and ferric chloride, respectively (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)) .
| "Old" base name of cation (metal) and -ic or -ous + Base name of anion (nonmetal) and -ide | |
|
-ous (for ions with lower charge)
|
-ic (for ions with higher charge)
|
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\):
Name each ionic compound.
- Co2O3
- FeCl2
Solution
| Explanation | Answer | |
|---|---|---|
| a |
We know that cobalt can have more than one possible charge; we just need to determine what it is.
|
cobalt(III) oxide |
| b |
Iron can also have more than one possible charge.
|
iron(II) chloride |
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Name each ionic compound.
- AuCl3
- PbO2
- CuO
- Answer a:
- gold(III) chloride
- Answer b:
- lead(IV) oxide
- Answer c:
- copper(II) oxide
Naming Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions
The process of naming ionic compounds with polyatomic ions is the same as naming binary ionic compounds. The cation is named first, followed by the anion. One example is the ammonium sulfate compound in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\): Naming Ionic Compounds
Write the proper name for each ionic compound.
- (NH4)2S
- AlPO4,
- Fe3(PO4)2
Solution
| Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|
|
a. The ammonium ion has a 1+ charge and the sulfide ion has a 2− charge. Two ammonium ions need to balance the charge on a single sulfide ion. The compound’s name is ammonium sulfide. |
ammonium sulfide |
|
b. The ions have the same magnitude of charge, one of each (ion) is needed to balance the charges. The name of the compound is aluminum phosphate. |
aluminum phosphate |
|
c. Neither charge is an exact multiple of the other, so we have to go to the least common multiple of 6. To get 6+, three iron(II) ions are needed, and to get 6−, two phosphate ions are needed . The compound’s name is iron(II) phosphate. |
iron(II) phosphate |
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5A}\)
Write the proper name for each ionic compound.
- (NH4)3PO4
- Co(NO2)3
- Answer a:
- ammonium phosphate
- Answer b:
- cobalt(III) nitrite
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) is a synopsis of how to name simple ionic compounds.
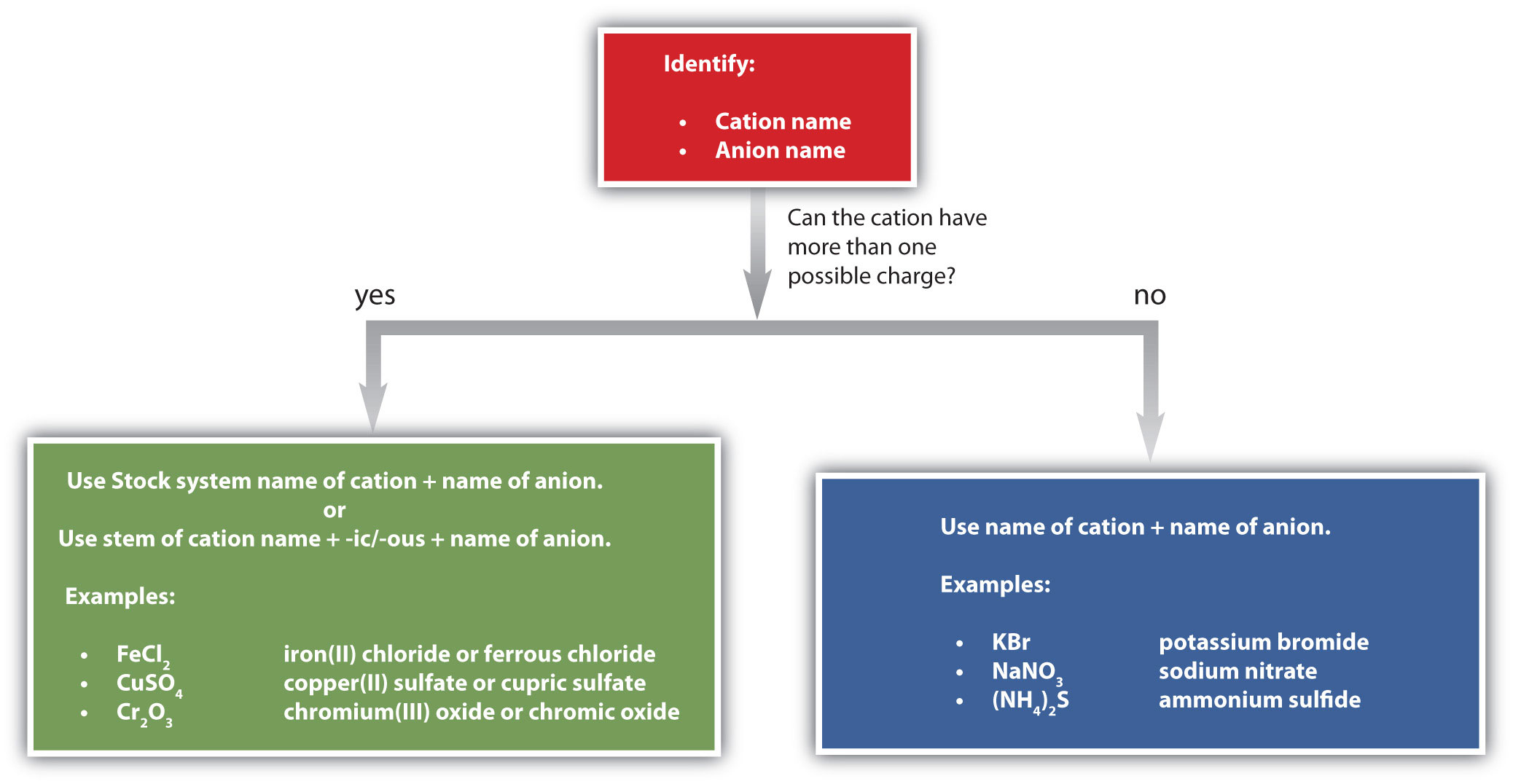
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5B}\)
Name each ionic compound.
- ZnBr2
- Al2O3
- (NH4)3PO4
- AuF3
- AgF
- Answer a:
- zinc bromide
- Answer b:
- aluminum oxide
- Answer c:
- ammonium phosphate
- Answer d:
- gold(III) fluoride or auric fluoride
- Answer e:
- silver fluoride
To Your Health: Hydrates
Some ionic compounds have water (H2O) incorporated within their formula unit. These compounds, called hydrates, have a characteristic number of water units associated with each formula unit of the compound. Hydrates are solids, not liquids or solutions, despite the water they contain.
To write the chemical formula of a hydrate, write the number of water units per formula unit of compound after its chemical formula. The two chemical formulas are separated by a vertically centered dot. The hydrate of copper(II) sulfate has five water units associated with each formula unit, so it is written as CuSO4•5H2O. The name of this compound is copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate, with the penta- prefix indicating the presence of five water units per formula unit of copper(II) sulfate.
Hydrates have various uses in the health industry. Calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4•½H2O), known as plaster of Paris, is used to make casts for broken bones. Epsom salt (MgSO4•7H2O) is used as a bathing salt and a laxative. Aluminum chloride hexahydrate is an active ingredient in antiperspirants. The accompanying table lists some useful hydrates.
| Formula | Name | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| AlCl3•6H2O | aluminum chloride hexahydrate | antiperspirant |
| CaSO4•½H2O | calcium sulfate hemihydrate (plaster of Paris) | casts (for broken bones and castings) |
| CaSO4•2H2O | calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) | drywall component |
| CoCl2•6H2O | cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate | drying agent, humidity indicator |
| CuSO4•5H2O | copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate | fungicide, algicide, herbicide |
| MgSO4•7H2O | magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (Epsom salts) | laxative, bathing salt |
| Na2CO3•10H2O | sodium carbonate decahydrate (washing soda) | laundry additive/cleaner |
Summary
- Ionic compounds are named by stating the cation first, followed by the anion.
- Positive and negative charges must balance.
- Some anions have multiple forms and are named accordingly with the use of roman numerals in parentheses.
- Ternary compounds are composed of three or more elements.
Contributions & Attributions
This page was constructed from content via the following contributor(s) and edited (topically or extensively) by the LibreTexts development team to meet platform style, presentation, and quality:
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)