6.12: Translation
- Page ID
- 279224
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The synthesis of proteins is one of a cell’s most energy-consuming metabolic processes. In turn, proteins account for more mass than any other component of living organisms (with the exception of water), and proteins perform a wide variety of the functions of a cell. The process of translation, or protein synthesis, involves decoding an mRNA message into a polypeptide product. Amino acids are covalently strung together in lengths ranging from approximately 50 amino acids to more than 1,000.
The Protein Synthesis Machinery
In addition to the mRNA template, many other molecules contribute to the process of translation. The composition of each component may vary across species; for instance, ribosomes may consist of different numbers of ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) and polypeptides depending on the organism. However, the general structures and functions of the protein synthesis machinery are comparable from bacteria to human cells. Translation requires the input of an mRNA template, ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors (Figure 9.4.1).
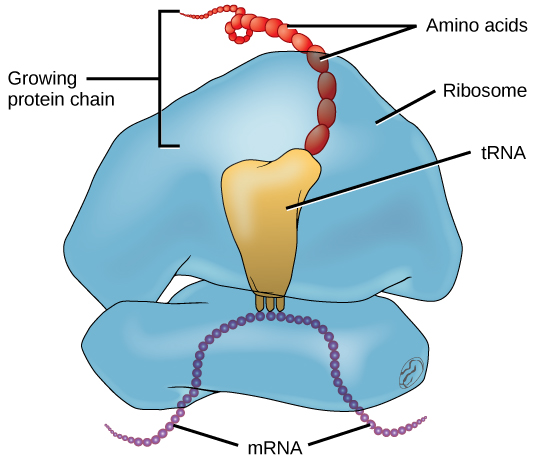
In E. coli, there are 200,000 ribosomes present in every cell at any given time. A ribosome is a complex macromolecule composed of structural and catalytic rRNAs, and many distinct polypeptides. In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is completely specialized for the synthesis and assembly of rRNAs.
Ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotes. Ribosomes are made up of a large and a small subunit that come together for translation. The small subunit is responsible for binding the mRNA template, whereas the large subunit sequentially binds tRNAs, a type of RNA molecule that brings amino acids to the growing chain of the polypeptide. Each mRNA molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction.
Depending on the species, 40 to 60 types of tRNA exist in the cytoplasm. Serving as adaptors, specific tRNAs bind to sequences on the mRNA template and add the corresponding amino acid to the polypeptide chain. Therefore, tRNAs are the molecules that actually “translate” the language of RNA into the language of proteins. For each tRNA to function, it must have its specific amino acid bonded to it. In the process of tRNA “charging,” each tRNA molecule is bonded to its correct amino acid.
The Genetic Code
To summarize what we know to this point, the cellular process of transcription generates messenger RNA (mRNA), a mobile molecular copy of one or more genes with an alphabet of A, C, G, and uracil (U). Translation of the mRNA template converts nucleotide-based genetic information into a protein product. Protein sequences consist of 20 commonly occurring amino acids; therefore, it can be said that the protein alphabet consists of 20 letters. Each amino acid is defined by a three-nucleotide sequence called the triplet codon. The relationship between a nucleotide codon and its corresponding amino acid is called the genetic code.
Given the different numbers of “letters” in the mRNA and protein “alphabets,” combinations of nucleotides corresponded to single amino acids. Using a three-nucleotide code means that there are a total of 64 (4 × 4 × 4) possible combinations; therefore, a given amino acid is encoded by more than one nucleotide triplet (Figure 9.4.2).
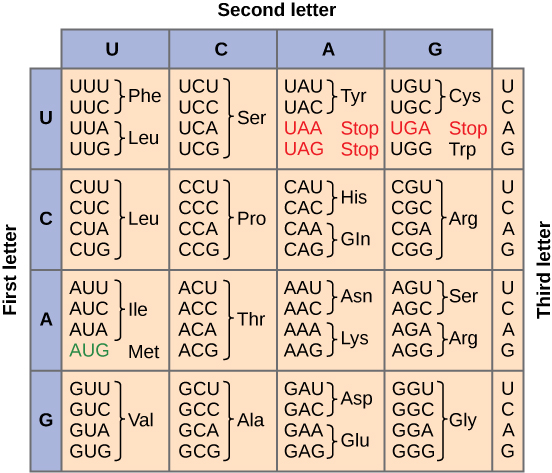
Three of the 64 codons terminate protein synthesis and release the polypeptide from the translation machinery. These triplets are called stop codons. Another codon, AUG, also has a special function. In addition to specifying the amino acid methionine, it also serves as the start codon to initiate translation. The reading frame for translation is set by the AUG start codon near the 5' end of the mRNA. The genetic code is universal. With a few exceptions, virtually all species use the same genetic code for protein synthesis, which is powerful evidence that all life on Earth shares a common origin.
Figure 9.4.3: Alternative figure showing the genetic code for translating each nucleotide triplet, or codon, in mRNA into an amino acid or a termination signal in a nascent protein.Image by Mouagip, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons.
The Mechanism of Protein Synthesis
Just as with mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis can be divided into three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Here we will explore how translation occurs in E. coli, a representative prokaryote, and specify any differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation.
Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. In E. coli, this complex involves the small ribosome subunit, the mRNA template, three initiation factors, and a special initiator tRNA. The initiator tRNA interacts with the AUG start codon, and links to a special form of the amino acid methionine that is typically removed from the polypeptide after translation is complete.
In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the basics of polypeptide elongation are the same, so we will review elongation from the perspective of E. coli. The large ribosomal subunit of E. coli consists of three compartments: the A site binds incoming charged tRNAs (tRNAs with their attached specific amino acids). The P site binds charged tRNAs carrying amino acids that have formed bonds with the growing polypeptide chain but have not yet dissociated from their corresponding tRNA. The E site releases dissociated tRNAs so they can be recharged with free amino acids. The ribosome shifts one codon at a time, catalyzing each process that occurs in the three sites. With each step, a charged tRNA enters the complex, the polypeptide becomes one amino acid longer, and an uncharged tRNA departs. The energy for each bond between amino acids is derived from GTP, a molecule similar to ATP (Figure 9.4.4). Amazingly, the E. coli translation apparatus takes only 0.05 seconds to add each amino acid, meaning that a 200-amino acid polypeptide could be translated in just 10 seconds.
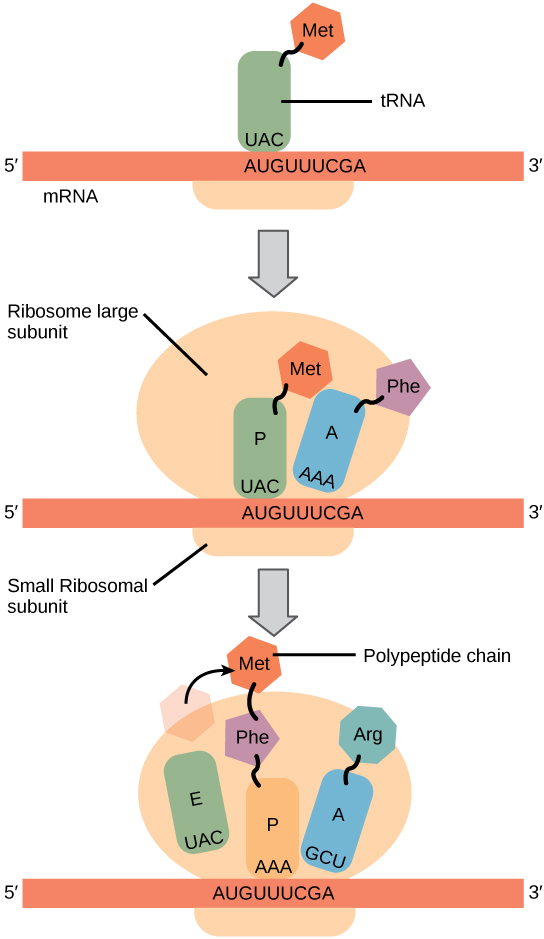
Termination of translation occurs when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered. When the ribosome encounters the stop codon, the growing polypeptide is released and the ribosome subunits dissociate and leave the mRNA. After many ribosomes have completed translation, the mRNA is degraded so the nucleotides can be reused in another transcription reaction.
CONCEPT IN ACTION
Transcribe a gene and translate it to protein using complementary pairing and the genetic code at this site.
Summary
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information in the cell from genes to mRNA to proteins. Genes are used to make mRNA by the process of transcription; mRNA is used to synthesize proteins by the process of translation. The genetic code is the correspondence between the three-nucleotide mRNA codon and an amino acid. The genetic code is “translated” by the tRNA molecules, which associate a specific codon with a specific amino acid. The genetic code is degenerate because 64 triplet codons in mRNA specify only 20 amino acids and three stop codons. This means that more than one codon corresponds to an amino acid. Almost every species on the planet uses the same genetic code.
The players in translation include the mRNA template, ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors. The small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA template. Translation begins at the initiating AUG on the mRNA. The formation of bonds occurs between sequential amino acids specified by the mRNA template according to the genetic code. The ribosome accepts charged tRNAs, and as it steps along the mRNA, it catalyzes bonding between the new amino acid and the end of the growing polypeptide. The entire mRNA is translated in three-nucleotide “steps” of the ribosome. When a stop codon is encountered, a release factor binds and dissociates the components and frees the new protein.
Glossary
- codon
- three consecutive nucleotides in mRNA that specify the addition of a specific amino acid or the release of a polypeptide chain during translation
- genetic code
- the amino acids that correspond to three-nucleotide codons of mRNA
- rRNA
- ribosomal RNA; molecules of RNA that combine to form part of the ribosome
- stop codon
- one of the three mRNA codons that specifies termination of translation
- start codon
- the AUG (or, rarely GUG) on an mRNA from which translation begins; always specifies methionine
- tRNA
- transfer RNA; an RNA molecule that contains a specific three-nucleotide anticodon sequence to pair with the mRNA codon and also binds to a specific amino acid


